Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Be New Syllabus Corrected
Hochgeladen von
sumikannuCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Be New Syllabus Corrected
Hochgeladen von
sumikannuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PROCESS PLANNING AND COST ESTIMATION
100
UNIT I PROCESS PLANNING 8 Introduction- Place of process planning-economics- Process & Production Planning, Process Planning & Concurrent Engineering-Types of production- standardization- Production design & selection. UNIT II DESIGN AND CONCEPTS OF PROCESS PLAN 8 Selection of processes, tools, cutting parameters & machine tools- Jigs and Fixtures Grouping of processes- Sequencing of operations- Selecting primary manufacturing processes for rough & refined needs- Process capability, Process Charts. UNIT III MANUAL AND COMPUTER AIDED PROCESS PLANNING 7 Retrieval type/variant approach, group technology generative approach, logics decision tress and tables, axiomatic approach AI expert systems feature recognition applications. UNIT IV DIRECT AND INDIRECT COST COMPONENTS 12 Labour costdirect, indirectestimationlabour normstime study rating labour cost variances; material costdirect, indirectestimationmaterial issue valuation material cost variancesproblems. Overhead cost - Elements factory, administrative, sales and distribution expensesmethods of absorbing overheads Direct Labour, Direct Material, Machine Hour Rate methods depreciation methods accounting for service department expenses problems. UNIT V BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS & COST MANAGEMENT 10 make or buy decision, assumptions, merits and demerits of break even analysis. Applications. Linear, multi product break-even analysis. Learning curves, product life cycle cost analysis Tools and techniquesactivity based costing - concepts, cost drivers; introduction to target costing - need and applications LECTURE : 45 TUTORIAL : 0 TOTAL : 45 REFERENCES 1 R.K.Rajput, Thermal Engineering , Laxmi Publications, New Delhi, Sixth edition, 2005 2 Kothandaraman C.P, Domkundwar and A.V. Domkundwar, A course in Thermal Engineering, Dhanpat Rai & Sons, Fifth Edition, 2002 3 Holman J.P. Thermodynamics, McGraw-Hill, 1985. 4 Arora C.P., Refrigeration and Air conditioning, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 1994 5 Sarkar B.K., Thermal Engineering, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi New Delhi, 1998 6 V.Ganesan, Internal Combustion Engines, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 1994
PROCESS PLANNING AND COST ESTIMATION 3 0 0 3
PROCESS PLANNING: Introduction- Place of process planning-economics- Process & Production Planning, Process Planning & Concurrent Engineering-Types of productionstandardization- Production design & selection. (4) DESIGN AND CONCEPTS OF PROCESS PLAN: Selection of processes, tools, cutting parameters & machine tools- Jigs and Fixtures - Grouping of processes- Sequencing of operations- Selecting primary manufacturing processes for rough & refined needs- Process capability, Process Charts. (5) MANUAL AND COMPUTER AIDED PROCESS PLANNING: Retrieval type/variant approach, group technology generative approach, logics decision tress and tables, axiomatic approach AI expert systems feature recognition applications. (6) ESTIMATING AND COSTING: Concepts, differences, different costing methods classification of costs cost grid-problems (4) DIRECT AND INDIRECT COST COMPONENTS: Labour costdirect, indirect estimationlabour normstime study rating labour cost variances; material costdirect, indirectestimationmaterial issue valuation material cost variancesproblems. Overhead cost Elements factory, administrative, sales and distribution expensesmethods of absorbing overheads Direct Labour, Direct Material, Machine Hour Rate methods depreciation methods accounting for service department expenses problems. (10) COST CALCULATIONS: Machined componentswelded components, forged components, powder metallurgy parts, calculation of sales cost, case studies, use of computers in cost estimation, cost of rejection. OPTIMUM MACHINING CONDITIONS: Taylors equation, deriving the equation for optimum economic cutting velocity selection of cutting speed for optimum cost, problems process capability analysis. (9) BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS: Concept, make or buy decision, assumptions, merits and demerits of break even analysis. Applications. Linear, multi product break-even analysis. (3) COST MANAGEMENT: Learning curves, product life cycle cost analysis -Tools and techniquesactivity based costing - concepts, cost drivers; introduction to target costing - need and applications. (4) Total 45 TEXT BOOKS: 1. Kannappan D, Mechanical Estimating and Costing, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 2003. 2. Frederic C Jelen and James H Black, Cost and Optimization Engineering, McGraw Hill Inc., New York, 1983. REFERENCES: 1. Thomas E.Vollmann et all, Manufacturing Planning and Control Systems, Galgotia Publications Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 1998. 2. Haslehurst M, Manufacturing Technology, ELBS, 1985. 3. Kesavon R Process Planning and Cost Estimation, New Age International Pvt. Ltd., Chennai, 2005.
