Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Latih Tubi Tingkatan 3
Hochgeladen von
noorfazillaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Latih Tubi Tingkatan 3
Hochgeladen von
noorfazillaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EXERSICE SUBTOPIC 8.
1 The Generation Of Electrical Energy
hydroelectric
Solar
energy. Wind
Geothermal Tides
Nucleur
chemical(diesel) heat(burning) D. Diesel generator kinetic(gas turns the turbines) electrical energy. 3. Complete the following diagram.
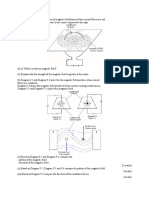
1. Figure 1 shows a pie chart of various of generators that produce electricity in Malaysia. Identify each of the sectors.
Thermal
Gas turbine
Diesel
2. Complete the table below to show the changes of energy in different types of generators. Generator The changes of energy A. Thermal generator Chemical(fuel) heat(burning) kinetic (steam turns the turbines) electrical energy. B. Hydroelectric generator C. Gas turbine generator potential(stored water) kinetic(water turns the turbines) electrical energy.
Renewable Clean
4. The Figure 2 shows a type of electrical energy generator.
chemical(pure gas) heat(burning) kinetic (gas turns the turbines) electrical
Figure 2 (a) Name the type of electrical energy generator in the Figure 2. . (b) What is the source of power used ? . (c) What cause the turbine to spin ?
iii. iv. v. 8. List two disadvantages of generation of electricity using a diesel generator. i.
. (d) What is the energy changes in this type of generator ? . 5. Name the five types of generators. i. ii. iii. iv. v. 6. Give two examples of alternative sources of energy. i. ii. 7. State the sources of energy used in different power station. i. ii.
ii.
EXERSICE SUBTOPIC 8.2 Transformer
1. Figure 2 shows a transformer. Name the labelled parts.
Alternating current supply Primary coil Secondary coil
(a) (b)
State the type of transformer shown in Figure 3. State the type of current needed for this transformer.
step up transformer
Alternating current supply (c) If the input voltage is 240 V, state the output voltage of
this transformer.
720V
2. State the differences between a step up transformer and a step down transformer. Step up transformer Step down transformer (b) Has more turns in the Primary coil. than in the Secondary coil. (c) The input voltage is greater than the output voltage. P : Q : (b) What is the similarity between transformers P and Q ? (a) Name transformer P and Q. 4. Compare and contrast transformers ;
(a) Has more turns in the Secondary coil than in the Primary coil. (c) The output voltage is greater than the input voltage.
3. Figure 3 shows a transformer.
. (c) What are differences between transformers P and Q ?
.
Soft iron core
5. Figure 4 shows a transformer.
(a) i. ii. (b) (a) (b) i. ii. (c) Describe the roles of transformers in the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. i. .. ii. ... Figure 4 Label the different parts of the transformer. Name the two types of transformer. P : Q :
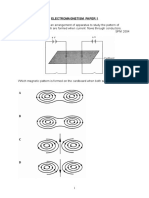
Figure 5 What do P and Q in the above Figure 5 represent ?
What type of transformer is shown in Figure 5 ?
(c) Which bulb will be brighter in the Figure 5 ? . (d) Name two factors that influence the voltage output in the secondary coil of the transformer.
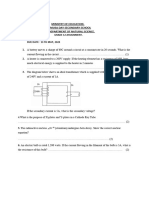
6. The Figure 5 shows a simple transformer. 7. Diagram 6.1 shows a cellular phone battery charger and a transistor radio connected to 240 V power outlets.
