Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
12 Chemistry Impq CH07 The P Block Elements 02
Hochgeladen von
Saurabh PatilOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
12 Chemistry Impq CH07 The P Block Elements 02
Hochgeladen von
Saurabh PatilCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
7.
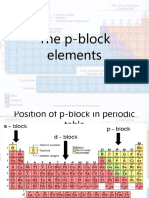
pBlockElements
Pointstoremember: Thegeneralvalenceshellelectronicconfigurationofpblockelementsns2np16 GROUP15ELEMENTS: Group15elements;N,P,As,Sb&Bi Generalelectronicconfiguration:ns2np3 PhysicalProperties: Dinitrogenisadiatomicgaswhileallothersaresolids. N&Parenonmetals.As&Sbmetalloids&Biisametals.thisisduetodecreaseinionization enthalpy&increaseinatomicsize. Electronegativitydecreasesdownthegroup. Chemicalproperties: o Commonoxidationstates:3,+3&+5. o Duetoinerteffect,thestabilityof+5statedecreasesdownthegroup&stabilityof+3state increases. o InthecaseofNitrogenallOxidationstatesfrom+1to+4tendtodisproportionateinacid solution,e.g.:3HNO3H2O+2NO AnamalousbehaviorofNitrogen:duetoitssmallsize,highelectronegativity,highionization enthalpyandabsenceofdorbital. N2hasuniqueabilitytoppmultiplebondswhereastheheavierofthisgroupdonotformp pbecausethereatomicorbitalsaresolarge&diffusethattheycannothaveeffective overlapping. Nitrogenexistsasdiatomicmoleculewithtriplebondbetweenthetwoatomswhereasother elementsformsinglebondsinelementalstate. Ncannotformdpduetothenonavailibilityofdorbitalswhereasotherelementscan. TrendsInProperties: StabilityNH3>PH3>AsH3>SbH3>BiH3 BondDissociationEnthalpyNH3>PH3>AsH3>SbH3>BiH3 ReducingcharacterNH3>PH3>AsH3>SbH3>BiH3 BasiccharacterNH3>PH3>AsH3>SbH3>BiH3 AcidiccharacterN2O3>P2O3>As2O3>Sb2O3>Bi2O3 Dinitrogen: Preparation CommercialpreparationBytheliquification&fractionaldistillationofair. LaboratorypreparationBytreatinganaqueoussolutionNH4Clwithsodiumnitrate. NH4Cl+NaNO2N2+2H2O+NaCl
ThermaldecompositionofammoniumdichromateolsogiseN2. (NH4)2Cr2O7N2+4H2O+Cr2O3 ThermaldecompositionofBariumorSodiumazidegivesverypureN2.
PROPERTIES Athightemperaturenitrogencombineswithmetalstoformionicnitride(Mg3N2)&withnon metals,covalentnitride. AMMONIAPREPARATION InlaboratoryitispreparedbyheatingammoniumsaltwithNaOHorlime. 2NH4Cl+Ca(OH)22NH3+2H2O+CaCl2 InlargescaleitismanufacturedbyHaberprocess N2+3H2=2NH3 H0=46.1kJ/mol Acc.toLechateliersprinciplethefavourableconditionsforthemanufactureofNH3 are: Optimumtemperature:700K Highpressure:200atm Catalytst:IronOxides Promoter:K2O&Al2O3 PROPERTIES Ammoniaisacolorlessgaswithpungentodour. Highlysolubleinwater. Insolids&liquidstatesitexistsasanassociatedmoleculeduetohydrogenbondingwitchaccountsfor highmelting&boilingpointsofNH3 TrigonalPyramidalshapeNH3molecule. AqueoussolutionofammoniaisweaklybasicduetotheformationofOHion. ZnSO4+2NH4OHZn(OH)2+(NH4)2SO4 Ammoniacanformcoordinatebondsbydonatingitsloneonnitrogen,ammoniaformscomplexes. CuSO4+4NH3[Cu(NH3)4]2SO4 Name Nitrousoxideor Laughinggas N2O Formula +1 Oxidationstate Chemicalnature Neutral
Nitricoxide Dinitrogentrioxide Dinitrogentetraoxide Dinitrogenpentaoxide
NO N2O3 N2O4orNO2 N2O5
+2 +3 +4 +5 NITRICACID
Neutral Acidic Acidic Acidic
PREPARATION:ostwaldsproceesitisbaseduponcatalyticoxidationofammoniabyatmospheric oxidation.Themainstepsare 1) 4NH3+5O2PT500K,9BAR4NO+6H2O 2) 2NO+O22HNO3+NO PROPERTIES: (i)conc.HNO3isastrongoxidizingagent&attacksmostmetalsgold&Pt.. (ii)Cr&AldonotdissolveHNO3becauseoftheformationofapositivefilmofoxideonthesurface. (iii)itoxidisesnonmetalslikeI2toHNO3,CtoCO2,StoH2so4 (iv)brownringtesisusedtodetectNO. PHOSPHOROUS: ALLOTROPICFORMS:White,redblack&black. WhitephosphorousismorereactiveredphosphorousbecausewhitePexistsasdiscreteP4molecules. inredPseveralP4moleculesarelinkedtoformedpolymericchain. PHOSPHINE Preparation:ItispreparedinlaboratorybyheatingwhitePwithconcentratednaohsolutioninan InertatmosphereofCO2[P4+3NaOH+3H2OPH3+3NaH2PO2] Phosphoroushalides PhosphorousformstwotypesofhalidesPX3&PX5(X=F,I,Br) Trihalideshavepyramidalshapeandpentahalideshavetrigonalbipyramidalstructure. OXOACIDSOFPHOSPHOROUS Theacidsin+3oxidationstatedisproportionatetohigher&loweroxidation. 4H3PO33H3PO4+PH3
AcidswhichcontainsPHbondhavestrongreducingproperties.EX:H3PO2 Areionisableandcausethebasicity.
