Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
4 Exercises
Hochgeladen von
Raihani KadirCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
4 Exercises
Hochgeladen von
Raihani KadirCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
[ SM. ST.
PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
(A) Directed Numbers / Decimal Numbers 2 marks
1
1
and express the answer as a decimal.
Calculate the value of 0.8 +
5
2
0.5)
(Ans :
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.2]
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1
Calculate the value of 4.26 0.8 1
2
4.908)
and express the answer as a decimal.
(Ans :
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.2]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Calculate the value of 14 (0.6)
2
3
and express the answer as a decimal.
(Ans :
14.9)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.1]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Calculate the value of
4 0.18
.
0 .9
(Ans : 0.8)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.2]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
(B) Whole Numbers / Integer Numbers 2 marks
5
Calculate the value of 96 3 (12 + 48 6).
(Ans : 36)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.1]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Calculate the value of 24 8 14.
(Ans : 17)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.1]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
(C) Fractions 2 marks
7
Find the Find the value of ( 2
(Ans :
29
39
1
2
3
) 2
and express the answer as a single fraction in its lowest term.
3
5
5
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.1]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Find the value of 1
(Ans :
3
20
1
2
4
and express the answer as a single fraction in its lowest term.
8
3
5
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.2]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Calculate the value of
(Ans :
2
3
1
3
5
and express the answer as a fraction in its lowest terms.
3
2
5
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.1]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
(D) Square, Square Roots and Cube, Cube Roots 3 marks
10
(a) Find the value of
(b)
0.512 .
Calculate the value of 42
27
.
8
(Ans : 24)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.3]
(a)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
11
(a) Find the value of
(b)
of
1
4
Calculate the value of (4.2
27 )2.
(Ans : 1.96)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.3]
(a)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
12
(a) Find the value of
(b)
0.49 .
Calculate the value of
25
1 .
16
(Ans :
1
64
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.3]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
13
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
(a) Find the value of
(b)
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
64 .
1
Calculate the value of
2
36 .
(Ans : 27)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.3]
(a)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
14
(a) Find the value of
(b)
Calculate the value of
1
.
27
( 16
81 .
(Ans : 49)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.2]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
(E) Transformations [ Translation ] 2 marks
15 In the diagram, P is the image of P under transformation M.
y
12
10
P
8
6
4
2
O
10
12
Describe in full transformation M.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.5]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
16
The diagram shows two polygon, H and H , drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides of 1 unit.
H
H
H is the image of H under transformation L. Describe in full transformation L
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.4]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
(F) Transformations [ Reflection ] 2 marks
17 The diagram in the answer space shows two quadrilaterals, ABCD and A B C D , drawn on a grid of
equal squares. On the diagram in the answer space, draw the axis of reflection.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.6]
A
B
C
D
C
A
B
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------18 The diagram in the answer space shows object P and straight line MN drawn on a grid of equal squares.
On the diagram in the answer space, draw the image of P under a reflection in the straight line MN.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.5]
M
P
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
19 The diagram in the answer space shows quadrilateral PQRS. R S is the image of RS under a reflection
in the straight line MN. On the diagram in the answer space, complete the image of quadrilateral PQRS.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.5]
N
S
S
R
R
P
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
20 The diagram shows two quadrilaterals, JKLM and J K L M , drawn on a Cartesian plane. J K L M
is the image of JKLM under transformation H.
y
K
4
2
O
2
4
L
2
M
6M8
10
L
K
Describe in full transformation H.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.3]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
(G) Transformations [ Rotation ] 2 marks
21 Diagram in below shows three triangles, P, Q, and R, which are drawn on a Cartesian plane.
y
12
10
8
R
4
2
4
(a)
(b)
2 O
Q
4
2.
Q is the image of P under a rotation of 90. State
(i)
the direction of the rotation,
(ii)
the coordinates of the centre of the rotation.
