Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
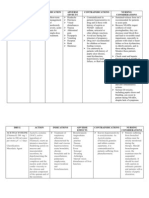
Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, Nausea
Hochgeladen von
Victor BiñasOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, Nausea
Hochgeladen von
Victor BiñasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NAME OF DRUG AMPICILLIN SULBACTAM 1.
5 gm
CLASSIFICATION Antiinfective Antibiotic Aminopenicillin
ACTION Antibiotic agent with broad spectrum of activity resulting from beta-lactamase inhibition. Sulbactam inhibits beta-lactamases most frequently responsible for transferred drug resistance. Because of this action, a wide range of beta-lactamases found in organisms resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins are inhibited.
INDICATION Treatment of infections due to susceptible organisms in skin and skin structures For intraabdominal infections For gynecologic infections For infections cause by ampicillin susceptible organisms
CONTRAINDICATION Hypersensitivity to penicillins; mononucleosis
ADVERSE EFFECTS GI: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention, candidiasis Hematologic: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia Urogenital:dysuria CNS: seizures
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES 1. Determine hypersensitivity to this drug. 2. Monitor I&O ratio and pattern. Report dysuria,urine retention and hematuria. 3. Report chills, wheezing, pruritus, respiratory distress or palpitations to physician immediately 4. Do not breast feed while taking this drug without consulting physician.
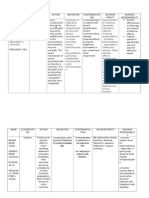
NAME OF DRUG CLINDAMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
CLASSIFICATION Anti-infective Antibiotic
ACTION
INDICATION Serious infections when less toxic alternatives are inappropriate. Treatment of acne vulgaris Treatment of bacterial vaginosis in nonpregnant women
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with allergy to clindamycin, history of asthma or other allergies, tartrazine (in 75- and 150-mg capsules); hepatic or renal dysfunction; lactation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS CV: Hypotension, cardiac arrest (with rapid IV infusion) GI: Severe colitis, including pseudomembranous colitis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, esophagitis, anorexia, jaundice, liver function changes Hematologic: Neutropenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, eosinophilia Hypersensitivity: Rashes, urticaria to anaphylactoid reactions Local: Pain following injection, induration and sterile abscess after IM injection, thrombophlebitis after IV use
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES 1. Culture infection before therapy. 2. Monitor BP and pulse in patients receiving this parenterally. 3.Report severe or watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, inflamed mouth or vagina, skin rash or lesions. 4.Take full prescribed course of oral drug. Do not stop taking without notifying health care provider.
Inhibits protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria, causing cell death.
Use caution with history of regional enteritis or ulcerative colitis; history of antibiotic-associated colitis.
NAME OF DRUG CLOPIDOGREL BISULFATE 75 mg tab
CLASSIFICATION
ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor antagonist Antiplatelet Anticoagulant
Inhibits platelet aggregation by blocking ADP receptors on platelets, preventing clumping of platelets.
Treatment of patients at risk for ischemic eventshistory of MI, ischemic stroke, peripheral artery disease Treatment of patients with acute coronary syndrome
Contraindicated with allergy to clopidogrel, active pathological bleeding such as peptic ulcer or intracranial hemorrhage, lactation. Use cautiously with bleeding disorders, recent surgery, hepatic impairment, pregnancy.
CNS: Headache, dizziness, weakness, syncope, flushing CV: Hypertension, edema Dermatologic: Rash, pruritus GI: Nausea, GI distress, constipation, diarrhea, GI bleed Other: Increased bleeding risk
1.Report promptly any unusual bleeding. 2. Avoid chronic aspirin or NSAID use unless approved by physician 3.Take daily as prescribed. May be taken with meals.
NAME OF DRUG FUROSEMIDE 40mg IV
CLASSIFICATION Loop diuretic
ACTION Inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, leading to a sodium-rich diuresis.
