Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
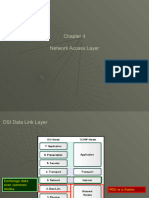
OSI Model: Layer Function Protocols/Standards Data Component Network Component
Hochgeladen von
vickypatel_63873791Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
OSI Model: Layer Function Protocols/Standards Data Component Network Component
Hochgeladen von
vickypatel_63873791Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
OSI Model
The open systems interconnection (OSI) model was created to standardize the rules of
networking in order for all systems to be able to communicate. In order for
communication to occur on a networking using different device drivers and protocol
stacks, the rules for communication must be explicitly defined. The OSI model deals
with the following issues;
• How a device on a network sends it's data, and how it knows when are where to
send it
• How a device on a network receives it's data, and how to know where to look for
it.
• How devices using different languages communicate with each other.
• How devices on a network are physically connected to each other.
• How protocols work with devices on a network to arrange data.
The OSI model is broken down into the following 7 layers.
Data Network
Layer Function Protocols/Standards
Component Component
This layer offers
the user interface
and specifies what's
Telnet, HTTP, FTP,
7) Application being done on the Messages Gateway
and SMTP.
network and how.
The sixth layer is
concerned with
extracting data
from the
6) application layer JPEG, GIF, MPEG,
Messages Gateway
Presentation and putting the data and ASCII.
in a format that can
be read based on
various file
standards.
5) Session Controls the DECnet, RPC, NFS Messages Gateway
beginning, middle, and SQL.
and end of
individual
networking
"sessions."
Layer 4 is involved
primarily as a
gateway between
the upper
4) Transport TCP, UDP, and SPX. Segments Brouter/Gateway
application-oriented
layers and the
lower network-
oriented protocols.
Defines end-to-end
delivery of
information. This Router
includes such IP,RIP,ICMP IPX,
functions as routing
Packets or
3) Network and routing NWLink
datagrams
protocols. Ex: this ATM Switch
layer defines the NetBEUI
addressing and
routing structure of
the Internet.
Logical •
Link
Control error
correction and
flow control
manages link
control and Bridge
defines SAPs
Switch
Specifies a direct
means of HDLC, SDLC,
2) ISDN Router
communication on Frame Relay, PPP,
Data Frames
the network. It's FDDI, and
Link Media Intelligent Hub
Access best thought of as a ATM,LAPB,
Contro one-hop protocol. NIC
•
communicates
with the
adapter card
• controls the
type of media
being used:
Defines the
physical
components that
make the network Repeater
function. This
includes cabling Multiplexer
standards and
electrical or light UTP,STP, Fiber, V.35, Hubs
1) Physical Bits
communication X.21,RS-232
methods. Standards • Passive
in the Physical • Active
layer are usually
defined by
international
standards
committees.
Partial list of TCP/IP protocols in relation to the seven-layer model
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- OSI Model Explained for Networking BeginnersDokument35 SeitenOSI Model Explained for Networking BeginnersZaimeth ArqueroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial DFT G2 AACS2034Dokument10 SeitenTutorial DFT G2 AACS2034TEOH YING JINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetworkingDokument55 SeitenNetworkingRey Allen TenosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntroDokument18 SeitenIntroSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network Report - CA2 - Tirtharaj Pati - 14201619089Dokument5 SeitenComputer Network Report - CA2 - Tirtharaj Pati - 14201619089Tirtharaj PatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WK6 Lecture PTC Model PDFDokument19 SeitenWK6 Lecture PTC Model PDFStephen AdingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCI c3Dokument44 SeitenHCI c3ghodke_a527Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 640-802 Study Guide: Tutorial Quick LinksDokument14 SeitenCCNA 640-802 Study Guide: Tutorial Quick Linksahmad_naser12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Network and Communication: Distributed Systems 1Dokument22 SeitenChapter 3: Network and Communication: Distributed Systems 1allanmuli18Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Model:: Application CiscoDokument16 SeitenOSI Model:: Application CiscoHAINHDT2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer and Multimedia Networks: OSI Layers and TCP/IP ProtocolsDokument35 SeitenComputer and Multimedia Networks: OSI Layers and TCP/IP ProtocolsAamir HiraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ministry of Water Resources and ElectricityDokument26 SeitenMinistry of Water Resources and ElectricitymeshelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4-7@networking ModelsDokument94 SeitenChapter 4-7@networking ModelsSilabat AshagrieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standards and Network Protocols: M.C. Juan Carlos Olivares RojasDokument109 SeitenStandards and Network Protocols: M.C. Juan Carlos Olivares RojasrizismNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Computer NetworkingDokument38 SeitenAdvance Computer NetworkingJayson Binesen DerechoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data communication Components: OSI model and TCP/IP protocol suiteDokument6 SeitenData communication Components: OSI model and TCP/IP protocol suiteSOHOM MAJUMDARNoch keine Bewertungen
