Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Slow K
Hochgeladen von
Devon TossellOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Slow K
Hochgeladen von
Devon TossellCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
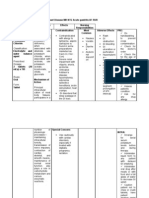
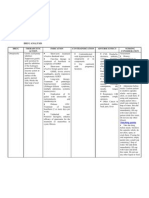
Generic Name Potassium chloride
Trade Name Slow K potassium chloride extendedrelease tablets
Classification mineral and electrolyte replacements/supplements
Dose
Route po
Time/frequency
Mechanism of action and indications (Why med ordered Maintain acid-base balance, isotonicity, and electrophysiologic balance of the cell Activator in many enzymatic reactions; essential to transmission of nerve impulses; contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle; gastric secretion; renal function; tissue synthesis; and carbohydrate metabolism Treatment/prevention of potassium depletion Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication. Explain to patient purpose of the medication and the need to take as directed,especially when concurrent digoxin or diuretics are taken. A missed dose should be taken as soon as remembered within 2 hr; if not, return to regular dose schedule. Do not double dose. Emphasize correct method of administration. GI irritation or ulceration may result from chewing enteric-coated tablets or insufficient dilution of liquid or powder forms. Someextended-release tablets are contained in a wax matrix that may be expelled in the stool. This occurrence is not significant. Instruct patient to avoid salt substitutes or low-salt milk or food unless approved by health care professional. Patient should be advised to read all labels to prevent excess potassium intake. Advise patient regarding sources of dietary potassium. Encourage compliance with recommended diet. Instruct patient to report dark, tarry, or bloody stools; weakness; unusual fatigue; or tingling of extremities. Notify health care professional if nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or stomach discomfort persists. Dosage may require adjustment. Emphasize the importance of regular follow-up exams to monitor serum levels and progress
Nursing Implications (what to focus on) Contraindications/warnings/interactions Hyperkalemia, Severe tissue trauma, Some products may contain tartrazine (FDC yellow dye #5) or alcohol; avoid using in patients with known hypersensitivity or intolerance Use cautiously in: Cardiac disease Common side effects abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting Lab value alterations caused by medicine Monitor serum chloride because hypochloremia may occur if replacing potassium without concurrent chloride. Monitor serum potassium before and periodically during therapy. Monitor renal function, serum bicarbonate, and pH. Determine serum magnesium level if patient has refractory hypokalemia; hypomagnesemia should be corrected to facilitate effectiveness of potassium replacement
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) None for this patient Nursing Process- Assessment (Pre-administration assessment) Monitor serum potassium levels, renal function, and serum bicarbonate Assessment Why would you hold or not give this med? If patient is showing signs of toxicity: dark, tarry, or bloody stools; weakness; unusual fatigue; or tingling of extremities Evaluation Check after Giving Prevention and correction of serum potassium depletion
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ib History Command Term PostersDokument6 SeitenIb History Command Term Postersapi-263601302100% (4)
- Service Manual: SV01-NHX40AX03-01E NHX4000 MSX-853 Axis Adjustment Procedure of Z-Axis Zero Return PositionDokument5 SeitenService Manual: SV01-NHX40AX03-01E NHX4000 MSX-853 Axis Adjustment Procedure of Z-Axis Zero Return Positionmahdi elmay100% (3)
- Atorvastatin Calcium Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenAtorvastatin Calcium Drug StudyFranz.thenurse6888100% (7)
- Drug Potassium Chloride KCLDokument1 SeiteDrug Potassium Chloride KCLSrkocher100% (3)
- Drug CardsDokument16 SeitenDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Clinical Medication ListDokument181 SeitenClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesVon EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Potassium ChlorideDokument2 SeitenPotassium ChlorideAdrianne BazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study ColestipolDokument3 SeitenDrug Study ColestipolAbby AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro K (Potassium Chloride)Dokument2 SeitenMicro K (Potassium Chloride)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Icu Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Drug Study (FINAL)Dokument31 SeitenDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potassium Chloride (Ktab)Dokument2 SeitenPotassium Chloride (Ktab)Marlisha D. BrinkleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potassium Salts Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenPotassium Salts Drug StudyCheezy BreadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyAl-nazer Azer AlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lascuna-Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseDokument1 SeiteNrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseJanet SheldonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Used in Liver DiseaseDokument17 SeitenDrugs Used in Liver Diseaseblast2111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Potassium ChlorideDokument1 SeiteDrug Potassium ChlorideSrkocherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyOdarp PradzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Dokument43 SeitenMedication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Kath Rubio0% (1)
- EzetimibeDokument3 SeitenEzetimibeapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenDrug StudyHelen ReonalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyCrystal Joy MisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVA Drug StudyDokument51 SeitenCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldactone SpironlactoneDokument1 SeiteAldactone SpironlactoneCassie100% (1)
- Docusate CalciumDokument1 SeiteDocusate CalciumMichael KuzbytNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5th Draft DrugsDokument7 Seiten5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug StudyChristine MatasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument11 SeitenDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vi. Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationsDokument4 SeitenVi. Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationsMilton CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metformin: Dosing & UsesDokument8 SeitenMetformin: Dosing & UsesMaria Alejandra Siachoque JaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- FurosemideDokument4 SeitenFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study Medcor AguinaldoDokument6 SeitenDrug Study Medcor AguinaldoYana PotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDokument11 SeitenDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Captopril (Drug Study)Dokument3 SeitenCaptopril (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (3)