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with allergy to furosemide, sulfonamides; allergy to tartrazine (in oral solution); anuria, severe renal failure; hepatic coma; pregnancy; lactation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS CNS: Dizziness, vertigo, paresthesias, xanthopsia, weakness, headache, drowsiness, fatigue, blurred vision, tinnitus, irreversible hearing loss CV: Orthostatic hypotension, volume depletion, cardiac arrhythmias, thrombophlebitis Dermatologic: Photosensitivity, rash, pruritus, urticaria, purpura, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme GI: Nausea, anorexia, vomiting, oral and gastric irritation, constipation, diarrhea, acute pancreatitis, jaundice GU: Polyuria, nocturia, glycosuria, urinary bladder spasm Hematologic: Leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, fluid and electrolyte imbalances, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia Other: Muscle cramps and muscle spasms
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES 1. Assess allergy to furosemide 2. Closely monitor BP during periods of diuresis and through period of dosage adjustment. 3. Monitor for s/sx of hypokalemia. 4. Monitor I&O ratio and pattern. 5.ingestion of potassiumrich foods daily to reduce or prevent potassium depletion 6. Give early in the day so that increased urination will not disturb sleep. 7.Reduce dosage if given with other antihypertensives; readjust dosage gradually as BP responds.
Oral, IV: Edema associated with CHF, cirrhosis, renal disease IV: Acute pulmonary edema Oral: Hypertension
NAME OF DRUG IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE
CLASSIFICATION
ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Anticholinergic Antimuscarinic drug Parasympatholytic
Anticholinergic, chemically related to atropine, which blocks vagally mediated reflexes by antagonizing the action of acetylcholine. Causes bronchodilation and inhibits secretion from serous and seromucous glands lining the nasal mucosa.
Bronchodilator for maintenance treatment of bronchospasm associated with COPD (solution, aerosol), chronic bronchitis, and emphysema Nasal spray: Symptomatic relief of rhinorrhea associated with perennial rhinitis, common cold
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to atropine or its derivatives, soy bean or peanut allergies (aerosol).
CNS: Nervousness, dizziness, headache, fatigue, insomnia, blurred vision GI: Nausea, GI distress, dry mouth Respiratory: Dyspnea, bronchitis, bronchospasms, URI, cough, exacerbation of symptoms, hoarseness Other: Back pain, chest pain, allergictype reactions, palpitations, rash
1.Use nebulizer mouthpiece instead of face mask to avoid blurred vision or aggravation of narrowangle glaucoma. 2.Ensure adequate hydration, control environmental temperature to prevent hyperpyrexia. 3.Have patient void before taking medication to avoid urinary retention. 4. Report rash, eye pain, difficulty voiding, palpitations, vision changes.
NAME OF DRUG PARACETAMOL 500mg
CLASSIFICATION
ACTION
INDICATION Analgesic-antipyretic in patients with aspirin allergy, hemostatic disturbances, bleeding diatheses, upper GI disease, gouty arthritis Arthritis and rheumatic disorders involving musculoskeletal pain (but lacks clinically significant antirheumatic and anti-inflammatory effects) Common cold, flu, other viral and bacterial infections with pain and fever Unlabeled use: Prophylactic for children receiving DPT vaccination to reduce incidence of fever and pain
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with allergy to acetaminophen. Use cautiously with impaired hepatic function, chronic alcoholism, pregnancy, lactation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS CNS: Headache CV: Chest pain, dyspnea, myocardial damage when doses of 58 g/day are ingested daily for several weeks or when doses of 4 g/day are ingested for 1 yr GI: Hepatic toxicity and failure, jaundice GU: Acute kidney failure, renal tubular necrosis Hematologic: Methemoglobinemia cyanosis; hemolytic anemiahematuria, anuria; neutropenia, leukopenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypoglycemia Hypersensitivity: Rash, fever
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES 1. Assess allergy to acetaminophen, impaired hepatic function, chronic alcoholism, pregnancy, lactation 2.Give drug with food if GI upset occurs. 3.Avoid the use of other over-the-counter preparations. They may contain acetaminophen, and serious overdosage can occur. If you need an over-the-counter preparation, consult your health care provider. 4.Report rash, unusual bleeding or bruising, yellowing of skin or eyes, changes in voiding patterns.
Antipyretic Analgesic (nonopioid)
Antipyretic: Reduces fever by acting directly on the hypothalamic heat-regulating center to cause vasodilation and sweating, which helps dissipate heat. Analgesic: Site and mechanism of action unclear.
NAME OF DRUG TRAMADOL HYDROCHLORIDE 500mg IV
CLASSIFICATION
ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
ADVERSE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Narcotic analgesic CNS agent Opiate agonist
Binds to mu-opioid receptors and inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin; causes many effects similar to the opioidsdizziness, somnolence, nausea, constipationbut does not have the respiratory depressant effects..
Relief of moderate to moderately severe pain
Contraindicated with allergy to tramadol or opioids or acute intoxication with alcohol, opioids, or psychoactive drugs. Use cautiously with pregnancy, lactation, seizures, concomitant use of CNS depressants or MAOIs, renal dysfunction, or hepatic impairment.
CNS: Sedation, dizziness or vertigo, headache, confusion, dreaming, sweating, anxiety, seizures CV: Hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia Dermatologic: Sweating, pruritus, rash, pallor, urticarial GI: Nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, constipation, flatulence Other: Potential for abuse, anaphylactoid reactions
1. Assess for level of pain relief and administer prn as needed but not to exceed the recommended total daily dose. 2.Monitor v/s and assess for orthostatic hypotension or signs of CNS depression. 3.Assess bowel and bladder function; report urinary frequency or retention. 4.Advise patient to report severe nausea, dizziness, severe constipation.
NAME OF DRUG OMEPRAZOLE 40 mg IV
CLASSIFICATION
ACTION Gastric acid-pump inhibitor: Suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the hydrogen-potassium ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cells; blocks the final step of acid production.
INDICATION Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer First-line therapy in treatment of heartburn or symptoms of GERD Short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer GERD, severe erosive esophagitis, poorly responsive symptomatic GERD Long-term therapy: Treatment of pathologic hypersecretory conditions (ZollingerEllison syndrome, multiple adenomas, systemic mastocytosis) Eradication of Helicobacter pylori with amoxicillin or metronidazole and clarithromycin Prilosec OTC: Treatment of frequent heartburn (2 or more days per week)Unlabeled use: Posterior laryngitis; enhance efficacy of pancreatin for the treatment of steatorrhea in cystic fibrosis
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to omeprazole or its components. Use cautiously with pregnancy, lactation.
ADVERSE EFFECTS CNS: Headache, dizziness, asthenia, vertigo, insomnia, apathy, anxiety, paresthesias, dream abnormalities Dermatologic: Rash, inflammation, urticaria, pruritus, alopecia, dry skin GI: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, dry mouth, tongue atrophy Respiratory: URI symptoms, cough, epistaxis Other: Cancer in preclinical studies, back pain, fever
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES 1. Monitor urinalysis for hematuria or proteinuria. 2. Report any changes in urinary elimination such as pain or discomfort associated with urination, or blood in urine. 3. Report severe diarrhea; drug may need to be discontinued. 4.Take the drug before meals.
Antisecretory agent Proton pump inhibitor
NAME OF DRUG ISOSORBIDE DINITRATE 10mg
CLASSIFICATION
ACTION Relaxes vascular smooth muscle with a resultant decrease in venous return and decrease in arterial BP, which reduces left ventricular workload and decreases myocardial oxygen consumption.
INDICATION Treatment and prevention of angina pectoris
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with allergy to nitrates, severe anemia, head trauma, cerebral hemorrhage, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, narrowangle glaucoma, postdural hypotension Use cautiously with pregnancy, lactation, acute MI, CHF.
ADVERSE EFFECTS CNS: Headache, apprehension, restlessness, weakness, vertigo, dizziness, faintness CV: Tachycardia, retrosternal discomfort, palpitations, hypotension, syncope, collapse, orthostatic hypotension, angina, rebound hypertension, atrial fibrillation, postdural hypertension Dermatologic: Rash, exfoliative dermatitis, cutaneous vasodilation with flushing GI: Nausea, vomiting, incontinence of urine and feces, abdominal pain, diarrhea GU: Dysuria, impotence, urinary frequency Other: Muscle twitching, pallor, perspiration, cold sweat, arthralgia, bronchitis
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES 1.Give sublingual preparations under the tongue or in the buccal pouch; discourage the patient from swallowing.. 2.Give oral preparations on an empty stomach, 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals; take with meals if severe, uncontrolled headache occurs. 3.Report blurred vision, persistent or severe headache, rash, more frequent or more severe angina attacks, fainting.
Antianginal Nitrate Vasodilator
NAME OF DRUG KALIUM DURULE
CLASSIFICATION Electrolytic and Water Balance Agent Replacement Solution
ACTION Principal intracellular cation,; essential for maintenance of intracellular isotonicity, transmission of nerve impulses, contraction of cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscles, maintenance of normal liver function, and for enzyme activity.