HydrogenatomwhichareattachedwithoxygeninPOHformareionisable
GROUP16ELEMENTS(CHALCOGENS) Grouo16Elements:O,S,SE,TE,PO Generalelectronicconfiguration:ns2np4 Element Oxygen Sulphur Se&Te Occurence
Comprises20.946%byvolumeoftheatmosphere. AssulphatessuchasgypsumCaSO4.2H2O,EpsomsaltMgSO4.7H2Oandsulphides SuchasgalenaPbS,zincblendeZnS,copperpyritesCuFeS2 Asmetalselenidesandtelluridesinsulphideores.
asadecayproductofthoriumanduraniumminerals.
ATOMIC&PHYSICALPROPERTIES Ionisationenthalpydecreasesfromoxygentopolonium. OxygenatomhaslessnegativeelectrongainenthalpythanSbecauseofthecompact natureoftheoxygenatom.HoweverfromtheSonwardsthevalueagainbecomesless negativeuptopolonium. Electronegativitygraduallydecreasesfromoxygentopolonium,metalliccharacter increasesfromoxygentopolonium. Oxygen&Sarenonmetals,seleniumandteleriumaremetalloids.Poisaradioactive metal. OxygenisadiatomicgaswhileS,Se&TeareoctaatomicS8,Se8&Te8moleculeswhichhas puckeredringstructure.
CHEMICALPROPERTIES Commonoxidationstate:2,+2,+4&+6. Duetoinerteffect,thestabilityof+6decreasesdownthegroupandstabilityof+4 increases.
Oxygenexhibits+1stateinO2F2,+2inOF2. Anamolousbehaviorofoxygenduetoitssmallsize,highelectronegativityandabsenceofd orbitals. TRENDINPROPERTIES AcidiccharacterH2O<H2S<H2Se<H2Te ThermalstabilityH2O>H2S>H2Se>H2Te ReducingcharacterH2S<H2Se<H2Te BoilingpointH2S<H2Se<H2Te<H2O ReducingpropertyofdioxidesSO2>SeO2>TeO2 StabilityofhalidesF>Cl>Br>I HALIDES DIHALIDES:sp3hybridisationbutangularstructure. TETRAHALIDES:sp3hybridisationseesawgeometry HEXAHALIDES:sp3d2,octahedralSF6 DIOXYGEN Preparedbyheatingoxygencontainingsaltslikechlorates,nitrares 2KClO3heat2KCl+3O2 2Fe3++SO2+2H2O2Fe2++SO42+4H+ 5SO2+2MnO4+2H2O5SO42+4H++2Mn2+ SO2moleculeisangular.
OXIDES
Abinarycompoundofoxygenwithanotherelementiscalledoxide.Oxidescanbeclassified onthebasisofnature AcidicOxides:Nonmetallicoxides.Aqueoussolutionsareacids.Neutralizebasesto formsalts.Ex:So2,Co2,N2O5etc. BasicOxides:metallicoxides.Aqueoussolutionsarealkalis.Neutralizeacidstoform salts.Ex:Na2O,K2o,etc. Amphotericoxides:somemetallicoxidesexhibitadualbehavior.Neutralizebothacids &basestoformsalts. Ex:Al2O3,SbO2,SnO,etc..
