Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fixed Prosthodontics
Hochgeladen von
Arxhenta ÇupiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fixed Prosthodontics
Hochgeladen von
Arxhenta ÇupiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fixed prosthodontics
90% of what you do in dentistry is prosthodontics .first we will start with the definition of prosthodontics. Its The dental specialty pertaining to the diagnosis, treatment planning, rehabilitation, and maintenance of the oral function, comfort, appearance, and health of patients with clinical conditions associated with missing or deficient teeth, and/or maxillofacial tissues using biocompatible substitutes. This definition is taken from Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms. So most of the time you deal with missing teeth ,or deficient teeth. Now fillings are part of prostho and it depends on the country, like if you study your speciality in USA, you have operative dentistry separate from prostho. if you study in Australia like the doctor :P, operative dentistry is part of prostho. Why do we need to replace missing teeth? 1- For function , mastication, some patients complain from missing posterior teeth and they cant chew correctly or they cant masticate very well, so when you replace their missing teeth their function is supposed to be improved. 2- Aesthetics, like some patients complains from missing upper interior teeth, from car accident for example, so you need to improve their Aesthetics. 3- Stability ,if the tooth is missing the adjacent tooth will start to move, and we call that in dentistry drifting , so when you replace this missing tooth you will maintain stability of the dental arch.
So basically three major functions for replacing a missing tooth: function, aesthetics and stability... if you are placing a posterior tooth you are placing function and stability. If you are placing an anterior tooth you are placing Aesthetics.
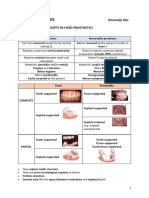
Now Prosthodontics: As a branch of dentistry we have: *fixed Prosthodontics *removable Prosthodontics *implant Prosthodontics (they still dont teach this in Jordan) *maxillofacial Prosthodontics (they dont teach it also, its left to specialist)
Fixed Prosthodontics:
The branch of Prosthodontics concerned with the replacement, and/or restoration of teeth by artificial substitutes that not readily removed from the mouth. The patient cannot take them out like the denture so its fixed. But the dentist can take them out in some cases, but in other cases he cannot until he cut the crown. This is why patients like fixed Prosthodontics much more the removable Prosthodontics, because they feel like its almost similar to their natural teeth. but the problem of fixed Prosthodontics that its much more expensive than removable Prosthodontics
We have two types of restoration in fixed prosthodontics:
* Intracoronal restorations, means that its in the tooth. * Extracoronal restorations, which means on the tooth or replacing a missing tooth.
Types of intracoronal restorations:
1- Direct restorations (fillings) We use a certain materials like Amalgam, Composite Resin, GIC (glass-ionomer cements), RMGIC (Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cements), Compomer.
amalgam fillings
composite fillings
Indirect restorations: Inlays: metal, ceramic, composite resin. The difference between inlays and fillings is that fillings we do them direct to the patients mouth. So we prepare the cavity, the nurse prepare the amalgam, and we insert it right away in the tooth (no need for lab), while inlays cannot be done right away, it needs a laboratory .Its not a direct filling. What is Inlays? It is a dental restorations made outside the tooth to correspond to the form of the prepared cavity by an impression (An impression is carried out by placing a viscous liquid material into the mouth usually in a customized tray. The material then sets to become an elastic solid, and when removed from the mouth retains the shape of the teeth), then the lab will bring the inlay back to the dentist which is then luted into the tooth.
Here in the pic its ceramic
Types of Extracoronal restorations:
1-Onlays: Metal, Ceramic, Metal-Ceramic. Only is a restoration that restores one or more cusps, and adjoining occlusal surfaces or the entire occlusal surface, and is retained by mechanical or adhesive means. Its simply inlay + cuspal coverage. Why do we need to cover the cusp? For many reasons one of them is to prevent fracture of the teeth .
This is from the lingual surface
Only part of the tooth is covered because if you cover the entire tooth it becomes a crown. *Incisor Onlay is not common at all because you need to have technician with very good skills to be able to construct such little restorations.
9 onlays
This is the patient mouth with onlays
2-Veneers: Ceramic, Composite Resin, Metal (veneers are very common) Its a thin sheet of material usually used as a finishing or ornamental facing.
In dentistry we have laminate veneers, and the most common one is porcelain because we use it in the facial surfaces in the upper anterior teeth. Porcelain laminate veneer: a thin bonded ceramic restoration that restores the facial or lingual surface and part of the proximal surfaces of teeth requiring aesthetic restoration. What is the advantage of veneers? Very conservative and its aesthetic if plant properly.
