Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ap Calc
Hochgeladen von
Zack Cpk Keller-CoffeyOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ap Calc
Hochgeladen von
Zack Cpk Keller-CoffeyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ap calc Squeeze theorom If hx less than fx which is less than gx for all x except possibly c Continuity and 1 sided
limoits The funtion is 100% continious from negative infinity to positive It can also be this withnig itslinits Rmovable discontinuity is just one hole in the line Non removable disctoninutity is like in a piece wise when there is a complete jump in the line or when yu have an assymptope Requirements for continuity F must be defines Lim f(x) must exist Lim f(x) must be F(c) 1 sided limits tools to determine 1 sided limits direct substituion graph it numerical Intermediaye value theorum Monk Pete If f is a continuous closed intercal [a,b] f(a) does not =f(b) and k is b/w f9a0 and f(b) then there is atleasr 1 point (c) in [a,b[ that f(c) = kg-777u87 Infintie limits and vertical asymptotes Infinite limits a limit in which f increases without bound as x approaches c Determining infinite limits Properties if lim f(x) is infinity and lim g(x)=l (as both approach c) Then limf(x) +- g(x) is infinity Lim of multiplying the 2 of them is infinity Lim as approaches 0(1+1/x^2)= 1+infinity Finding vertical asymptotes Only exist when the denominator is 0 but the numerator does not Chain rule For Composite functions
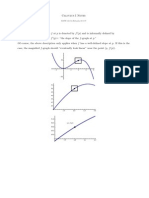
Related Rates Method for solving multiple variable for time DR/DT= 1ft/sec Whe r=4ft Find DA/DT 2piR x dr/dt Applications of derivitives Finding extremum on an interval Extreme value teorem Iff is continuous on a closed intercal a,b then f has both a minimum and maximum on the interval Definition of a xritical number: let f be defined at c. if fprimeof c =0 o if f isnot differeantiable at c, then c is a critical number of f Relative extrema occur only at critical numbers: If f has a relative minimim or relative maximum at x=c then c is a critical number of f Guidelines for finding extrema on a closed interval To find te extrema of a continups function f on a closed interval a,b ue the following steps: Find the critical numbers of f in a,b Evaluate f at each critical point a,b Evaluate f and each endpoint a,b The least of these values is the minimum the greatest is the maximum Rolles theorem Let f bre continuopus on the closed interval a,b and difere tiable on the open interva a,b if f(a)=f(b) then there is at east one number c in a,b such that fprime of c =0 The mean value theorem If f is continuous pn the closed interval a,b and differentiable on the open onterval a,b then there exists a number c in a,b Optimization problems An open box of maximum colume is made from a square piece of material 24 inches on a sideby cutting equal squars from the cornrs and turning up the sides B write the volume as a function of x Use calculus to find the critical number if the function is part b and find the maximum volume Us a graphing utility to graph the function in part b and verify the maximum
Taking the intregral of rational functions Quiz on 4.6 and 5.1 and 5.2 U-susitution involving rationale functions Ln lxl+x= sigma 1/x dx The trapezoidal rule For those tricky functions that we cant intregrate Lets derive a formula, not so that we can memorize it but so we understand how rto streamline this process and be able to deriv it again in the future if necessary Area of trapazoid= H-2 (b1+b2) Review of LOG properties!!!!!!!! 2^x=8 x=3 16^x=4 x=1/2 3^x=10 x=log base 3 then 10 c10 d8 9c b7
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Lecture 4Dokument58 SeitenLecture 4Hoàng HàNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Optimization: Fundamentals and ApplicationsVon EverandMathematical Optimization: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cal1 Chapter 3Dokument80 SeitenCal1 Chapter 3Vân Anh Nguyễn NgọcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absolute Extrema (Also Called Global Minimum or Maximum) : Absolute Max Absolute MinDokument3 SeitenAbsolute Extrema (Also Called Global Minimum or Maximum) : Absolute Max Absolute MinSophia S.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus TermsDokument3 SeitenCalculus TermsEngSafwanQadousNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalculusDokument33 SeitenCalculusjerry riceNoch keine Bewertungen
