Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Common Errors How To AvoidT Hem X Phy Light Human Eye 10
Hochgeladen von
Abhishek KumarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Common Errors How To AvoidT Hem X Phy Light Human Eye 10
Hochgeladen von
Abhishek KumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CLASS 10LIGHT & Human Eye
COMMON MISTAKES AND HOW TO AVOID THEM
1.
Topic Light- spherical mirrors
Common slips made Confusion between concave and convex mirror Forget to draw arrows in ray diagrams The position for which a virtual image is formed in a concave mirror m = v/u
2. 3.
Light Spherical mirrors
How to avoid A concave mirror has a cave in it so that the bear can walk into it! That was just a memory mnemonic to help you remember that a concave mirror is curved inwards. Always remember to put arrows whenever you draw a ray diagram. When object is between focus and pole of the mirror m = -v/u for mirrors. The mirror formula
4.
Sign of magnification
1 1 1 = + has a + sign f u v
5.
Sign of power of spherical mirrors
Confusion whether the focal length of a concave mirror is positive or negative.
6.
Spherical mirrors
Ray diagrams without using a pencil, scale and compass. Assumption that you know all the ray diagrams!
7.
Refraction light
8.
Refraction of light
Confusion in which direction does light bend when it enters a denser medium Solving numericals in which you have to find the speed of light in a medium and the speed of light comes out to be more than 3x108m/s.
in it and its magnification has a negative sign in it. You might find this memory mnemonic useful! Convex has an x in it. This looks like a + sign. This helps you remember that the focal length of a convex mirror is positive. Recall that the focal length of a convex lens is also positive. A neat diagram drawn with the help of pencil, scale and compass to draw the mirror certainly fetches more marks. You need to practice drawing ray diagrams, without keeping the book open in front of you. Dont forget to summarize the characteristics of the image after drawing the ray diagram. Remember it bends towards the normal when it enters a denser medium and away from the normal on entering a rarer medium. This is not possible. A very common mistake is to use n = v/c instead of n = c/v. The correct formula is n = c/v.
9.
Refraction of light
10.
Refraction of light Spherical Mirrors
11.
Confusion whether velocity, wavelength or frequency changes when light is refracted. Meaning of the statement refractive index of water is 1.33 Confusion between uses of concave mirrors and convex mirrors
Remember velocity and wavelength change. Frequency does not change. Another important point to remember is that velocity = wavelength x frequency. It means that the speed of light in that medium will be c/1.33. Concave mirrors have a small field of view so objects are placed at close range. So concave mirrors can be make-up mirrors, dentist mirrors etc. Convex mirrors have a large field of view so objects placed in a wide range will be visible. So to see the traffic behind you or as a store surveillance mirror you will use a convex mirror. A positive value of magnification implies that the image is erect and virtual. A value of 1/3 implies that the size of the image is 1/3rd the size of the object. Do not forget to change the focal length given in cm to m. Only then will be the power = 1/f be in dioptres(D). You must learn the definition as this is a frequently asked question. It is the ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length To view objects placed nearby, the ciliary muscles need to contract which strains the eye. While viewing far off objects the muscles are relaxed so viewing distant objects is more comfortable. Note carefully how to draw the ray diagram for eye with corrective lens and do not get confused with the object position and image position. Note carefully that the angle of deviation is the angle between the direction of the incident ray and the emergent ray. Practice drawing this ray diagram and learn labels of all angles and rays on it. Remember that rainbow and spectrum in a prism are due to dispersion. Twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric
12.
Sign of magnification
13.
Power
Say value of magnification is +1/3. Then what can you conclude about nature and size of image? Given focal length in cm find power Definition of power of accommodation
14.
Human eye
15.
Human eye
16.
Defects of vision
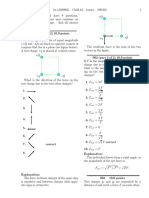
Confusion in the fact when is the eye more relaxed, while viewing objects placed close by or those placed far away. Ray diagrams of eye with corrective lens
17.
