Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing Care Plans For Burned Patient
Hochgeladen von
Junah Marie Rubinos PalarcaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Care Plans For Burned Patient
Hochgeladen von
Junah Marie Rubinos PalarcaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
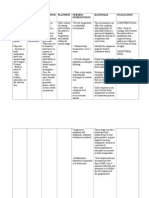
Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective airway clearance related to edema secondary to circumferential burns as evidenced by burned
areas in neck and chest, difficulty of breathing, cyanosis and RR of 10 bpm. Expected Outcome Client will be able to demonstrate clear breath sounds, respiratory rate within normal range, be free of dyspnea and cyanosis within 2 days of nursing intervention. Nursing Intervention 1. Obtain history of injury. Note presence of preexisting respiratory conditions, history of smoking. Evaluation Discharge Planning Goal met, client 1. Patient should finish able to demonstrate any prescription for clear breath antibiotics, even if sounds, normal he/she is feeling well. 2. Assess gag/swallow reflexes; note respiratory rate, If there is any drooling, inability to swallow, free of dyspnea and concern of an allergic hoarseness, wheezy cough. cyanosis as reaction, please call evidenced by: the doctor. 3. Monitor respiratory rate, rhythm, 2. Patients should start Absence of depth; note presence with small, frequent wheezing of pallor/cyanosis and carbonaceous meals. Diet Absence of or pink-tinged sputum. restrictions on dyspnea discharge vary from Absence of 4. Auscultate lungs, noting patient to patient, and cyanosis stridor,wheezing/crackles, diminished will be reviewed with RR of 18 breath sounds, brassy cough. the patient before bpm. discharge. 5. Note presence of pallor or cherry3. Taking naps and red color of unburned skin. engaging in light activity will help. 6. Investigate changes in Patients should avoid behavior/mentation, strenuous activity, ex.., restlessness, agitation, driving, heavy lifting, confusion. and contact sports, until cleared by the 7. Elevate head of bed. Avoid use of doctor at the followpillow under head, as indicated. up visit 8. Encourage coughing/deepbreathing exercises and frequent position changes. 9. Administer humidified oxygen via appropriate mode, e.g., face mask. 10. Prepare for/assist with intubation or tracheostomy, as indicated.
4. Patients may have physical or occupational therapy home visits to assist in their recovery. 5. Inform for follow-up visit.
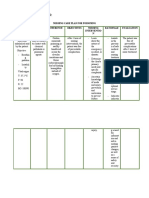
Nursing Diagnosis Impaired gas exchange related to carbon monoxide poisoning secondary to smoke inhalation as evidenced by difficulty of breathing, severe headache, nausea and vomiting, pale, PR-142 bpm, RR-10 bpm.
Expected Outcome Client will be able to maintain adequate tissue oxygenation within 8 hours of nursing intervention.
Nursing Intervention 1. Note respiratory depth, rate, use of accessory muscles, pursed lip breathing. 2. Auscultate breath sounds, note areas of decreased/adventitious breath sounds as well as fremitus. 3. Monitor vital signs and cardiac rhythm. 4. Evaluate pulse oximetry to determine oxygenation, 5. Review other pertinent laboratory data. (ABGs, CBC, CXR.) 6. Elevate head of bed/position client appropriately, mobilization as indicated to maintain airway. 7. Encourage deep breathing exercises, chest-physiotherapy to promote optimal lung expansion and drainage of secretions. 8. Maintain adequate I/O, for mobilization ofsecretions. 9. Encourage adequate rest and limit activities to within client tolerance. 10. Provide psychological support, active-listening to reduce anxiety. 11. Administer medications as indicated to treat underlying conditions. 12. Keep environment allergen free to reduce irritant effect of dust and chemicals on airways. 13. Emphasize the importance of nutrition in improving stamina and reducing the work of breathing.
Evaluation Goal met, client able to maintain adequate tissue perfusion as evidenced by stable vital signs stable vital signs t37C, PR-86 bpm, RR-18 bpm. And absence of : DOB Severe headache Nausea and vomiting Paleness
Discharge Planning 1. Review how and when to take these medications, what the drugs are used for, and any possible side effects before leaving the hospital. If there is any concern of an allergic reaction, please advice to call the doctor. 2. Encourage to have nutritious diet with plenty of fluids is important in the healing process. Diet restrictions on discharge vary from patient to patient, and will be reviewed with the patient before discharge. 3. Taking naps and engaging in light activity will help. Patients should avoid strenuous activity, driving, heavy lifting, and contact sports, until cleared by the doctor at the follow-up visit. 4. During recovery, patients may need equipment such as crutches, a wheelchair, or a shower seat. 5. Patients will be told how often theyll need to be seen for follow-up appointments after discharge
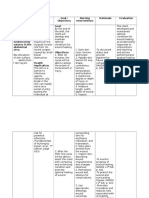
Nursing Diagnosis Fluid volume deficit related to increased capillary permeability and evaporative losses from the burn wound as evidenced by confusion, dry mucous membranes, urinary output of 10 cc per hour, T-38.9 C, PR142bpm, BP-80/40 mmhg.