This patient complained of midline diastema .first thing to do is examination. Here she needed ortho treatment but she refused to take it so we went for restoration treatment to close the gab. Also her teeth had composite fillings so our doctor decided to veneer all of the incisors teeth, central lateral, central lateral plus closing the midline diastema : D Just he did very conservative preparation of the teeth, impression, send to the lab, the lab constructed the veneers.
And these are the veneers in her mouth... because they closed the midline diastema she had a wider central teeth but she was happy with that. So veneers are very conservative, less than 0.5 mm preparation you can achieve a very aesthetic result with very minimal preparation.
*another case where a patient had discolored teeth (in the lower interior teeth), we decided to do lower 6 veneers, and this design of veneer is called veneer with an overlap because it goes with lingual surface of the teeth.
The veneers in patient mouth
3-Crowns (the most widely used restorations after the fillings): Metal (not for anterior teeth), Ceramic, Metal-Ceramic . Crown is an artificial replacement that restores missing tooth structure by surrounding part or all of the remaining structure with a material such as cast metal, porcelain, or a combination of materials such as metal and porcelain.
It can cover the whole tooth and we call it a full coverage crown, or it can cover part of the tooth which we call it partial crown. But the most widely used is the coverage crown.
*We have different materials of crown :
*FGC: full gold crown and this is the most predictable treatment in prosthodontics and it has the best survival rate. But unfortunately for 2 reasons its not as common these days as before, gold is very expensive and patients dont like it these days because aesthetics. Some dentists prescribe golden crown if the patient accept to pay the extra fees for gold, because the lab charges us crown + gold weight.
*PFM: Porcelain fused to metal (the most used) Why do we use metal underneath the ceramic? Because ceramic alone is brittle compared to the metal, and metal alone is not aesthetic so we combine both. *Ceramic crowns (metal free): the strongest ceramic is zirconium, we have pressed ceramic, and Alumina ceramic . Ceramic crowns give us the best aesthetic results but the main disadvantage relative to PFM that they can break.
This is a case: patient came complaining of worn upper anterior teeth (damage in the anterior teeth) so already endo treatment done and have post and core (post are part of fixed prosthodontics) (the first pic ) *A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently build-up tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth structure to properly retain the crown, due to loss of tooth structure to either decay or fracture. Post and cores are therefore referred to as foundation restorations. (its here the metal material, appears in the last pic from the lingual surface)
Now when the tooth does not have enough height to retain the final restoration of the crown. Then what can we do? In this case the tooth is not vital and needs endodontic treatment, then we just prepare through the canal and we cement a post or a pin. What happens ? The crown becomes longer or higher. Without these post and cores there is a high chance for the crown to be lost. *Note that its PFM crowns in the pic, and know that crowns are the mostly done procedure in prosthodontics.
4-Fixed Partial Denture (Bridge): Metal, Ceramic, Metal-Ceramic Is basically 2 crowns but they are replacing a missing tooth. For example a patient has one of his teeth missing, how can we restore his tooth ? 1- if the patient is happy then no treatment, you can leave it as it is ,like the eighth tooth or the seventh tooth for example its optional to replace them, unless we are worried about stability . 2- We can use a partial denture (removable prosthodontics) but its not a good option for every patient especially young patients. 3- We can use a bridge to replace a missing tooth or we just can replace it by implant
*The term fixed partial denture (FPD) is used in America and Canada while the term bridge is used in Australia and Britain. Fixed partial denture is Restoration that is securely retained to natural teeth to replace missing teeth.
Securely retained means that the patient cant take it out, it not like removable partial denture, its retained to the adjacent teeth to the missing tooth.
In this case for example a patient is complaining of missing the anterior tooth, to OUR DOCTOR, the best treatment is implant, because you dont sacrifice any tooth structure, plus the implant supported restoration have better success rate if planned properly better than bridge. In this case the patient couldnt afford implant therapy because its very expensive, so we decided to provide him with a bridge.
This is From the canine to the canine, we call it six unit bridge (each one is called a unit) and 6 unit bridge does not mean it replaced 6 teeth , in this case 6 unit bridge replaced three teeth so the number of units does not mean exactly the number of teeth to be replaced.
But usually when you have single missing tooth and you prepared the tooth interior and the tooth posterior, you will have three unit bridge, so three unit bridge replaces one missing tooth. And the way they charge you is: each one with the same cost (for example a unit costs 100 JD, so 3 Unit Bridge is 300 JD).
