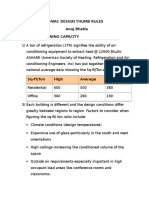
Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
List of Engineering Branches
Hochgeladen von
mep.Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
List of Engineering Branches
Hochgeladen von
mep.Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
List of engineering branches
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Engineering is the discipline, art, and profession, that applies scientific theory to design, develop, and analyze technological solutions. In the contemporary era, engineering is generally considered to consist of the major basic branches of chemical engineering, civil engineering, electrical engineering andmechanical engineering.[1] There are numerous other engineering subdisciplines and interdisciplinary subjects that are derived from concentrations, combinations, or extensions of the major engineering branches.
Contents
[hide]
1 Chemical engineering 2 Civil engineering 3 Electrical engineering 4 Mechanical engineering 5 Interdisciplinary and specialized fields 6 See also 7 References
[edit]Chemical
engineering
Chemical engineering comprises the application of physical and biological sciences to the process of converting raw materials or chemicals into more useful or valuable forms. Subdiscipline Scope Major specialties
Biomolecular engineering
Focuses on the manufacturing ofbiomolecules.
Ceramic engineering, the theory and processing of raw oxide material (e.g. alumina oxide), and advanced material
Materials engineering
Involves the properties of matter and its applications to engineering
that are polymorphic, polycrystalline, oxide, and non-oxide ceramics
Crystal engineering, the design and synthesis of molecular solid-state structures
Molecular engineering
Focuses on the manufacturing ofmolecules.
Focuses on the design, operation, Process engineering control, and optimization of chemical processes
Petroleum refinery engineering, the design of processes related to the manufacture ofrefined products
Subdiscipline
Scope
Major specialties
Plastics engineering, the design of the production process of plastics products
Paper engineering, the design of the production process of paper products
[edit]Civil
engineering
Civil engineering comprises the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and natural built environments. Subdiscipline Scope Major specialties
Ecological engineering, the design, monitoring and construction of ecosystems
Fire protection engineering, the application of engineering to protect people and environments from fire and smoke
Environmental engineering The application of engineering to the improvement and protection of the environment
Sanitary engineering, the application of engineering methods to improve sanitation of human communities
Hydraulic engineering, the planning, development and maintenance of water resourcesand the application of hydrology
Municipal or urban engineering, civil engineering applied to municipal issues such as water and waste management, transportation networks, subdivisions, communications, hydrology, hydraulics, etc.
Geotechnical engineering
Concerned with the behavior of geological materials at the site of a civil engineering project
Mining engineering, the exploration, extraction and processing of raw materials from the earth
Earthquake engineering, the behaviour of structures subject to seismic loading
Structural engineering The engineering of structures that support or resist structural loads
Wind engineering, the analysis of wind and its effects on the built environment
Architectural engineering, application of engineering principles to building design and construction
Transport engineering The use of engineering to ensure safe and efficient transportation of people and goods
Ocean engineering, the design of offshore structures
Traffic engineering, a branch of transportation engineering
Subdiscipline
Scope
Major specialties
focusing on the infrastructure necessary for transportation
[edit]Electrical
Highway engineering Railway systems engineering
engineering
Electrical engineering comprises the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. Subdiscipline Scope Major specialties
Software engineering, The application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of
Computer engineering
The design and control of computing devices with the application of electrical systems
software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software.
Hardware engineering, Designing, developing, and testing various computer equipment. Can range from circuit boards and microprocessors to routers.
Electronic engineering The design of circuits that use the electromagnetic properties of electrical components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes and transistors to achieve a particular functionality.
Control engineering, focuses on the modeling of dynamic systems and the design of controllers using electrical circuits, digital signal processors and microcontrollers
Optical engineering The design of instruments and systems that utilize the properties of electromagnetic radiation. The generation, transmission and distribution of electricity, and the design of devices such as transformers, electric generators, electric motors, high voltage engineering and power electronics.
Telecommunications engineering
Power engineering
[edit]Mechanical
engineering
Mechanical engineering comprises the design, analysis and usage of heat and mechanical power for the operation of machines and mechanical systems. Subdiscipline Scope Major specialties
Aerospace
Also known as Aeronautical engineering concerns the design, construction, and science of bothair and space vehicles, primarily
Subdiscipline Engineering
Scope on the systems level. Further concerned with the science of force and physics that are particular only to performance in Earth's atmosphere and the expanse of space.
