Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2013
Hochgeladen von
Norliza SapatanohCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2013
Hochgeladen von
Norliza SapatanohCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
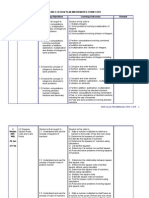
YEARLY LESSON PLAN MATHEMATICS FORM TWO 2013 LEARNING AREA/WEEKS Directed Numbers Week 1 - 3 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student
will be taught to 1.1 Perform computations involving multiplication and divison of integers to solve problems LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. i. Multiply integers ii. Solve problems involving multiplication of integers iii. Divide integers iv. Solve problems involving division of integers i. Perform computations involving combined operations of a) addition b) subtraction c) multiplication and division of integers ii. Solve problems involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of integers including the use of brackets i. compare and order fractions and decimals. ii. Perform addition , subtraction,multiplication or division on decimals i. Perform addition , subtraction, multiplication or division involving two directed numbers ii. Perform computations involving combination of two or more operations on directed numbers including the use of brackets iii. Pose and solve problems ivolving directed numbers TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES 1.Use concrete materials such as coloured chips 2. Complete multiplication table by recognizing patterns 3. Solve problems related to real life situations 1. 2. Student use calculators to compare and verify answers Solve problems related to real life situations such as money and temparature SKILLS Working out identyfying
1.2 Perform computations involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of integers to solve problems
Relationship Application
1.3 Extend the concept of integers to fractions and decimals to solve problems
1. Compare fractions and decimals using number a) number lines b) scientific calculator
Week 4
1.5 Perform computations involving directed numbers (integers,fractions and decimals)
Perform operations on a) integers b) fractions c) decimals d) both fractions and decimals
Working Out
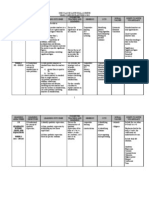
LEARNING AREA/WEEKS 2. Squares, square roots,cubes and cube roots Week 5 - 7
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to 2.1 Understand and use the concept of squares of numbers
LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. i. State a number multiplied by itself as a number to the power of two vice versa ii. Determine the squares of numbers without using calculators iii. Estimate the squares of numbers iv. Determine the squares of numbers using calculators v. List perfect squares vi. Determine if a number is a perfect square. vii. Pose and solve problems involving squares of numbers i. Determine the relationship between squares and square roots ii. Determine the square roots of perfect squares without using calculators iii. Determine the square roots of numbers withpout using calculators iv. Multiply two square roots v..Estimate square roots of numbers vi. Find the square roots using vii. Pose and solve problems involving square and square roots i. State a number multiplied by itself twice as a number to the power of three and vice versa ii. Determine cubes of numbers without using calculators iii. Estimate cubes of numbers iv. Determine cubes of numbers using calculators v. Pose and solve problems involving cubes of numbers
1. 2.
3. 4. 5.
TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES Recognise squares of numbers as the areas of the associated squares Use pencil-and paper method,mental and speed calculations to evaluate squares of numbers where appropriate Use estimation to check whether answers are reasonable Explore square numbers using calculators Explore perfect squares
SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES Identification Relatioship Working Out Application
2.2 Understand and use the concept of square
1. Explore the concept of square roots using areas of squares 2. Investigate multiplications involving square roots of: a) the same number b) different numbers 3. Use estimation to check whether answers are reasonable 4. Use calculators to explore the relationship between squares and square roots
Exploration Relationship Limit to : Fraction with numer. and denom. is a perfect squares Decimals that can be written in the form of square of another decimal
2.3 Understand and use the concept of cube of numbers
1. Recognise cube of a number as the volume of the associated cube 2. Use pencil-paper method, speed and mental calculations to evaluate cubes of numbers 3. Explore estimation of cubes of numbers 4. Explores cubes of numbers using calculators
Relationship Emphasise
LEARNING AREA/WEEKS Week 8 - 9
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to 2.4 Understand and use the concept of cube roots of numbers
LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. i. Determine the relationship between cubes and cube roots ii. Determine the cube roots of integers without using the calculators iii. Determine the cube roots of numbers without using the calculators iv. Estimate cube roots of numbers v. Determine cube roots of numbers using calculators vi. . Pose and solve problems involving cubes and cube roots vii. Perform computations involving addition , subtraction,multiplication,division and mihed operations on squares, square roots,cubes and cube roots i. Identify unknowns in algebraic terms in two or more unknowns ii. Identify unknowns in algebraic terms in two or more unknowns as the product of the unknowns with a number iii. Identify coefficients in given algebraic terms in two or more unknowns iv. Identify like and unlike algebraic terms in two or more unknowns v. State like terms for a given algebraic term i. Find the product of two algebraic terms ii. Find the quotient of two algebraic term iii. Perform multiplication and division involving algebraic terms i. Write algebraic expressions for given situations using letter
TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES 1. Use calculators to explore the relationship between cubes and cube roots
SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES Inquiry Relationship
2. Explore estimation of cube roots of numbers 3. Explore the relationship between cubes and cube roots using calculators
3. Algebraic Expressions II Week 10 - 11
3.1 Understand the concept of algebraic terms in two or more unknowns
1. Student identify unknowns in given algebraic terms 2. Use examples of everyday situations to explain algebraic terms in two or more unknows
Identify Relationship
3.2 Perform computations -involving multiplication and division of two or more terms
Week 12 - 13
3.3 Understand the concept of algebraic expressions
1. Explore multiplication and division of algebraic terms using the concrete materials or pictorial representations 2. Perform multiplication and division 1. Use situations to demonstrate the concept of algebraic expression
Working Out Explopration
Investigation Recognisation
symbols LEARNING AREA/WEEKS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. ii. Recognise algebraic expressions in two or more unknowns iii. Determine the number of terms in given algebraic expressions in two or more unknowns iv. Simplify algebraic expressions by collecting like terms v. Evaluate expressions by substituting numbers for letters i. Multiply and divide algebraic expressions by a number ii. Perform a) addition b) subtraction involving two algebraic expressions iii. Simplify algebraic expressions i. State the relationship between two quantities by using the symbol = and = i. Recognise linear algebraic terms ii. Recognise linear algebraic expressions iii. Determine if a given equation is a a) a linear equation b) a linear equation in one unknown iv. Write linear equations in omne unknown for give statements and vice versa i. Determine if a numerical value is a solution of a given linear equation in one unknown ii. Determine the solution of a linear equation in one unknown by trial and improvement method iii. Solve and verify linear equations in one unknown by inspection and systematic trial, using whole numbers, with or without the use
2. Investigate the difference between expressions . TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES
SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES
3.4 Perform computations involving algebraic expressions
4. Linear Equations Week 14 - 15
4.1 Understand and use the concept of equality 4.2 Understand and use the concept of linear equations in one unknown