INDICATION To prevent and treat potassium deficit secondary to diuretic or corticosteroid therapy.
CONTRAINDICATION Severe renal impairment; severe hemolytic reactions; untreated Addisons disease; crush syndrome; early postoperative oliguria; acute dehydration
ADVERSE EFFECTS GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal distention UROGENITAL: oliguria, anuria HEMATOLOGIC: hyperkalemia RESPIRATORY: respiratory distress CV: cardiac depression, arrhythmias, or arrest
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES 1.Monitor I&O ratio and pattern. If oliguria occurs, stop infusion promptly and notify physician. 2. Avoid licorice: large amounts can cause both hypokalemia and sodium retention. 3.Do not use any salt substitute unless it is specifically ordered by the physician 4.Notify physician of persistent vomiting because losses of potassium can occur 5. Report continuing signs of potassium deficit to physician: weakness, fatigue, polyuria, polydipsia
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesVon EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument11 SeitenDrugsElisa Libo-onNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDokument10 SeitenName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contra-Indications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsmidskiescreamzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIIVon EverandAlert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study (Pedia)Dokument7 SeitenDrug Study (Pedia)Caurrine Monsalud100% (1)
- Drugstudy Last DutyDokument5 SeitenDrugstudy Last DutyJoeven HilarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug Studysarah1217Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDokument9 SeitenDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyRachel PerandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StuyJJASGHDokument7 SeitenDrug StuyJJASGHJan Pierre RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudiesDokument16 SeitenDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Ncp&drugstudDokument12 SeitenNcp&drugstudSarah Mae Billano BermudezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument12 SeitenDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDokument11 SeitenCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Analysis (RN) - 3Dokument9 SeitenDrug Analysis (RN) - 3Joannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- Drug Study 68-75Dokument8 SeitenDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug StudyJoel MadjosNoch keine Bewertungen
- KetorolacDokument5 SeitenKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study (AFP)Dokument10 SeitenDrug Study (AFP)Summer SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of DrugDokument10 SeitenName of DrugBianx PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenDrug StudyCris Constantino San JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument19 SeitenDrug StudyCzarinah Ela MesiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Medication ListDokument181 SeitenClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Drug Study Celecoxib NubainDokument4 SeitenDrug Study Celecoxib NubainMaiko TyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugstudy and SoapieDokument17 SeitenDrugstudy and SoapieYasi EcheniqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cefuroxime Drug AnaDokument4 SeitenCefuroxime Drug AnaCarpz DarpzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDokument7 SeitenPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDokument26 SeitenGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDokument6 SeitenDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDokument1 SeiteCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDokument8 SeitenDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument11 SeitenDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDokument19 SeitenDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument19 SeitenDrug StudyNorma CordovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDokument11 SeitenName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Drugs StudyDokument13 SeitenComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5th Draft DrugsDokument7 Seiten5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Name Classificatio N Mechanis MOF Action Indication Contrain Dication Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument6 SeitenDrug Name Classificatio N Mechanis MOF Action Indication Contrain Dication Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesPrincess TinduganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - CapDokument5 SeitenDrug Study - CapABARAJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument24 SeitenDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study NRMFDokument11 SeitenDrug Study NRMFKristine ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NalbuphineDokument5 SeitenNalbuphineGab PagalilauanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDrug StudyVal FielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument33 SeitenDrug StudyLag Lag AlbercaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Cards BarryDokument6 SeitenDrug Cards BarryJessica Lynn DyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS NRMFDokument6 SeitenDS NRMFElla FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Albuterol Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenAlbuterol Drug StudyMaria Charlene OrpillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Cap RHPDokument7 SeitenDrug Study Cap RHPJan DeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jam (Drug Study)Dokument11 SeitenJam (Drug