Prism
Marking the angle of deviation in the ray diagram
18.
Various phenomena
Reason for the observation of a rainbow, spectrum in a prism,
twinkling of stars, blue color of the sky. Do not club all the reasons together and just write dispersion or refraction etc. randomly. 19. Numerical for myopic eye For numericals involving correction of distant vision, what is the object distance? For numericals involving correction of short sightedness, what is the object distance? Confusion between presbyopia and the need for bifocal lenses.
refraction. Color of the sky is due to scattering.
The object distance is taken as infinity and 1/u = 0.
20.
Numerical for hypermetropic eye Presbyopia
The object distance is taken as 25cm, unless some other value is specified, for near point, in the question This eye defect is age related and is due to weakening of the ciliary muscles. Did you know that the Greek word "presbus" means "old person". Bifocal lenses can be used by a person (young or old) who suffers from both myopia and hypermetropia.
21.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CBSE PastYearPaper X Science 2009 PDFDokument8 SeitenCBSE PastYearPaper X Science 2009 PDFAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- X CBSE S A1 Science PastYear Paper XDokument10 SeitenX CBSE S A1 Science PastYear Paper XAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Physics PDFDokument9 Seiten01 Physics PDFAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 196sample PaperDokument3 Seiten196sample PaperAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- m100 1sF02Dokument3 Seitenm100 1sF02Abhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iitjee Chemistry Sample Paper - Iv: SolutionsDokument3 SeitenIitjee Chemistry Sample Paper - Iv: SolutionsAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IITJEE CHEMISTRY SAMPLE PAPERDokument8 SeitenIITJEE CHEMISTRY SAMPLE PAPERAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12185ENGLISHDokument5 Seiten12185ENGLISHAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Peason - Inorganic ChemistryDokument417 SeitenThe Peason - Inorganic ChemistryAbhishek Kumar68% (28)
- POwer of Vedic MathsDokument151 SeitenPOwer of Vedic MathsAbhishek Kumar90% (10)
- Vidya Mandir Sample Papers 1Dokument16 SeitenVidya Mandir Sample Papers 1Abhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi PhyDokument9 SeitenXi PhyIchwant BanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuickRevNotes LongComposition EngDokument3 SeitenQuickRevNotes LongComposition EngAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 51Dokument4 SeitenPresentation 51Abhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jam PhysicsDokument2 SeitenJam PhysicsanishvanchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iitjee Mathematics Sample Paper - Ii: SolutionsDokument6 SeitenIitjee Mathematics Sample Paper - Ii: SolutionsAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalculusDokument3 SeitenCalculusAbhishek Kumar0% (1)
- PortrAIT of LadyDokument3 SeitenPortrAIT of LadyAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- English CoreDokument12 SeitenEnglish CoreAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuickRevNotes LongComposition EngDokument3 SeitenQuickRevNotes LongComposition EngAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry XiDokument7 SeitenChemistry XiAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus For Iit Jee PDFDokument510 SeitenCalculus For Iit Jee PDFAbhishek Kumar77% (94)
- English PDFDokument6 SeitenEnglish PDFAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Details: Click Here For Lyrics of All Hindi SongsDokument1 SeiteDetails: Click Here For Lyrics of All Hindi SongsAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi - S and - P - TafsDokument15 SeitenXi - S and - P - TafsAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narayana... Iit Jee PaperDokument26 SeitenNarayana... Iit Jee PaperAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science Sample Papers For Class 11Dokument3 SeitenComputer Science Sample Papers For Class 11Abhishek Kumar100% (1)
- Maths Paper With SolutionDokument18 SeitenMaths Paper With SolutionAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 MathsDokument8 Seiten05 MathsAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- monErrorsHowToAvoid ChA.P X Math0Dokument3 SeitenmonErrorsHowToAvoid ChA.P X Math0Abhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Distribution of Shear Stresses in Circular ShaftsDokument5 SeitenDistribution of Shear Stresses in Circular ShaftsSnehasish IsharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units Offered S1 2015 Engineering DegreeDokument4 SeitenUnits Offered S1 2015 Engineering DegreescytheVSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch22 h3 Solutions PDFDokument4 SeitenCh22 h3 Solutions PDFld393563Noch keine Bewertungen