(Ans : (2, 4) )
R is the image of P under transformation M. Describe in full the transformation M.
[4 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.7]
(a)
(i)
(ii)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
22 The diagram in the answer space shows trapezium ABCD drawn on a grid of equal squares. C D is the
image of CD under a rotation 180 about the point
trapezium ABCD.
P.
On the diagram,
complete the image of
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.5]
A
D
B
P
C
D
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
10
(H) Transformations [ Congruent ] 2 marks
23 The diagram in the answer space shows polygon ABCDEF and straight line PQ drawn on a grid of equal
squares. Starting from the line PQ, drawn polygon PQRSTU which is congruent to polygon ABCDEF.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.6]
F
E
D
C
P
O
Q
O
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------24 The diagram in the answer space shows quadrilateral ABCD and straight line EF drawn on a grid of
equal squares. Starting from the line EF, draw quadrilateral EFGH which is congruent to quadrilateral ABCD.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.5]
C
D
A
B
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
11
(I) Transformations [ Enlargement ] 2 3 marks
25 The diagram in the answer space shows two quadrilaterals, JKLM and J K L M , drawn on a grid of
equal squares. On the diagram in the answer space, mark P as the centre of enlargement.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.6]
J
J
M
L
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
26
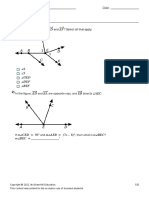
In the diagram, triangle EFG and HIJ are similar.
I
65
65
75
40
G
State
(a)
the angle in triangle HIJ which corresponds to FEG.
(b)
the side in triangle HIJ which corresponds to the side EF in triangle EFG.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.19]
(a)
(b)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------27 In the diagram, ACE and ABD are straight lines. BC is parallel to DE.
4 cm
C
6 cm
A
9 cm
Find the length, in cm, of AD.
D
(Ans : 15)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.13]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
12
(J) Linear Eqautions 3 marks
28
Solve each of the following equations :
(a)
k = 14 k.
(b)
f +
(Ans : 7)
3
(6 4f ) = 31.
2
(Ans : 8)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.14]
(a)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
29 Solve each of the following questions :
(a)
2n = 3n 4.
(b)
2k =
(Ans : 4)
3 7k
.
5
(Ans :
3
17
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.15]
(a)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
30 Solve each of the following equations :
(a)
12
= 3.
n
(b)
2 (k 1) = k + 3.
(Ans : 4)
(Ans : 5)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.10]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
31
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
13
Solve each of the following linear equations :
(a)
x + 10 = 4
(b)
5x 4
= x
3
(Ans : 2)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.4]
(a)
(b)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------32
Solve each of the following equations :
(a)
p + 5 = 11
(b)
x 1 =
x + 3
2
(Ans : 5)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.7]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
14
(K) Linear Inequalities 2 / 3 marks
33
(a) Solve the inequalities 2 + x 5.
(b)
List all the integer value of x which satisfy both the inequalities
(Ans : 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)
x
3 1 and 3 x < 0.
2
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.10]
(a)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
34 Solve the inequality 7 5x < 6 x.
1
4
(Ans : x >
)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.18]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------x
35 List all the integer values of x which satisfy both the inequalities
1 and 1 2x < 5.
2
(Ans : 1, 0, 1, 2)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.14]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
36
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
15
Solve each of the following inequalities :
(a)
w 6 < 2
(b)
8 + 4v 9 2v
(Ans : v 6 )
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.10]
(a)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
37
List all the integer values of p which satisfy both inequalities p + 3 < 5 and 2 3p 8.
(Ans : 2, 1, 0, 1)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.14]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
16
(L) Algebraic Expressions [ Expansion ] 2 3 marks
38 Simplify (3x 1)2 (7x + 4).
(Ans : 9x2 13x
3)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.9]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
39 Simplify (2p q)2 + q (4p q).
(Ans :
4p2)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.11]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
40 Simplify 3 (2p 5) + (p 3)2.
(Ans : p2
6)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.11]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------41
Expand each of the following expressions
(a)
q (2 + p)
(b)
(3m n)2
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.8]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
42
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
17
Simplify :
2p 3q (p + 5q)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.8]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------43
Expand each of the following expressions
(a)
2g (5 k)
(b)
(h 5) (3h + 2)
(Ans : 3h2 13h 10)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.11]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(M)
44
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
18
Algebraic Expressions [ Factorization ] 2 3 marks
Factorise completely :
(a)
9xy 3x2.
(b)
p2 6 (p + 1) (8 p).
(Ans : (p + 2) (p 7) )
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.16]
(a)
(b)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------45
Factorise completely each of the following expressions
(a)
4e 12ef .
(b)
3x2 48.
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.12]
(a)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
46 Factorise completely 50 2m2 .
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.9]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------47
Factorise completely each of the following expressions :
(a)
2y + 6
(b)
12 3x2
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.7]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
19
(N) Algebraic Fractions 3 marks
48 Express
2p 1
mp
1 p
3
2
2m mp
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
(Ans :
)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.17]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
49 Express
m 1
3m 2
m + 2
1
2m
6m 2
as a single fraction in its lowest term.
(Ans :
)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.13]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
50 Express
v 1
3mv
1
5 2v
5m
15mv
as a single fraction in its lowest term.
(Ans :
)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.12]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
51
Express
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
5
2 3w
+
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
3n
6n
20
(Ans :
4 w
2n
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.9]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
52
Express
1
n4
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
n
3n
(Ans :
7 n
3n
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.12]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
21
(O) Algebraic Formulae 2 3 marks
53 Given that
p=
5k + 6
2
2( p 3)
= 5, express p in terms of k.
k
(Ans :
)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.13]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
54 Given
4y 3
= 2 , express y in terms of p.
y+ p
(Ans : n =
2p + 3
2
)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.14]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
55 Given F =
n=
5F
3k
3n nk
, express n in terms of F and k.
5
(Ans :
)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.13]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
56
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
Given r2 + 7 = p, express r in terms of p.
22
(Ans : r =
p7 )
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.11]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
57
Given qr + s = p, express r in terms of p, q and s.
(Ans : r =
p s
q
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.6]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
23
(P) Loci 5 marks
58 The diagram in the answer space shows four squares, PKJN, KOLJ, NJMS, and JLRM.
are three moving points in the diagram.
W, X and Y
(a)
W moves such that it is equidistant from the straight lines PS and QR. By using the letters in the
diagram, state the locus of W.
(b)
On the diagram, draw
(i)
the locus of X such that XJ = JN,
(ii)
the locus of Y such that its distance from the point Q and point S are the same.
(c) Hence, mark with the symbol , all the intersection of the locus of X and the locus of Y.
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.15]
(a)
(b), (c)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------59 The diagram in the answer space shows a square PQRS, drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides of 1
unit. M, Y and Z are three moving points in the diagram.
(a)
M is a point which moves such that its distance from the point Q and point S are the same. By using the
letters in the diagram, state the locus of M.
(b)
On the diagram, draw
(i)
the locus for the point X that is constantly 5 units from the line QR,
(ii)
the locus for the point Y that is constantly 7 units from the point R.
(c) Hence, mark with the symbol , the intersection of the locus of X and the locus of Y.
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.9]
(a)
(b), (c)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
24
60 The diagram in the answer space shows a square PQRS, drawn on a grid of equal squares with sides of 1
unit. W, X and Y are three moving points in the diagram.
(a) W is the point which moves such that it is equidistant from the straight lines PQ and PS. By using the
letters in the diagram, state the locus of W.
(b) On the diagram, draw
(i) the locus for the point X that is constantly 5 units from point P,
(ii) the locus for the point Y that is constantly 4 units from the straight line QR.
