Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors
Hochgeladen von
James John GalacOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors
Hochgeladen von
James John GalacCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pathophysiology
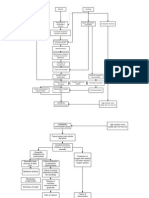
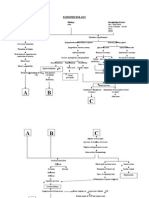
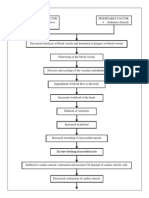
Predisposing factors: -Hereditary -Gender: Male -Age: Precipitating factors: -Hypertension -Cardiovascular disease -Cigarette smoking -High cholesterol -Being overweight -Heavy Drinking -Obstructive sleep apnea -Diabetes Milletus
Narrowing of blood vessels
Formation of plaque deposit
Occlusion of major vessels
Increase pressure in the blood vessels
Due to thrombosis, some neurons die because of lack of oxygen and nutrients
CVA (Stroke)
Cerebral Ischemia
Initiation of ischemic cascade
Anaerobic metabolism of mitochondria, which generates a large amount of lactic acid
Transient Ischemic Attack (weakness of the face, fingers, hands, arms)
Altered Cerebral Metabolism and decrease cerebral perfusion
Damage of the hemisphere of brain
Increased Intracranial pressure
Impaired perfusion and function
-Numbness on the left side of the brain -Trouble speaking -Difficulty of walking, dizziness -Sudden severe headache If not managed If manage
Space occupying blood clot put more pressure on the brain tissue
-Pallative care -Frequent vital sign and neuro vital sign
The ruptured cerebral vessels may constrict to limit blood loss, however, this vasospasm will result to further ischemia and necrosis of brain tissue Good improvement Good cerebral perfusion
BRAIN DEATH
Good Prognosis
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pathophysiology of CVADokument1 SeitePathophysiology of CVAYoussry JaranillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteCerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyBerde KangleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Factors and Pathophysiology of StrokeDokument4 SeitenRisk Factors and Pathophysiology of StrokeSherlyn KirisakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenStroke PathophysiologyMaureen Balagtas89% (9)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDokument2 SeitenGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- Causes and Effects of Cerebrovascular DiseaseDokument2 SeitenCauses and Effects of Cerebrovascular DiseaseTerence Valdehueza67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentPaulo de Jesus86% (7)
- Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic and Embolic DiseasesDokument2 SeitenModifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic and Embolic DiseasesJoy Rachelle Fermin100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke FinalAcohCChao67% (3)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenStroke PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Cva-Hpnii-Hemorrhagic StrokeLarisse de Leon82% (11)
- Pathophysiology CVA (Final2)Dokument10 SeitenPathophysiology CVA (Final2)Jayselle Costes FelipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic Pathophysiology CVADokument10 SeitenSchematic Pathophysiology CVAheiyu100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAy100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CVADokument2 SeitenPathophysiology CVASewyel Garburi100% (6)
- Pathophysiology of CVADokument1 SeitePathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology Diagram - StrokeDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology Diagram - Strokemisstheatricality130100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- CVA PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology CVADokument1 SeitePathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of CVADokument7 SeitenPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Pathophysiology CKDDokument1 SeitePathophysiology CKDReymon Mary JanineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke PathophysiologyDokument5 SeitenStroke Pathophysiologycinnabon_heart9100% (3)
- Pathophysiology CVDDokument1 SeitePathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of CHFDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of CHFImae Mayo60% (5)
- A Case Study On Ischemic Stroke: J.H. Cerilles State CollegeDokument21 SeitenA Case Study On Ischemic Stroke: J.H. Cerilles State CollegeNicole Aranding100% (4)
- Case Study On CVADokument34 SeitenCase Study On CVAGimcy Dela Fuente50% (2)
- Pathophysiology HypertensionDokument1 SeitePathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1Dokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1kristel_nicole18yaho60% (5)
- CVA Nursing Case StudyDokument76 SeitenCVA Nursing Case StudyGabriel Apalisok100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (10)
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDokument1 SeitePathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On CVADokument19 SeitenCase Study On CVAmolukas10190% (42)
- Rheumatic Heart Disease PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenRheumatic Heart Disease Pathophysiologyjethro sanchez100% (1)
- Patho MIDokument2 SeitenPatho MIbanyenye25100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CVADokument11 SeitenPathophysiology CVAallyana kim figueroa lavarias100% (1)
- Cva CPDokument53 SeitenCva CPApol Pen100% (2)
- Schematic Diagram of StrokeDokument1 SeiteSchematic Diagram of StrokeCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Pathophysiology ESRDDokument9 SeitenPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure ExplainedDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure ExplainedMar Ble50% (2)
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVADokument4 SeitenPathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CHFDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Patho StrokeDokument14 SeitenPatho StrokeKyla R. PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebrovascular Accident CVADokument8 SeitenCerebrovascular Accident CVAFlora Angeli PastoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Path o Client BasedDokument3 SeitenPath o Client BasedJane TuazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casebased PathoDokument2 SeitenCasebased PathoJm MapulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- StrokeDokument66 SeitenStrokeJoshua Smith100% (1)
- Circulatory DiseasesDokument33 SeitenCirculatory DiseasesMar YelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDokument3 SeitenSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lacunar Infarct and SyndromesDokument40 SeitenLacunar Infarct and Syndromeslovelots1234100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJet Ray-Ann GaringanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CvaDokument79 SeitenCvaAnn Heerah100% (1)
- Cerebrovascular Accident ReportDokument16 SeitenCerebrovascular Accident ReportAngelu Gabrielle CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDokument12 SeitenCerebrovascular AccidentNinaii LozaritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke: Abyot From Harrison, DR Belachew and DR Yared HandoutDokument32 SeitenStroke: Abyot From Harrison, DR Belachew and DR Yared HandoutashuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Evaluation FormDokument1 SeiteActivity Evaluation FormJames John GalacNoch keine Bewertungen
- COPAR Community OrganizingDokument4 SeitenCOPAR Community OrganizingJames John GalacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter To LRCDokument2 SeitenLetter To LRCJames John GalacNoch keine Bewertungen
- NursingDokument2 SeitenNursingJames John GalacNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Code of Ethics For Nurses 2012Dokument12 SeitenCode of Ethics For Nurses 2012Ar Jhay100% (1)