1. Use situations to explain computations involving algebraic expressions 2. Add and subtract algebraic expressions by removing bracket and collecting like terms01 1. Use concrete examples to illustrate = and = 1. Discuss why given algebraic terms and expressions are linear 2. Given a list of terms, students identify linear terms 3. Select linear expressions given a list of algebraic expressions 4. Select linear equations given a list of algebraic equations 1. Use concrete examples to explain solution of a linear equation in one unknown
Relationshio Identificatio
Illustration Relationship Recognisation
4.3 Understand the concept of solutions of linear equations in one unknown
Investigation Working out
of calculators LEARNING AREA/WEEKS LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. iv. Solve equation in the form of ax + b = c, where a,b,c are integers and x is an unknown v. Solve linear equations in one unknown vi. Pose and solve problems involving i. Compare two quantities in the form a: b ii. Determine whether given ratios are equivalent ratios iii. Simplify ratios to the lowest terms iv. State ratios related to a given ratio i. State whether two pairs of quantities is a proportion ii. Determine if a quantity is proportional to another quantity given two values for each quantity iii. Find the value of a quantity given the ratio of the two quantities and the value of another quantity iv. Find the value of a quantity given the ratio and the sum of the two quantities v. Find the sum of two quantities given the ratio of the quantities and the difference between the quantities vi. Pose and solve problems involving ratios and proportions vii. Find the value ofeach of the three quantities ,given: a) the ratio and the sum oh three quantities b) the ratio and the difference TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES 2. Solve equations in the form of: a) x + a = b b) x - a = b c) ax = b d) x = b a 1. Use everyday examples to introduce the concept of ratio 2. Use concrete examples to explore: a) equivalent ratios b) related ratios SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES Investigation Working out
5. Ratios,Rates and Proportions Week 16 - 17
5.1 Understand the concept of ratio of two quantities
Exploration Identification
5.2 Understand the concept of proportion to solve problems
1.Use everyday examples to introduce the concept of proportion 2. Verify the method of cross multiplication and use it to find the missing terms of a proportion
Investigation Relationship Working Out
between two of the three quantities LEARNING AREA/WEEKS 6.0 Phytagoras Theorem Week 21 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to 6.1 Understand the relationship between the sides of a rightangled triangle LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. i. Identify the hypotenuse of a rightangled triangle ii. Determine the relationship between the length s of the sides of a right-angled triangle iii. Find the length of a missing side of a right-angled triangle using the P.T iv. Find the length of sides of geometric shapes using the P.T. v. Solve problems using the P.T i. Determine whether a triangle is a right-angled triangle ii. Solve problems involving the converse P.T. i. Construct a line segment of given length ii. Construct a triangle given the length of the sides iii. Construct: a) perpendicular bisector of a given line segment b)perpendicular to a line passing through a point of the line c)perpendicular to a line passing through a point of not on the line iv. Construct a) angle of 60o and 120o b) bisector of an angle v. Construct triangles given: a) one side and two angles b)two sides and one angle vi. Construct TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES 1. Show different cases where the hypotenuse drawn different orientation. SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES Relationship Identification
6.2 Understand and use the converse of the P.T. 7.0 Geometrical Construction 7.1 Perform constructions using straight edge (ruler and set square) and compass
1. Explore and investigate difference converse of P.T 1. Relate to properties of rhombusand isosceles triangle
Expoloration Investigation Construction Thinking Imagination
Week 22
a)parallel lines b) parallelogram given its sides and an angle LEARNING AREA/WEEKS 8.0 Coordinates Week 23 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to 8.1 Understand and use the concept of coordinates LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. i. Identify the x-axis , y axis and the origin on a Cartesian plane ii. Plot points and state the coordinate of the points given distances from the x-axis and y axis iii. Plot points and state the distances of the points from the x-axis and y axis given coordinates of the points iv. State the coordinates of points on Cartesian plane i. Mark the values on both axes by extending the sequence of given values on the axes ii.State the scales used in given coordinate axes iii. Mark the values on both axes, with reference to the scales given iv. State the coordinates of a given point with reference to the scales given v. Plot points, given the coordinates,with reference to the scales given v. Pose and solve problems using coordinates i. Find the distance between two points ii. Pose and solve problems involving distance between two points i. Identify and find the coordinate of the midpoint ii. Pose and solve problems TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES Introduce Cartesian Coordinates as a systematic way of marking the lovation of a point SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES Identification Notes: Involve all the 4 quadrants