Expected Outcome Client will be able to maintain fluid volume at a functional level after 2 days of nursing intervention.
Nursing Intervention 1. Assess and monitor vital signs and note for the capillary refill and strength of pulses. 2. Monitor urinary output of client. 3. Assess for the estimate of wound drainage and insensible loss. 4. Strictly document the amount and type fluid used during replacement therapy 5. Weigh client daily. 6. Investigate changes in mentation. 7. Observe for presence of gastric distention, hematemesis, and tarry stools. 8. Insert and maintain an indwelling catheter as indicated. 9. Insert and maintain large bore IV cannula. 10. Administer intravenous fluids as indicated. 11. Monitor laboratory results like hemoglobin, hematocrit, and electrolyte levels. 12. Administer medications like diuretics, potassium, and antacids.
Evaluation Goal met, client able to maintain a functional level of fluid volume as evidenced by: moist mucous membranes adequate urinary output (35 cc per hour), stable vital signs (37C, PR-86 bpm, RR-18 bpm, BP-90/60 mmhg)
Discharge Planning 1. Review how and when to take these medications, what the drugs are used for, and any possible side effects before leaving the hospital. 2. A well-rounded, nutritious diet with plenty of fluids is important in the healing process. 3. Activity is important for increasing the circulation, preventing loss of muscle strength, and improving general well-being. 4. Home Care Supplies and Equipment during recovery, patients may need equipment such as crutches, a wheelchair, or a shower. 5. For wound and bandage care, The patients incision should be kept clean and dry. The patient (or a designated person) should gently cleanse the skin around the incision daily with mild soap and water. Steri-strips can be allowed to fall off on their own. Check with the doctor about when to start showering or bathing. All instructions for more specialized wound care will be provided by the nurse or doctor.
SITUATION
A 36 year old man working in a factory was found after the fire had erupted in the building. He sustained a deep-partial burn on his face, neck, chest and right leg. He was brought subsequently to the nearest hospital. On the way to the hospital, the client complained of difficulty of breathing, severe headache, and continuously asking what had happened. After thorough examination it has been found that the client has laryngeal edema due to circumferential burn on the neck, blanch test of 4 seconds, paleness and dry mucous membranes. With vital signs of: t-38.9 pr-142 rr-10bpm bp-80/40 mmhg. urinary output of 10 cc per hour
NURSING CARE PLANS ACCORDING TO PRIORITY OF CARE ACTUAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS 1. Ineffective airway clearance related to edema secondary to circumferential burns. 2. Impaired gas exchange related to carbon monoxide poisoning secondary to smoke inhalation. 3. Fluid volume deficit related to increased capillary permeability and evaporative losses from the burn wound. 4. Infective tissue perfusion related to hypovolemia. 5. Acute pain related to destruction of skin. 6. Altered nutrition less than body requirements related to hypermetabolic state. 7. Impaired skin integrity related to disruption of skin surface/layers 8. Impaired physical mobility related to pain/discomfort. 9. alteration in comfort related to burn injury and treatment. 10. Fear anxiety related to memory of trauma experienced. 11. Knowledge deficit regarding condition related to information misinterpretation. POTENTIAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS. 1. Risk for infection related to burn injury.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nursing Care Plan For Burn NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Burn NCPderic80% (44)
- Nursing Care Plan - BurnDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan - Burnderic90% (10)
- NCP BurnDokument9 SeitenNCP Burnbanyenye2533% (3)
- 6639burn NCPDokument18 Seiten6639burn NCPDivina Grace Renon Camba100% (1)
- NCP Burn Risk InfectionDokument1 SeiteNCP Burn Risk InfectionBraingie Racho50% (4)
- NCP in BurnsDokument2 SeitenNCP in BurnsMayet De Castro Lejano80% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For The Patient With Burn Injury - Acute Pain Related To Tissue and Nerve InjuryDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For The Patient With Burn Injury - Acute Pain Related To Tissue and Nerve InjuryAngel Garcia67% (3)
- CHN NCPDokument2 SeitenCHN NCPIna Marie Calungcaguin Castro100% (1)
- NCP TetanusDokument6 SeitenNCP Tetanusbjhilario100% (1)
- Burns Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Risk For InfectionDokument1 SeiteBurns Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Risk For InfectionCyrus De AsisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disturbed Body ImageDokument3 SeitenDisturbed Body Imagenura100% (1)
- Risk For InfectionDokument2 SeitenRisk For InfectionSuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- Infection NCPDokument1 SeiteInfection NCPMsOrangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenNursing Care PlanKwini Jeyn50% (2)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDokument3 SeitenImpaired Skin IntegrityGerardeanne Reposar100% (2)