- My ReviewerDokument17 SeitenMy ReviewerMary Ann Leona SelgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - 1a With 4 - 4Dokument4 Seiten4 - 1a With 4 - 4nickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cal INotesDokument5 SeitenCal INotesAamir AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules of LimitsDokument4 SeitenRules of Limitsalecksander2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture # 6 MTH 104: Calculus and Analytical GeometryDokument14 SeitenLecture # 6 MTH 104: Calculus and Analytical GeometryZahid RasoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Calc BC Midterm Study GuideDokument7 SeitenAP Calc BC Midterm Study Guideannalie3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aod Differential CalculusDokument18 SeitenAod Differential CalculusSubham roushanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global and Local ExtremaDokument5 SeitenGlobal and Local ExtremaRadoslav RadoslavovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture #6Dokument23 SeitenLecture #6Mohamed ElsafanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concavity and The Second Derivative Test: Harvey Mudd College Math TutorialDokument4 SeitenConcavity and The Second Derivative Test: Harvey Mudd College Math TutorialArtist RecordingNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadDokument36 SeitenUniversity of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadHazem AlmasryNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Calculus AB Formula Sheet - Google DocsDokument17 SeitenAP Calculus AB Formula Sheet - Google DocsBronzmer LaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch04 GraphingDokument2 SeitenCh04 Graphingabhishek netiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2Dokument36 SeitenCH 2Trabelsi YosraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math IV Lab: Different Methods To Find RootsDokument9 SeitenMath IV Lab: Different Methods To Find RootsMuhammad Usama 796-FET/BSME/F18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solution of Nonlinear EquationsDokument4 SeitenSolution of Nonlinear Equationstarun gehlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 3 1 - Extrema On An IntervalDokument4 SeitenSection 3 1 - Extrema On An Intervalapi-294440065Noch keine Bewertungen
- Extreme ValuesDokument24 SeitenExtreme ValuesAmna MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical InductionDokument17 SeitenMathematical InductionJayaram BhueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math For Econ (MIT)Dokument8 SeitenMath For Econ (MIT)BorisTurkinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiation & Maxima & MinimaDokument30 SeitenDifferentiation & Maxima & Minimaakki2511Noch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods of Integration: Richa SharmaDokument51 SeitenNumerical Methods of Integration: Richa SharmafanusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infinite FunctionDokument2 SeitenInfinite FunctionAsean PanineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit and ContinuityDokument17 SeitenLimit and ContinuityAyash JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Calculus Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenAP Calculus Cheat Sheet3d5w2dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of DifferentiationDokument84 SeitenApplications of Differentiationrohan rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits and Continuity: Thu Mai, Michelle Wong, Tam VuDokument17 SeitenLimits and Continuity: Thu Mai, Michelle Wong, Tam VusampritcNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Calculus BC Study GuideDokument5 SeitenAP Calculus BC Study GuideJohn MoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements and Applications of Calculus: LimitsDokument59 SeitenElements and Applications of Calculus: Limitsavi100% (1)
- Calc Study NotesDokument6 SeitenCalc Study NotesCorryLaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Functions: 1.1 Definition of FunctionDokument9 Seiten1 Functions: 1.1 Definition of FunctionKen NuguidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bisection MethodDokument9 SeitenBisection MethodAtika Mustari SamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics-I All Unit NotesDokument121 SeitenMathematics-I All Unit NotescoachingteslaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Computation (COMS 3210) Bigass Study Guide: Spring 2012Dokument30 SeitenScientific Computation (COMS 3210) Bigass Study Guide: Spring 2012David CohenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods PDFDokument100 SeitenNumerical Methods PDFRichard ReynaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Locating Roots: Chapter Two Non Linear EquationsDokument13 Seiten2.1 Locating Roots: Chapter Two Non Linear EquationsAbel MediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maximum and Minimum ValuesDokument11 SeitenMaximum and Minimum ValuesShiraz NajatNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Explain With Example That Rate of Convergence of False Position Method Is Faster Than That of The Bisection Method.Dokument3 Seiten"Explain With Example That