Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Diagnostic Exams and Labs - Edited 4pm Sept.20
Hochgeladen von
Jazzmin Angel ComalingCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Diagnostic Exams and Labs - Edited 4pm Sept.20
Hochgeladen von
Jazzmin Angel ComalingCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
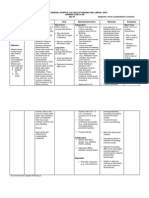
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Diagnostic testing functions as for basic screening, establishing (initial) diagnoses, evaluating current medical case,
and for monitoring Date Done September 2, 2012 Name of Test/ Procedure Electrocardiogram course of illness and response to treatment. Indication for the Normal Findings Actual Results test / Procedure It provides a continuous picture of electrical activity during a complete cycle. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 1035) Normal cardiac cycle components (one normal cardiac cycle is represented by the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave; additionally, a U wave may be observed). This cycle is repeated continuously and rhythmically. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 1035) Sinus tachycardia Twave abnormality, to consider inferior ischemia Interpretation and Analysis An abnormal result of ECG may be due to the patients history of cardiac arrest. Interfering factors may include episodic anxiety and hyperventilation which are associated with prolonged PR interval, sinus tachycardia, and ST depression with or without T-wave inversion. This may be due to autonomic nervous system imbalances. Myocardial ischemia with irritability in the ischemic region, leading to ventricular fibrillation.
In ventricular fibrillation, the electrical signals that control the pumping of the heart suddenly become rapid and chaotic. As a result, the lower chambers of the heart, then the ventricles begin to quiver (fibrillate) instead of contract, and they can no longer pump blood from the heart to the rest of the body resulting from cardiac arrest. (Medical and Surgical Nursing by Ignatavicius and workman, 5th Edition, page 186)
September 3, 2012
Chest X-ray
It is used to diagnose cancer,
Normal-appearing and normally positioned chest,
Pulmonary hyperaeration
Pulmonary hyperaeration may be due to the bronchial
tuberculosis and other pulmonary diseases, and disorders of the mediastinum and bony thorax. The chest x-ray provides a record of the sequential progress or development of a disease. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 715)
bony thorax (all bones present, aligned, symmetrical, and normally shaped), soft tissues, mediastinum, lungs, pleura, heart, and aortic arch. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 715)
subsegmental atelectasis, left lower lung, atheromatous aorta and scoliosis as prescribed
asthma. Subsegmental atelectasis may be due to mucus plugging in bronchial asthma. Atheromatous aorta may be due to aging. Scoliosis of the patient is an idiopathic type of scoliosis. Pulmonary hyperaeration results in an increased radiolucency on Xray. It may occur in partial obstruction of a large airway, as in congenital lobar emphysema, bronchial atresia and mucous plugs in asthma. A blockage in the bronchial tubes can cause obstructive atelectasis, possible causes of blockage include mucus
plug and they are common in people with cystic fibrosis and during severe asthma attacks. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 1039) Atheromatous aorta means that the aorta, which is the largest artery in the body, has thickened and contains deposits of cholesterol on its linings. This is a normal process in aging, or if seen earlier, is due to cholesterol plaque deposition. (Medical and Surgical Nursing by Ignatavicius and workman, 5th Edition, page 684)
Idiopathic scoliosis may be due to multiple, poorly understood inherited factors, most likely from the mother's side. However, the severity often varies widely among family members who have the condition, suggesting that other factors must be present. It may be initially diagnosed in adults during evaluation for other back complaints or disorders, although the curve is unlikely to be significant. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 1185)
LABORATORY STUDIES
Complete Blood Count Date Done September 2, 2012
This test is used to evaluate anemia, leukemia, reaction to inflammation and infections, peripheral blood cellular characters, State of hydration and dehydration, Polycythemia, Hemolytic disease of the newborn, to manage Name of Test/ Procedure Hematocrit chemotherapy decisions. Indication for the test / Normal Actual Procedure The hematocrit is a measurement of the percentage of red cells in the total volume of blood. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 298) There is also a tendency toward lower Hct values in men and women older than 60 years of age, corresponding to lower RBC values in this age group. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 73) Findings 42% - 52% Results 41.8% Interpretation and Analysis Decreased hematocrit may be due to aging process.