4. Banga T R and Sharma S C, Mechanical Estimating and Costing, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi, 2002.
LEAN MANUFACTURING
3003
INTRODUCTION: Objectives of lean manufacturing-key principles and implications of lean manufacturing- Traditional Vs lean manufacturing Lean benefits. (6) LEAN MANUFACTURING CONCEPTS: Value creation and waste elimination- Major kinds of waste- pull production-different models of pull production-continuous flow-continuous improvement / Kaizen- Worker involvement. (7) GROUP TECHNOLOGY: Part family- Production flow analysis Composite part concept Machine cell design -Case studies. (5) LEAN MANUFACTURING TOOLS & METHODOLOGIES: Standard work communication of standard work to employees -standard work and flexibility -visual controlsquality at the source- 5S principles -preventive maintenance-total quality management-total productive maintenance -changeover/setup time -batch size reduction. (10) VALUE STREAM MAPPING: The as-is diagram-the future state map-application to the factory simulation scenario-line balancing -poke yoka- Kanban overall equipment effectiveness. (7) JUST IN TIME MANUFACTURING: Introduction - elements of JIT - Kanban system. (6) IMPLEMENTING LEAN: Road map-senior management Involvement-best practices. (4) TEXT BOOKS: 1. Mikell P. Groover (2002) Automation, Production Systems and CIM. REFERENCES: 1) Design and Analysis of Lean Production Systems, Ronald G. Askin & Jeffrey B. Goldberg, John Wiley & Sons, 2003 2. Rother M. and Shook J, 1999 Learning to See: Value Stream Mapping to Add Value and Eliminate Muda , Lean Enterprise Institute, Brookline, MA. 3)Richard B Chase F Robert Jacobs and Nicholas J Aquilano, Operations Management for Competitive Advantage, McGraw Hill/Irwin; Tenth Edition, 2003. 4) Poke - Yoke, "Improving Product Quality by Preventing Defects", Productivity Press, 1992.
MAINTENANCE ENGINEERING
3 0 0 3
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS 8 Introduction to repair and Maintenance -Maintenance as business - Maintenance systems such as reactive, preventive, predictive or proactive systems - Human resources management in Maintenance management -maintainability- Inherent and overall availability. - Mean time between failures, mean time to repairs and mean down time - Testability and supportability Design for Maintenance - Poor maintainability aspects - Design for reliability. UNIT II CONDITION BASED MAINTENANCE 7 Condition based monitoring of equipment and systems - condition monitoring techniques such as a) Vibration analysis, b) Ultrasonic detection techniques, c) Thermography, d) Oil and lubricant analysis, e) Motor condition monitoring (MCM) -Shaft alignments through laser Vibration instruments -Outline on Thermography UNIT III MAINTENANCE TECHNIQUES SUCH AS RELIABILITY CENTRED MAINTENANCE (RCM). 10 Reliability centred Maintenance-Failure Mode and Effect Analysis-Root cause Analysis- logic tree analysis-Criticality matrix - Total Productive Maintenance, Overall Equipment EffectivenessLean manufacturing- TPM and TPO- Relationship between OEE and world-class MaintenanceLadder of Maintenance improvement Computerized Maintenance management system in a business scenario- data Acquisition for effective management of CMMS. UNIT IV ASSET PLANNING AND SCHEDULING OF ACTIVITIES IN MAINTENANCE 10 Asset and spare part management, - Conventional spare Parts management techniques such as Economic Order Quantity, two bin systems - Latest trends in monitoring through bar codes, mobile computer and wireless data transmissions -. Different aspects of planning and scheduling of Maintenance, such as shutdowns Critical aspects of both routine and shut down Maintenance -. bar charts - PERT network during shut down -Man power Training and utilization of skilled manpower -Sequencing of activities. UNIT V SAFETY AND OTHER ASPECTS OF MAINTENANCE 10 Safety Engineering. - Hazard analysis -General rules and guidelines in safety and hazard prevention - Analytical tools - Hazard analysis- Fault Tree Analysis - Sneak Circuit analysis Integrated approach to Maintenance- Statistical distributions such as normal, gamma and Weibull in Maintenance- Maintenance effectiveness. TOTAL: 45 PERIODS TEXT BOOK: 1. Maintenance Engineering and Management: K.Venkataraman-PHI Learning2007 REFERENCES: 1. Kelly. A and Harris, M. J, Management of Industrial maintenance, Butter worth & Co., 1978 2. David J. Smith, Reliability and Maintainability in Perspective, McMillan,2 nd Edition, 1985. 