- NCP Impaired SkinDokument3 SeitenNCP Impaired SkinRuby AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Acute PainDokument2 SeitenNCP Acute PainMimi Nacor100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Worksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificDokument4 SeitenWorksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificCj MayoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karen Elizabeth B. Valdez Rle 2 Cues and Clues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenKaren Elizabeth B. Valdez Rle 2 Cues and Clues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Implementation Rationale EvaluationKaren ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Imapired Skin IntegrityDokument5 SeitenNCP Imapired Skin IntegrityAno BaItoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument13 SeitenNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- NCP For PoisoningDokument2 SeitenNCP For PoisoningLorie Yvonne Quibin Agullana100% (1)
- Short Term: Independent: Independent: Short TermDokument2 SeitenShort Term: Independent: Independent: Short TermAndre ImperialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDokument4 SeitenNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDokument2 SeitenNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityAshley Kate SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan of CataractDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan of CataractDimzmonyo100% (1)
- Central Nervous System Nursing Care PlanDokument11 SeitenCentral Nervous System Nursing Care PlanUday Kumar100% (1)
- NCP Leptospirosis - NewDokument5 SeitenNCP Leptospirosis - Newglaiza_requintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Infection)Dokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan Infection)Kez Domine100% (1)
- NCP Cataract SurgeryDokument5 SeitenNCP Cataract SurgeryKristaJaneCelmarBagcatNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Risk For Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionDokument2 SeitenNCP - Risk For Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionRene John Francisco50% (4)
- NCP Midterm Uncontrolled DMDokument12 SeitenNCP Midterm Uncontrolled DMYlron John Tapar100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisDokument3 SeitenNursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisVaneca Go67% (9)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument5 SeitenNursing Care PlanJohn Paul Delos Santos100% (1)
- NCP Epidural HemDokument32 SeitenNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument7 SeitenNCPChris Denver BancaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burn NCPDokument37 SeitenBurn NCPmildred alidonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeDokument3 SeitenNCP (Deficient Fluid VolumeNica RespondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostate Cancer NCPDokument1 SeiteProstate Cancer NCPKathleen Dimacali0% (1)
- NCP For CHDDokument2 SeitenNCP For CHDMonica Rivera100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanda 11 Edi. P. 620-621Dokument3 SeitenNanda 11 Edi. P. 620-621Besael Baccol0% (1)
- Nursing Students Peritonitis Care PlanDokument2 SeitenNursing Students Peritonitis Care PlanJide Manuel100% (1)
- Disturbed Visual Sensory Perception Related: Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenDisturbed Visual Sensory Perception Related: Nursing Care PlanMae Therese B. MAGNONoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionDokument16 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionFreisanChenMandumotan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Asessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAsessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationHikari 光 Shidou50% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDokument7 SeitenDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanjamieboyRN91% (32)
- NCP IcuDokument12 SeitenNCP IcuHazel Palomares50% (2)
- NCP FVDDokument2 SeitenNCP FVDMarlon AnryNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP TonsilitisDokument11 SeitenNCP TonsilitisGra Cie50% (6)
- NCP Risk For InfectionDokument3 SeitenNCP Risk For Infectionbanyenye25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Care of Pt.Dokument6 SeitenCare of Pt.hobradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept On Surgery: Postoperative CareDokument44 SeitenConcept On Surgery: Postoperative CareMelisa ClaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- SURGERY For Nurses PDFDokument98 SeitenSURGERY For Nurses PDFirene8000100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDokument16 SeitenNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Care of The Surgical PatientDokument25 SeitenGeneral Care of The Surgical PatientWendy Jeng100% (1)