Eosinophils
It plays a role in allergic
.9-2.9%
3.1%
Increased eosinophils may be due to bronchial asthma.
reaction, possibly inactivating histamine. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 234) Eosinophilia (increased eosinophils) occurs in conditions such as, allergies, hay fever, and asthma (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page Neutrophils It is for the reaction to inflammation, and it constitutes a primary defense against microbial invasion through the process of phagocytosis. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 52) 43-65% 68.1% 56) Increased neutrophils may be due to infection. Neutrophilia (increased neutrophils) may occur in conditions such as inflammation and tissue necrosis (myocardial infarction). (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 53)
Clinical Chemistry
Blood chemistry testing identifies many chemical blood constituents. It is often necessary to measure several blood chemicals to establish a pattern of abnormalities. A wide range of tests can be grouped under the
headings of enzymes, electrolytes, blood sugars, lipids, hormones, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and drug Date done September 2, 2012 Name of Test/ Procedure Potassium Indication for the Test/ Procedure It evaluates changes in body potassium levels and diagnoses acidbase and water imbalances. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 961) investigation. Normal Actual Result/ Findings 3.5-5.1 umol/L Findings 2.93 umol/L Interpretation and Analysis Hypokalemia (decreased potassium) may be due to intake of corticosteroids and beta-andrenergic agonists. Diuretics, corticosteroids, and beta-adrenergic agonists or antagonists are drugs that may increase potassium loss through the kidneys. (Medical and Surgical Nursing by Ignatavicius and workman, 5th Edition, page 227)
Date done September 3, 2012
Name of Test/ Procedure Fasting Blood Glucose
Indication for the Test/ Procedure It is often the first test done to check
Normal Findings 70-110mg/dl
Actual Result/ Findings 160mg/dl
Interpretation and Analysis Increased glucose may be due to convulsions.
for prediabetes and diabetes. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 326) Elevated blood glucose (hyperglycemia) occurs in acute emotional or physical stress situations (such as, myocardial infarction (MI), cerebrovascular accident, and convulsions) (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 328) 0.42-1.67 mmol/L 0.26 mmol/L Decreased triglycerides may be due to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases which is asthma. Decreased level of triglyceride can occur with conditions such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary diseases and brain infarction. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 431) Increased high density lipoprotein maybe due to stress which can be associated with epilepsy and bronchial asthma.
Triglycerides
It evaluates suspected atherosclerosis and measures the body's ability to metabolize fat. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 430)
HDL (High Density Lipoprotein)
It is the good cholesterol, is used to asses Coronary Artery Disease risk and monitor persons
0.91-1.68 mmol/L
2.54 mmol/L
with known low High Density Lipoprotein levels. It inversely proportional to Chronic Heart Disease risk and are a primary independent risk factor. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 424) Increased level is associated with stress and current illness. (Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests by Fischbach, 7th Edition, page 424)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Osteomyelitis HandoutDokument4 SeitenOsteomyelitis HandoutJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Era Ladies' Dorm 2Dokument3 SeitenNew Era Ladies' Dorm 2Jazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Volunteers of Dental Mission 2013Dokument1 SeiteThe Volunteers of Dental Mission 2013Jazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dipyridamole and FuroDokument11 SeitenDipyridamole and FuroJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Patient TL Age: Years Old Diagnosis: Physical AssessmentDokument11 SeitenName: Patient TL Age: Years Old Diagnosis: Physical AssessmentJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pleural EffusionDokument1 SeitePleural EffusionJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Process: Subjective CuesDokument12 SeitenNursing Care Process: Subjective CuesJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Risk For Bleeding Related To Decreased Platelet CountDokument2 SeitenNCP Risk For Bleeding Related To Decreased Platelet CountKC Ignacio83% (24)