OZONE PREPARATION
Preparedbysubjectingcold,dryoxygentosilentelectricdischarge. 3O22O3
PROPERTIES Duetotheeasewithwhichitliberatesatomsofnascentoxygen,itactsasapowerful
oxidizingagent.Foreg:itoxidisesleadsulphidetoleadsulphateandiodideionsto iodine. PbS+4O3PbSO4+4O2
SULPHURDIOXIDE PREPARATION
BurningofSinair S+O2SO2 Roastingofsulphideminerals (Ironpyrites) 4FeS2+11022Fe2O3+8SO2 (Zincblend)2ZnS+3O22ZnO+2SO2
PROPERTIES
Highlysolubleinwatertoformsolutionofsulphurousacid SO2+H2OH2SO3 SO2reactswithCl2toformsulphurylchloride SO2+Cl2SO2Cl2
ItreactswithoxygentoformSO3inpresenceofV2O5catalyst 2SO2+O22SO3
MoistSO2behavesasareducingagent.ItconvertsFe(III)ionstoFe(II)ions& decolourisesacidifiedpotassiumpermanganate(VII)solution(Itisthetestforthe gas). SULPHURICACID PREPARATION Itismanufacturedbycontactprocesswhichinvolves3steps 1. BurningofSorSulphideoresinairtogenerateSO2. 2. ConversionofSO2toSO3inpresenceofV2O5catalyst 3. AbsorptionofSO3inH2SO4togiveoleum. PROPERTIES 1. Inaqeoussolutionitionizesin2steps H2SO4+H2OH3O++HSO4 HSO4+H2OH3O++SO42 2. ItisastrongdehydratingagentEg:charringactionofsugar C12H22O11H2SO412C+11H2O 3. Itisamoderatelystrongoxidizingagent. Cu+2H2SO4(conc.)CuSO4+SO2+2H2O C+2H2SO4(conc.)CO2+2SO2+2H2O GROUP17ELEMENTS(HALOGENS) Group17elements:F,Cl,Br,I,At Generalelectronicconfiguration:ns2np5 Element Occurence Fluorine Cl.Br,I Asinsolublefluorides(fluorsparCaF2,Cryoliteand fluoroapattie) Seawatercontainschlorides,bromidesandiodides of Sodium,potassiummagnesiumandcalcium,butis mainlysodiumchloridesolution(2.5%bymass). Certainformsofmarinelife(variousseaweeds)
ATOMIC & PHYSICAL PROPERTIES i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. Atomic & ionic radii increase from fluorine to iodine. Ionization enthalpy gradually decreases from fluorine to iodine due to increase in atomic size. Electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less than that of chlorine. It is due to small size of fluorine & repulsion between newly added electron &electrons already present in its small 2p orbital. Electronegativity decreases from fluorine to iodine. Fluorine is the most electronegative element in the periodic table. The color of halogens is due to absorption of radiations in visible region which results in the excitation of outer electrons to higher energy level. Bond dissociation enthalpy of fluorine is smaller than that of chlorine is due to electron-electron repulsion among the lone pair in fluorine molecules where they are much closer to each other than in case of chlorine. The trend: Cl-Cl>Br-Br>F-F>I-I. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OXIDATION STATES:-1.However, chlorine, bromine &iodine exhibit +1, +3, +5, +7 oxidation states also. Fluorine forms two oxides OF2 and O2F2. These are essentially oxygen fluorides because of the higher electronegativity of fluorine than oxygen. Anomalous behavior of fluorine- due to its small size, highest electronegativity, low F-F bond dissociation enthalpy and absence of d-orbitals. TRENDS IN PROPERTIES Oxidizing property F2>Cl2>Br2>I2 Acidic strength- HF<HCl<HBr<HI Stability & bond dissociation enthalpy- HF>HCl>HBr>HI Stability of oxides of halogens- I>Cl>Br Ionic character of halides MF>MCl>MBr>MI CHLORINE PREPARATION 1. MnO2 +4HClMnCl2+Cl2+2H2O 2. 4NaCl+MnO2+4H2SO4MnCl2+4 NaHSO4+2H2O+Cl2 3. 2KMnO4+16HCl2KCl+2MnCl2+8H2O+5Cl2 4. DEACONS PROCESS 4HCl+O2CuCl22Cl2+2H2O 5. By electrolysis of brine solution. Cl2 is obtained at anode.