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument15 SeitenDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKD Case StudyDokument8 SeitenCKD Case StudyEspiridionNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTP DM ParesisDokument4 SeitenHTP DM ParesisTami GemarinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenDrug Studyanon_11638632Noch keine Bewertungen
- HEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Dokument7 SeitenHEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Leoni HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Losartan PotassiumDokument3 SeitenLosartan Potassiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- TriamtereneDokument2 SeitenTriamtereneapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- Patient AssignmentDokument6 SeitenPatient AssignmentRj MagalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDokument5 SeitenDrug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDan DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM, KLDokument5 SeitenLM, KLVictor CondeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismDokument9 SeitenDrug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismRene John FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS Bernie Evan Doku FinnishDokument10 SeitenDS Bernie Evan Doku FinnishBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpironolactoneDokument3 SeitenSpironolactoneapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug StudyRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labs Drug Study 1Dokument17 SeitenLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDokument12 SeitenCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Potassium ChlorideDokument2 SeitenPotassium ChlorideSetiram Zenitram50% (2)
- Pravastatin SodiumDokument3 SeitenPravastatin Sodiumapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument17 SeitenDrug StudyJoan RabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast FAD Formula :Lose weight with FAD Diets: Eat Right N Wise, #1Von EverandFast FAD Formula :Lose weight with FAD Diets: Eat Right N Wise, #1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fix Your Genes to Fit Your Jeans: Optimizing Diet, Health and Weight Through Personal GeneticsVon EverandFix Your Genes to Fit Your Jeans: Optimizing Diet, Health and Weight Through Personal GeneticsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networker Performance Tuning PDFDokument49 SeitenNetworker Performance Tuning PDFHarry SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hole CapacityDokument2 SeitenHole CapacityAbdul Hameed OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISBN Safe Work Method Statements 2022 03Dokument8 SeitenISBN Safe Work Method Statements 2022 03Tamo Kim ChowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movie Piracy in Ethiopian CinemaDokument22 SeitenMovie Piracy in Ethiopian CinemaBehailu Shiferaw MihireteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Specification For 33KV VCB BoardDokument7 SeitenTechnical Specification For 33KV VCB BoardDipankar ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 1 W13 SolutionDokument5 SeitenHomework 1 W13 SolutionSuzuhara EmiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outdoor Air Pollution: Sources, Health Effects and SolutionsDokument20 SeitenOutdoor Air Pollution: Sources, Health Effects and SolutionsCamelia RadulescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument15 SeitenChronic Kidney Diseaseapi-270623039Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rockaway Times 11818Dokument40 SeitenRockaway Times 11818Peter J. MahonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1: Overview of Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA)Dokument37 SeitenModule 1: Overview of Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA)PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OZO Player SDK User Guide 1.2.1Dokument16 SeitenOZO Player SDK User Guide 1.2.1aryan9411Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monergism Vs SynsergismDokument11 SeitenMonergism Vs SynsergismPam AgtotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- V737 OverheadDokument50 SeitenV737 OverheadnewahNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Thi Hoc Ki 1 Mon Tieng Anh Lop 5 Co File NgheDokument10 SeitenDe Thi Hoc Ki 1 Mon Tieng Anh Lop 5 Co File Nghetuyen truongNoch keine Bewertungen
- E MudhraDownload HardDokument17 SeitenE MudhraDownload HardVivek RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study of Coustomer Satisfaction in Demat Account At: A Summer Training ReportDokument110 SeitenA Case Study of Coustomer Satisfaction in Demat Account At: A Summer Training ReportDeepak SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carob-Tree As CO2 Sink in The Carbon MarketDokument5 SeitenCarob-Tree As CO2 Sink in The Carbon MarketFayssal KartobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing FinalDokument15 SeitenMarketing FinalveronicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Contract Rousseau PDFDokument9 SeitenPsychological Contract Rousseau PDFSandy KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organization and Management Module 3: Quarter 1 - Week 3Dokument15 SeitenOrganization and Management Module 3: Quarter 1 - Week 3juvelyn luegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMR 13 Math 201 SyllabusDokument2 SeitenSMR 13 Math 201 SyllabusFurkan ErisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 3 - LPDokument21 SeitenTask 3 - LPTan S YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Construction of Optimal Portfolio Using Sharpe's Single Index Model - An Empirical Study On Nifty Metal IndexDokument9 SeitenThe Construction of Optimal Portfolio Using Sharpe's Single Index Model - An Empirical Study On Nifty Metal IndexRevanKumarBattuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bana LingaDokument9 SeitenBana LingaNimai Pandita Raja DasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aleksandrov I Dis 1-50.ru - enDokument50 SeitenAleksandrov I Dis 1-50.ru - enNabeel AdilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Famous Russian PianoDokument10 SeitenFamous Russian PianoClara-Schumann-198550% (2)
- Golf Croquet Refereeing Manual - Croquet AustraliaDokument78 SeitenGolf Croquet Refereeing Manual - Croquet AustraliaSenorSushi100% (1)
- Dialogue Au Restaurant, Clients Et ServeurDokument9 SeitenDialogue Au Restaurant, Clients Et ServeurbanuNoch keine Bewertungen