Week 24 - 25
8.2 Understand and use the concept of scales for the coordinate axes
1. Explore the effects of the shapes of the objects by using different scales 2. Explore thje effects of shapes of objects using different scales
Emphasise Investigation
8.3 Understand and use the concept of distance between two p[oints on a Cartesian plan 8.4 Understand and use the concept of midpoints
1. Discuss different method of finding distance between two points Introduce the concept of midpoint Investigation
9.0 Loci in two dimensions Week 27 LEARNING AREA/WEEKS 10.0 Circles Week 28
9.1 Understand the concept of twodimensional loci
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to 9.2 Understand the concept of the intersection of two loci 10.1 Recognise and draw parts of a circle
10.2 Understand and use the concept of circumference to solve problems
Week 29
10.3 Understand and use the concept of arc of a circle to solve problems
involving midpoints i. Describe and sketch the locus of a moving object ii. Determine the locus of points iii. Construct the locus of a set of all points. LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. i. Determine the intersection of the two loci i. Identify circle as a set of points equidistant from a fixed point ii. Identify parts of a circle ii. Draw a circle based on the condition given iv. Detrmine the center and radius of a circle by construction i. Estimate the value of phi ii. Derive the formula of the circumference of a circle iii. Find the circumference of a circle iv. Find the diameter and radius v. Solve problems involving circumference of a circle i. Derive the formula of the length of an arc ii. Find the length of an arc iii. Find the angle at the centre iv. Find the length of radius of a circle v. Solve problems involving arcs of a circle i. Derive the formula of the area of a circle ii. Find the area, radius or diameter of a circle iii. Solve problems involving area of a circle i. Derive the formulka of the area of a sector
i. Use everyday examples ii. Discuss the locus og a given diagrams TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES Use everyday examples to explain. Introduce the concept of the circle as a locus
Inspection Working out
SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES Interpretation Working out
Measure diameter and circumference of circular objects
Developmental
Explore the relationship between the length of arc and angle at the centre
Exploration Inspection
10.4 Undertsand and use the concept of area of a circle to solve problems
Explore the relationship between the radius and the area
Include finding the area of the annulus
Week 30
10.5 Understand and use the concept of area of sector of a
Include combined shapes
Investigation Working out
circle to solve problems
ii. Find the area of a sector iii. Find the angle at the centre iv. Find the radius v. Solve problems involving area of a sectors and area of circles LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. i. Identify a transformation as a one to one correspondence i. Identify a translation ii. Determine the image of an object under a translation iii. Describe a translation a)by stating the direction and movement in b) in the form TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES Explore the concept of transformation using concrete materials Explore translation given in the form SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES Inquiry Working out investigate
LEARNING AREA/WEEKS 11.0 Transformations Week 31 - 32
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to 11.1 Understand the concept of transformation 11.2 Understand and use the concept of translation
11.3 Understand and use the concept of reflection
11.4 Understand and use the concept of rotation
iv. Determine the properties of translation v. Determine the coordinates under a translation of the image or objects vi. Solve problems involving translations i. Identify a reflection ii. Determine the image of an object under a reflection iii. Determine the properties of reflections iv. Determine the image of an object and the axis of reflection v. Determine the coordinates of the image or objects vi. Describe a reflection vii. Solve problems involving reflections i. Identify a rotation ii. Determine the image of an object under a rotation iii. Determine the properties of rotation
a b
Explore the concept of images and objects under a translation
a b