PROPERTIES i. With cold and dilute Cl2 produces a mixture of chloride and hypochlorite but with hot and concentrated alkalis it gives chloride and chlorate. 2NaOH+Cl2NaCl+NaOCl+H2O 6NaOH+3Cl25NaCl+NaClO3+3H2O ii. With dry slaked lime it gives bleaching powder. 2Ca (OH) 2+2Cl2Ca (OH) 2+CaCl2+2H2O iii. It is a powerful bleaching agent; bleaching action is due to oxidation Cl2+H2O2HCl+(O) Colored substance+(O)colorless substance iv. Action of concentrated H2SO4 on NaCl give HCl gas. NaCl+H2SO4420KNaHSO4+HCl 3:1 ratio of conc. HCl & HNO3 is known as aquaregia & it is used for dissolving noble metals like Au and Pt. OXOACIDS OF HALOGENS (SEE TABLE 7.10& FIG.7.8) Interhalogen compounds are prepared by direct combination of halogens. Ex: ClF, ClF3, BrF5, IF7 They are more reactive than halogens because X-X is weaker than X-X bonds in halogens (except F-F). TYPE XX3 XX5 XX7 STRUCTURE Bent T-shaped Square pyramidal Pentagonal bipyramidal
GROUP 18 ELEMENTS GROUP 18 ELEMENTS: He, Ne, Ar,Kr,Xe &Rn
General electronic configuration:ns2np6 Atomic radii- large as compared to other elements in the period since it corresponds to Vander Waal radii. Inert due to complete octet of outermost shell, very high ionization enthalpy & electron gain enthalpies are almost zero. The first noble compound prepared by Neil Bartlett was XePtF6&Xenon. O2+PtF6-.led to the discovery of XePtF6 since first ionization enthalpy of molecular oxygen (1175kJmol-1) was almost identical with that of xenon (1170kJmol-1). PROPERTIES Xe+F2--------673K, 1bar--XeF2 Xe (g) +2F2 (g) ----873k, 7barXeF4(s) Xe (g) +3F2 (g) ----573k, 6070barXeF6(s) XeF6+MFM+ [XeF7]XeF2+PF5[XeF]+[PF6]XeF6+2H2OXeO2F2+4HF(partial hydrolysis) SOLVED QUESTIONS 1 MARK QUESTIONS 1. Ammonia has higher boiling point than phosphine. Why? -AMMONIA FORMS INTERMOLECULAR H-BOND. 2. Why BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of group 15 elements ? 3. Why does PCl3 fume in moisture ? In the presence of (H2O) , PCl3 undergoes hydrolysis giving fumes of HCl . PCl3 + 3H2O H3PO3 + 3HCl 4. What Happens when H3PO3 is Heated ? It disproportionate to give orthophosphoric acid and Phosphine .
4H3PO3 3H3PO4 PH3 5. Why H2S is acidic and H2S is neutral ? The S---H bond is weaker than O---H bond because the size of S atomis bigger than that of O atom . Hence H2S can dissociate to give H+ Ions in aqueous solution . 6. Name two poisonous gases which can be prepared from chlorine gas ? Phosgene (COCl2) , tear gas (CCl3NO2) 7. Name the halogen which does not exhibit positive oxidation state . Flourine being the most electronegative element does not show positive oxidation state . 8. Iodine forms I3- but F2 does not form F3- ions .why? Due to the presence of vacant D-orbitals , I2 accepts electrons from I-ions to form I3ions , but because of d-orbitals F2 does not accept electrons from F-ions to form F3 ions. 9. Draw the structure of peroxosulphuric acid . 10. Phosphorous forms PCl5 but nitrogen cannot form NCl5. Why? Due to the availability of vacant d-orbital in p.
2MARKQUESTION(SHORTANSWERTYPEQUESTION) 1.WhyisHFacidstoredinwaxcoatedglassbottles? ThisisbecauseHFdoesnotattackwaxbutreactswithglass.ItdissolvesSiO2 presentinglassforminghydrofluorosilicicacid. SiO2+6HFH2SiF6+2H2O 2.Whatislaughinggas?Whyisitsocalled?Howisitprepared? Nitrousoxide(N2O)iscalledlaughinggas,becausewheninhaleditproduced hystericallaughter.Itispreparedbygentlyheatingammoniumnitrate.
NH4NO3N2O+2H2O 3.Givereasonsforthefollowing: (i)Conc.HNO3turnsyellowonexposuretosunlight. (ii)PCl5behavesasanionicspeciesinsolidstate. (i)ConcHNO3decomposetoNO2whichisbrownincolour&NO2dissolvesin HNO3toityellow. (ii)Itexistsas[PCl4]+[PCl6]insolidstate. 4.WhathappenswhenwhitePisheatedwithconc.NaOHsolutioninan atmosphereofCO2?Giveequation. Phosphorusgaswillbeformed. P4+3NaOH+3H2OPH3+3NaH2PO2 5.Howisozoneestimatedquantitatively? Whenozonereactswithanexcessofpotassiumiodidesolution Bufferedwithaboratebuffer(Ph9.2),Iodideisliberatedwhichcanbetitrated againstastandardsolutionofsodiumthiosulphate.Thisisaquantitativemethod forestimatingO3gas. 6.AreallthefivebondsinPCl5moleculeequivalent?Justifyyouranswer. PCl5hasatrigonalbipyramidalstructureandthethreeequatorialPClbondsare equivalent,whilethetwoaxialbondsaredifferentandlongerthanequatorial bonds. 7.NO2iscolouredandreadilydimerises.Why? NO2containsoddnumberofvalenceelectrons.Itbehavesasatypicalodd molecules.Ondimerization;itisconvertedtostableN204moleculewitheven numberofelectrons.