Major specialties
Acoustical engineering
Concerns the manipulation and control of vibration, especially vibration isolation and the reduction of unwanted sounds
Manufacturing engineering
Concerns dealing with different manufacturing practices and the research and development of systems, processes, machines, tools and equipment.
Thermal engineering
Concerns heating or cooling of processes, equipment, or enclosed environments
Automotive engineering, the design, manufacture and operation of motorcycles, automobiles,
Vehicle engineering
The design, manufacture and operation of the systems and equipment that propel and control vehicles
buses and trucks
Naval architecture, the design, construction, operation and support of marine vehicles and structures
[edit]Interdisciplinary
and specialized fields
Scope Major specialties
Discipline
Bioprocess engineering, the design and development of equipment and processes for the manufacturing of
Agricultural engineering
The application of engineering principles to agricultural fields such as farm power and machinery, biological material process, bioenergy, farm structures, and agricultural natural resources
products from biological materials
Food engineering, concerns food processing, food machinery, packaging, ingredient manufacturing, instrumentation, and control.
Aquaculture engineering, the study of cultured aquatic species and the production systems used in their culture.
Applied engineering
The field concerned with the application of management, design, and technical
Automation/Control systems/Mechatronics/Robotics
Discipline
Scope skills for the design and integration of systems, the execution of new product designs, the improvement of manufacturing processes, and the management and direction of physical and/or technical functions of a firm or organization. Applied Engineering degreed programs typically include instruction in basicengineering principles, project management, industrial processes, production and operations management, systems integration and control, quality control, and statistics.[2]
Major specialties
Computer-aided Drawing & Design (CADD) Construction Electronics General Graphics Manufacturing Nanotechnology
Biomedical engineering, the application of engineering principles and techniques to the medical and biological sciences
Biological engineering The application of engineering principles to the fields of biology and medicine.
Genetic engineering, the design and development of techniques to directly manipulate an organism's genes
Biochemical engineering, the design and construction of unit processes that involve biological organisms or molecules
Tissue engineering Protein engineering, the development of useful or valuable proteins
Mechanical engineering,
Building services engineering, technical building services, architectural engineering, or building engineering is the engineering of the internal environment and environmental impact of a building. It essentially brings buildings and structures to life.
HVAC: Heating, ventilation and air conditioning Refrigeration Plumbing or public health (MEP) engineering:Water services, drainage and plumbin g
Building services engineering
Electrical engineering,
Artificial lighting and emergency lighting, ICT: Communication lines, telephones and IT networks
Low voltage (LV) systems, containment, distribution, distribution boards and switchgear
Lightning protection Security, CCTV, and alarm systems
Discipline
Scope
Major specialties
Vertical transportation: Escalators and lifts Fire engineering, including fire detection and fire protection
Natural lighting design Building facades engineering Energy supply - gas, electricity and renewablesources Solar engineering, Solar Energy Engineering includes designing and building services based on solar energy,
Energy engineering
Energy engineering is a broad field of engineering dealing with energy efficiency, energy services, facility management, plant engineering, environmental compliance and alternative energy technologies. Domain of Energy Engineering expertise combines selective subjects from the fields Chemical, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering. It is an interdisciplinary program which has relativity with electrical, mechanical and chemical engineering
solar energy product development, solar PV systems, Solar Product Manufacturing and Solar Systems Integration. Wind engineering, Wind engineering analyzes effects of wind in the natural and the built environment and studies the possible damage, inconvenience or benefits which may result from wind. In the field of structural engineering it includes strong winds, which may cause discomfort, as well as extreme winds, such as in a tornado, hurricane or heavy storm, which may cause widespread destruction
Manufacturing engineering, the ability to plan the practices of manufacturing, to research and develop the tool, processes, machines and equipment, and to integrate the facilities and systems for producing quality products with optimal expenditure.
Industrial engineering The design and analysis of logistical and resource systems.
Component engineering, the process of assuring the availability of suitable components required to manufacture a product.
Systems engineering, focuses on issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, automatic control of machinery for complex engineering projects
Construction engineering, the planning and management of construction projects
Textile Engineering, The design and analysis of logistical and resource systems, product design, and
Discipline
Scope
Major specialties
development.
Safety engineering, assuring that a life-critical system behaves as needed even when pieces fail
Reliability engineering, optimising asset maintenance to minimise whole of life cost
Mechatronics A hybrid of mechanical and electrical engineering, Commonly intended to examine the design of automation systems.