Explore the image of an object by drawing Explore the concept of images and objects under a reflection
Investigation Working out
Explore the image of an object by drawing Explore the concept of images and objects under a rotation
Investigation Working out
LEARNING AREA/WEEKS Week 33
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to 12.5 Understand and use the concept of isometry 12.6 Understand and use the concept of congruence
13.0 Solid Geometry II Week 34 - 35
12.7 Understand and use the properties of quadrilaterals using concepts of transformations 13.1 Understand geometric properties of prisms,pyramids,cylinders, cones using concrete models 13.2 Understand the concept of nets
iv. Determine the image of an object and the axis of rotation v. Determine the coordinates of the image or objects vi. Describe a rotation vii. Solve problem involving rotation LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. i. identify an isometry ii. Determine whether a given transformation is an isometry iii. Construct pattern using isometry i. Identify if two figures are congruent ii. Identify congruency between two figures iii. Solve problems involving congruence i. Determine the properties of quadrilateral using reflectios and rotations i. State the geometric properties of prisms , pyramids, cylinders, cones and spheres i. Draw nets for prisms , pyramids, cylinders, cones and spheres ii. State the types of solids given their nets ii. Construct the types of solids given their nets i. State mand calculate the surface area of prisms , pyramids, cylinders, cones and spheres ii. Calculate the surface area of spheres using the standard formula iv. Find dimensions of a solid v. Solve problems involving surface areas
TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES Explore isometry by drawing
SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES Investigation
Explore congruency under translations,reflections and rotations
Identification
Explore the properties of various quadrilaterals Explore and investigate properties of geometric solids using concrete models Explore the similarities and differences between nets of solids
Investigation
Investigation
Relationship
13.3 Understand the concept of surface area
Explore and derive the formulae of the surface areas
Working out
10
14.0 Statistics Week 36
14.1 Understand the concept of data
i. Classify data according to those can be collected by counting and measuring ii. Collect and record data systematically LEARNING OUTCOMES: Student will be able to. i. Determine the frequency of data ii. Determine the data of different frequency iii. Organise data by constructing tally charts and frequency tables iv. Obtain information from frequency tables i. Construct pictograms to represent data ii. Obtain information from pictograms iii. Solve problems involving pictograms iv. Construct bar charts to represent data v. Obtain information from bar charts vi. Solve problems involving bar charts vii.Represent data using line graphs vii. Obtain information from line graphs viii. Solve problems involving line graphs
Discuss methods of collecting data
Investigation
LEARNING AREA/WEEKS
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Student will be taught to 14.2 Understand the concept of frequency
TEACHING AND LEARNING ACTIVITIES Use activities to introduce the conceptof frequecy
SKILLS/POINTS TO NOTES Relation
Week 37
14.3 Represent and interpret data in i. pictograms ii. bar charts iii. line graphs
Use everyday situations to introduce pictograms, bar charts and line graphs
Application
27/10 6/11 FINAL EXAM 21/11 3/1 HOLIDAY
11
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Basic Math Skills Workbook PDFDokument60 SeitenBasic Math Skills Workbook PDFAndy Rodrigues83% (18)
- Mathematics For Elementary Teachers 1515100580Dokument461 SeitenMathematics For Elementary Teachers 1515100580Norliza Sapatanoh100% (1)
- ASVAB Math WorkbookDokument76 SeitenASVAB Math WorkbookBlake FryeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Math-Hacker Book PDFDokument797 SeitenThe Math-Hacker Book PDFAnderson Alfred100% (1)
- Scheme of Work Mathematics Form 2Dokument16 SeitenScheme of Work Mathematics Form 2Stephanie Kimi100% (2)
- Grade 8 Fraction Division Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenGrade 8 Fraction Division Lesson Planapi-538028309100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Observation 6Dokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Observation 6api-448690566Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMKK Imtiaz Kuala Terengganu Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2012Dokument12 SeitenSMKK Imtiaz Kuala Terengganu Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2012norhasmizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Tanjung Adang, Gelang Patah, Johor Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2009Dokument12 SeitenSMK Tanjung Adang, Gelang Patah, Johor Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2009Adibah AliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2009-AdleenDokument11 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2009-AdleenFadhlina FadilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Form 2Dokument18 SeitenMathematics Form 2Hilmi Abd GhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2016Dokument12 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2016Mohd Sabri0% (1)