(c) Hence, mark with the symbol , the intersection of the locus of X and the locus of Y.
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.18]
(a)
(b), (c)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
61
(a) The diagram shows a rhombus MNOP.
(b)
X is a moving point in the rhombus such that it is always equidistant from the straight lines PM and PO.
By using the letters in the diagram, state the locus of X.
The diagram in the answer space shows a regular hexogon ABCDEF. Y and Z are two moving points in
the hexagon. On the diagram, draw
(i) the locus of Y such that YD = DE,
(ii) the locus of Z such that it is equidistant from point B and point F.
(c) Hence, mark with the symbol the intersection of the locus of Y and the locus of Z.
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.16]
(a)
(b), (c)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
25
62 The diagram in the answer space shows a circle with centre O, drawn on a grid of equal squares with
sides of 1 unit. AOB is a diameter of the circle. X, Y and Z are three moving points inside the circle.
(a)
X is the point which moves such that it is constantly 3 unit from the point O. Describe fully the locus
of X.
(b)
On the diagram, draw
(i) the locus of the point Y which moves such that its distance is constantly 2 units from the
line AB.
(ii) the locus of the point Z which moves such that it is equidistant from the point A and the
point B.
(d) Hence, mark with the symbol the intersections of the locus of Y and the locus of Z.
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.10]
(a)
(b), (c)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
26
(Q) Geometrical Constructions 5 6 marks
63 Set squares and protractors are not allowed for this question.
The diagram in the answer space shows a straight line AB.
(a)
Using only a ruler and a pair of compasses,
(i) construct a triangle ABC, beginning from the straight line AB such that BC = 6 cm, and
AC = 5 cm,
(ii) hence, construct the perpendicular to the straight line AB which passes through the point C.
(b)
Based on the diagram constructd in (a), measure the perpendicular distance between point C and the
straight line AB.
(Ans : 4.55)
[6 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.19]
(a)
(b)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
64 Set squares and protractors are not allowed for this question.
The diagram shows a triangle DEF.
5 cm
45
E
(a)
Using only a ruler and a pair of compasses, construct the diagram using the measurements given,
beginning from the straight line DE provided in the answer space.
(b)
Based on the diagram constructd in (a), measure the distance, in cm, between the point D and the
point F.
(Ans : 6.7)
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.10]
(a)
D
E
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
27
65 Set squares and protractors are not allowed in part (a) of this question.
The diagram shows a triangle PQR.
120
P
6 cm
(a)
Using only a ruler and a pair of compasses, construct triangle PQR using the measurements given,
beginning from the straight line PQ provided in the answer space.
(b)
Based on the diagram constructd in (a), measure PRQ using a protractor.
(Ans : 25)
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.20]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
66
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
28
(a) The diagram shows a triangle JKL.
K
J
L
Measure JKL in the diagram, using a protractor.
(b)
The diagram shows a quadrilateral MNPQ.
P
120
M
(i)
Using only a ruler and a pair of compasses, construct the diagram using the measurements given.
(ii)
Based on the diagram constructed in 18 (b)(i), measure the length, in cm, of PQ.
(Ans : 6.1)
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.18]
(a)
(b)
(i)
(ii)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
67
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
29
(a) The diagram shows a quadrilateral PQRS.
Q
P
Measure PQR, using a protractor.
(b)
The diagram shows a parallelogram ABCD. The point E lies on AB such that DE is perpendicular
to AB. Using only a ruler and a pair of compasses, construct the diagram, beginning from the lines AB
and AD provided in the answer space.
A
D
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.17]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
30
(R) Graph of Functions 4 marks
68 Use the graph paper provided in this question.
The table shows the values of two variables x and y, of a function.
x
32
11
13
34
Draw the graph of the function using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 10 unit on the
y-axis.
