Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2
Hochgeladen von
Amirah AmanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2
Hochgeladen von
Amirah AmanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
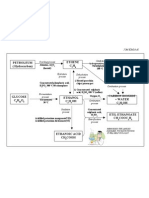
CHAPTER 2: CARBON COMPOUNDS
Organic compound: -from living things -mainly from Carbon and Hydrogen -may also contain oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine, potassium, sodium, sulphur. - examples: petrol, protein, amino acid -characteristics: do not conduct electricity in solid, liquid, or gaseous change do not dissolve in water, but dissolve in organic solvent low melting and boiling point Inorganic compound: -from non-living things -mainly without Carbon atom -examples: iron(II) oxide, copper(II) sulphate, zinc nitrate, ammonia HYDROCARBONS Compounds that are made up of Hydrogen and Carbon atoms only
SATURATED have only single bonds between the Carbon atoms example: ethane
UNSATURATED have double or triple bonds between the Carbon atoms example: ethene, ethylene
Root name for naming hydrocarbon 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 methethpropbutpenthexheptoctnondec-
ALKANE -general formula: CnH2n+2, n=1,2,3, -saturated hydrocarbon -each Carbon atom is bonded to four other atoms by single covalent bond NAMING Root + ending (-ane) 1. Determine number of Carbon atoms 2. Choose the prefix/root 3. ending -ane C8H18 :-Carbon:8 -ending: -name: STRUCTURAL FORMULAE How to draw structural formula of C3H8 1. Position the 3 carbon atoms in a row 2. Join the carbon atoms by single bonds : oct: -ane : octane Name these alkanes: C6H14: _____________________ C5H12: _____________________ C2H6 : _____________________
Pentane:
3. Place 4 single bonds around each carbon atom
Hexane:
4. Attach a hydrogen atom to each empty bond of Carbon atom
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANE Less dense than water not soluble in water attraction between molecules: weak low melting and boiling points soluble and miscible in organic solvents weak vand der waal bon cannot conduct electricity
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANE ALKAN COMBUSTI HALOGENATI
complete combustion (excess oxygen, O2)
incomplete combustion (limited oxygen, O2)
substitution reaction (chlorination) e.g: methane
alkane + O2 CO2 + H2O
alkane + O2 CO+ H 2O alkane + O2 C+
CH4(g) + Cl2(g) HCl(g) + CH3Cl(g)
chloromethane
CH3Cl(g) + Cl2(g) HCl(g) + CH2Cl2(g) dichloromethane CH2Cl2(g) + Cl2(g) HCl(g) +
ALKENE -general formula: CnH2n, n=,2,3, -unsaturated hydrocarbon -functional group: C=C double bond NAMING Root + ending (-ene) 1. Determine number of Carbon atoms 2. Choose the prefix/root 3. ending -ene C8H16 :-Carbon:8 -ending: -name: STRUCTURAL FORMULAE How to draw structural formula of C3H8 1. Position the 3 carbon atoms in a row 2. Join the first 2 carbon atom with = : oct: -ene : octene
Name these alkenes: C4H8: _____________________ C5H10: _____________________ C3H6 : _____________________
heptene:
Octene: 3. Remaining carbon with single bond
4. 4 single bonds around each empty bond of carbon atom
4. Attach hydrogen atom to each empty bond of Carbon atom
STRAIGHT CHAIN ALKENE BRANCHED CHAIN ALKENE C5H10 CH3CH2CHCHCH3 C5H10 CH2C(CH3)CH2CH3
root-num of C containing double bondene pent-2-ene
side chain: alkyl group longest chain: 4 carbon atom root: but- = at C num : 1 but-1-ene side chain: methyl at C-2 name: 2-methylbut-1-ene
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKENE ALKENE STATE BOILING POINT MELTING POINT DENSITY SOLUBILITY DENSITY Ethene Propen e Gas Butene Penten e Liquid Hexene Hepten e Liquid Octene
Gas Gas Liquid Liquid Low, but -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> increase Not soluble in water Does not conduct electricity
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenDetailed Lesson PlanFelipe Jimenez91% (11)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Electrolysis of Molten CompoundDokument1 SeiteElectrolysis of Molten CompoundAmirah AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes: H H C H HDokument6 SeitenAlkanes: H H C H HAmirah AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacture of Sulphuric AcidDokument8 SeitenManufacture of Sulphuric AcidAmirah AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relation Betwee N HCDokument1 SeiteRelation Betwee N HCAmirah AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 17 ElementsDokument3 SeitenGroup 17 ElementsAmirah AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps To Name Branched AlkenesDokument1 SeiteSteps To Name Branched AlkenesAmirah AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Alkanes and AlkenesDokument3 SeitenComparing Alkanes and AlkenesAmirah Aman100% (1)
