Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pathophysiology of Angina Pectoris
Hochgeladen von
Leroy LoyOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pathophysiology of Angina Pectoris
Hochgeladen von
Leroy LoyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pathophysiology of Angina Pectoris Angina is the sign of myocardial ischemia. Main presentation is retrosternal chest pressure.
Coronary flow reserve is the maximal increase in coronary blood flow from vasodilation above levels. Demand for coronary blood flow increases with heart rate, contractility (sympathetic activation), and myocardial wall tension (high afterload (HTN) or preload). Large arteries offer little resistance to coronary blood flow. Coronary arterioles are highest resistance. Normally these coronary arterioles can dilate to meet oxygen demand, but in atherosclerosis they cant. Myocardial blood flow = resting
(diastolic pressure) - (end - diastolic pressure) arteriole resistance
**Compressive forces of the heart are highest on the coronary arterioles of the subendocardium. Therefore, the LV subendocardium is at highest risk for ischemia. The subendocardium has the lowest coronary flow reserve due to the high extrinsic compressive forces. **Adenosine is a metabolite of ATP produced during exercise or ischemia. It is a powerul vasodilator that helps restore oxygen supply by dilating coronary arterioles. Atherosclerotic Stenoses of the Large Arteries CAD will cause narrowing/stenosis of the larger vessels. Arterioles will dilate to preserve adequate blood flow. Above 60% stenosis, coronary arterioles are maximally dilated. Basal flow rate is preserved, but there there is no coronary flow reserve left. Any increased oxygen demands above basal state will cause angina. Above 90% stenosis, even basal flow rate is impaired and this will cause unstable angina. Endothlial Dysfunction NO is released by normal endothelium in response to many signals, including ACh. If endothelium is dysfunctional, ACh stimulates smooth muscle cells instead of endothelium, causing paradoxical vasoconstriction. **Patients with atherosclerosis show reduced/absent vasodilation in response to ACh. In fact, during exercise they will actually have coronary vasoconstriction. **Nitroglycerin is a direct smooth muscle dilator that doesnt require endothelium for effectiveness. All vessels dilate with nitroglycerin, whether theres good endothelium or not. In the morning and during exercise, catecholamines increase. Catecholamines constrict vessels in people with atherosclerosis, so most angina and MIs occur with stress, exercise, or in the morning. These patients have variable coronary flow reserve due to endothelial dysfunction and coronary stenosis. Clinical Evaluation of Angina Angina presents as substernal chest pressure occuring with exertion or stress that is relieved with rest or nitroglycerin. It is classified 1-5. Evaluation includes exercise stress test, catheterization (perfusion imaging), echocardiogram, CT.
Treatment for stable CAD is ABCDE: --Aspirin, ACE inhibitors --Beta-blockers --Cholesterol lowering, cigarette cessation --Diet, Diabetes control (more for BP and lipid lowering than for their hyperglycemia) --Exercise Revascularization can be done with bypass surgery or angioplasty. Recommended if there is multivessel CAD, very poor stress test, or debilitating angina.