- 225 FullDokument17 Seiten225 FullJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coverage: Unit 0-1 and CBTDokument2 SeitenCoverage: Unit 0-1 and CBTJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancient Greek LiteratureDokument2 SeitenAncient Greek LiteratureJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- PMLS Lesson 5Dokument7 SeitenPMLS Lesson 5Althea EspirituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Drinks Are Bad RealDokument4 SeitenEnergy Drinks Are Bad RealMadihi NorhadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Girl InterruptedDokument7 SeitenGirl Interruptedapi-365678992Noch keine Bewertungen
- Axa Group Corporate PresentationDokument35 SeitenAxa Group Corporate PresentationRajneesh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siobhan (2017) - Smudging of The Motor Cortex Is Related To The Severity of Low Back PainDokument7 SeitenSiobhan (2017) - Smudging of The Motor Cortex Is Related To The Severity of Low Back PainLuciana AraújoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacteria Found in UrineDokument7 SeitenBacteria Found in UrineAria DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilator Graphics & Trouble-Shooting - EditedDokument64 SeitenVentilator Graphics & Trouble-Shooting - EditedAbhishek SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication AdministrationDokument8 SeitenMedication AdministrationMarku LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Rubrics by Farookh MasterDokument589 SeitenMental Rubrics by Farookh MasterPranesh Peter91% (22)
- Occupational Health Form: General DetailsDokument2 SeitenOccupational Health Form: General DetailsKhushal khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acadia PharmaceuticalsDokument3 SeitenAcadia PharmaceuticalsAman DecoraterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise #1 10Dokument10 SeitenExercise #1 10John Paul FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Pediatric Pain Scales Neonatal Infant Pain Scale (NIPSDokument2 SeitenUsing Pediatric Pain Scales Neonatal Infant Pain Scale (NIPSSevina Eka ChannelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Anaesthetic Management To Extensive Thoracic Trauma-Hossam AtefDokument60 SeitenEmergency Anaesthetic Management To Extensive Thoracic Trauma-Hossam AtefHossam atefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioengineering Transla Med - 2022 - Chopade - Alzheimer S and Parkinson S Disease Therapies in The ClinicDokument23 SeitenBioengineering Transla Med - 2022 - Chopade - Alzheimer S and Parkinson S Disease Therapies in The ClinicurosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics Midterms Rationale 2nd Sem 2018 2019Dokument21 SeitenObstetrics Midterms Rationale 2nd Sem 2018 2019Gene Paulo UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLEDokument42 SeitenSLETrishenth FonsekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DctsDokument30 SeitenDctsInuyashayahoo100% (1)
- Aneurysm: Symptoms of An AneurysmDokument3 SeitenAneurysm: Symptoms of An AneurysmArun MuralidharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQ4PDokument3 SeitenAQ4PAhmed GaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Apolinario Mabini Syphilis Rumors and Late 19th Century Philippine Power PlayDokument15 SeitenThe Apolinario Mabini Syphilis Rumors and Late 19th Century Philippine Power PlayHaneul KImNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is Doa 10 Cup TestDokument1 SeiteIs Doa 10 Cup TestUqi.Noch keine Bewertungen
- SupradynDokument5 SeitenSupradynashrayagrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Braden ScaleDokument1 SeiteBraden ScaleRandall StevensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kleptomania Term PaperDokument6 SeitenKleptomania Term Paperbctfnerif100% (1)
- Che 225 Control of Communicable DiseasesDokument19 SeitenChe 225 Control of Communicable DiseasesAbdullahi Bashir SalisuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertical Root Fracture !Dokument42 SeitenVertical Root Fracture !Dr Dithy kkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 14 Antepartum Nursing Assessment NotesDokument8 SeitenCH 14 Antepartum Nursing Assessment NotesMary LowryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urtricaria SDokument8 SeitenUrtricaria SpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser Questions & AnswersDokument2 SeitenLaser Questions & AnswersChudaman MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen