Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 13: Reproduction and Growth: Panitia Biology Negeri Kelantan 2007
Hochgeladen von
Syllvia SunnivaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 13: Reproduction and Growth: Panitia Biology Negeri Kelantan 2007
Hochgeladen von
Syllvia SunnivaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
CHAPTER 13 : REPRODUCTION AND GROWTH Multiple Choice Question. For Question 1 to 40, each question is followed by four alternative options A, B, C and D. Choose one correct answer for each question and blacken the corresponding space in your objective answer. . 4.1 1. Gamete Formation. Which of the statements below about reproduction is true. A. B. C. D. 2. Sexual reproduction gives rise to new individuals that are identical to their parents. asexual reproduction in invertebrates occurs only by binary fission. Sexual reproduction produces genetic variations in the offspring. Budding and fragmentation are two types of sexual reproduction.
The formation of the male gametes takes place in A. B. C. D. Ovary Testes Sperm Ovum
3.
The human ovum cell l. ll. lll. lV. A. B. C. D. is formed in the ovary is produced by meiosis Is a diploid cell Fuse with a sperm to form a zygote l, ll and lll l, ll and lV ll, lll and lV l, ll, lll and lV
13-1
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
4.
In spermatogenesis, the primordial germ cells undergo mitotic division to form A. B. C. D. Spermatogonia Sperm Diploid spermatogonia Haploid spermatogonia
5.
After ovulation, the follicle cells that are left in the ovary form a structure called A. B. C. D. Follicle Corpus luteum Ovum Oocyte
4.2
Role Of Hormones In The Menstrual Cycle Hormone X
DIAGRAM 13.1 6. Diagram 13.1 shows the different levels of hormone X during a menstrual cycle. What is hormone X. A. B. C. D. Oestrogen Progesterone Luteinizing hormone Follicle stimulating hormone.
13-2
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
7.
Which of the following statements about menstrual cycle is not true A. B. C. D. In most female, a typical menstrual cycle takes about 28 days. During the menstrual cycle, a primary follicle develops to form a graafian follicle. The corpus luteum in the ovary releases progesterone to stimulates the growth and development of blood vessels in the endometrium Follicle stimulating hormone, luteinising hormone, oestrogen and progesterone are the hormones that control the menstrual cycle.
DIAGRAM 13.2 8. Diagram 13.2 shows the changes in uterine lining in a women. Which of the following occurs at phase Z. A. B. C. D. 9. The women have miscarriage Endometrium is repaired and thickens. Many blood vessels develop in uterine lining. Menstruation occurs
Ovulation is a process where A. B. C. D. The excess blood and tissue of the endometrium leave the uterus through the vagina. The secondary oocyte is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube. Two nuclei fuse to produce a zygote. The blastocyst attaches to the endometrium of the uterus.
13-3
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
10.
Menopause is a normal change in a womens life when her menstruation stops. What is the symptoms of menopause. l. ll. lll. lV. A. B. C. D. Sleeping problems Osteoporosis Mood changes. Abdominal pain. l, ll and lll l, ll and lV ll, lll and lV l, lll and lV
4.3 11.
Early Development Of A Zygote In Humans Which of the following shows the development of the human zygote in the right sequence? A. B. C. D. Zygote morula blastocyst embryo Zygote morula embryo blastocyst Zygote blastocyst morula embryo Zygote embryo morula blastocyst
P Q
DIAGRAM 13.3 12. Diagram 13.3 represents part of the female reproductive system. Where does implantation occurs? A. B. C. D. P Q R S
13-4
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
13.
Which of the following shows the correct sequence of a sperm entering the human female reproductive system. A. B. C. D. Cervix vagina fallopian tube uterus Vagina cervix fallopian tube uterus Cervix vagina uterus fallopian tube Vagina cervix uterus fallopian tube
14.
Two eggs released from an ovary and fertilized by two different sperms will form A. B. C. D. Identical twins Fraternal twins Artificial twins Similar twins.
15.
All of the substances below can pass from the mother to the foetus through placenta except A. B. C. D. Mineral salts Amino acids Nitrogenous waste Red blood cell.
4.4 16.
Contributions Of Science And Technology To Human Reproduction. The statements below refers to a technique used to overcome infertility. For women who have blocked or damaged fallopian tube. Fertilisation takes place in laboratory glassware rather than inside the body. Embryos are injected in the womens uterus to allow implantation to occur. In vitro fertilization injection of FSH Artificial insemination Vasectomy.
The technique used is A. B. C. D.
13-5
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
17.
Infertility is caused by A. B. C. D. the practice of family planning Low ovum count. Damage in the female fallopian tube. Marriage at a late age.
18.
Sexually transmitted diseases is a disease that A. B. C. D. Is spread from one person to another during sexual contact. Cannot be avoided Is only caused by viruses. Cannot be treated with antibiotics.
19. l.
Sexually transmitted diseases include Syphilis Gonorrhea Hepatitis B AIDS l and ll l, ll and lll l, ll and lV l, ll, lll and lV ll. lll. lV. A. B. C. D.
20.
Below are methods used in family planning, except A. B. C. D. Intrauterine divice Oral contraceptive pills. Artificial insemination Ligation
13-6
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
4.5 : The Concept Of Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plant 21. After fertilization, an ovule will become A B C D 22. Seed Fruit Ovary Embryo sac
Diagram 13.4 shows the cross section of an ovule. Which nucleus will fuse with the male nucleus to form a zygote.
J K L M
DIAGRAM 13.4 A B C D 23. J K L M
The end products of double fertilization in plants are.. A B C D A triploid zygote and a triploid nucleus. A triploid zygote and a diploid nucleus. A diploid zygote and a diploid nucleus A diploid zygote and a triploid nucleus.
13-7
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
24.
The embryo of the seedling obtain its food from the.. I II III IV A B C D Radicle Plumule Cotyledon Endosperm I and II only I and IV only III and IV only II, III, and IV only
25.
Which part of the flower does meiosis takes place ? A B C D Anther Sepal Style Petal
4.6 26.
Growth In Multicellular Organisms Which of the following statements are true about growth? I II III IV A B C D It is an irreversible process. It involves an increase in size. There is an increase in organ functions There is an increase in the number of cells II and IV only I, II and III only I, III and IV only I,II,III and IV
27.
Which of the following shows the correct sequence of events in growth? A B C D Cell enlargement, cell division,cell differentiation Cell division,cell differentiation, cell enlargement Cell division,cell enlargement,cell differentiation Cell differentiation,cell enlargement, cell division
13-8
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
28.
The diagram shows a longitudinal section of a root.
DIAGRAM 13.5 The function of cell in region R is to A B C D 29. absorb water divide actively repair damaged cells develop into xylem and phloem
A cell experience the following changes during growth:
A. B. C. D. 30.
Becomes a mature cell Changes gradually to form a specific cell with certain functions Cell division stage Cell differentiation stage Cell maturation stage Cell elongation stage
This stage of changes is called
Which process contributes to growth in multicellular organism A. B. C. D. Meiosis Mitosis Degeneration Regeneration
13-9
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
4.7 : The Growth Curve The graph show the change in weight of a cat with time. Based on the graph, answer questions 31 and 32
weight
Time
31. What is the shape of this graph A. B. C. D. 32. Exponential Linear Sigmoid J
What happen at stage R A. B. C. D. A growth rate is slow, only involved the cell division and cell elongation occurs Growth rate slow. Most of the cell have matured and cell division is to replaced dead and worn out cells Growth rate is zero but cell division still occurs Growth rate increases, cell undergoes vigorous cell division and elongation
33.
The process by which insects and other invertebrates change the exoskeleton is A. B. C. D. Ecdysis Growth Primary growth Secondry growth.
13-10
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
Length of body (mm)
Time (day)
DIAGRAM 13.6 34. Which of the following organism has a growth curve as shown in the A. B. C. D. 35. Earthworm Amoeba Cockroach Coconut tree diagram above
Which of the following is the most accurate parameter of growth A. B. C. D. Height Volume Fresh mass Dry mass
13-11
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
4.8: 36.
Primary And Secondary Growth In Plants During secondary growth in plant, which tissues gives rise to secondary phloem and xylem A. B. C. D. Apical meristem Vascular cambium Cork Cork cambium
37.
The first stage in secondary growth is the formation of the A. B. C. D. Cambium ring Xylem tissue Phloem tissue Cortex tissue
W X Y Z
DIAGRAM 13.7 38. The diagram shows the cross section of the dicotyledonous stem. Which part develop into secondary tissue after the plant undergoes secondary growth A. B. C. D. W and X W and Z X and Y Y and Z
13-12
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
39.
Which of the followings are found in the zone of cell differentiation of a shoot tip I. II. III. IV. A B C D Phloem Xylem Sclerencyma Cells with large vacuoles II and IV only I, II and IV only I, II and III only I, II, III and IV
40.
Wood is actually A. B. C. D. Cambium Cortex Secondary Phloem Secondary xylem
13-13
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
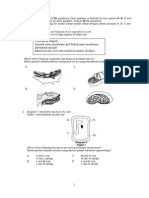
Structured Items Answer all questions. Write your answer in the speces provided in the question paper. 4.1 Gamete Formation 1. Diagram 13.8 shows a schematic diagram of sperm and ovum formation
DIAGRAM 13.8 (a) Name process A, B,C, D, and E Process A: Process B: Process C:
13-14
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
Process D: Process E: [5 marks] (b) Where does the process of sperm formation occurs? [1 mark] (c) If one of the sperms fertilizes an ovum, what will be formed? [1 mark] (d) Give two differences between sperm formation and ovum formation.
[2 marks] (e) Explain how does the structure of a human sperm helps its function.
[3 marks]
13-15
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
4.2 2.
Role Of Hormones In The Menstrual Cycle The graph below shows the changes in the hormone levels of four types of hormones which control the menstrual cycle .
Hormone levels/ Arbitrary units
P Q R S
Time/days
(a)
What is menstrual cycle?
[1 mark] (b) Name the hormones labeled P: Q: R: S: [4 marks] (c) State two functions of follicle stimulating hormone in a menstrual cycle.
[2 marks]
13-16
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
(d)
Give two symptoms of premenstrual syndrome.
[2 marks] (e) Explain the relationship between the level of progesterone hormone and the thickness of the uterus wall/endometrium.
[3 marks] 4.3 Early Development Of A Zygote In Humans
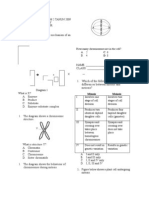
DIAGRAM 13.9 3. Diagram (a) In the diagram, label the structures: l. Secondary oocyte ll. Blastocyst lll. Zygote lV. Uterus [4 marks] (b) Implantation of blastocyst requires endometrium to be thickened with a rich supply of blood vessel. What hormone is needed for this action. 13.9 shows the development of an ovum in the female reproductive system after fertilization.
13-17
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
[1 mark] (c) In the fallopion tube, the zygote undergoes a series of cell division to produce a solid ball cells called [1 mark] (d) If there is no sperm in the fallopian tube when ovulation occurs, what will happen to the ovum.
[3 marks] (e) The embryo in diagram splits into two identical embryos. What types of twin will be formed. Explain your answer.
[3 marks]
4.4
Contributions Of Science And Technology To Human Reproduction. Stimulating the ovaries
13-18
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
Extraction of the egg
Incubation and fertilisation
Transfer of embryo into the uterus 4. The sequence above shows one of the technique used to overcome infertility. (a) Name the technique used. [1 mark] (b) When is this technique used? [1 mark] (c) Where does fertilization occurs in the technique mentioned in (a). [1 mark] (d) Name the baby born by this technique [1 mark] (e) When using this technique, the woman receiving the embryo is usually the woman who donated the eggs. In cases when a woman cannot undergoes pregnancy, what should be done to the embryo?
[2 marks] (f) (i) If the sperm counts of a husband is too low, suggests a technique that can be carried out to overcome this impotency problem. [1 mark] (ii) Describe the technique mentioned in (f)(i).
13-19
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
[ 3 marks] 4.5 : 5. The Concept Of Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plant Diagram 13.10 shows a pollen grain before it is transferred to the stigma.
DIAGRAM 13.10 (a) Name the nucleus in diagram 13.10 [1 mark] The pollen grain is transferred to the stigma of a flower as in a pollination process. It is then left for one day. Diagram 13.11 shows part of the pollen grain obtained.
DIAGRAM 13.11 (b) (i) Name structure X ?
13-20
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
[1 mark] (ii) Name the nucleus in the space provided in diagram 13.11. [1 mark] (iii). Name the process that occur in the pollen grain as shown in diagram 13.11 ? [1 mark] (iv). Name the solution that stimulates the process in (b).(iii)? [1 mark] (c) (i). In diagram 13.12, draw the growth and the development of structure X until it reaches the embryo sac.
DIAGRAM 13.12 [1 mark] (ii) Name the process that takes place when the nucleus in structure X reaches the embryo sac. [ 1 mark] (iii). Explain the process mentioned in (c ). ii ?
13-21
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
[2 marks] (d) Describe briefly the development of fruits and seeds in a plant
[ 3 marks ]
4.6 : 6.
Growth In Multicellular Organisms In an experiment to study the growth pattern of an insect, the length of the insects body is measured at certain time intervals. The results obtained are recorded in Table 1 Growth stage Stage 0 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 Adult Time interval of each stage Body length (mm) (days) 150 15 20 20 15 50 250 TABLE 1 (a). Based on table 1 , draw a graph in the space provided to show the growth of the insect. Label the growth stages. [3 marks] 5 25 50 100 130 160 200
13-22
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
13-23
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
(b).
What is the shape of the insects growth curve? [1 mark]
(c).
From the graph drawn, explain the changes in the body length change at the interval of 0 to 150 days?
[2 marks] (d). What is the name given to the insect offspring at stage 1-5? [1 mark] (e). Name the process that the insect undergoes to enable the growth process to occur. [1 mark] (f). Explain how this process increases the body size.
[3 marks]
13-24
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
4.7 : 7.
The Growth Curve Diagram 13.13(a) shows the growth curve of a rat and diagram 13. 13(b) shows the growth curve of a cockroach.
Body mass (g) Exponential phase
Maturity phase
Length body (cm)
Phase 1
Phase 2
Phase 3
Time (weeks)
Time (days)
(a) DIAGRAM 13.13 (a)
(b)
State the shape of the growth curves shown in diagram 13.13(a) and 13.13(b).
13-25
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
Growth curve of a rat
: [2 marks]
Growth curve of a cockroach : (b) (i) State phase 1 labeled in diagram 13. 13(a). [1 mark] (ii) describe the growth that occurs in phase I
[2 marks] (c) (i) On figure 13.13(a), mark and label two more phases in the growth curve. [1 mark] (ii) Explain the processes that take place in each phase you have labeled.
[2 marks] (d) (i) What is represented by X in figure 13.13(b)? [1 mark] (ii) Describe what occurs during X.
[2 marks]
13-26
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
4.8: 8.
Primary And Secondary Growth In Plants Diagram 13.14 shows the longitudinal section of the tip of a dicotyledon shoot and its stem.
DIAGRAM 13.14 (a) Explain the importance of the tissue labeled A.
[2 marks]
13-27
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
(b)
State the type of growth at the tip of the shoot and at the stem. State its significant changes. (i) At the shoot Type of growth Significant change (ii) At the stem Type of growth Significant change : : [4 marks] : :
(c)
(i)
Name the tissues involved in the growth of stem
[2 marks] (ii) Explain the importance of the type of growth in a stem to a plant
[2 marks] (d) Base on diagram 13.14 draw and label a diagram to show the cross section of stem through C. [3 marks]
13-28
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
Essay Items Answer all questions 4.1 1. Gamete Formation.
Oogenesis is the process of ovum formation in the ovary
Explain how oogenesis occurs in mammals. [10 marks] 4.2 2. Role Of Hormones In The Menstrual Cycle The menstrual cycle is controlled by a complex interaction of hormones. State all the hormone involved and its function. [10 marks] 4.3 3. Millions of sperms enter the uterus but a few reach the upper part of the fallopian tube and only one sperm fertilizes the ovum. Explain the formation of a zygote and describe the stages in the development of a zygote before implantation occurs. Early Development Of A Zygote In Humans
13-29
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
[10 marks] 4.4 4. Contributions Of Science And Technology To Human Reproduction. (a) A woman has her uterus removed. If she wants to have a baby with her husband, suggest what she can do. Briefly describe the method suggested. [7 marks] (b) A couple decides to wait for a few years before starting a family. Suggest birth control methods that can be used in a family planning programme. [3 marks] 4.5 : 5, The Concept Of Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plant (a) Diagram 13.15 shows an embryo sac of a plant.
3 antipodal cells
2 polar nuclei Egg cell 2 synergid cells
DIAGRAM 13.15 Describe how an embryo sac is form in the ovule of a flowering plant. [10 marks] (b) Diagram 13.16 shows a longitudinal section of the carpel of a flower during fertilization.
13-30
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
DIAGRAM 13.15 DIAGRAM 13.16 Describe how the process of fertilization is carried out when the male gametes reach the emryo sac. [6marks] (c) In what ways is fertilization in a plant similar to and different from fertilization in a mammal? [6 marks] 4.6 ; 6. Growth In Multicellular Organisms (a) (b) Define growth. [2 marks] Describe the three stage of growth. [10 marks] 4.7 : The Growth Curve 7. Diagram 13.17 shows the growth curve of a maize plant, using dry mass as a parameter of growth
Dry mass of plant (g)
13-31
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
C C A B
DIAGRAM 13.17 (a) (b) (c) Explain how the dry mass of maize plants can be measured over a period of time.
Time (day)
[6 marks] [11 marks]
Explain the growth curve of maize plants as shown in diagram 13.17 Explain why dry mass is the most accurate parameter of growth. [3 marks]
4.8: 8.
Primary And Secondary Growth In Plants
In plants, the growth process occurs at the shoot end, root end and stem
(a)
With the help of a diagram, describe the growth process that occurs at the plants root end. [10 marks]
(b)
The dicotyledonous stem carries out secondary growth. What is the purpose of secondary growth in plants? By using your knowledge in biology, write a report to show how the objective of secondary growth is achieved. [10 marks]
13-32
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
PANITIA BIOLOGY NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
13-33
BIOLOGY QUESTION BANK
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MCQs-Bank Obestetrics-Dr-Ahmed-Walid - Proffesor of Obs & Gyn - Benha Faculty of MedicineDokument140 SeitenMCQs-Bank Obestetrics-Dr-Ahmed-Walid - Proffesor of Obs & Gyn - Benha Faculty of MedicineAhmed AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The NKTI Medical Laboratory: National Kidney and Transplant InstituteDokument1 SeiteThe NKTI Medical Laboratory: National Kidney and Transplant InstituteMalagant EscuderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY PAPER 1 KEY POINTSDokument25 SeitenBIOLOGY PAPER 1 KEY POINTSNur HidayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam2 98Dokument8 SeitenExam2 98ramadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Biology Holiday HomeworkDokument8 SeitenChapter 3 Biology Holiday HomeworkAayush RastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Questions 1 Reproduction Development 2012Dokument18 SeitenPractice Questions 1 Reproduction Development 2012John gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 5 - Q2 PT 2022-2023Dokument6 SeitenScience 5 - Q2 PT 2022-2023Mary Grace V. CanlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions: ReproductionDokument12 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions: ReproductionJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Human Reproduction QuestionareDokument4 SeitenHuman Reproduction QuestionarePRATAP SEEMTOSH SINGH100% (1)
- Community Post 7 - Human ReproductionDokument26 SeitenCommunity Post 7 - Human Reproductionagrimg80Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Biology Olympiad Theory Exam #2Dokument24 SeitenInternational Biology Olympiad Theory Exam #2Mahta HadaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50-Question Biology Exam with Detailed AnswersDokument26 Seiten50-Question Biology Exam with Detailed AnswersrhimalinyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 General Biology2 Q4 Module 1 Reproduction and Development. For PrintingDokument13 SeitenGrade 12 General Biology2 Q4 Module 1 Reproduction and Development. For Printingairamaymalicdem052Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Reaching The Age of Adolescence Objective QuestionsDokument10 SeitenCBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Reaching The Age of Adolescence Objective Questionsg c lallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Que Class 10Dokument20 SeitenRevision Que Class 10Naren KarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci.10 Weeks 1-3Dokument4 SeitenSci.10 Weeks 1-3Jaime CrispinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleDokument76 SeitenUnit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleBAYAN NADER YOSRI JABARI 22010404Noch keine Bewertungen
- Caraga Biology Test Reveals Cell ProcessesDokument13 SeitenCaraga Biology Test Reveals Cell ProcessesDearest NotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd QTR Multiple Choice Work Sheet BIO X LearnersDokument11 Seiten3rd QTR Multiple Choice Work Sheet BIO X LearnersIan DibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Reproduction TestsDokument3 SeitenHuman Reproduction TestsKunchaya PitayawongroekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9/MCQ/Answer SchemeDokument9 SeitenChapter 9/MCQ/Answer SchemeALIAH AYUNI AIMAN BINTI MOHAMED NIZAM MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmbryologyDokument4 SeitenEmbryologyHermann CHEMEUHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Microorganisms and human body systemsDokument13 SeitenMicroorganisms and human body systemsBARAATHY SRI A/P UTHRAPATHY Moe100% (1)
- Section A-Objective Type (MCQ & AR Questions) : CHAPTER - 3 Human ReproductionDokument5 SeitenSection A-Objective Type (MCQ & AR Questions) : CHAPTER - 3 Human ReproductionnbmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 EmbryologyDokument13 Seiten2 EmbryologyManisanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Biology Topics from 2004-2007 SPM ExamsDokument19 SeitenAnalysis of Biology Topics from 2004-2007 SPM ExamsqwertyuiopssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nagyantok High School Science 10 Third Quarter Periodical TestDokument3 SeitenNagyantok High School Science 10 Third Quarter Periodical TestPhoebe Sudweste QuitanegNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cabalan - Sas-Lecture #23Dokument8 SeitenCabalan - Sas-Lecture #23kierstyn cabalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet - Reaching the Age of AdolescenceDokument6 SeitenWorksheet - Reaching the Age of AdolescenceitsansafNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 LFSC Composite Revision Document - FinalDokument177 Seiten2023 LFSC Composite Revision Document - Finalntombelaqiniso62Noch keine Bewertungen