Study)Vincent QuitorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDokument3 SeitenName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenDrug StudyFritzie Beatrice NomusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Dokument12 SeitenPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Cancer IntroDokument9 SeitenBreast Cancer IntroLiezel CauilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Health History of Breast CancerDokument6 SeitenNursing Health History of Breast CancerVictor BiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphysio of BreastDokument3 SeitenAnaphysio of BreastVictor BiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Examination APDokument7 SeitenPhysical Examination APVictor BiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CystitisDokument14 SeitenCystitisVictor BiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CystitisDokument14 SeitenCystitisVictor BiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigestiveDokument14 SeitenDigestiveVictor BiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver CirrhosisDokument4 SeitenLiver CirrhosisVictor BiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Definition of OsteomyelitisDokument5 SeitenI. Definition of OsteomyelitisVictor BiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Compression FracturesDokument6 SeitenClassification of Compression FracturesKaustubh KeskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DHN 374 News BriefDokument2 SeitenDHN 374 News Briefapi-340516995Noch keine Bewertungen
- CAL GluconateDokument29 SeitenCAL Gluconatehumag143100% (1)
- DaDokument8 SeitenDaS7 edgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varisara Kriya PDFDokument14 SeitenVarisara Kriya PDFGottimukkala Muralikrishna100% (1)
- Parasitology Lec 3.01a Intestinal NematodesDokument16 SeitenParasitology Lec 3.01a Intestinal NematodesEnaWahahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2ton Steel 56.8gDokument4 Seiten2ton Steel 56.8gYasir AzmatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Residual Breast Tissue After Mastectomy, How Often and Where It Is LocatedDokument11 SeitenResidual Breast Tissue After Mastectomy, How Often and Where It Is LocatedBunga Tri AmandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FDA Medical RecordDokument4 SeitenFDA Medical RecordSanty Dara KrisnawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guinea Pigs PDFDokument1 SeiteGuinea Pigs PDFYaserAbbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mindful Medical Practice - Clinical Narratives and Therapeutic InsightsDokument169 SeitenMindful Medical Practice - Clinical Narratives and Therapeutic InsightsSkg KonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nmims India Pharma MarketDokument36 SeitenNmims India Pharma MarketAjay SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diss 1 3 7 OCR Rev PDFDokument5 SeitenDiss 1 3 7 OCR Rev PDFKunotamashi KanakacheroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyromania-The Urge To Set Fires For Pleasure, Gratification, or Release of Tension Ezhae SymptomsDokument2 SeitenPyromania-The Urge To Set Fires For Pleasure, Gratification, or Release of Tension Ezhae SymptomsptbarnabicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharma Krishna N., Exploration of The History of Physiotherapy (The Scientific Research Journal of India. SRJI Vol-1 No-1 Year 2012)Dokument4 SeitenSharma Krishna N., Exploration of The History of Physiotherapy (The Scientific Research Journal of India. SRJI Vol-1 No-1 Year 2012)Dr. Krishna N. SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Kinesiotaping HandoutDokument11 SeitenMaster Kinesiotaping HandoutcosasdeangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grief & Grieving ProcessDokument39 SeitenGrief & Grieving Processelmerconde100% (4)
- Hand AssessmentDokument22 SeitenHand AssessmentVaikunthan RajaratnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inborn Errors or MetabolismDokument25 SeitenInborn Errors or MetabolismSamdiSutantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dhulikhel Water Supply ProjectDokument4 SeitenDhulikhel Water Supply ProjectSujan Singh50% (2)
- Dexmedetomidine Vs Propofol - RCT - Merry Andriany 406162043Dokument7 SeitenDexmedetomidine Vs Propofol - RCT - Merry Andriany 406162043Merry AndrianyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 5 Day Old Previsit QuestionnaireDokument4 Seiten2 5 Day Old Previsit Questionnairesarthak cheemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Dictionary For Psychotherapists PDFDokument1.375 SeitenA Dictionary For Psychotherapists PDFMonica100% (2)
- Reflection On Feeding Elderly ClientsDokument2 SeitenReflection On Feeding Elderly ClientsLaydee GiaAmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hospital Outdoor Spaces - Therapeutic Benefits and Design ConsiderationsDokument15 SeitenHospital Outdoor Spaces - Therapeutic Benefits and Design Considerationsmimk2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- CPAP SlidesDokument52 SeitenCPAP SlidesAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Pines City Colleges: College of NursingDokument3 SeitenPines City Colleges: College of NursingMara Jon Ocden CasibenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pain NCPDokument2 SeitenAcute Pain NCPfbarlicosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue v09Dokument4 SeitenCatalogue v09KRISHNA L BAISETTINoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy Palliative Care and End of Life Care Per 15-02-2021Dokument33 SeitenPhilosophy Palliative Care and End of Life Care Per 15-02-2021rizki ikhsanNoch keine Bewertungen