Robotics Instrumentation engineering Avionics, the design of electronics and systems on board an aircraft or spacecraft
Nanoengineering Nuclear engineering
The practice of engineering on the nanoscopic scale The application of nuclear processes to engineering
Reservoir engineering, the application of scientific principles to study the flow of fluids in underground reservoirs so as to obtain a high economic recovery.
Petroleum engineering
The application of engineering principles to drilling for and producing crude oil and natural gas
Drilling engineering, the design and application of equipment and techniques to drill wells.
Production engineering, the design and application of equipment and techniques to bring well fluids to the surface and then separate out the various components.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Gsas-Cgp Online Exam: (Sample Questions)Dokument10 SeitenGsas-Cgp Online Exam: (Sample Questions)renrama100% (1)
- ICP Cleanroom Level 1Dokument4 SeitenICP Cleanroom Level 1Asok AyyappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cam and Follower: Definition, Types, Working Principle, and ApplicationsDokument17 SeitenCam and Follower: Definition, Types, Working Principle, and Applicationsniaz kilamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Office Furniture Specification PDFDokument2 SeitenOffice Furniture Specification PDFAshley0% (1)
- Operation AnalysisDokument16 SeitenOperation AnalysisLyne LerinNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoQ For MoE BuildingsDokument265 SeitenBoQ For MoE BuildingsMichaelKipronoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility Study of LED Bulbs FactoryDokument2 SeitenFeasibility Study of LED Bulbs FactoryAmjad AtiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sirkpompa Optima Ing Brs PDFDokument20 SeitenSirkpompa Optima Ing Brs PDFpepa 007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Allianz ArenaDokument2 SeitenAllianz ArenaDanut CalugarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi-Level Car Parking System by Using Solar Energy..Dokument39 SeitenMulti-Level Car Parking System by Using Solar Energy..Ajay Verma100% (4)
- Calculation of Cooling of Commercial BuildingDokument39 SeitenCalculation of Cooling of Commercial BuildingFareed AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On District Cooling System in Hong Kong 6-11-2016Dokument61 SeitenA Study On District Cooling System in Hong Kong 6-11-2016HEI532532Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hvac Design Thumb Rules PDFDokument52 SeitenHvac Design Thumb Rules PDFmohd yusuf ansariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CII IGBC Annual Review - 2016 2017Dokument56 SeitenCII IGBC Annual Review - 2016 2017anupama100% (2)
- ECBC - Transformer PDFDokument24 SeitenECBC - Transformer PDFSOYAL CHAUHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Change RatesDokument2 SeitenAir Change RatesSanthosh ThekkethottiyilNoch keine Bewertungen
- VRF Thesis EditedDokument69 SeitenVRF Thesis EditedMurtaza Sabir50% (2)
- Green Management Approach - Made EasyDokument7 SeitenGreen Management Approach - Made Easyvidyut3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atrium BuildBoston B67Dokument39 SeitenAtrium BuildBoston B67aliag9270Noch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar TopicsDokument2 SeitenSeminar TopicsKarma DugyelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering EconomicsDokument28 SeitenEngineering EconomicsTeeni AbeysekaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Audit FinaleDokument37 SeitenEnergy Audit Finale17930Noch keine Bewertungen
- MME-Electrical-Session-2 Network Theorems PDFDokument74 SeitenMME-Electrical-Session-2 Network Theorems PDFgpuonlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consultancy Fee Guidelines As Approved by The Council On February 6, 2012 PDFDokument11 SeitenConsultancy Fee Guidelines As Approved by The Council On February 6, 2012 PDFbittuchintu100% (1)
- Design Basis Report: Construction of ProposedDokument123 SeitenDesign Basis Report: Construction of Proposedprabhash kumar100% (1)
- Energy Conservation Building CodeDokument5 SeitenEnergy Conservation Building CodeVisalakshi ChockalingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV PM Om 04 06 2019Dokument6 SeitenCV PM Om 04 06 2019soumya19800000000Noch keine Bewertungen