DONE by: SENDOS AL-JALAM LAMA KHALIL
Now ehda2 5as jeddan la Farah belal, AYAH Haj Yahya , Diana Alsardia, and Rawan Qashqoosh =D AND RAMADAN KAREEM FOR ALL =)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Immediate Complete DenturesDokument74 SeitenImmediate Complete DenturesPuneet Pandher100% (1)
- Prostho 3Dokument109 SeitenProstho 3Inès BelhaissiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Veneer Series PT 1Dokument6 SeitenVeneer Series PT 1Cornelia Gabriela OnuțNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gingival Finish LinesDokument15 SeitenGingival Finish LinesAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKANoch keine Bewertungen
- GTC 1 - Introduction To Fixed Prosthodontics (PPSG Lectures)Dokument52 SeitenGTC 1 - Introduction To Fixed Prosthodontics (PPSG Lectures)rositadewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crown and Bridge: A) 1. Complete Coverage (Full Veneer Crown) : ItDokument5 SeitenCrown and Bridge: A) 1. Complete Coverage (Full Veneer Crown) : ItRihan RihanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment Planning Single Maxillary Anterior Implants for DentistsVon EverandTreatment Planning Single Maxillary Anterior Implants for DentistsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fpdintroduction 100203103114 Phpapp02Dokument42 SeitenFpdintroduction 100203103114 Phpapp02Sangeetha BommineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Principles of Cavity Preparation (Lecture by DR - Wedad Etman @AmCoFam)Dokument38 SeitenThe Principles of Cavity Preparation (Lecture by DR - Wedad Etman @AmCoFam)AmericanCornerFamily92% (24)
- Dental Materials (Review Center)Dokument11 SeitenDental Materials (Review Center)yellow rangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental Restoration or Dental Filling: Elaborate: Ceban Gabriela Teacher: Doronin NataliaDokument12 SeitenDental Restoration or Dental Filling: Elaborate: Ceban Gabriela Teacher: Doronin NataliaGabriela CebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Fixed ProsthodonticsDokument15 SeitenIntroduction To Fixed ProsthodonticsSyamilBunyamin100% (1)
- Crown&Bridge Lec.1Dokument6 SeitenCrown&Bridge Lec.1Dr-Ibrahim GhanimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management-Of-Mutilated-Teeth - (1) (1) - 1Dokument57 SeitenManagement-Of-Mutilated-Teeth - (1) (1) - 1Khushboo Gupta75% (4)
- Bridge Indikasi & DesainDokument86 SeitenBridge Indikasi & DesainFrieda Ayu PrihadiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crown and BrigeDokument157 SeitenCrown and BrigeAyad IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed ProsthodonticsDokument12 SeitenFixed Prosthodonticsapi-19840404100% (1)
- DENTURES: The Ultimate Guide to Dentures & Denture Care for a Beautifully Restored SmileVon EverandDENTURES: The Ultimate Guide to Dentures & Denture Care for a Beautifully Restored SmileNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMPLANTOLOGI Compressed Compressed (1) - MinDokument122 SeitenIMPLANTOLOGI Compressed Compressed (1) - MinNayafilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines: The Crown and Bridge TechniqueDokument23 SeitenGuidelines: The Crown and Bridge TechniqueAlex Burde100% (1)
- By: Mohammad Al-Tamimi: To ProsthodonticsDokument8 SeitenBy: Mohammad Al-Tamimi: To ProsthodonticsPrince AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental RestorationsDokument3 SeitenDental Restorationsverasliliam70Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Fixed ProsthodonticsDokument6 SeitenAn Introduction To Fixed Prosthodonticsمؤمل رياض سعد كاظمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Mouth Reconstruction - by John UtamaDokument11 SeitenFull Mouth Reconstruction - by John Utamajutama8289Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz No Need QuizDokument11 SeitenQuiz No Need Quizapi-19840404Noch keine Bewertungen
- BridgesDokument3 SeitenBridgesNajeeb UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Prosthodontics Course (Crowns)Dokument46 SeitenFixed Prosthodontics Course (Crowns)ardesh abdilleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q: Why Do Teeth Drift Mesially, Not Distally?Dokument8 SeitenQ: Why Do Teeth Drift Mesially, Not Distally?Shazrin AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial English - Blok 6Dokument4 SeitenTutorial English - Blok 6rania azzahraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostho Lec - OverdenturesDokument14 SeitenProstho Lec - Overdenturesdrgayen6042Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Removable Partial Denture IIDokument16 SeitenIntroduction To Removable Partial Denture IIkilolopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction & Terminology Fixed Prosthodontics: A Brief IntroductionDokument10 SeitenIntroduction & Terminology Fixed Prosthodontics: A Brief IntroductionAli UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17) Orthodontic Glossary - Understanding Your Treatment - American Association of OrthodontistsDokument21 