8.WritethebalancedchemicalequationforthereactionofCl2withhotand concentratedNaOH.Isthisreactionadispropotionationreaction?Justify: 3Cl2+6NaOH5NaCl+NaClO3+3H2O Yes,chlorinefromzerooxidationstateischangedto1and+5oxidationstates. 9.Accountforthefollowing. (i)SF6islessreactivethan. (ii)0fthenoblegasesonlyxenonchemicalcompounds. (i)InSF6thereislessrepulsionbetweenFatomsthanInSF4. (II)Xehaslowionisationenthalpy&highpolarisingpowerduetolargeratomic size. 10.WithwhatneutralmoleculeisClOIsoelectronic?IsthatmoleculeaLewis base? CiF.Yes,itisLewisbaseduetopresenceoflonepairofelectron. 3MARKQUESTIONS 1(i)whyisHeusedindivingapparatus? (ii)Noblegaseshaveverylowboilingpoints.Why? (iii)WhyisIClmoereactivethanI2? (I)Itisnotsolubleinbloodevenunderhighpressure. (ii)Beingmonoatomictheyhaveweakdispersionforces. (ii)IClbondisweakerthanllbond 2.Completethefollowingequations. (i)XeF4+H2O (ii)Ca3P2+H2O
(iii)AgCl(s)+NH3(aq) (i)6XeF4+12H2O4Xe+2XeO3+24HF+3O2 (ii)Ca2P2+6H2O3Ca(OH)2+2PH3 (iii)AgCl(s)+2NH3(aq)[Ag(NH3)2]Cl(aq) 3.(i)HowisXeOF4prepared?Drawitsstructure. (ii)WhenHCLreactswithfinelypowderediron,itformsferrouschlorideandnot ferricchloride.Why? (i)PartialhydrolysisofXeOF4 XeF6+H2OXeOF4+2HF Structuresquarepyramidal.SeeFig7.9 (ii)Itsreactionwithironproducesh2 Fe+2HClFeCl2+H2 Liberationofhydrogenpreventstheformationofferricchloride. 5MARKQUESTION 1.Accountforthefollowing. (i)NoblegasformcompoundswithF2&O2only. (ii)Sulphurshowsparamagneticbehavior. (iii)HFismuchlessvolatilethanHCl. (iv)Whitephosphorousiskeptunderwater. (v)Ammoniaisastrongerbasethanphosphine. (i)F2&O2arebestoxidizingagents.
(ii)InvapourstatesulphurpartlyexistsasS2moleculewhichhastwounpaired electronsintheantibondingpi*orbitalslikeO2and,hence,exhibit paramagnetism. (iii)HFisassociatedwithintermolecularHbonding. (iv)Ignitiontemperatureofwhitephosphorousisverylow(303K).Thereforeon explosuretoair,itspontaneouslycatchesfireformingP4O10.Thereforetoprotect itfromair,itiskeptunderwater. (v)DuetothesmallersizeofN,lonepairofelectronsisreadilyavailable. 2.WhenConc.H2SO4wasaddedtoanunknownsaltpresentinatesttube,a browngas(A)wasevolved.Thisgasintensifiedwhencopperturningswereadded intotesttube.Oncoolinggas(A)changedintoacolourlessgas(B). (a)IdentifythegasesAandB (b)Writetheequationsforthereactionsinvolved ThegasAisNO2whereasBisN2O4. XNO3+H2SO4XHSO4+HNO3 Salt(conc.) Cu+4HNO3(Conc.)Cu(NO3)2+2NO2+2H2O BlueBrown(A) 2NO2(oncooling)N2O4 Colourless(B) 3.Arrangethefollowingintheincreasingorderofthepropertymentioned. (i)HOCl,HClO2,HClO3,HClO4(Acidicstrength) (ii)As2O3,ClO2,GeO3,Ga2O3(Acidity) (iii)NH3,PH3,AsH3,SbH3(HEHbondangle)
(iv)HF,HCl,HBr,HI(Acidicstrength) (v)MF,MCl,MBr,MI(ioniccharacter) (i)Acidicstrength:HOCl<HClO2<HCIO3<HCIO4 (ii)Acidity:Ga2O3<GeO2<AsO3<CIO2 (iii)Bondangle:SbH3<AsH3<PH3<NH3 (iv)Acidicstrength:HF<HCl<HBr<HI (v)Ioniccharacter:MI<MBr<MCl<MF ASSIGNMENTS Veryshotanswertypequestions: 1)PH3haslowerboilingpointthanNH3.Explain. 2)Whyarehalogenscoloured. 3)Whatarechalcogens? 4)WhichnoblegasisRadioactive? 5)Explainwhyfluorinealwaysexhibitanoxidationstateof1only. 6)Whichcompoundledtothediscoveryofcompoundsofnoblegas? 7)Namethemostelectronegativeelement. 8)WhyisOF6compoundnotknown? 9)WhyisN2notparticularlyreactive? 10)Ammoniaactsasaligned.Explain. Shortanswertypequestions: 1)WritePhosphorousismorereactivethanredphosphorous.Explain.