50 Figure 6.1 (a) State one inference regarding the voltage of electrical power required by the two appliances. (b) A group of students carry out an experiment to study how different transformers connected to the same power supply can output different voltages of electrical power. Diagram 6.2 shows the set up of apparatus used by the students in their investigation. 50
50
40
50
30
Figure 6.3 Table 8.4 shows the readings of the voltmeter when there are 50 turns in the secondary coil. Figure6.2 They changes the number of turns in the secondary coil without changing the number of turns in primary coil and record the resulting voltmeter readings. Figure 6.3 shows the readings of the voltmeter observed by the group of students. Number of turns in Number of turns in Voltmeter reading Primary coil Secondary coil Number of turns in Primary coil Number of turns in Secondary coil Voltmeter reading Table 6.4 50 50 20 50 40 50 30
(i)
Based on Figure 6.3, record in Table 6.4, the respective readings the voltmeter when there are 40 turns and 30 turns in the secondary coil. (ii) Based on the readings in Table 6.4, draw a line graph of voltmeter reading against number of turns in secondary coil on the provided axes.
(iii) Based on line graph drawn in (ii), (a) State the relationship between the number of turns in the secondary coil and the reading of the voltmeter. (b) Predict the respective readings of the voltmeter when there are 20 turns and 10 turns in the secondary coil. Number of turns in Secondary coil 20 10 (iv) State the manipulated variable in this experiment. Voltmeter reading ( V )
(v) Make a conclusion regarding the relationship between the number of turns in the secondary coil of a transformer and the voltage of the current output by the transformer.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Von EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Group Discussion G Group Discussion HDokument5 SeitenGroup Discussion G Group Discussion HMohd Afiffi BaharuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsVon EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial TRANSFORMERkem Cuti 2011Dokument7 SeitenTutorial TRANSFORMERkem Cuti 2011Mohamad Rizal MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 P2Dokument20 SeitenChapter 7 P2Amelia SuidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnet DemagnetizationDokument11 SeitenElectromagnet DemagnetizationSyazlina SamsudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 P2Dokument18 SeitenChapter 9 P2faisal850720035887Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDokument8 Seiten9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Chapter 4: Electronics: A. B. C. D. EDokument8 SeitenTutorial Chapter 4: Electronics: A. B. C. D. EMohamad Rizal MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Field Strength of CoilDokument16 SeitenMagnetic Field Strength of CoilDewan Olin ChotepadaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 P2Dokument20 SeitenChapter 7 P2siewkiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 CXC Elec Paper 2Dokument15 Seiten2014 CXC Elec Paper 2api-255989257Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Darren Set 1-1Dokument11 SeitenPhysics Darren Set 1-1duncan pengchew limNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.pecutan ElektromagnetDokument11 Seiten1.pecutan ElektromagnetAnna Latifah CammryNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRSM08P2SAQ8: Structured Question: (Force On Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field)Dokument10 SeitenMRSM08P2SAQ8: Structured Question: (Force On Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field)ChewLee TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air University Electrical Engg Deptt EE 342 (Electrical Machines) Quiz - 8 (B)Dokument1 SeiteAir University Electrical Engg Deptt EE 342 (Electrical Machines) Quiz - 8 (B)Ali AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 TransformerDokument7 Seiten9 TransformerMThana BalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADE 12 ASSIGNMENTDokument7 SeitenGRADE 12 ASSIGNMENTmutalebrighton45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Diode and TransistorDokument7 SeitenLatihan Diode and TransistorayydenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Soalan Final JJ102 Electrical TechnologyDokument11 SeitenContoh Soalan Final JJ102 Electrical TechnologyAh TiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Work, Energy&PowerDokument9 Seiten12 Work, Energy&PowersyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Machines and Electrical Drives Exam QuestionsDokument2 SeitenDC Machines and Electrical Drives Exam QuestionsJangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENEL2ELH1 - Electrical EngineeringDokument10 SeitenENEL2ELH1 - Electrical EngineeringqanaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE6352 16marks QBDokument5 SeitenEE6352 16marks QBThayja Rae Opiana MaganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568Dokument7 SeitenElec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568family7482pleaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample 2Dokument3 SeitenSample 2Sujeev GyawaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electrical Engineering - Question Bank For Term End ExamDokument8 SeitenBasic Electrical Engineering - Question Bank For Term End Examkrishnaprasad908312Noch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity TEST: Name: ClassDokument3 SeitenCurrent Electricity TEST: Name: ClassRobbie TurnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Gates and Circuits Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument13 SeitenLogic Gates and Circuits Multiple Choice QuestionsnguyentrongtinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uses of the Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRODokument21 SeitenUses of the Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CROKalai SelviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air University Electrical Engg Deptt EE 342 (Electrical Machines) Quiz - 6&7 (A)Dokument1 SeiteAir University Electrical Engg Deptt EE 342 (Electrical Machines) Quiz - 6&7 (A)Ali AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Third Semester Diploma Examination in Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical TechnologyDokument3 SeitenThird Semester Diploma Examination in Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical TechnologyeegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- L-2ff-2/EEE Date: 25/09/2022Dokument25 SeitenL-2ff-2/EEE Date: 25/09/2022Rajesh RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure Questions: 1. SPM 2013: QUESTION 3Dokument22 SeitenStructure Questions: 1. SPM 2013: QUESTION 3Cart KartikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bda 14303Dokument8 SeitenBda 14303Mahfuzah MustaphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee324 - Electrical Machines and DrivesDokument6 SeitenEe324 - Electrical Machines and DrivesDavid Jnr PeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12phy ch7Dokument1 Seite12phy ch7guggu esNoch keine Bewertungen
- Res (Ele Iv) Nov 2012Dokument2 SeitenRes (Ele Iv) Nov 2012jyothigkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial - Problem Sets - 1 - 2023Dokument6 SeitenTutorial - Problem Sets - 1 - 2023tagore TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eds PDFDokument4 SeitenEds PDFvinayakshettypeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM 2003Dokument18 SeitenSPM 2003faisalsmkpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3021 Electrical - Electronics Engg - QPDokument4 Seiten3021 Electrical - Electronics Engg - QPMuhd Shabeeb ANoch keine Bewertungen
- List of FiguresDokument3 SeitenList of FiguresaymenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 11 Electromagnetism RevisionDokument27 SeitenYear 11 Electromagnetism RevisionLawrenceOnthugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be8255 Rejinpaul April May 2018Dokument2 SeitenBe8255 Rejinpaul April May 2018LokeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 1-Group 1: What Is The Effective Resistance of The Connection Shown in The Picture Below? A. BDokument5 SeitenWorksheet 1-Group 1: What Is The Effective Resistance of The Connection Shown in The Picture Below? A. BayydenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheet 2 - PhysicsDokument25 SeitenActivity Sheet 2 - PhysicsRida AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines FundamentalsDokument8 SeitenElectrical Machines FundamentalsUdayKiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Sheets May Be Supplied On Demand: Page 1 of 2Dokument2 SeitenGraph Sheets May Be Supplied On Demand: Page 1 of 2sarang acNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCTE 2331 Electrical Machines ExamDokument7 SeitenMCTE 2331 Electrical Machines ExamAmir ALQedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Basic Electrical EngineeringDokument4 Seiten3 Basic Electrical EngineeringJyothsna VayyalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Theory 09-10 Even 02 SemDokument4 SeitenCircuit Theory 09-10 Even 02 Semsrinimeha@gmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Assignment CurrentDokument9 SeitenPhysics Assignment Currentsuhaibali7292Noch keine Bewertungen