Seiten17) Orthodontic Glossary - Understanding Your Treatment - American Association of OrthodontistsJawad TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulp EctomyDokument4 SeitenPulp EctomyAdji HidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Prosthodontics Lesson 1Dokument10 SeitenFixed Prosthodontics Lesson 1Bota Bianca FrancescaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prosthodontics (Prosthetic Dentistry or Prosthodontia) : Prof. Adel F. IbraheemDokument4 SeitenProsthodontics (Prosthetic Dentistry or Prosthodontia) : Prof. Adel F. IbraheemGhina AdilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al-Anbar University, Dental Faculty, Prosthodontics Unit Dr. Salah Kh. Al-Rawi 3 Year/ 1 LecDokument3 SeitenAl-Anbar University, Dental Faculty, Prosthodontics Unit Dr. Salah Kh. Al-Rawi 3 Year/ 1 LecSamer AlRefaayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Prosthodontics - Lesson 1Dokument10 SeitenFixed Prosthodontics - Lesson 1Rose SkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capping Cusps With Amalgam (Last Edi)Dokument12 SeitenCapping Cusps With Amalgam (Last Edi)Jewana J. GhazalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - 3 TaftaDokument8 SeitenCase Study - 3 TaftaKhushboo MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implant Script 1implants History DefinitionDokument10 SeitenImplant Script 1implants History DefinitionPrince AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implant and OrthodonticsDokument5 SeitenImplant and OrthodonticsNguyen NganNoch keine Bewertungen
- (3b) Acrylic RPDDokument7 Seiten(3b) Acrylic RPDbkprosthoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prosthesis SelectionDokument41 SeitenProsthesis Selectionshahinshamshiri0% (1)
- Inlays & Onlays Clinical Experiences and Literature Review: Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & TherapyDokument7 SeitenInlays & Onlays Clinical Experiences and Literature Review: Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & TherapycindyannisamelatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Can You Replace Your Crocked Teeth With Dental Implants India?Dokument9 SeitenHow Can You Replace Your Crocked Teeth With Dental Implants India?IndianHealthGuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- FPD - lec.SAS.2 Introduction 1Dokument10 SeitenFPD - lec.SAS.2 Introduction 1abegailnalzaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indirect Restoration That Covered On or More Cusp and It Is Located Between Oclusal Surfaces of The Posterior Tooth Too Damage The Basics FillingDokument4 SeitenIndirect Restoration That Covered On or More Cusp and It Is Located Between Oclusal Surfaces of The Posterior Tooth Too Damage The Basics FillingBagas Luthfi AlfatNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Removable Dentures Work?Dokument2 SeitenHow Do Removable Dentures Work?Laura PotoracNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ProthesisDokument56 SeitenIntroduction To Prothesisreem eltyebNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.veneers and Laminates: 1. LumineersDokument4 Seiten2.veneers and Laminates: 1. Lumineerssfhussain8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed AppliancesDokument16 SeitenFixed AppliancesAmmar Aldawoodyeh100% (1)
- Intro, Types and AlternativDokument47 SeitenIntro, Types and AlternativKhan MksksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00 Intro Department of ProsthodonticsDokument31 Seiten00 Intro Department of ProsthodonticsLalit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - 10) Pulp Therapy For The Young Permanent DentitionDokument15 Seiten4 - 10) Pulp Therapy For The Young Permanent Dentitionبراءة أحمد السلاماتNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overdenture 4th Year 15-3-2020Dokument52 SeitenOverdenture 4th Year 15-3-2020Ahmed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Many Types and What?Dokument5 SeitenHow Many Types and What?Samah FadelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental Specialities: Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDokument5 SeitenDental Specialities: Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryRadu DraghiceanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- File 925Dokument26 SeitenFile 925SadishNoch keine Bewertungen
- OVERDENTURESDokument15 SeitenOVERDENTURESAditya SavirmathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Onlay InlayDokument7 SeitenOnlay InlaySarino RagilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operative Dentistry Lecture 1Dokument55 SeitenOperative Dentistry Lecture 1Mohsin HabibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Diastema / Gapped Teeth: Done By:Abdulaziz Taleb AlshammariDokument13 SeitenManagement of Diastema / Gapped Teeth: Done By:Abdulaziz Taleb AlshammariAlshammari AbdulazizNoch keine Bewertungen