- 424a 2016Dokument5 Seiten424a 2016IrsyadnurJ.MargiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Validation of ENVI-met PMV Values by In-Situ Measuremen TsDokument6 SeitenValidation of ENVI-met PMV Values by In-Situ Measuremen TsHendra CesmamulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BASF Ultraform N2200 G53Dokument2 SeitenBASF Ultraform N2200 G53paradoxid78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Analysis Iso Cat III DLPDFDokument8 SeitenVibration Analysis Iso Cat III DLPDFWisnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duct Design For "Super" SupermarketDokument47 SeitenDuct Design For "Super" Supermarketkevin_thian_1100% (4)
- Materials Express: Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy at Different Strain AmplitudesDokument6 SeitenMaterials Express: Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy at Different Strain Amplitudesadarshravindran1991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Changes Emission of Greenhouse Gases Human Nature ContributionDokument5 SeitenClimate Changes Emission of Greenhouse Gases Human Nature ContributionMuhammad Asim ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9702 - s18 - QP - 21 (Dragged) PDFDokument2 Seiten9702 - s18 - QP - 21 (Dragged) PDFNezza WidarkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15112739-T-T01-01 STS Crane (4x24AL PST) - SGNDokument10 Seiten15112739-T-T01-01 STS Crane (4x24AL PST) - SGNdheeraj SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gamma Attenuation and ShieldingDokument11 SeitenGamma Attenuation and ShieldingAhmedAmer1Noch keine Bewertungen
- IIT JAM Physics Sample Theory for Entrance ExamsDokument20 SeitenIIT JAM Physics Sample Theory for Entrance ExamsVikram KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Lower Limb Prosthetic Foot Made From Composite Polymer Blends1Dokument12 SeitenExperimental and Numerical Investigation of Lower Limb Prosthetic Foot Made From Composite Polymer Blends1Jawad K. OleiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP, PE, PVC, POM, PET, PA6G material characteristicsDokument1 SeitePP, PE, PVC, POM, PET, PA6G material characteristicsandytuorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studying Pendulum MotionDokument13 SeitenStudying Pendulum MotionMubashir AijazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo EconomicsDokument22 SeitenThermo EconomicsArvin SohrabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASCE-AIr Cooled CondensersDokument9 SeitenASCE-AIr Cooled CondensersYanan CamarazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper 01 SolvedDokument29 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper 01 SolvedLalbahadur RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Solid State PhysicsDokument1 SeiteOverview of Solid State PhysicsHenkVriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verification of steam ejector refrigeration model performanceDokument8 SeitenVerification of steam ejector refrigeration model performance고현Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Che463Dokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Che463Rafiqah RahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Offer Colloid Mill Vertical Model JM-L65ADokument7 SeitenCommercial Offer Colloid Mill Vertical Model JM-L65ARoLopNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRI-STEEL MANUFACTURING PIPE SCHEDULESDokument2 SeitenBRI-STEEL MANUFACTURING PIPE SCHEDULESN RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger Thermal Calculation by Rey FiedacanDokument5 SeitenHeat Exchanger Thermal Calculation by Rey FiedacanRajdeepsinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sonoluminescence by F. Ronald YoungDokument256 SeitenSonoluminescence by F. Ronald Youngbennhallett100% (1)
- International Journal of Coal Geology: John Coggan, Fuqiang Gao, Doug Stead, Davide ElmoDokument10 SeitenInternational Journal of Coal Geology: John Coggan, Fuqiang Gao, Doug Stead, Davide Elmopradhith kattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 1474-1987Dokument31 SeitenBS 1474-1987raftipdo0aNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIR and Optical FibresDokument25 SeitenTIR and Optical FibresschlemielzNoch keine Bewertungen