- Ms Flash CardsDokument15 SeitenMs Flash CardsMia MalazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perioperative Nursing Hand Out - Postop-1Dokument22 SeitenPerioperative Nursing Hand Out - Postop-1Jamie NarcisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Clients With Burns and ShockDokument7 SeitenManagement of Clients With Burns and ShockJunah Marie Rubinos Palarca0% (1)
- History of Nursing and Nursing EducationDokument74 SeitenHistory of Nursing and Nursing EducationJunah Marie Rubinos Palarca100% (1)
- Sample Dream School LibraryDokument49 SeitenSample Dream School LibraryJunah Marie Rubinos PalarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Set-Up For A Sample Dream School PresentationDokument43 SeitenPhysical Set-Up For A Sample Dream School PresentationJunah Marie Rubinos PalarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Ode of EthicsDokument87 SeitenNursing Ode of EthicsJunah Marie Rubinos PalarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation On NephrolithiasisDokument40 SeitenCase Presentation On NephrolithiasisJunah Marie Rubinos Palarca100% (4)
- Management of Clients With Burns and ShockDokument84 SeitenManagement of Clients With Burns and ShockJunah Marie Rubinos PalarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Response PlanDokument8 SeitenRisk Response Planapi-639207174Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kübra Şendoğan CVDokument5 SeitenKübra Şendoğan CVKübra ŞendoğanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel SystemDokument24 SeitenFuel SystemHammad Uddin JamilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Claudia Maienborn, Semantics, 381Dokument34 SeitenClaudia Maienborn, Semantics, 381robert guimaraesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substitution Reactions - PMDokument64 SeitenSubstitution Reactions - PMprasoon jhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E WiLES 2021 - BroucherDokument1 SeiteE WiLES 2021 - BroucherAshish HingnekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet Brahma (2023)Dokument8 SeitenDatasheet Brahma (2023)Edi ForexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual ML 1675 PDFDokument70 SeitenManual ML 1675 PDFSergio de BedoutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualDokument24 SeitenChemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualElaineStewartieog100% (50)
- Norm ANSI PDFDokument1 SeiteNorm ANSI PDFAbdul Quddus Mat IsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDL E-Catalogue 2021-22 With ApticoDokument78 SeitenEDL E-Catalogue 2021-22 With Apticotkteetopoi1Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Path Vol 9 - William JudgeDokument472 SeitenThe Path Vol 9 - William JudgeMark R. JaquaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontrollers DSPs S10Dokument16 SeitenMicrocontrollers DSPs S10Suom YnonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIR REliefDokument32 SeitenBIR REliefJayRellvic Guy-ab67% (6)
- Operator Training ManualDokument195 SeitenOperator Training ManualIgnacio MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adolescence Problems PPT 1Dokument25 SeitenAdolescence Problems PPT 1akhila appukuttanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics Sheet 5 Energy ADokument19 SeitenHydraulics Sheet 5 Energy AMohamed H AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Dokument80 SeitenIBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Abubakar SidikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaibigan, Kabarkada, Kaeskwela: Pinoy Friendships and School LifeDokument47 SeitenKaibigan, Kabarkada, Kaeskwela: Pinoy Friendships and School LifeGerald M. LlanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement For Construction of Concrete Batching Plant (Combined)Dokument72 SeitenMethod Statement For Construction of Concrete Batching Plant (Combined)NP Dien100% (1)
- Annual Report 2022 2Dokument48 SeitenAnnual Report 2022 2Dejan ReljinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide For Sustainable Design of NEOM CityDokument76 SeitenGuide For Sustainable Design of NEOM Cityxiaowei tuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Conduct For Public OfficialDokument17 SeitenCode of Conduct For Public OfficialHaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trox Quick Selection GuideDokument47 SeitenTrox Quick Selection GuideErwin LouisNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGL102 Othello Act 3 Discussion QuestionsDokument2 SeitenENGL102 Othello Act 3 Discussion QuestionsDaniel DenningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project 2 Analysis of Florida WaterDokument8 SeitenProject 2 Analysis of Florida WaterBeau Beauchamp100% (1)
- The Impact of Online Games To The AcademicDokument20 SeitenThe Impact of Online Games To The AcademicJessica BacaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competent Testing Requirements As Per Factory ActDokument3 SeitenCompetent Testing Requirements As Per Factory Actamit_lunia100% (1)
- Green ChemistryDokument17 SeitenGreen ChemistryAaditya RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables: You Should LearnDokument8 SeitenSolving Systems of Linear Equations in Three Variables: You Should LearnTheodore JoaquinnNoch keine Bewertungen