- B PH 7 Q Mpboard EngDokument3 SeitenB PH 7 Q Mpboard Enggoutamlovewanshi70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuits 5 QPDokument8 SeitenElectric Circuits 5 QPFaraz AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Et 202 (B)Dokument3 SeitenEt 202 (B)murugan_collegemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode Rectifier Circuits ExplainedDokument3 SeitenDiode Rectifier Circuits ExplainedHaslina ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5Dokument13 SeitenForm 5Vanusha AzzrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 3 Chap 7 Exercise Complete)Dokument19 SeitenScience Form 3 Chap 7 Exercise Complete)Henry Hoe100% (2)
- Ec PH Manual 06 09 2016Dokument20 SeitenEc PH Manual 06 09 2016YoussefNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Second Term Exam of EnglishDokument2 SeitenThe Second Term Exam of Englishsof chimiste100% (1)
- KoneCranes Manuals 2898Dokument136 SeitenKoneCranes Manuals 2898Jairo Garcia Domenique67% (18)
- McIntosh MDA5000 Car Source Mobile Digital To Analog ConvertorDokument2 SeitenMcIntosh MDA5000 Car Source Mobile Digital To Analog ConvertorNicolus CageNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMMCDokument16 SeitenPMMCRavi Shankar 31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optical ComDokument20 SeitenOptical ComMelsougly BryceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4.2 Electrical Energy ManagementDokument61 SeitenUnit 4.2 Electrical Energy ManagementJoeb DsouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigger CircuitDokument9 SeitenTrigger CircuitMouliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features Description: Toy Motor Driver Series MX214Dokument8 SeitenFeatures Description: Toy Motor Driver Series MX214jaluadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electric Machines A Primer With MatlabDokument411 SeitenFundamentals of Electric Machines A Primer With MatlabKONANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limiting Circuits Experiment GuideDokument31 SeitenLimiting Circuits Experiment Guideعبدالرحمن النويصرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthing System of Instrument EquipmentDokument2 SeitenEarthing System of Instrument EquipmentSaravanan ThangaveluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Er9000en 21204 1.00Dokument106 SeitenEr9000en 21204 1.00Alexandru AnghelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ujt OscillatorDokument4 SeitenUjt OscillatorSANTI MVEDJI Jean PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Physics Unit 3 Objective QuestionDokument12 SeitenApplied Physics Unit 3 Objective QuestionNitin YogeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sem 20180426 Ats Iem FL1Dokument2 SeitenSem 20180426 Ats Iem FL1Choco Mila BeidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kipor generator shop manual guide to specifications, wiring diagrams and repairDokument38 SeitenKipor generator shop manual guide to specifications, wiring diagrams and repairantoniomecpt100% (1)
- De-Embedding Transmission Line Measurements For Accurate Modeling of IC DesignsDokument7 SeitenDe-Embedding Transmission Line Measurements For Accurate Modeling of IC DesignsXin LINoch keine Bewertungen
- Programming Amd'S Cmos EpromsDokument11 SeitenProgramming Amd'S Cmos EpromsrwpaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DatasheetDokument8 SeitenDatasheetTom TomNoch keine Bewertungen
- CD4016Dokument8 SeitenCD4016api-3708997100% (1)
- Long Line Application CARRIER-R22Dokument52 SeitenLong Line Application CARRIER-R22Bruce OreNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAX803/MAX809/ MAX810 3-Pin Microprocessor Reset Circuits: General Description Benefits and FeaturesDokument8 SeitenMAX803/MAX809/ MAX810 3-Pin Microprocessor Reset Circuits: General Description Benefits and FeaturesMaria TzagarakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FuseDokument0 SeitenFusekaushikray06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductors Notes PDFDokument20 SeitenSemiconductors Notes PDFVishalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.boq Ges P-1Dokument6 Seiten6.boq Ges P-1RoshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galvanic CP test stationsDokument4 SeitenGalvanic CP test stationsImran khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series RLC Circuit Voltage and Impedance AnalysisDokument8 SeitenSeries RLC Circuit Voltage and Impedance AnalysisJeffrey JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Velleman Pcsu200 Usb Oszi GeneratorDokument18 SeitenVelleman Pcsu200 Usb Oszi Generatorsandro2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors and Actuators SyllabusDokument14 SeitenSensors and Actuators SyllabusKeerthan R VarmaNoch keine Bewertungen