- Math lesson plan for Form 2 studentsDokument18 SeitenMath lesson plan for Form 2 studentsChe'ras IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan 2012 Mathematics Form 2Dokument14 SeitenYearly Plan 2012 Mathematics Form 2FikriSalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcome Remark 1. Directed Numbers. Students Will Be Able To:i. MultiplyDokument20 SeitenDate Learning Objectives Learning Outcome Remark 1. Directed Numbers. Students Will Be Able To:i. MultiplyHe Si RuNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Math Form 2Dokument16 SeitenRPT Math Form 2Hartini KosnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Madai WDT 178, 91209 KUNAK, SABAH. Mathematics Form 2 Yearly Lesson Plan 2012Dokument20 SeitenSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Madai WDT 178, 91209 KUNAK, SABAH. Mathematics Form 2 Yearly Lesson Plan 2012Nik NabihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Teaching PlanDokument7 SeitenYearly Teaching PlanSean GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Form2 2012Dokument14 SeitenYearly Form2 2012ainarahyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Akademik Sekolah-Sekolah Negeri Kelantan: Catatan: Masukkan Tarikh Seperti Di Dalam Takwim SekolahDokument14 SeitenStandard Akademik Sekolah-Sekolah Negeri Kelantan: Catatan: Masukkan Tarikh Seperti Di Dalam Takwim SekolahFarid YusofNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two - 2008Dokument27 SeitenFirst Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two - 2008dirza82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tingkatan 2 Week Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Remark 1. Directed NumbersDokument8 SeitenTingkatan 2 Week Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Remark 1. Directed NumbersMuhammad ElhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 2Dokument13 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 2Yd MnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan - Form2Dokument16 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan - Form2petersiewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Teaching Plan For Mathematics Form 2 2012 Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Point To Note Vocabulary Directed NumberDokument8 SeitenYearly Teaching Plan For Mathematics Form 2 2012 Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Point To Note Vocabulary Directed NumberMohd Nazmi RahimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bidor: Shceme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2012Dokument9 SeitenSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bidor: Shceme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2012Zarina JusohNoch keine Bewertungen
- School: SM Agama Kota Tinggi Subject: Mathematics Form: 2Dokument7 SeitenSchool: SM Agama Kota Tinggi Subject: Mathematics Form: 2adawiyah_04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Mathematics Form One: Whole NumbersDokument15 SeitenYearly Plan Mathematics Form One: Whole NumbersMas NorulhudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH m3 f3Dokument19 SeitenRPH m3 f3Lynne JbNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Math Form2Dokument7 SeitenRPT Math Form2Teobeng LimauNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form One - 2016Dokument21 SeitenFirst Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form One - 2016Tan LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMK DATO’ SRI AMAR DIRAJA MATHEMATICS SUBJECT FORMDokument8 SeitenSMK DATO’ SRI AMAR DIRAJA MATHEMATICS SUBJECT FORMzarina binti jusohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form OneDokument14 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form OneAshwinii SegarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two SMK Raja Mahadi KlangDokument12 Seiten2010 Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two SMK Raja Mahadi KlangLooyee ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Grade 4 08 11Dokument7 SeitenMath Grade 4 08 11api-246939068Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2013Dokument31 SeitenScheme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2013Puteri NorhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Maths Form 4Dokument24 SeitenYearly Plan Maths Form 4JiaJia LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Maths Form 4 2012Dokument24 SeitenRPT Maths Form 4 2012Satu Dua TigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math F4 (2013)Dokument49 SeitenMath F4 (2013)Mohd Azizi Mohd NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Math F 1 2014Dokument13 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan Math F 1 2014wawacunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Teaching Plan Maths Form 1 (2011)Dokument12 SeitenYearly