Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
#Corneal Diseases
Hochgeladen von
ameerabestCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
#Corneal Diseases
Hochgeladen von
ameerabestCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bacterial keratitis Predisposing factors - Contact lens wear - Chronic ocular surface disease - Corneal hypoaesthesia C/P - Expanding
oval, yellow-white, dense stromal infiltrate - Stromal suppuration and hypopyon
Fungal keratitis Frequently preceded by ocular trauma with organic matter
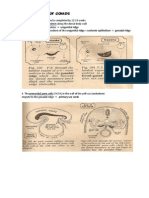
INFECTIVE CORNEAL ULCERS Acanthamoeba keratitis - Contact lens wearers at particular risk - Symptoms worse than signs - Small, patchy anterior stromal infiltrates - Perineural infiltrates (radial keratoneuritis) - Ulceration, ring abscess & small, satellite lesions - Stromal opacification
Herpes simplex keratitis
Herpes zoster keratitis
- Greyish-white ulcer which may be surrounded by feathery infiltrates - Slow progression - occasionally hypopyon
- Dendritic ulcer with terminal bulbs May enlarge to become geographic Epithelial : 1 - dendritic Criteria of dendritic ulcer : - Dendritiform shape - Recurrences - Hyposthesis - No vascularization 2 - geographic Stromal : 1 - interstitial 2- disciform 3- Metaherpetic - Aciclovir 3% ointment x 5 daily - Trifluorothymidine 1% drops 2-hourly
Varicella Zoster virus Dermatitis Keratitis Iridocyclitis Retinitis Optic neuritis
Rx
- topical ciprofloxacin 0.3% or ofloxacin 0.3%
- Topical antifungal agents - Penetrating keratoplasty if unresponsive Yeast fungi : candida Filamentous : fusarium , aspergillus Criteria : - trauma by organic matter/ CL - ulcer with feathery edges and satellite lesions - deep stromal infiltrations - A ch reaction - hypopyon steroids contraindicated!! antifungal topical ( diflucan ) systemic ( sporanox ) surgery : hot PKP
- chlorhexidine or polyhexamethylenebigua nide
- early systemic Acyclovir - +/- systemic steroids
ulcers!!
**HYPOPYON ULCER! Acute serpiginous ulcer , ulcus serpens Criteria : - central ulcer with undermined edge - central posterior abscess - hypopyon
Rx of ulcers
Emergency , close follow up Culture & sensitivity Frequent topical antibiotic drops Subconjunctival antibiotics Fortified antibiotic drops Systemic antibiotics
NON-INFECTIVE CORNEAL ULCER MOORENS ULCERS Limited form - usually unilateral, affects elderly Progressive form - bilateral, affects younger patients C/P 1. Peripheral ulcerative keratitis 2. Circumferential and central spread 3. End-stage scarring and vascularization EXPOSURE ULCERS Due to loss of protection of lids in lagophthalmos : Bells palsy, LL ectropion, proptosis NEUROPARALYTIC KERATITIS
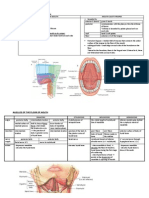
SUPERFICIAL NON-SUPPURATIVE ULCERS SUPERFICIAL PUNCTATE KERATITIS Viral : Adenovirus,Herpes Vernal catarrh Superior limbic kc Photophthalmia : UVR Stain : rose bengal Lacrimation, redness, photophobia signs: Scarring +/- vascularization Post traumatic Post vernal catarrh Post trachomatous Post infections RECURRENT EPITHELIAL EROSION Recurrent attacks of eye irritation or severe pain and lacrimation and photophobia on awakening in the morning Epithelia corneal defect with heaped irregular loose epithelium due to weak BM adhesion
corneal ulceration in lower cornea
little
Rx
systemic steroids and/or cytotoxic drugs
- freq. tears substitute, - therapeutic CL - lid tapping at night - tarsorrhaphy - causal treatment
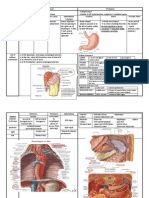
CORNEAL DEGENERATIONS ARCUS SENILIS BAND SHAPED KERATOPATHY bilateral, annular, peripheral lipoid calcium deposition infiltration of corneal stroma - 2ry to chronix eye disease (eg: absoulute glaucoma, chr old age! uveitis) * young age = ARCUS JUVENILIS (hypercholesterolemia)
CORNEAL ECTASIA KERATOCONUS nd - in 2 decades + females conical ectasia of central cornea + thinning + scarring
CORNEAL EDEMA impairment of epitheliul & endothelial pumping fx corneal swelling Causes: 1. IOP ( acute angle closure glaucoma/ congenital glaucoma) 2. Endothelial damage - trauma (birth trauma/ during cataract surgery) - post-inflammatory endothelial dysfx ( uveitis, keratitis, graft rejection) 3. Epithelial damage - mechanical/chemical/radiation stromal edema VA epithelial edema significant VA impairment + painful surface breakdown
C/P
Vogt Lucid interval Asymptomatic
band-shaped horizontal opacity in middle 1/3 of cornea
painless + progress VA + Irregular MYOPIC astigmatism - scissoring red reflex - Munsons sign - break in endothelium & Descemet membrane acute corneal hydrops + pain + rapid VA - Fleischers ring (iron deposits) Inv : topography + pachymetry - Glasses (early cases) - Rigid CL - Corneal cross linkage - NaCl acute hydrops - Keratoplasty ( when CL no longer correct Irregular astigmatism/ central cornea is scarred or edematous)
Rx
NO Rx
sodium versenate
- treat inflammation + IOP - hypertonic agents (NaCl, Colloid osmotic solution) - Therapeutic soft CL - Keratoplasty