- System and Network Administration Network EssentialsDokument45 SeitenSystem and Network Administration Network EssentialsArsalan JahaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARTIGO EN - Article - Instituto Politécnico de Beja, Escola Superior de Tecnologia e GestãoDokument5 SeitenARTIGO EN - Article - Instituto Politécnico de Beja, Escola Superior de Tecnologia e GestãoJaejaneiro NtlNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 640-802 Study Guide: A P S T N D PDokument8 SeitenCCNA 640-802 Study Guide: A P S T N D PPietersen VinothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 03 - Network Requirements and Layered Architectures (1)Dokument25 SeitenLecture 03 - Network Requirements and Layered Architectures (1)kijabryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCP/IP Model Layers Cheat Sheet: by ViaDokument1 SeiteTCP/IP Model Layers Cheat Sheet: by ViaĐào N. AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna2 1Dokument54 SeitenCcna2 1Alok SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap5 Osi 2015Dokument20 SeitenChap5 Osi 2015semakulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Reference ModelDokument25 SeitenOSI Reference ModelPushpendra MahilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module III Session IIDokument44 SeitenModule III Session IIManav JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Model ExplainedDokument25 SeitenOSI Model ExplainedMu JiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defining Networks With The OSI ModelDokument29 SeitenDefining Networks With The OSI ModelPradeep ManralNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetworkDokument82 SeitenNetworkDavidoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Protocols and ServicesDokument4 SeitenNetwork Protocols and ServicesMay Ann Agcang SabelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Link Issues: Relates To Lab 2Dokument17 SeitenData Link Issues: Relates To Lab 2Tabish KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCOM 509: TCP/IP - Internet Protocols: Instructor: Scott T. TranDokument148 SeitenTCOM 509: TCP/IP - Internet Protocols: Instructor: Scott T. TranHarsha KiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Layers and ProtocolsDokument5 SeitenOSI Layers and Protocolsapi-3805926Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSI and TCP - IP Lecture SlideDokument28 SeitenOSI and TCP - IP Lecture SlideBobby IgbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To CCNA ExamDokument24 SeitenIntroduction To CCNA ExamsgmundaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (FEG2) - Cyber Networking - Part 05aDokument22 Seiten(FEG2) - Cyber Networking - Part 05aMD NASIR UDDINNoch keine Bewertungen
- C172 Study Guide (Feb 2021 Update)Dokument22 SeitenC172 Study Guide (Feb 2021 Update)Michael ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Protocol and TCPDokument5 SeitenNetwork Protocol and TCPJoshua SantillanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The OSI Model: Understanding The Seven Layers of Computer NetworksDokument22 SeitenThe OSI Model: Understanding The Seven Layers of Computer NetworksMona AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - 6 Data Communication and Networking: BY Muhammad AfzalDokument36 SeitenLecture 5 - 6 Data Communication and Networking: BY Muhammad AfzalHamzah AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN & IOT - Module 1 - IntroductionDokument123 SeitenCN & IOT - Module 1 - Introductionpalakkhurana012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna1 CH4Dokument73 SeitenCcna1 CH4User OneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm revision of OSS, TCP/IP and OSI modelsDokument25 SeitenMidterm revision of OSS, TCP/IP and OSI modelsgjjjgjgjhghghjghjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer-Network-Cheetsheet 2Dokument18 SeitenComputer-Network-Cheetsheet 2Nguyễn Ngọc PhụngNoch keine Bewertungen
- osi-tcp cskDokument28 Seitenosi-tcp cskAngamuthuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clase 4. HDLC&PPP PDFDokument49 SeitenClase 4. HDLC&PPP PDFCarmita PinduisacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI ModelDokument4 SeitenOSI ModelJeff kigenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks PDFDokument2 SeitenComputer Networks PDFKIRTI ROHIRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Computer Networking: Babul Islam Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering University of RajshahiDokument81 SeitenAdvanced Computer Networking: Babul Islam Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering University of RajshahiBabul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1-Modified-Introduction For Wireless NetworksDokument48 SeitenLec 1-Modified-Introduction For Wireless NetworksnawafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10 Merged PDFDokument128 SeitenWeek 10 Merged PDFNikitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2-Network Reference ModelsDokument29 SeitenTopic 2-Network Reference Modelssamuel amareNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Model TuteDokument6 SeitenOSI Model TuteRishanRulzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session-4 (Network Software)Dokument15 SeitenSession-4 (Network Software)Siddardha YarlagaddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The OSI Reference ModelDokument21 SeitenThe OSI Reference ModelNaureen HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDokument118 SeitenIntroduction To Computer Networkskaynaan YareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layering in Computer NetworkingDokument59 SeitenLayering in Computer NetworkingJOENoch keine Bewertungen