Rate of Convergence of False Position Method Is Faster Than That of The Bisection Method.gauravsanadhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 01 Extrema On An IntervalDokument8 Seiten3 01 Extrema On An IntervaljakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Roots of EquationDokument20 SeitenChapter 2 Roots of EquationDawit MengisteabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key ConceptsDokument2 SeitenKey Conceptsapi-318274656Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes IB Math SLDokument25 SeitenNotes IB Math SLmimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Calculus ReviewerDokument5 SeitenBasic Calculus ReviewerGabrielle OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument4 SeitenLecture 1B BoysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chbe 553 Notes 1Dokument6 SeitenChbe 553 Notes 1सुबेदी गौरवNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Derivatives: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnDokument5 SeitenApplications of Derivatives: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnJuhi NeogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XII-Maxima and MinimaDokument33 SeitenClass XII-Maxima and MinimaNaman SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Calculus AB Study SheetDokument4 SeitenAP Calculus AB Study SheetKohji Ashitaka SugiokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absolute ExtremumDokument8 SeitenAbsolute ExtremumClasolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 8Dokument17 SeitenLecture 8amjadtawfeq2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Big Omega: Definition: A Theoretical Measure of The Execution of AnDokument6 SeitenBig Omega: Definition: A Theoretical Measure of The Execution of AnKiran SamdyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of The DerivativesDokument54 SeitenApplication of The DerivativesMarc RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Calculus BC Study GuideDokument4 SeitenAP Calculus BC Study GuideHarshil SahaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Year Seminar Notes2Dokument2 SeitenFirst Year Seminar Notes2Zack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walker v. Birmingham (1967 (5-4)Dokument1 SeiteWalker v. Birmingham (1967 (5-4)Zack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Year Seminar Notes3Dokument2 SeitenFirst Year Seminar Notes3Zack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hollingsworth v. Perry (2013)Dokument2 SeitenHollingsworth v. Perry (2013)Zack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maryland VDokument2 SeitenMaryland VZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clapper v. Amnesty InternationalDokument2 SeitenClapper v. Amnesty InternationalZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kansas V CheeverDokument4 SeitenKansas V CheeverZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grutter VDokument2 SeitenGrutter VZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 SentencesDokument1 SeiteChapter 3 SentencesZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planned Parenthood of Southern Pennsylvania VDokument1 SeitePlanned Parenthood of Southern Pennsylvania VZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plessy VDokument1 SeitePlessy VZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roe v. WadeDokument1 SeiteRoe v. WadeZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Male Female Pepsi 3.042 2.615 Coke 3.667 4.077 Store Brand 2.917 2.846 Male Female Pepsi 4 4.167 Coke 3.67 4 Store Brand 3.67 1.917Dokument1 SeiteMale Female Pepsi 3.042 2.615 Coke 3.667 4.077 Store Brand 2.917 2.846 Male Female Pepsi 4 4.167 Coke 3.67 4 Store Brand 3.67 1.917Zack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- " (U) Less The Equal Protection Clause of The Fourteenth Amendment Now Be Held To Embody A Principle of Taint,' Found in Some PrimitiveDokument2 Seiten" (U) Less The Equal Protection Clause of The Fourteenth Amendment Now Be Held To Embody A Principle of Taint,' Found in Some PrimitiveZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2 Stats NotesDokument2 SeitenChap 2 Stats NotesZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio OutlineDokument5 SeitenBio OutlineZack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cap Lain List 1750Dokument2 SeitenCap Lain List 1750Zack Cpk Keller-CoffeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths IIT-JEE Best Approach' (MC SIR) : MonotonocityDokument11 SeitenMaths IIT-JEE Best Approach' (MC SIR) : MonotonocityMohit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maxima and Minima - GATE Study Material in PDFDokument7 SeitenMaxima and Minima - GATE Study Material in PDFSupriya SantreNoch keine Bewertungen