- UFMFV7-15-2 Control - CW PDFDokument7 SeitenUFMFV7-15-2 Control - CW PDFBraveSoulBoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ToR - Electrical EngineerDokument4 SeitenToR - Electrical EngineerBruno SamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEP Scope of WorkDokument2 SeitenMEP Scope of WorkMuhammed Talha QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vinod Desu: Work ExperienceDokument3 SeitenVinod Desu: Work ExperienceNEB MEPNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 PDFDokument60 Seiten1 PDFdexterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0003 - Password Based Access Control System With Motorized Gate Buzzer and LCD DisplayDokument3 Seiten0003 - Password Based Access Control System With Motorized Gate Buzzer and LCD DisplayPrasad RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINALDokument21 SeitenFINALRajesh ShingreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Safety Requirements For General Warehouses PDFDokument6 SeitenFire Safety Requirements For General Warehouses PDFecruz_yhwhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshops at The Big 5 2014 Salim 1Dokument9 SeitenWorkshops at The Big 5 2014 Salim 1Arul SankaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW Careerride ComDokument9 SeitenWWW Careerride ComNavin KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation and Maintenance of A Substation-Libre PDFDokument60 SeitenOperation and Maintenance of A Substation-Libre PDFShareef KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bod SampleDokument2 SeitenBod SamplepanjemadjoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence and Robotics MCQ SPPU Questions and AnswersDokument1 SeiteArtificial Intelligence and Robotics MCQ SPPU Questions and AnswersAvadesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - Building Management System - Limitations, Advantages, Disadvantages Components and Integration in Buildings.Dokument13 SeitenLecture 5 - Building Management System - Limitations, Advantages, Disadvantages Components and Integration in Buildings.hewelirNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC Draughtsman Sample CVDokument5 SeitenHVAC Draughtsman Sample CVAseer AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM01 - CFD For Building and Facilities DesignDokument46 SeitenSM01 - CFD For Building and Facilities Designsuperhunter007Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 320 SyllabusDokument3 SeitenECON 320 SyllabusSajid IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linda Updated CVDokument3 SeitenLinda Updated CVlindajm78Noch keine Bewertungen
- NICMAR AssignmentDokument41 SeitenNICMAR AssignmentChandra ShekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Guideline ETISALATDokument26 SeitenBuilding Guideline ETISALATMohammed Zubair50% (2)
- LPG Gas Detection and Alert SystemDokument11 SeitenLPG Gas Detection and Alert SystemNitin Sharma0% (1)
- Ansi Tia 942 2005 DtacenterDokument68 SeitenAnsi Tia 942 2005 Dtacenterjhonatan villanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Plan For Ice Cream ParlourDokument2 SeitenProject Plan For Ice Cream Parloursekhar_jvjNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Evolution and Future of Wired CommunicationsDokument2 SeitenThe Evolution and Future of Wired CommunicationsHubert SemenianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility Study For Solar Cooling SystemsDokument86 SeitenFeasibility Study For Solar Cooling SystemsPopa Florin100% (1)
- Hvac PresentationDokument16 SeitenHvac PresentationManeesh DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Alarm Controller ReportDokument18 SeitenFire Alarm Controller ReportAnil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- S F A M T B T S P T F Ethiopian Electric Utility (Eeu)Dokument12 SeitenS F A M T B T S P T F Ethiopian Electric Utility (Eeu)Ahmed AbdellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 425 (PPD) Syllabus-First Sem 2021-2022-FinalDokument13 SeitenME 425 (PPD) Syllabus-First Sem 2021-2022-FinalArhon Barcelon100% (1)
- Green Buildings Lessons Learnt IGBCDokument21 SeitenGreen Buildings Lessons Learnt IGBCvabsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PVRS 1 Pearl Submittal Template v1.3Dokument19 SeitenPVRS 1 Pearl Submittal Template v1.3Shyam_Nair_9667Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Project ReportDokument45 SeitenDesign Project ReportRohit P LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Engineering BranchesDokument3 SeitenList of Engineering Branches_WeLsey_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Viterbo - BSCpE - 1E Assignment No. 1 - CPECOMDokument4 SeitenViterbo - BSCpE - 1E Assignment No. 1 - CPECOMPaul Isaac ViterboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline of EngineeringDokument9 SeitenOutline of Engineeringriz2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Meeting Minutes TemplateDokument2 SeitenFormal Meeting Minutes Templatemep.