[4 marks]
[2004, No.18]
69 Use the graph paper provided in this question.
The table shows the values the of two variables, x and y, of a function.
x
0.5
1.5
10
10
By using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 2 unit on the y-axis, draw the graph of the
function.
[4 marks]
[2005, No.20]
70
Use the graph paper to answer this question.
The table shows the values of two variables x and y, of a function.
x
13
27
45
67
The scale on the x-axis is 2 cm to 1 unit.
The scale on the y-axis is 2 cm to 10 units.
By using the scale given, draw the graph of the function.
71
[4 marks]
[2006, No.19]
Use the graph paper to answer this question.
The table shows the values of two variables, x and y, of a function.
(a)
72
32
18
By using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 4 unit on the y-axis, draw the graph of
the function.
[4 marks]
[2007, No.17]
Use the graph paper to answer this question.
The table shows the values of two variables, x and y, of a function.
x
19
17
The x-axis and the y-axis are provided on the graph paper
(a)
By using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and of 2 cm to 5 on the y-axis, draw the graph of the
function.
(b)
Based on the table, plot the points on the graph paper.
(c)
Hence, draw the graph of the function.
[4 marks]
[2008, No.16]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
31
(S) Statistics 3 6 marks
73 The data below shows the marks obtained by 20 participants in a quiz.
1
(a)
Using the data, complete the frequency table in the answer space.
(b)
State the mode.
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.8]
(a)
Marks
Frequency
(b)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------74 The table shows the number of books in the reading corners of three classes.
Class
Number of books
Aman
75
Bestari
60
Cerdas
90
The information of Bestari class is shown fully in pictograph in the answer space. Complete the pictograph to
represent all the information in the table.
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.20]
Number of books in the reading corner
Class
Number of books
Aman
Bestari
Cerdas
represent .. books
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
32
75 The table shows the number of students who play four types of games
Types of games
Ping-pong
Badminton
Hockey
Hand ball
Number of students
15
25
12
The information for badminton is shown fully in the pie chart in the answer space. Construct the pie chart to
represent all the information in the table.
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.19]
Badminton
90
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------76 The table shows the profit made from a sales of nasi lemak at a stall over five days.
Day
Monday
Tuesday
Wednesday
Thursday
Friday
Profit (RM)
32
40
24
28
28
On diagram in the answer space, draw a line graph to represent all the information in the table. Use the scale
2 units to RM8 on the vertical axis.
[4 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.7]
Profit (RM)
Day
Mon
Tues
Wed
Thurs
Fri
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
33
77 The diagram below is a pie chart which shows the number of pupils in five groups who complete an assignment during a motivational camp.
Lekiu
Tuah
10
12
x Jebat
2x
Lekir
Kasturi
8
It is given that the total number of pupils who complete the assigement is 36.
(a)
Find the value of x.
(Ans : 2)
(b)
Calculate the angle of the sector representing the Tuah group. Show your working.
(c)
State the mode of your data.
(Ans : 100)
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.8]
(a)
(b)
(c)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------78
The table shows three activities participated by a ground of 50 students.
Activities
Number of students
Chess
24
Hockey
Choir
18
(a)
Find the value of M.
(Ans : 8)
(b)
Hence, represent all the data by drawing a bar chart in the answer space.
[4 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.13]
(a)
(b)
Number of students
28
24
20
16
12
8
4
0
Chess
Hockey
Choir
Activities
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
79
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
34
The diagram shows the scores obtained by 15 Police Cadets in a shooting competition.
1, 2, 4, 3, 1, 2, 4, 1, 3, 2, 1, 3, 1, 1, 3
(a)
Using the data, complete the frequency table in the answer space.
(b)
State the median.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.14]
(a)
Score
Frequency
1
2
3
4
(b)
Median =
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------80 The table in the answer space shows the number of gold medals obtained by four schools in a sports competition. The information for school L is shown fully in the pie chart in the diagram in the answer space.
Complete
(a)
the angles of the sectors for school M and school N in the table in the answer space.