- m2k Opm Lapper1Dokument8 Seitenm2k Opm Lapper1JoanzarzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinants: BY Anshuman Sharma Class Xii ADokument17 SeitenDeterminants: BY Anshuman Sharma Class Xii AAjitesh AwasthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commutative Algebra QuestionsDokument9 SeitenCommutative Algebra QuestionsBrian FowlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Practice Questions: © Oxford University Press 2021 1Dokument3 SeitenAdditional Practice Questions: © Oxford University Press 2021 1AineeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 8Dokument27 SeitenNcert Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 8Nilofer AnjumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lim F (X) L X C: AP Calculus AB Course Study Guide Limits and ContinuityDokument6 SeitenLim F (X) L X C: AP Calculus AB Course Study Guide Limits and ContinuityPinkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 9Dokument4 SeitenMath 9RevanVilladozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade Vii First 1ST QuarterDokument3 SeitenGrade Vii First 1ST QuarterericmilamattimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Linear Algebra Biswa Nath Datta PART I - Ch1-6Dokument413 SeitenNumerical Linear Algebra Biswa Nath Datta PART I - Ch1-6lpvasam100% (5)
- TIMO Mock 2019 卷P3fDokument9 SeitenTIMO Mock 2019 卷P3fDo Yun100% (1)
- 4.6 Linear Approximation With AnswersDokument29 Seiten4.6 Linear Approximation With AnswersNavya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap5 - Work and EnergyDokument51 SeitenChap5 - Work and Energystu735113006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ordinary Differential EquationsDokument2 SeitenOrdinary Differential EquationsrodwellheadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idst 2016 SA 05 HashingDokument68 SeitenIdst 2016 SA 05 HashingA Sai BhargavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Kbat Mat t5 2015Dokument6 SeitenSoalan Kbat Mat t5 2015Omar Danni AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential CalculusDokument98 SeitenDifferential CalculusThanyani NeswiswiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Math 145 - SummaryDokument22 SeitenEng Math 145 - SummaryHannah Du toitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter06 Part1Dokument20 SeitenChapter06 Part1Moh'd M. GharbiehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Math DLLDokument5 SeitenGen Math DLLNoraisa Macabaas100% (1)
- g9 3q Simplifying RadicalsDokument10 Seiteng9 3q Simplifying RadicalsDorothy Julia Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- HomeworkDokument11 SeitenHomeworkAmritansha SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3Dokument5 SeitenAssignment 3Anonymous fvqwynpvJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 2nd Chapter 4 ExercisesDokument7 SeitenMathematics 2nd Chapter 4 ExercisesMehedi HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distributed SystemsDokument66 SeitenDistributed SystemsaditiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 14 6382 Gamma FunctionDokument20 SeitenNotes 14 6382 Gamma FunctionbomidiyashwanthkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS321 Numerical AnalysisDokument53 SeitenCS321 Numerical AnalysisJoy loboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combinatorial Optimization: Sheet 1Dokument5 SeitenCombinatorial Optimization: Sheet 1Subhash KorumilliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Solution of 2D Heat EquationDokument25 SeitenNumerical Solution of 2D Heat Equationataghassemi67% (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Von EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeVon EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsVon EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingVon EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeVon EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormVon EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Von EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorVon EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryVon EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)Von EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Who Tells the Truth?: Collection of Logical Puzzles to Make You ThinkVon EverandWho Tells the Truth?: Collection of Logical Puzzles to Make You ThinkBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsVon EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (9)
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathVon EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldVon EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (80)
- Magic Multiplication: Discover the Ultimate Formula for Fast MultiplicationVon EverandMagic Multiplication: Discover the Ultimate Formula for Fast MultiplicationNoch keine Bewertungen