2)Whydonoblegaseshavecomparativelylargeatomicsizes? 3)ArrangeindecreasingorderofIoniccharacter MF,MCl,MBr,MI 4)Phosphinicacidbehavesasamonoproticacid 5)Arrangethefollowingintheorderofpropertyindicated: a)AS2O3,ClO2,GeO2,Ga2O3__Increasingacidity b)H2O,H2S,H2Se,H2Te__Increasingacidstrength. 6)Arrangeindecreasingorderofbondenergy: F2,Cl2,Br2,I2 7)Completethefollowing: i)HNO3+P4O10
ii)IO3+I+H+ 8)Givethechemicalreactionsinsupportoffollowingobservations: a)The+5oxidationstateofBiislessstablethan+3oxidationstate. b)Sulphurexhibitsgreatertendencyforcatenationthanselenium.
9)Howwouldyouaccountforfollowing? i)EnthalpyofdissociationofF2ismuchlessthanthatofCl2. ii)Sulphurinvapourstateexhibitsparamagnetism. 10)Drawstructuresoffollowing: a)PreoxomonasalphuricacidH2SO5 b)XeF4
LevelIII 1.Completeandbalance: i)F2+H2OCold ii)BrO3+F2+OH iii)Li+N2(cold) iv)NH3+NaOCl 2)DespitelowerelectronaffinityofF2,isstrongeroxidisingagentthanCl2. Explain. 3)Givereasons: a)Nitricoxidebecomesbrownwhenreleasedinair. b)PCl5isionicinnatureinthesolidstate. 4)WhichofthetwoismorecovalentSbCl3orSbCl5? 5)AdditionofCl2toKlsolutiongivesifbrowncolourbutexcessatifturnsit colourless.Explain. IdentifyhybridizationstateofcentralatomanduseconceotofVSEPRtheory.also itsshape(geometry)anddrawthestructure. PCl3 PCl5 BrF3 XeF2 XeF4 XeOF4 XeO3 XeF6 SF4 sp3 sp3d sp3d sp3d sp3d2 sp3d2 sp3 sp3d3 sp3d bp=3 bp=5 bp=3 bp=2 bp=4 bp=5 bp=3 bp=6 bp=4 lp=1 lp=0 lp=2 lp=3 lp=2 lp=1 lp=1 lp=1 lp=1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The P Block ElementsDokument21 SeitenThe P Block ElementsP. Jacksen Sam PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- P Block ElemetsDokument16 SeitenP Block ElemetsAnthony KevinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The P-Block Elements (Summary)Dokument49 SeitenThe P-Block Elements (Summary)nickan876Noch keine Bewertungen
- P Block 15TH Group Elements NotesDokument11 SeitenP Block 15TH Group Elements Notesiipud072.giridhar.k MESKKPUCNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE P - Block Elements-Anil-Hsslive PDFDokument19 SeitenTHE P - Block Elements-Anil-Hsslive PDFKochuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- P - Block Elements Group 16Dokument51 SeitenP - Block Elements Group 16AnshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The P Block ElementsDokument21 SeitenThe P Block ElementssrideviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter:-Group 16 Elements: Elements Symbol At. No. At. WTDokument10 SeitenChapter:-Group 16 Elements: Elements Symbol At. No. At. WTAayush gaming funNoch keine Bewertungen
- The P-Block Elements - WatermarkDokument28 SeitenThe P-Block Elements - Watermarkaadidharaskar11Noch keine Bewertungen
- UPDATED PBlock ElementsDokument100 SeitenUPDATED PBlock ElementsAarohi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSSLiVE-XII-Che-7 The P - Block Elements 2Dokument17 SeitenHSSLiVE-XII-Che-7 The P - Block Elements 2Ranit Mukherjee0% (1)
- Groups 13 14Dokument28 SeitenGroups 13 14Nikoli MajorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The P - Block Elements 2Dokument16 SeitenThe P - Block Elements 2prateekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 7 The P-Block Elements: SynopsisDokument23 SeitenChapter - 7 The P-Block Elements: SynopsisPrashant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkali Metals and Alkaline Earth MetalsDokument16 SeitenAlkali Metals and Alkaline Earth MetalsPrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 4 Lecture (Compatibility Mode)Dokument26 SeitenCHAPTER 4 Lecture (Compatibility Mode)Shakeel AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 14Dokument2 SeitenGroup 14fiqaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry: Period 3 ElementsDokument5 SeitenInorganic Chemistry: Period 3 ElementsUng Hie HuongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chuong 4Dokument41 SeitenChuong 4Tiến Anh MaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- S-Block Elements & Their CompoundsDokument33 SeitenS-Block Elements & Their CompoundsAbhishek Shukla100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Pblock ElementDokument46 SeitenChapter 7 Pblock ElementAmrit BorahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Group 16 in P Block ElementsDokument4 SeitenChemistry of Group 16 in P Block Elementsakino.mitsunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P Block Elements1Dokument80 SeitenP Block Elements1aleena'Noch keine Bewertungen
- P Block Elements-Group 16Dokument41 SeitenP Block Elements-Group 16Sanskriti Keshkar100% (5)