Teaching Plan Maths Form 1 (2011)mychris80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fourth Grade Syllabus 2015Dokument8 SeitenFourth Grade Syllabus 2015api-274977607Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Standard Form Week 1 4/1 - 6/1/12 1.1 UnderstandDokument31 Seiten1.0 Standard Form Week 1 4/1 - 6/1/12 1.1 UnderstandNur BainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSJ Convent Bukit Nanas Mathematics Lesson Plan Form 4 2009Dokument26 SeitenMSJ Convent Bukit Nanas Mathematics Lesson Plan Form 4 2009Elfysia FredolinNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOCUSED MATHEMATICS LESSON PLANS FORM 1 2013Dokument8 SeitenFOCUSED MATHEMATICS LESSON PLANS FORM 1 2013Nadia RichardNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Three - 2008Dokument23 SeitenFirst Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Three - 2008dirza82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Math f3Dokument33 SeitenYearly Plan Math f3Faziyana Busu NollahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Form 2 CSDokument17 SeitenMathematics Form 2 CSAnita MuhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: Form 4 / 2013 Week Topics/Learning Area Learning Outcomes Points To NoteDokument29 SeitenMathematics: Form 4 / 2013 Week Topics/Learning Area Learning Outcomes Points To NoteAmri AwalludinNoch keine Bewertungen
- YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS FORM 5Dokument21 SeitenYEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS FORM 5Bukhary ZahariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Teaching PlanDokument5 SeitenYearly Teaching PlanCikgu SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Math F2Dokument13 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Math F2Hafiz100% (1)
- RPT: Mathematic Form 3Dokument15 SeitenRPT: Mathematic Form 3zulmajdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT Mat T3Dokument8 SeitenRT Mat T3Candace ClayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Remarks 1. Whole NumbersDokument9 SeitenWeek Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Remarks 1. Whole NumbersadelymohdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Methodist Telok Datok Scheme of Work Form 2 Year 2014Dokument16 SeitenSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Methodist Telok Datok Scheme of Work Form 2 Year 2014Norliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Core Math Standards Jigsaw 3rd GradeDokument2 SeitenCommon Core Math Standards Jigsaw 3rd Gradeapi-28847298Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5Dokument21 SeitenForm 5dirza82Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCSSMathTasks Grade4 2014newDokument79 SeitenCCSSMathTasks Grade4 2014newRivka ShareNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade4Dokument17 Seiten2016NJSLS-M Grade4Gene HermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 5 Math SyllabusDokument4 SeitenGrade 5 Math SyllabusCharm GaculaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade Level 7 Learning Area/ Quarter / Domain Mathematics Quarter 2 Date Section ZaraDokument5 SeitenGrade Level 7 Learning Area/ Quarter / Domain Mathematics Quarter 2 Date Section ZaraJoan BabaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4Von EverandExplorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teachers M01 PATTERNS AND NUMBER SEQUENCES GUIDE PPT 2Dokument12 SeitenTeachers M01 PATTERNS AND NUMBER SEQUENCES GUIDE PPT 2Norliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motivation 2Dokument1 SeiteMotivation 2Norliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain TeaserDokument10 SeitenBrain TeaserNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 2015Dokument2 SeitenForm 2 2015Norliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManagementDokument2 SeitenManagementNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blind CountDokument2 SeitenBlind CountNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directed NumbersDokument7 SeitenDirected NumbersNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- T1 2015Dokument3 SeitenT1 2015Norliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- National School Reform Faculty Blind Count: Developed in The Field by Educators Affiliated With NSRFDokument2 SeitenNational School Reform Faculty Blind Count: Developed in The Field by Educators Affiliated With NSRFNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain TeaserDokument10 SeitenBrain TeaserNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Exercises To Sharpen Your BrainDokument3 Seiten4 Exercises To Sharpen Your BrainMar DeeyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negative Impact For Cultural Differences in The WorkplaceDokument3 SeitenNegative Impact For Cultural Differences in The WorkplaceNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework Questions Solved Step-by-StepDokument7 SeitenHomework Questions Solved Step-by-StepNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Practices in EducationDokument3 SeitenBest Practices in EducationNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negative