(b)
the pie chart in the diagram in the answer space to represent all the information in the table.
[5 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.15]
(a)
School
Number of gold medals
Angle of sector
10
30
60
180
20
30
(b)
L
180
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
35
(T) Scale Drawings 2 3 marks
81 The diagram shows a trapezium.
16 m
6m
10 m
On the grid in the answer space, draw the diagram using the scale 1 : 200. The grid has equal squares with
sides of 1 cm.
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.8]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------82 The diagram shown polygon P drawn on a grid of squares with sides of 1 unit.
On the grid in the answer space, redraw polygon P using the scale 1 :
1
. The grid has equal squares with
2
sides of 1 unit.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.17]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
83
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
36
The diagram shows a polygon.
45 m
20 m
10 m
35 m
On the grid in the answer space, redraw the polygon using scale 1 : 500. The grid has equal squares with
sides of 1 cm.
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.9]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
37
(U) Nets of Geometric Solids 2 3 marks
84 The diagram shows a right pyramid with a square base.
5 units
6 units
Draw a full scale the net of the pyramid on the grid in the answer space. The grid has equal squares with sides
of 1 unit.
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.7]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------85 The diagram shows a prism. One of the surfaces of the net of the prism is drawn on a square grid with
sides of 1 unit in the answer space.
4 units
7 units
3 units
Complete the net of the prism.
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.15]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
38
(V) Indices 2 5 marks
86 Given that 2x 2 = 2 (16) , find the value of x.
(Ans : 7)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.11]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
87 Simplify (2mk2)4 (k2)3 m5k9.
1 5
(Ans :
16m k )
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.12]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
88 Evaluate
3
2
3 2 12 2
2
83
(Ans :
/ 1 12 )
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.16]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
89 Given that 32x 1 = (3x) (32), calculate the value of x.
( Ans :
3)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.17]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
90 Simplify
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
k4 k
k 2
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
39
(Ans : k7 )
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.15]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
91
the value of 32 18 2
.
22
(Ans : 108)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.16]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
92
(a) Find the value of 5 2 5 2 .
(b)
(Ans : 5)
Simplify ( hg4 )3 h2.
(Ans : h5g12 )
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.12]
(a)
(b)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------93
Simplify :
m 2 m 5
m4
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.18]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
94
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
40
Find the value of :
(a)
23 2 1
(b)
( 2 3 36 ) 3
(Ans : 16)
1
( Ans :
9
2
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.19]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
(W)
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
41
Trigonometry 2 4 marks
95 In the diagram, C is the midpoint of the straight line DB.
A
13 cm
5 cm x
B
Find the value of tan x.
(Ans : 5 )
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2004, No.4]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------96 The diagram shows a right angled triangle EFG and DEF is a straight line.
G
4 cm
x
D
E 2 cm F
1
(Ans : 2 )
[2 marks]
Find the value of cos x.
Answer :
[2005, No.4]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------97 In the diagram, QTS is a straight line.
P
8 cm
Q
x
y
S
12 cm
R
Given that sin x =
4
12
and tan y =
, calculate the length, in cm, of TS.
5
5
(Ans : 7)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2005, No.5]
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
42
98 The diagram shows two right angled triangles, DAB and CDB.
5 cm
x
C
It is given that tan y =
5
1
and sin x = ,
12
2
12
13
(a)
Find the value of cos y.
(Ans :
(b)
Calculate the length, in cm, of BC.
(Ans : 26 )
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2006, No.6]
(a)
(b)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------99
The diagram shows two right angled triangles, PQT and SQR. PQR and TQS are straight lines.
T
15 cm
P
Q
x
5 cm
It is given that sin x =
5
3
and cos y = .
13
5
5
12
(a)
Find the value of tan x.
(Ans :
(b)
Calculate the length, in cm, of PQR.