- Packet Sniffer Project Document PDF FreeDokument90 SeitenPacket Sniffer Project Document PDF FreeSurendra ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingVon EverandComputer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsVon EverandTCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachVon EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Basic El. Chapter 1Dokument4 SeitenBasic El. Chapter 1vickypatel_63873791Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4.0 Repeaters, Bridges, Routers, and Gateways: A Comparative Study: 4.1 RepeatersDokument5 Seiten4.0 Repeaters, Bridges, Routers, and Gateways: A Comparative Study: 4.1 Repeatersvickypatel_63873791Noch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Network DeviceDokument3 Seiten04 Network Devicevickypatel_63873791100% (1)
- 1.0 The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) ModelDokument5 Seiten1.0 The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Modelvickypatel_63873791100% (1)
- 03 Information Exchange ProcessDokument2 Seiten03 Information Exchange Processvickypatel_63873791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 TopologyDokument5 SeitenChapter 2 Topologyvickypatel_63873791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Tips Multi Pitch ClimbingDokument2 SeitenTech Tips Multi Pitch ClimbingTomnatic100% (3)
- FM 7910Dokument18 SeitenFM 7910HiTechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Storage Networking Technology Certified Storage Engineer (Scse, s10-201)Dokument17 SeitenBasic Storage Networking Technology Certified Storage Engineer (Scse, s10-201)slimanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retaining Wall GuidelineDokument38 SeitenRetaining Wall Guidelinesom_bs79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Turchi 260-S 830 Joule Pile Driver Productivity & PerformanceDokument7 SeitenTurchi 260-S 830 Joule Pile Driver Productivity & Performancejuan apazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NetworksDokument51 SeitenComputer NetworksSempijja JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Ceberus EcoDokument60 SeitenManual Ceberus EcoAad Pupu SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Michael BuckleyDokument15 SeitenMichael BuckleyPEFC InternationalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lem Ar 297 in - 108 4.2 Haf V0001 IvecoDokument28 SeitenLem Ar 297 in - 108 4.2 Haf V0001 IvecoFagner LucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Quality Standards ISO 8573Dokument9 SeitenAir Quality Standards ISO 8573nidhink18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report Electric Vehicles en Page 26Dokument86 SeitenReport Electric Vehicles en Page 26Mohsin Hassan SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEON LampDokument14 SeitenNEON LampVijay GajjalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Design Guidelines and Standard DrawingsDokument84 SeitenEngineering Design Guidelines and Standard DrawingsUdomsin Wutigulpakdee100% (1)
- Plcopen and Opc Ua A Perfect MatchDokument30 SeitenPlcopen and Opc Ua A Perfect Match李光明Noch keine Bewertungen
- My HobbyDokument9 SeitenMy HobbyDwi Puspita ParawangsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VHLP4 6WDokument4 SeitenVHLP4 6WLincoln Felicio e MacedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jofra CalDokument8 SeitenJofra CalFR PERANoch keine Bewertungen
- Stauff One Valves UsDokument120 SeitenStauff One Valves UsAsela BandaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conventional Zone Interface Module P/N 55-055 and 55-060 2-Wire Detector Compatibility DocumentDokument10 SeitenConventional Zone Interface Module P/N 55-055 and 55-060 2-Wire Detector Compatibility DocumentErnesto OtazuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectwindows Tutorial: Turbo C ++Dokument172 SeitenObjectwindows Tutorial: Turbo C ++Lalit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- W2k Net - Chapter1 - Designing A Windows 2000 NetworkDokument19 SeitenW2k Net - Chapter1 - Designing A Windows 2000 NetworktheplagueisbackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symantec Network Security Administration GuideDokument432 SeitenSymantec Network Security Administration GuideTibor CsizovszkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hoja de Datos TelurometroDokument2 SeitenHoja de Datos TelurometrocimatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAQ - FactoryTalk Historian SE CollectivesDokument2 SeitenFAQ - FactoryTalk Historian SE CollectivesjaysonlkhNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASE A1 Engine Repair Practice Test QuestionsDokument55 SeitenASE A1 Engine Repair Practice Test Questionstarek100% (3)
- Cyclo ReductorDokument50 SeitenCyclo ReductorIng. Juan ZerpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tl-Wpa4220 Kit V1 Qig PDFDokument2 SeitenTl-Wpa4220 Kit V1 Qig PDFΔημήτρηςNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loctite Thread SealingDokument8 SeitenLoctite Thread SealingngazawooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kurdistan Region of Iraq Investors MapDokument1 SeiteKurdistan Region of Iraq Investors Maphasan_676489616Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermosiphon seal supply system overviewDokument4 SeitenThermosiphon seal supply system overviewkeyur1109Noch keine Bewertungen