3. Gwidon W Stachowiak and Andrew W. Batchelor, Engineering Tribology, Butterwork-Heinmann, 2001 4. John V.Grimaldi & Rollin H.Simonds, Safety Management, AITBS Publishers.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- BE Mech II Yr A Sec Production Tech ATT PercentageDokument6 SeitenBE Mech II Yr A Sec Production Tech ATT PercentagesumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Agenda: Team Orientation DayDokument3 SeitenAgenda: Team Orientation DaysumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 7541 1462 5100 1 SyllabusDokument8 Seiten7541 1462 5100 1 SyllabussumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Integrated Product and Process Development Unit I A. IntroductionDokument19 SeitenIntegrated Product and Process Development Unit I A. IntroductionsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Dr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, Pollachi - 642 003Dokument1 SeiteDr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, Pollachi - 642 003sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Dr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, PollachiDokument1 SeiteDr. Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, PollachisumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Apt I NumbersDokument2 SeitenApt I NumberssumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Ivyeara&b Hostel Stdnts DataDokument2 SeitenIvyeara&b Hostel Stdnts DatasumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE SW EEE Opting - List 2010 2015Dokument5 SeitenBE SW EEE Opting - List 2010 2015sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Lec 28Dokument13 SeitenLec 28sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Itc LTD Interview QuestionsDokument2 SeitenItc LTD Interview QuestionssumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Bank Po General English Model QuestionsDokument7 SeitenBank Po General English Model QuestionssumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
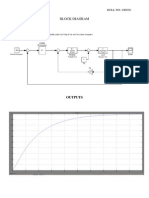
- Block Diagram: NAME: N.Pavitra ROLL NO.:10E626Dokument3 SeitenBlock Diagram: NAME: N.Pavitra ROLL NO.:10E626sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
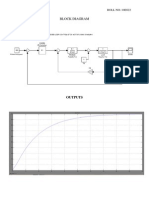
- Block Diagram: NAME: E.Pradeep ROLL NO.:10E627Dokument3 SeitenBlock Diagram: NAME: E.Pradeep ROLL NO.:10E627sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- DR - Mahalingam College of Engineering & Technology, Pollachi - 3Dokument12 SeitenDR - Mahalingam College of Engineering & Technology, Pollachi - 3sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Block Diagram: NAME: B.Muthukannan ROLL NO.:10E622Dokument3 SeitenBlock Diagram: NAME: B.Muthukannan ROLL NO.:10E622sumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- C - Question Paper Quark Media House India Pvt. LTD.: 1. What Is The Output of The Following CodeDokument9 SeitenC - Question Paper Quark Media House India Pvt. LTD.: 1. What Is The Output of The Following CodesumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SampleDokument4 SeitenSamplesumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Results (Provisional) : PSG College of TechnologyDokument1 SeiteResults (Provisional) : PSG College of TechnologysumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apriso SmanufacturingDokument17 SeitenApriso SmanufacturingArvin PagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 11 22 Philippines Legal Challenges To Election Technology 0Dokument23 Seiten2017 11 22 Philippines Legal Challenges To Election Technology 0Cia ednaAbacahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- BSI ISO 22301 Self Assesment ChecklistDokument3 SeitenBSI ISO 22301 Self Assesment Checklistootchay100% (4)