(Ans : 21)
[3 marks]
Answer :
[2007, No.10]
(a)
(b)
[ SM. ST. PETER TELIPOK ]
100
[ LEE CHIONG TEE ]
[ PMR MATEMATIK 50/2, 2004 - 2008 ]
43
The diagram shows a right angled triangle PQR.
P
y
Q
It is given that cos y =
39 cm
R
5
, calculate the length, in cm, of PQ.
13
(Ans : 15)
[2 marks]
Answer :
[2008, No.20]
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- IB Trigonometry 1 Questions SL AnswersDokument12 SeitenIB Trigonometry 1 Questions SL AnswersChosen LambNoch keine Bewertungen
- North Western Province - 2022 (Grade - 11 - English Medium) (With Answers)Dokument18 SeitenNorth Western Province - 2022 (Grade - 11 - English Medium) (With Answers)navinduchandikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Write in Numerals and Number WordsDokument9 SeitenA. Write in Numerals and Number WordsRaihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT Year 2 Paper 1Dokument6 SeitenMT Year 2 Paper 1Mohd ZarrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Y2 skbt2Dokument11 SeitenY2 skbt2Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sksibol Y2Dokument7 SeitenSksibol Y2Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Year 2Dokument4 SeitenMath Year 2ani_1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Four Hundred and Fourteen A. 440 B. 414 C. 444 D. 404Dokument7 SeitenFour Hundred and Fourteen A. 440 B. 414 C. 444 D. 404Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mty2 p2Dokument9 SeitenMty2 p2Narisa AliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Yr 2 QuestionDokument12 SeitenMath Yr 2 QuestionROSLINARAHIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekolah Kebangsaan Sedenak (Panitia Matematik) Mathematics 2008 1 HourDokument6 SeitenSekolah Kebangsaan Sedenak (Panitia Matematik) Mathematics 2008 1 HourRaihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- ObjectivesDokument2 SeitenObjectivesRaihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- PKBSM 3 T 2Dokument10 SeitenPKBSM 3 T 2Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Year 2Dokument10 SeitenMathematics Year 2Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 SECTION A: Answer All The QuestionsDokument7 SeitenPaper 2 SECTION A: Answer All The QuestionsRaihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Show Your Working.: Section ADokument9 SeitenShow Your Working.: Section ARaihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Year 2 2008Dokument11 SeitenMathematics Year 2 2008Ryoma EchizenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Hundred and Thirteen: Section ADokument6 SeitenFour Hundred and Thirteen: Section ARaihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Paper 2Dokument5 SeitenYear 2 Paper 2Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Hundred and TwentyDokument7 SeitenSix Hundred and TwentySaya UnigfxNoch keine Bewertungen
- SK Kangkar Pulai, Jalan Ilmu Kg. Melayu, 81300 J. Bahru. Mathematics Year 2 Paper 1 Circle The Correct AnswersDokument6 SeitenSK Kangkar Pulai, Jalan Ilmu Kg. Melayu, 81300 J. Bahru. Mathematics Year 2 Paper 1 Circle The Correct AnswersRaihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Year2Dokument15 SeitenMaths Year2Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Akhir M3 THN 2Dokument8 SeitenExam Akhir M3 THN 2Atuque MzkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section BDokument3 SeitenSection BRaihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Matematik Year 2Dokument8 SeitenSoalan Matematik Year 2Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- A - Count and Write The Number in NumeralsDokument11 SeitenA - Count and Write The Number in NumeralsKavitha VithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Ujian Pra PROBIM 2010Dokument4 SeitenSoalan Ujian Pra PROBIM 2010Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank Soalan Y2 PPD (Section B)Dokument4 SeitenBank Soalan Y2 PPD (Section B)Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer All Questions.: Sulit 015/1Dokument5 SeitenAnswer All Questions.: Sulit 015/1Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write The Following Numbers in Words. 315 : Answer All QuestionsDokument5 SeitenWrite The Following Numbers in Words. 315 : Answer All QuestionsRaihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Ujian Pasca PROBIM 2010Dokument4 SeitenSoalan Ujian Pasca PROBIM 2010Raihani KadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animals 1Dokument2 SeitenAnimals 1Dhara MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision - Module 11Dokument9 SeitenRevision - Module 11Mahra AlketbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nine-Point CircleDokument9 SeitenThe Nine-Point CircleMr. Bran100% (1)