- RevisDokument28 SeitenRevisPrabhakar BandaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- خلاصة 2ث chemistry ترم ثانىDokument4 Seitenخلاصة 2ث chemistry ترم ثانىKhaled WalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- ..-EAMCET-QR-Chemistry-Sr Chem-10.VA Group Elements - 171-175 - PDFDokument12 Seiten..-EAMCET-QR-Chemistry-Sr Chem-10.VA Group Elements - 171-175 - PDFPragyanshu ParadkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- METALS AND NON METALS NoteDokument38 SeitenMETALS AND NON METALS NoteYusuf AkinyooyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 15 - The Elements NitrogenDokument19 SeitenGroup 15 - The Elements NitrogenHarold Isai Silvestre GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iva Group ElementsDokument11 SeitenIva Group Elementsravindrababu2908Noch keine Bewertungen
- KarbonDokument35 SeitenKarbonrizki dwi pangestiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 9 - Properties of MetalDokument30 SeitenActivity 9 - Properties of MetalAbbey Frosty'Knight Dawn MortaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- P BlockDokument52 SeitenP BlockYogendra GangwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- P BlockDokument52 SeitenP BlockYogendra GangwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRP 15, 16 New P BlockDokument76 SeitenGRP 15, 16 New P BlockVedantNoch keine Bewertungen
- P Block Short NotesDokument22 SeitenP Block Short Notesthapliyaldivyanshu274Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reactions of Period 3 ElementsDokument17 SeitenReactions of Period 3 ElementsSNEHA TIMSINANoch keine Bewertungen
- D Block Lecture1aDokument16 SeitenD Block Lecture1aRobiul AlomNoch keine Bewertungen
- P-Block ElementsDokument56 SeitenP-Block Elementssc21fs301017Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alkali Metals NotesDokument23 SeitenAlkali Metals Notesaayush basnetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 6ADokument36 SeitenGroup 6ATITI HARYATINoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 6ADokument36 SeitenGroup 6ATITI HARYATINoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 P Block SNDokument10 SeitenClass 12 P Block SN09 Krishna TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- D F Block IIT JEE PDFDokument26 SeitenD F Block IIT JEE PDFRajeev KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alloyed With Cu., Found in Britain, Was An Early SourceDokument7 SeitenAlloyed With Cu., Found in Britain, Was An Early Sourcetru99_nlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochemistry - F4Dokument5 SeitenElectrochemistry - F4felixNoch keine Bewertungen
- P Blockelements 1608Dokument51 SeitenP Blockelements 1608د.حاتممرقهNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 15 Elements: - D (Pi) BondDokument7 SeitenGroup 15 Elements: - D (Pi) BondSanju PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals and Non-MetalsDokument37 SeitenMetals and Non-MetalsNeeraj Ilal100% (1)
- Main Group Chemistry (Group Va) - Part A - DR AkinsikuDokument46 SeitenMain Group Chemistry (Group Va) - Part A - DR AkinsikuMichael SulolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P-Block ElementsDokument14 SeitenP-Block ElementsAviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gupta Classes For Any Help Contact: 9953168795, 9268789880: 16 Column ElementsDokument0 SeitenGupta Classes For Any Help Contact: 9953168795, 9268789880: 16 Column ElementsPrithviraj NetkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Elements: P-BlockDokument36 SeitenThe Elements: P-BlockIndonesia HarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry PresentationDokument43 SeitenChemistry PresentationgabyyyyyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The P-Block ElementsDokument6 SeitenThe P-Block ElementsSteveMathewKuruvillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D & F Block Element (Unit Viii)Dokument15 SeitenD & F Block Element (Unit Viii)triptigupta317Noch keine Bewertungen
- Silicon in Organic Synthesis: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringVon EverandSilicon in Organic Synthesis: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- A System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the BlowpipeVon EverandA System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the BlowpipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideVon EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Bye Laws - 04,08,40,42Dokument25 SeitenBye Laws - 04,08,40,42Saurabh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Chemistry Notes ch11 The P Block Element PDFDokument14 Seiten11 Chemistry Notes ch11 The P Block Element PDFron sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HindiDokument5 SeitenHindiSaurabh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- City Service Center Name Contact Person: S S EnterprisesDokument8 SeitenCity Service Center Name Contact Person: S S EnterprisesSaurabh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climatic