Impact For Cultural Differences in The WorkplaceDokument3 SeitenNegative Impact For Cultural Differences in The WorkplaceNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practising Pythagoras ProblemsDokument2 SeitenPractising Pythagoras ProblemsNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negative Impact For Cultural Differences in The WorkplaceDokument3 SeitenNegative Impact For Cultural Differences in The WorkplaceNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shapes Symmetry Tessellation GuideDokument2 SeitenShapes Symmetry Tessellation GuideNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransformationsDokument3 SeitenTransformationsNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decimal Numbers: Other Decimals Are Those Which Go On Forever and Don't Have Digits Which Repeat. ForDokument2 SeitenDecimal Numbers: Other Decimals Are Those Which Go On Forever and Don't Have Digits Which Repeat. ForNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numbers NotesDokument2 SeitenNumbers NotesNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proportion NotesDokument2 SeitenProportion NotesNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loci NotesDokument2 SeitenLoci NotesNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnglesDokument4 SeitenAnglesNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 3 PenjelmaanDokument12 SeitenBab 3 Penjelmaananon_14988687Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fractions: Division by ZeroDokument1 SeiteFractions: Division by ZeroNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numbers NotesDokument2 SeitenNumbers NotesNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loci NotesDokument2 SeitenLoci NotesNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Whole Integer NumbersDokument1 SeiteMathematics Whole Integer NumbersNorliza SapatanohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Aptitude 160817Dokument38 SeitenQuantitative Aptitude 160817Mansi KasliwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch02 Data RepresentationDokument76 SeitenCh02 Data RepresentationizzmohdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 1 Hand Out Worku GibiDokument35 SeitenGrade 1 Hand Out Worku GibiMuyedin MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- MACARANG DIAGNOSTIC TESTDokument3 SeitenMACARANG DIAGNOSTIC TESTmarlonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 6 Fractions Worksheet - ANSWERSDokument2 SeitenYear 6 Fractions Worksheet - ANSWERSMaameama FrempongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Language CompanionDokument133 SeitenPython Language CompanionrahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Numbers Utch BisDokument1 SeiteReal Numbers Utch BisDiego Hernández Pizaña 6-SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subtract Mixed NumbersDokument2 SeitenSubtract Mixed Numbersapi-262591436Noch keine Bewertungen
- Number System 2011 To 2018Dokument22 SeitenNumber System 2011 To 2018Jerry PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Resource Package: Quarter I Subject: MATH Date: - Day: 1 Content StandardDokument12 SeitenMathematics Resource Package: Quarter I Subject: MATH Date: - Day: 1 Content StandardLowie D GacetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siop Lesson - DivisionDokument3 SeitenSiop Lesson - Divisionapi-240247923100% (1)
- MathDokument9 SeitenMathNathalie RicaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of ExponentDokument1 SeiteProperties of ExponentatsilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test in MathDokument22 SeitenSummative Test in MathSamuel Zamora SisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB Reference ManualDokument101 SeitenMATLAB Reference ManualyonsgomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATHEMATICS 5 5 Cot 1Dokument19 SeitenMATHEMATICS 5 5 Cot 1John Heidrix AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diwali Assignment Unit-1 20BAI10214Dokument9 SeitenDiwali Assignment Unit-1 20BAI10214KshitizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ws 10Dokument3 SeitenWs 10Shiju KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRT DivDokument8 SeitenSRT Divdeepika0821843Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test in Math 4 (July 19)Dokument3 SeitenSummative Test in Math 4 (July 19)Florecita Cabañog100% (1)
- Mathematical Symbols List (+,-,X, - , , - , - ,... ) PDFDokument12 SeitenMathematical Symbols List (+,-,X, - , , - , - ,... ) PDFHardik PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic ExercisesDokument4 SeitenLogic ExercisesJunnel FadrilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slides Ch2Dokument28 SeitenSlides Ch2sara bakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Converting Fractions To Decimals: Grade 6 Fraction WorksheetDokument2 SeitenConverting Fractions To Decimals: Grade 6 Fraction WorksheetshilpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMTH Grade 6 AAC Public OverviewDokument14 SeitenSMTH Grade 6 AAC Public OverviewAshleyNoch keine Bewertungen