- Different Methods of Proof Objectives: HSA Geometry Activities Activity 5Dokument57 SeitenDifferent Methods of Proof Objectives: HSA Geometry Activities Activity 5Leomill Mendiola II0% (1)
- The LA TheoremDokument4 SeitenThe LA TheoremJcee EsurenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Quadrilaterls ActivitiesDokument7 SeitenLesson Plan Quadrilaterls ActivitiesHero-name-mo?Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circle - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoDokument10 SeitenCircle - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoChetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics & Dynamics of MechanismsDokument1 SeiteKinematics & Dynamics of MechanismsKarthikKaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- CENG 196 Problem Set Midterms 2Dokument2 SeitenCENG 196 Problem Set Midterms 2Arc Mayenard Beltran100% (1)
- Trignometry TableDokument2 SeitenTrignometry TableSantosh BadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icse 2023 - 511 MatDokument11 SeitenIcse 2023 - 511 MatLeelawati SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design - Spur GearsDokument5 SeitenMachine Design - Spur GearsKleeanne Nicole UmpadNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEST I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Read Each Item Carefully. Choose The Letter Only of Your Answer, Write It On The Space Provided Before Each ItemDokument8 SeitenTEST I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Read Each Item Carefully. Choose The Letter Only of Your Answer, Write It On The Space Provided Before Each ItemHermann Dejero LozanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Fpred 23Dokument21 Seiten2 Fpred 23nbpass09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Instructional Support Material 4th QDokument17 SeitenGrade 9 Instructional Support Material 4th QJay ar SagmitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Math 4Dokument28 SeitenLesson Plan in Math 4Annaliza QuidangenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Test Paper Subject: Mathematics: Faculty Training Programme (PCCP-FTPDokument8 SeitenSample Test Paper Subject: Mathematics: Faculty Training Programme (PCCP-FTPNitish RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cosine Rule Worksheet #01, Shape & Space Revision From GCSE Maths TutorDokument2 SeitenThe Cosine Rule Worksheet #01, Shape & Space Revision From GCSE Maths TutorgcsemathstutorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Similar Figures (A+V) ANSDokument3 SeitenSimilar Figures (A+V) ANSYOONG CHUAN LOONGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometrical Solution To Fermat Problem With Ordinary WeightsDokument38 SeitenGeometrical Solution To Fermat Problem With Ordinary Weightsarun rajaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projection of Planes (CAED)Dokument5 SeitenProjection of Planes (CAED)Akarsh manNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors Short NotesDokument4 SeitenVectors Short NotesShaankariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallography Point GroupsDokument10 SeitenCrystallography Point GroupsSireesh Babu MaddinediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeep 211 GGDokument17 SeitenJeep 211 GGAlexa Heart LaurinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch3 - Crystal Structures & CrystallographyDokument17 SeitenCh3 - Crystal Structures & CrystallographyNguyễn Quốc HưngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Area and VolumeDokument38 SeitenSurface Area and Volumethinkiit80% (5)
- Inversion - Mathematical ExcaliburDokument4 SeitenInversion - Mathematical ExcaliburAltananyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 10 DiagnosticDokument2 SeitenMath 10 DiagnosticFloraville Lamoste-MerencilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP Sols 2.0 Vectors & 3D Geometry (New Syllabus)Dokument8 SeitenDPP Sols 2.0 Vectors & 3D Geometry (New Syllabus)jeeadv.mains2024Noch keine Bewertungen