- BongraftingDokument4 SeitenBongraftingjaxine labialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservative Treatment and PeriodontiumDokument4 SeitenConservative Treatment and PeriodontiumReham RashwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Romantic EraDokument1 SeiteThe Romantic EraArxhenta ÇupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Other Uses, See .: Thanksgiving DayDokument8 SeitenFor Other Uses, See .: Thanksgiving DayArxhenta ÇupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- c4 TwilightDokument1 Seitec4 TwilightArxhenta ÇupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ramadan (Calendar Month)Dokument8 SeitenRamadan (Calendar Month)Arxhenta ÇupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiwaliDokument22 SeitenDiwaliArxhenta ÇupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passover From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument22 SeitenPassover From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaArxhenta ÇupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Other Uses, See .: Carnival (Disambiguation)Dokument41 SeitenFor Other Uses, See .: Carnival (Disambiguation)Arxhenta ÇupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Article Is About The Christian Festival. For Other Uses, SeeDokument32 SeitenThis Article Is About The Christian Festival. For Other Uses, SeeArxhenta ÇupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Longterm Survey All Ceramic Inlays Onlays Quintessnce 2020Dokument11 SeitenLongterm Survey All Ceramic Inlays Onlays Quintessnce 2020Raghu PratapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alloys For FPDDokument101 SeitenAlloys For FPDsapnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daveiga 2016Dokument35 SeitenDaveiga 2016Andrei OanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerasmart Cerasmart Cerasmart Cerasmart Cerasmart Cerasmart: UniversalDokument20 SeitenCerasmart Cerasmart Cerasmart Cerasmart Cerasmart Cerasmart: Universalสุวิทย์ สะกิดตลิ่งNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sublay Versus Underlay in Open Ventral Hernia RepairDokument7 SeitenSublay Versus Underlay in Open Ventral Hernia Repairtracycui13Noch keine Bewertungen
- TIEDokument4 SeitenTIEIrwandi MuslimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inlay OnlayDokument6 SeitenInlay OnlayNur HayatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NBDE Questions2Dokument98 SeitenNBDE Questions2Bonnie SengNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 JPD Volume 120 Issue 3 September PDFDokument7 Seiten2018 JPD Volume 120 Issue 3 September PDFamelya vaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lava Ultimate Frame Ifu Na-En PDFDokument4 SeitenLava Ultimate Frame Ifu Na-En PDFcriveliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 - 002 All-Ceramic Inlays and OnlaysDokument3 Seiten05 - 002 All-Ceramic Inlays and Onlayssiddu76Noch keine Bewertungen
- Luting Agents and Cementation Procedures: Key TermsDokument19 SeitenLuting Agents and Cementation Procedures: Key TermsCamelia DamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cracked Tooth Syndrome in An Unrestored Maxillary Premolar A Case Report Batalhasilva2014Dokument9 SeitenCracked Tooth Syndrome in An Unrestored Maxillary Premolar A Case Report Batalhasilva2014LeandroMartinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sirona Dental CAD - CAM System Inlab 3D - Sirona - TechnicalDokument284 SeitenSirona Dental CAD - CAM System Inlab 3D - Sirona - TechnicalAnna M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Reinforced Composite in Dentistry 2Dokument7 SeitenFiber Reinforced Composite in Dentistry 2Drg Sri Pandu UtamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L7 WaxDokument5 SeitenL7 WaxAaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terminologi Ilmu Material Kedokteran Gigi: Istilah Dalam Bahasa Inggeris ADokument38 SeitenTerminologi Ilmu Material Kedokteran Gigi: Istilah Dalam Bahasa Inggeris AkhamilatusyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Design For All-Ceramic Inlay-Retained Fixed Partial Dentures: A Report of 2 CasesDokument8 SeitenA New Design For All-Ceramic Inlay-Retained Fixed Partial Dentures: A Report of 2 CasesSiti FerianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceramic 1. 2021 - ModDokument38 SeitenCeramic 1. 2021 - ModShahriar honarmandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Which Hard Tissue Augmentation Techniques Are The Most Succesful in Furnishing Bony Support For Implant PlacementDokument25 SeitenWhich Hard Tissue Augmentation Techniques Are The Most Succesful in Furnishing Bony Support For Implant PlacementJuan Andres CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Prosthodontics Lesson 1Dokument10 SeitenFixed Prosthodontics Lesson 1Bota Bianca FrancescaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brilliant Crios: High Performance - Made BrilliantDokument10 SeitenBrilliant Crios: High Performance - Made BrilliantmiauNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Properties of MaterialDokument2 SeitenGeneral Properties of MaterialSk Lee0% (1)