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Documents Required For Non-ECRDokument3 SeitenDocuments Required For Non-ECRmep.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complete BroucherDokument155 SeitenComplete Brouchermep.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Ways To Find Out What's Going To Be On The Final - Chegg BlogDokument5 Seiten10 Ways To Find Out What's Going To Be On The Final - Chegg Blogmep.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Expressor CompressorDokument81 SeitenExpressor Compressormep.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shaik Khader Basha: Career ObjectiveDokument2 SeitenShaik Khader Basha: Career Objectivemep.Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Ecat Magazine 1.0 (By Uet Tribune)Dokument55 SeitenThe Ecat Magazine 1.0 (By Uet Tribune)Anonymous n7eRdoKiiv100% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering Dissertation TitlesDokument5 SeitenMechanical Engineering Dissertation TitlesCustomPaperServicesUK100% (1)
- ES 411 - Eng'g Management SyllabusDokument7 SeitenES 411 - Eng'g Management SyllabusJames Adrian Abalde SaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opinion On Construction in Times of PandemicDokument2 SeitenOpinion On Construction in Times of PandemicLizeth MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VT Acceptance (ASME B31.1-2012) PDFDokument1 SeiteVT Acceptance (ASME B31.1-2012) PDFPhan Minh PhungNoch keine Bewertungen
- 005-Sample Method Statement CivilDokument2 Seiten005-Sample Method Statement CivilS.C.Satish Chander100% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae UmairDokument2 SeitenCurriculum Vitae UmairAhsaan RizviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saravanakumar Testing 4years 10MonthsExperienceDokument4 SeitenSaravanakumar Testing 4years 10MonthsExperienceRathika SoundararajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Warehouse Robots, Goods-To-Man AutomationDokument7 SeitenAutomated Warehouse Robots, Goods-To-Man AutomationronalddragoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mathematics - IiDokument2 SeitenEngineering Mathematics - IiKattykeyan Katty0% (1)
- Hydraulic Turbine and Associated EquipmentDokument47 SeitenHydraulic Turbine and Associated Equipmentpavankumar0010% (1)
- SYNOPSIS Sample ReportDokument19 SeitenSYNOPSIS Sample ReportShivraj KolambekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDEP Board Reviewflyer Feb-Jun 2018 FINALDokument2 SeitenCDEP Board Reviewflyer Feb-Jun 2018 FINALRyan Etrata50% (2)
- Mil-Std-882e System Safety Course - OutlineDokument2 SeitenMil-Std-882e System Safety Course - Outlineseunghyun songNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Finnish Wooden TownDokument6 SeitenModern Finnish Wooden TownChechu MenendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SfcaDokument95 SeitenSfcaविश्वेश सिंहNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Formula Revision I-Engg Math (Arohi Malviya)Dokument51 SeitenComplete Formula Revision I-Engg Math (Arohi Malviya)ajaymurmu175Noch keine Bewertungen
- SpringerDokument2.886 SeitenSpringerwilmer flores astoraymeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BP 2632 GBDokument24 SeitenBP 2632 GBالمهندسوليدالطويلNoch keine Bewertungen
- Office of Admissions: Application For Scholastic and Technical Aptitude TestDokument2 SeitenOffice of Admissions: Application For Scholastic and Technical Aptitude TestJoniel Vince FelimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF en Funke Oil Air Cooling Units enDokument8 SeitenPDF en Funke Oil Air Cooling Units enUdayan BasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design For XDokument22 SeitenDesign For XKarandeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sho001 Nap Ifc M2 06 RCM DR SS 5001 03 0aDokument1 SeiteSho001 Nap Ifc M2 06 RCM DR SS 5001 03 0aMohanad EldarerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deped K To 12 Technology and Livelihood Education - PlumbingDokument8 SeitenDeped K To 12 Technology and Livelihood Education - Plumbingyachiru12175% (4)
- E41.50.530.N Avril2011 ENDokument14 SeitenE41.50.530.N Avril2011 ENEhsan Arbabtafti100% (1)
- Civil Engineer Resume - Posted by Anupriya NiranjanDokument21 SeitenCivil Engineer Resume - Posted by Anupriya NiranjanPrema SelvarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shrink Disc MAV 2008 Standard Duty: FeaturesDokument6 SeitenShrink Disc MAV 2008 Standard Duty: Featuresemrah nalbantNoch keine Bewertungen
- H200 H201 H202 MEng BEng Civil Engineering With Year in IndustryDokument23 SeitenH200 H201 H202 MEng BEng Civil Engineering With Year in IndustryJohn PapadopoulosNoch keine Bewertungen