- 14 Chemical For ComsumersDokument29 Seiten14 Chemical For ComsumersAmirah AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Soap and DetergentDokument9 Seiten1 Soap and DetergentKhairul Abadi PutehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.03.12 Density Lab ReportDokument3 Seiten10.03.12 Density Lab ReportCyou97100% (1)
- Circular Motion PhysicsDokument4 SeitenCircular Motion Physicsdhion13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Materi Part 2 - Physical and Chemical Properties-PrintDokument32 SeitenMateri Part 2 - Physical and Chemical Properties-PrintOkky HeljaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STD G0566 RepeatDokument2 SeitenSTD G0566 RepeatTirtana PrasetiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch11p3p2p1 Ballot DraftDokument6 SeitenCh11p3p2p1 Ballot Draftmpinto121Noch keine Bewertungen
- KVPY 2012 Stream SB SX Solved PaperDokument32 SeitenKVPY 2012 Stream SB SX Solved PaperdevkgunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 and 4 Physical ScienceDokument11 SeitenModule 3 and 4 Physical ScienceBlake DoomedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Montie Carlo S O S of La Itice Models For CromoleculesDokument52 SeitenMontie Carlo S O S of La Itice Models For CromoleculespovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 WeldingDokument11 SeitenAssignment 1 WeldingLee Eyyh DeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter # 17 Advent of Modern PhysicsDokument5 SeitenChapter # 17 Advent of Modern PhysicsSIR USMAN KHAN100% (4)
- Force Pressure and Strain Measurements For TraditiDokument22 SeitenForce Pressure and Strain Measurements For TraditiSerhat TüysüzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajpcr PDFDokument6 SeitenAjpcr PDFAndrianna NastasyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallization PDFDokument74 SeitenCrystallization PDFMohammed Akif ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Topic 1 QuestionsDokument27 SeitenChem Topic 1 QuestionsOscarHigson-SpenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Test of Construction MaterialsDokument25 SeitenField Test of Construction MaterialsAntarjyami PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 2251 - 96 R00 - RdiynteDokument2 SeitenD 2251 - 96 R00 - RdiynteRuben YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dangerous Goods Hazmat Material Training Cat-10Dokument24 SeitenDangerous Goods Hazmat Material Training Cat-10Claudio GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Specification: Product Name: Eltesol SC 40/sodium Cumene SulphonateDokument1 SeiteTechnical Specification: Product Name: Eltesol SC 40/sodium Cumene SulphonateMOGES ABERANoch keine Bewertungen
- CPCDokument39 SeitenCPCNaresh NaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manfred Held - Liners For Shaped ChargesDokument7 SeitenManfred Held - Liners For Shaped ChargesGhoree23456Noch keine Bewertungen
- IR ThermographyDokument28 SeitenIR Thermographymathjon100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Structure of AtomDokument48 SeitenChapter 2 Structure of AtomRehan AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green ChemistryDokument12 SeitenGreen ChemistrymidhunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural StateDokument6 SeitenNatural StatejrsanabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 6702Dokument22 SeitenEc 6702Madhan ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D129Dokument1 SeiteAstm D129Sylab InstrumentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Quality Control of Some Dermo-Cosmetic Product PDFDokument6 SeitenThe Quality Control of Some Dermo-Cosmetic Product PDFGordana ZavisicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Isoamyl Acetate PDFDokument4 SeitenSynthesis of Isoamyl Acetate PDFJenny MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS 10500: 2012 Table 2 General Parameters Concerning Substances Undesirable in Excessive AmountsDokument4 SeitenIS 10500: 2012 Table 2 General Parameters Concerning Substances Undesirable in Excessive AmountsMukunda DhakalNoch keine Bewertungen