(Raymond removed an image describing factors influencing myocardial oxygen supply and demand.)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Clock of Destiny Book-1Dokument46 SeitenClock of Destiny Book-1Bass Mcm87% (15)
- Risk For InfectionDokument7 SeitenRisk For InfectionAnn Michelle TarrobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MJDF Mcqs - Mixed - PDFDokument19 SeitenMJDF Mcqs - Mixed - PDFAyesha Awan0% (3)
- 1 Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument11 Seiten1 Impaired Gas ExchangeKristian Dave DivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetaminophen ToxicityDokument14 SeitenAcetaminophen ToxicityJam MajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument53 SeitenNursing Care PlanAsma AlsaketNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGI MANIMTIM - COVID-19 in PregnancyDokument1 SeitePGI MANIMTIM - COVID-19 in PregnancyKim Adarem Joy ManimtimNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP CopdDokument4 SeitenNCP CopdMarion Dela VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Happ Lab 1Dokument5 SeitenHapp Lab 1Jerwin TullaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Head InjuryDokument5 SeitenAcute Head InjuryRitesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJustine Mae A. LoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FluidDokument45 SeitenFluidloglesb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDokument3 SeitenImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- IbuprofenDokument2 SeitenIbuprofenKate AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Patient X Age: 14 Y/oDokument4 SeitenName: Patient X Age: 14 Y/oRyan Jay Patacsil100% (1)
- Week 1 InfographicDokument2 SeitenWeek 1 InfographicHannah BangkilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating RoomDokument13 SeitenOperating RoomrichardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 007Dokument34 SeitenChapter 007calfornianursingacadNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP FinalDokument4 SeitenNCP FinalKathrina CraveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver TransplantsDokument6 SeitenLiver Transplantssadaq84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokument14 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP-Ineffective Breathing Pattern-ManaoisDokument2 SeitenNCP-Ineffective Breathing Pattern-ManaoisDan Dan ManaoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence-Based Nursing: I. Clinical QuestionDokument4 SeitenEvidence-Based Nursing: I. Clinical QuestionRay Jorge MarmetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pain (AGE) NCPDokument1 SeiteAcute Pain (AGE) NCPMike SoySauce LibrojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay About DiabetesDokument3 SeitenEssay About DiabetesKin Demotica100% (1)
- Nasogastric Tube Feeding ML4763 PDFDokument7 SeitenNasogastric Tube Feeding ML4763 PDFStereo PodNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP ProperDokument9 SeitenNCP Properstephanie eduarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument2 SeitenActivity IntoleranceGrace IgnacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MotiliumDokument5 SeitenMotiliumAkram KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Belief ModelDokument8 SeitenHealth Belief ModelRUIZ JAKE CANCILLER. VELARDENoch keine Bewertungen
- Physician'S Order/Progress Notes: 23 S. Avila Male JhonDokument2 SeitenPhysician'S Order/Progress Notes: 23 S. Avila Male JhonKrizha Angela Nicolas100% (1)
- NCP RiskDokument2 SeitenNCP RiskNorries Jonell CaballarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Pandemic To The Psychological Aspects of Nursing StudentsDokument25 SeitenImpact of Pandemic To The Psychological Aspects of Nursing StudentsBrandon AreteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of The Mother, Child at Risk or With Problems (Acute and Chronic)Dokument6 SeitenCare of The Mother, Child at Risk or With Problems (Acute and Chronic)Elizabeth ZamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationTedd CamilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample NCP Table With Sample Priorotization and Justification of ProblemsDokument8 SeitenSample NCP Table With Sample Priorotization and Justification of ProblemsCharm TanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
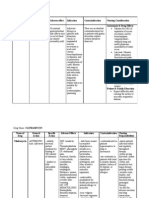
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDokument6 SeitenDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeJaymark LambinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure SoresDokument43 SeitenPressure SoresArpanpatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Cesarean Section DeliveryDokument5 SeitenPost Cesarean Section Deliveryᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX Fracture PDFDokument8 SeitenDX Fracture PDFSherree HayesNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Eastern Philippines: Scientific RationaleDokument3 SeitenUniversity of Eastern Philippines: Scientific RationaleJane MinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaDokument6 SeitenPa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaPaula YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsDokument8 SeitenPropranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsArlyn MarcelinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDokument65 SeitenCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- Cap MRDokument3 SeitenCap MRRhio Grulla RamboyongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotating TourniquetDokument3 SeitenRotating TourniquetTom-tom LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For Acute PainDokument4 SeitenNCP For Acute PainimnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument6 SeitenNCPSarah Younes AtawnehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Teaching Plan Non Pharmacological Pain ManagementDokument2 SeitenHealth Teaching Plan Non Pharmacological Pain ManagementJohn Carl ElpedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5ncp AnemiaDokument8 Seiten5ncp Anemiabeverly_domingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For Breast CancerDokument2 SeitenNCP For Breast Cancergeng gengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument13 SeitenNursing Care Planyumiko0% (1)