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDokument3 Seiten@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDokument2 Seiten@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cme Bronchial AsthmaDokument28 SeitenCme Bronchial AsthmaameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @tumors of The Breast 1Dokument2 Seiten@tumors of The Breast 1ameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semen AnalysisDokument3 SeitenSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- OSCE DermaDokument8 SeitenOSCE DermaameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genital EmbryologyDokument6 SeitenGenital EmbryologyameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandDokument5 SeitenParotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- PleuraDokument6 SeitenPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- #Chest TraumasDokument4 Seiten#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- Extracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)Dokument2 SeitenExtracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)ameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- #MediastinumDokument4 Seiten#Mediastinumameerabest100% (1)
- #LungDokument1 Seite#LungameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- PharynxDokument2 SeitenPharynxameerabest0% (1)
- Mouth Cavity, Palate, TongueDokument8 SeitenMouth Cavity, Palate, Tongueameerabest100% (1)
- Oesophagus & StomachDokument3 SeitenOesophagus & StomachameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Is Caviar Disease (Sublingual Varices) Associated With Trauma?Dokument2 SeitenIs Caviar Disease (Sublingual Varices) Associated With Trauma?Mardiyah PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acne RosaceaDokument28 SeitenAcne Rosaceanathy_soares100% (1)
- Management of Dog Bites: Thorough History TakingDokument6 SeitenManagement of Dog Bites: Thorough History TakingElvisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Science 121 (2020) 529-541Dokument13 SeitenSafety Science 121 (2020) 529-541Dewi SunnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emergency Trolley: Perhimpunan Dokter Ahli Emergensi IndonesiaDokument30 SeitenThe Emergency Trolley: Perhimpunan Dokter Ahli Emergensi IndonesiaAhmad Syamsul ThelionAremaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ayurvedic Treatment of Malaria in Hindi Ilaj Ke 10 Aasan UpayDokument3 SeitenAyurvedic Treatment of Malaria in Hindi Ilaj Ke 10 Aasan UpayGovindNoch keine Bewertungen
- OM Extended Aeration PDFDokument25 SeitenOM Extended Aeration PDFHendra SusantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancient Mesopotamia Medicine HistoryDokument4 SeitenAncient Mesopotamia Medicine HistoryJhhhcfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activated Sludge Aeration Tank Calculations-US Units Final-Locked-11!12!18Dokument30 SeitenActivated Sludge Aeration Tank Calculations-US Units Final-Locked-11!12!18Cristian Ortiz100% (1)
- Consumer Chemistry: Quarter 4 - Module 3Dokument22 SeitenConsumer Chemistry: Quarter 4 - Module 3wetlog lolololimNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSRQ CompleteDokument10 SeitenTSRQ CompletedrsheapherdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach Considerations: Nita V Bhatt, MD, MPH Clinical Instructor, Resident Physician, Department ofDokument7 SeitenApproach Considerations: Nita V Bhatt, MD, MPH Clinical Instructor, Resident Physician, Department ofHiLmy ZakiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP-DP NCM112LecDokument4 SeitenNCP-DP NCM112LecShane CabucosNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPD Claim Form 2020Dokument1 SeiteOPD Claim Form 2020RafayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Surgery NotesDokument214 SeitenClinical Surgery Notessarahsarahsarahsarah100% (6)
- A Brief Review On Ayurvedic Concept of Immunity and ImmunizationDokument12 SeitenA Brief Review On Ayurvedic Concept of Immunity and ImmunizationsanjnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pielago NCPDokument2 SeitenPielago NCPtaehyungieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BATLSDokument70 SeitenBATLSVitor Hugo G CorreiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catheter Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI)Dokument36 SeitenCatheter Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI)aringkinkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey HouseholdDokument14 SeitenSurvey HouseholdACIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulin IndexDokument13 SeitenInsulin IndexbookbookpdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Mucous CystsDokument10 SeitenWhat Are Mucous CystsNena TamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talking Hearts About UsDokument2 SeitenTalking Hearts About UsklocekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Osce Assessment and DocumentationDokument9 SeitenPediatric Osce Assessment and Documentationapi-583545759Noch keine Bewertungen
- RTT Brochure 12pp - Jan 2019 - DigitalDokument19 SeitenRTT Brochure 12pp - Jan 2019 - DigitalAnastasia Ionas100% (3)
- Manual Service CavitadorDokument29 SeitenManual Service CavitadorErik Sanchez HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tips of Operations - VAC TherapyDokument32 SeitenTips of Operations - VAC TherapyRandika PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 919 - 0410Dokument6 SeitenChemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 919 - 0410PromagEnviro.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- ObesityDokument5 SeitenObesityrshprNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garcinia Cambogia MonographDokument5 SeitenGarcinia Cambogia Monographeddee90Noch keine Bewertungen