- Ipil, Zamboanga SibugayDokument2 SeitenIpil, Zamboanga SibugaySunStar Philippine NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Process ManagementDokument20 SeitenBusiness Process ManagementAhmad Tariq BhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HECK, T.F. The Birth of The Classic Guitar and Its Cultivation in Vienna Reflected in The Career and Composition of Mauro Giuliani.Dokument534 SeitenHECK, T.F. The Birth of The Classic Guitar and Its Cultivation in Vienna Reflected in The Career and Composition of Mauro Giuliani.Juan Pedro Resina100% (4)
- COMELEC List of Candidates For Antipolo CityDokument4 SeitenCOMELEC List of Candidates For Antipolo CitySteve B. SalongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Human Resource PlanningDokument21 SeitenHuman Resource PlanningNavdeep Bisla80% (5)
- Data GovernanceDokument7 SeitenData GovernancesamydogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank BC 204 (B) Entrepreneurship Development Unit-1Dokument2 SeitenQuestion Bank BC 204 (B) Entrepreneurship Development Unit-1novateurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Categorizing The Philippine Constitutions, 1935-1987Dokument1 SeiteCategorizing The Philippine Constitutions, 1935-1987Chacha Ortega NaquilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1712 4919 1 PBDokument12 Seiten1712 4919 1 PBNur Ayisah HutabaratNoch keine Bewertungen
- TQM & Quality Presentation For Operations ManagementDokument23 SeitenTQM & Quality Presentation For Operations ManagementIsuru Wijewardene100% (1)
- Responsibility in Engineering EthicsDokument6 SeitenResponsibility in Engineering EthicsBernard BaluyotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Governance of HulDokument13 SeitenCorporate Governance of Hulanushree_mohta_10% (1)
- SMB4004 Topic 3Dokument34 SeitenSMB4004 Topic 3Norainah Abdul GaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alliance Concrete ForecastingDokument7 SeitenAlliance Concrete ForecastingS r kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical and Social Issues in Information SystemDokument25 SeitenEthical and Social Issues in Information SystemfrankrivNoch keine Bewertungen
- p2 Process Model 2017Dokument1 Seitep2 Process Model 2017Miguel Fernandes0% (1)
- WCSM Supplier Evaluation & Selection Chapter 07Dokument40 SeitenWCSM Supplier Evaluation & Selection Chapter 07bach2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Movement For Multi-Party DemocracyDokument2 SeitenMovement For Multi-Party DemocracyIsaac C SimuchimbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Lean Implementati ON: Dr. Muhammad JunaidDokument17 SeitenLean Implementati ON: Dr. Muhammad Junaidjunaid aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 10 Deadly Sins of Information Security ManagementDokument12 SeitenThe 10 Deadly Sins of Information Security Managementmarina meshiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Businessobjects Planning and ConsolidationDokument2 SeitenSap Businessobjects Planning and ConsolidationharrychopraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Metrics For Data Governance and Data Stewardship - EWSolutionsDokument3 SeitenPerformance Metrics For Data Governance and Data Stewardship - EWSolutionsBGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developing Marketing Strategies and PlansDokument43 SeitenDeveloping Marketing Strategies and PlansRika SusantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 AggPlanDokument27 Seiten08 AggPlanMahmutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsDokument2 SeitenCertified List of Candidates For Congressional and Local Positions For The May 13, 2013 2013 National, Local and Armm ElectionsSunStar Philippine NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goods and Service DesignDokument3 SeitenGoods and Service DesignNayab NoumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nov2008 VIP EN 3Dokument304 SeitenNov2008 VIP EN 3mraneriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersVon EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- Fire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesVon EverandFire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisVon EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemVon EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNoch keine Bewertungen