- Assignment 5 - Fernandez, Dexter IvanDokument1 SeiteAssignment 5 - Fernandez, Dexter IvanIvan FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument6 SeitenNCPgenevieve kryzleiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ko BabyDokument3 SeitenNCP Ko BabyDaniel ApostolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug and NCPDokument15 SeitenDrug and NCPgeelawlietNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument9 SeitenNCPLeolene Grace BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ursing ARE LAN: Short Term Goal: Independent Intervention: Independent InterventionDokument2 SeitenUrsing ARE LAN: Short Term Goal: Independent Intervention: Independent InterventionGiselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Angina PectorisDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Angina PectorisShalini ShanmugalingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASHRAE Final Operating Room 508 PDFDokument13 SeitenASHRAE Final Operating Room 508 PDFSilisteanu AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication MethodDokument30 SeitenCommunication MethodMisganaw GishenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Ways To Support Your Babys Learning Today Monti KidsDokument19 Seiten7 Ways To Support Your Babys Learning Today Monti KidsMareim A HachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Venere Jeanne Kaufman: July 6 1947 November 5 2011Dokument7 SeitenVenere Jeanne Kaufman: July 6 1947 November 5 2011eastendedgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0378432004002465 MainDokument20 Seiten1 s2.0 S0378432004002465 MainMuhammad JameelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kpolovie and Obilor PDFDokument26 SeitenKpolovie and Obilor PDFMandalikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Sea 500 Ats ManDokument18 SeitenDeep Sea 500 Ats ManLeo Burns50% (2)
- Damage To Bottom Ash Handling SysDokument6 SeitenDamage To Bottom Ash Handling SyssanjeevchhabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggestions On How To Prepare The PortfolioDokument2 SeitenSuggestions On How To Prepare The PortfolioPeter Pitas DalocdocNoch keine Bewertungen
- FBISE Grade 10 Biology Worksheet#1Dokument2 SeitenFBISE Grade 10 Biology Worksheet#1Moaz AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yuzu InstallerDokument3 SeitenYuzu InstallerJohnnel PrietosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Stakeholders in Health Care SystemDokument5 SeitenMajor Stakeholders in Health Care SystemANITTA S100% (1)
- Service M5X0G SMDokument98 SeitenService M5X0G SMbiancocfNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Practicals Class Xii 2022 23Dokument1 SeiteList of Practicals Class Xii 2022 23Night FuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaybalay CityDokument28 SeitenMalaybalay CityCalvin Wong, Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Ijrerd-C153Dokument9 Seiten20 Ijrerd-C153Akmaruddin Bin JofriNoch keine Bewertungen
- New KitDokument195 SeitenNew KitRamu BhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal KORELASI ANTARA STATUS GIZI IBU MENYUSUI DENGAN KECUKUPAN ASIDokument9 SeitenJurnal KORELASI ANTARA STATUS GIZI IBU MENYUSUI DENGAN KECUKUPAN ASIMarsaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unix SapDokument4 SeitenUnix SapsatyavaninaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining For Business Analyst AssignmentDokument9 SeitenData Mining For Business Analyst AssignmentNageshwar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top Survival Tips - Kevin Reeve - OnPoint Tactical PDFDokument8 SeitenTop Survival Tips - Kevin Reeve - OnPoint Tactical PDFBillLudley5100% (1)
- Security Policy 6 E CommerceDokument6 SeitenSecurity Policy 6 E CommerceShikha MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog de Aparatura Si Instrumentar Veterinar Eikemeyer-GermaniaDokument336 SeitenCatalog de Aparatura Si Instrumentar Veterinar Eikemeyer-GermaniaDr. Dragos CobzariuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mystakidis2022 MetaverseDokument13 SeitenMystakidis2022 MetaverseVennela NandikondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agile in ISO 9001 - How To Integrate Agile Processes Into Your Quality Management System-Springer (2023)Dokument67 SeitenAgile in ISO 9001 - How To Integrate Agile Processes Into Your Quality Management System-Springer (2023)j.paulo.mcNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Based Prepaid Electricity System With Theft Detection Using Arduino For The Domestic UserDokument13 SeitenGSM Based Prepaid Electricity System With Theft Detection Using Arduino For The Domestic UserSanatana RoutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 - Evolution and Classification: Regents BiologyDokument24 SeitenUnit 7 - Evolution and Classification: Regents BiologyTalijah JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMS156Dokument64 SeitenCMS156Andres RaymondNoch keine Bewertungen