Responsive Energy Efficient Passive Techniques in Buildings - IE Journal, Apr 2003.Dokument10 SeitenClimatic Responsive Energy Efficient Passive Techniques in Buildings - IE Journal, Apr 2003.Saurabh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dansko Phase III West Grove, PADokument30 SeitenDansko Phase III West Grove, PASaurabh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.Skill Ripjawsx Ddr3 8 GB (1 X 8 GB) PC Ram (F3-10666Cl9S-8Gbxl)Dokument13 SeitenG.Skill Ripjawsx Ddr3 8 GB (1 X 8 GB) PC Ram (F3-10666Cl9S-8Gbxl)Saurabh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itp For Tank Fabrication & Installation Work1 - Rev02Dokument22 SeitenItp For Tank Fabrication & Installation Work1 - Rev02mister pogi100% (3)
- SHS Micro Financing in NepalDokument24 SeitenSHS Micro Financing in NepalparipranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 140KDokument63 Seiten140KRuben Chumacero100% (3)
- Motor Circuit Analysis StandardsDokument4 SeitenMotor Circuit Analysis StandardsThe Matrix100% (1)
- Signature RedactedDokument49 SeitenSignature RedactedG Pavan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tn100-Tutorial Questions OverallDokument15 SeitenTn100-Tutorial Questions OverallEng BahanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Analysis of PSV Connected Piping Systems Using Caesar IIDokument6 SeitenStress Analysis of PSV Connected Piping Systems Using Caesar IIwisesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Chemical Reactions and EquationsDokument10 Seiten1-Chemical Reactions and Equationsmayank007aggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZRIMADokument494 SeitenZRIMAأبو الأمين المغربيNoch keine Bewertungen
- TPE331-14 Turboprop Engine PDFDokument2 SeitenTPE331-14 Turboprop Engine PDFJoaquinBarretoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shs Module v2020 #m1.2Dokument6 SeitenShs Module v2020 #m1.2Peter Anton RoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMF InstructionsDokument4 SeitenAMF Instructionspapasp105305Noch keine Bewertungen
- SHS Core - Earth and Life Science CGDokument13 SeitenSHS Core - Earth and Life Science CGShendy AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FTPDokument10 SeitenFTPMichael ParkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akm 204E - Fluid Mechanics Lecture Notes # 3: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Cihan BAYINDIRDokument24 SeitenAkm 204E - Fluid Mechanics Lecture Notes # 3: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Cihan BAYINDIRMelisa MeralNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 6L GM Vortec SRVCDokument320 Seiten1 6L GM Vortec SRVCFred100% (2)
- Lecture 12Dokument43 SeitenLecture 12salem bahsan100% (1)
- Lockout Tagout ProgramDokument6 SeitenLockout Tagout ProgramYuli AstutyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification Aeration BlowerDokument52 SeitenSpecification Aeration BlowerPendeta MudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Threaded Style BackDokument6 SeitenThe Threaded Style Backsharif339Noch keine Bewertungen
- Symmetry: Tailored Workspaces-Optimized FacilityDokument7 SeitenSymmetry: Tailored Workspaces-Optimized Facilityab_bn_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eks Energy PresentationDokument17 SeitenEks Energy PresentationFrancisco Javier Marín SuárezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 - Metode ElektrogravimetriDokument19 Seiten04 - Metode ElektrogravimetriNurul Aulia HusainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainable Performance in The Construction Industry: CEMEX STUDY 18/5/10 14:34 Page 1Dokument4 SeitenSustainable Performance in The Construction Industry: CEMEX STUDY 18/5/10 14:34 Page 1Nikhil SatavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Wire Earth Return (SWER) : Course Instructor: Peter ArmstrongDokument16 SeitenSingle Wire Earth Return (SWER) : Course Instructor: Peter ArmstrongnambaccucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqueous LiCl CaCl2 Solution Props UnlockedDokument31 SeitenAqueous LiCl CaCl2 Solution Props UnlockedExal Eduardo Cabrera VelazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reclosers: Form 6 Microprocessor-Based Pole Mount Recloser Control Installation and Operation InstructionsDokument48 SeitenReclosers: Form 6 Microprocessor-Based Pole Mount Recloser Control Installation and Operation InstructionsTrịnh Huy ĐảmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substrate Integrated Waveguide Microwave Encyclopedia Microwaves101Dokument5 SeitenSubstrate Integrated Waveguide Microwave Encyclopedia Microwaves101Dr-Pritam Singh BakariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - BoilerDokument17 SeitenCase Study - BoilerMohd Shafuaaz KassimNoch keine Bewertungen