- Xavier University Third Bimonthly Exam QuestionsDokument7 SeitenXavier University Third Bimonthly Exam QuestionsSam TagardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryology MCQDokument10 SeitenEmbryology MCQTofik MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short questions on menstruation, reproduction and biologyDokument4 SeitenShort questions on menstruation, reproduction and biologyVivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 - First Summative TestDokument3 SeitenQ2 - First Summative TestMilagros ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- TQ Science10 Q3 ST1Dokument3 SeitenTQ Science10 Q3 ST1mae cudalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1955_fdocDokument5 Seiten1955_fdoctyleryawh2072Noch keine Bewertungen
- Childhood Voyages in Development 5Th Edition Rathus Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument36 SeitenChildhood Voyages in Development 5Th Edition Rathus Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkelly.mack540100% (12)
- TQ q3 Science 10 Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaDokument8 SeitenTQ q3 Science 10 Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaKhim YabesNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFDokument12 SeitenHow Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFSomik JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1Dokument10 SeitenBIOLOGY II FBI1224 2022 Question Paper 1zoulzz0903Noch keine Bewertungen
- Female and Male Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument12 SeitenFemale and Male Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyVân vui vẻNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction 2024 PDFDokument1 SeiteReproduction 2024 PDFKhan MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 1 BIO XDokument2 SeitenWorksheet 1 BIO XJungli GodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aga Khan University Examination Board Higher Secondary School Certificate Class Xii Examination MAY 2015 Biology Paper I Time: 40 Minutes Marks: 30Dokument8 SeitenAga Khan University Examination Board Higher Secondary School Certificate Class Xii Examination MAY 2015 Biology Paper I Time: 40 Minutes Marks: 30AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives Code Percenta Ge No. of Items Item Placement 40% 10 1-10Dokument4 SeitenObjectives Code Percenta Ge No. of Items Item Placement 40% 10 1-10Analyn CalaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Bio HL M23 Paper 1Dokument16 SeitenIB Bio HL M23 Paper 1Lynn BabakrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIDokument33 SeitenReproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIlhayes1234100% (5)
- Class X Science Term 2 ReproductionDokument11 SeitenClass X Science Term 2 ReproductionMokshita JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology End-Of-Course Practice ExamDokument23 SeitenBiology End-Of-Course Practice ExamMacner JobeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test From EmbryologyDokument25 SeitenTest From EmbryologyTreasure ChinenyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives Code Percenta Ge No. of Items Item Placement 40% 10 1-10Dokument4 SeitenObjectives Code Percenta Ge No. of Items Item Placement 40% 10 1-10Jojo AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- USABO 18 Semifinal Final1 Wo AnsDokument39 SeitenUSABO 18 Semifinal Final1 Wo AnsShubh ChawdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Quarter Exam Regular ReviewerDokument5 Seiten4th Quarter Exam Regular ReviewerRodel RectoNoch keine Bewertungen
- True / False QuestionsDokument23 SeitenTrue / False QuestionsShawnetz CoppNoch keine Bewertungen
- P2 2019 SMK Methodist PDFDokument11 SeitenP2 2019 SMK Methodist PDFBryanLeeChienYungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penilaian Kurikulum 2 Tahun 2009Dokument6 SeitenPenilaian Kurikulum 2 Tahun 2009yantraksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryology Review for Dr. ElHodibyDokument10 SeitenEmbryology Review for Dr. ElHodibyw yNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regents Cells and Human BodyDokument8 SeitenRegents Cells and Human Bodyapi-303120399Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio7 4Dokument17 SeitenBio7 4Nomap makNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In HumansVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Reproduction In HumansBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (2)
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsVon EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- TARIKH: 20 MEI 2019 Hari: Isnin Cuti Umum Sempena Hari WesakDokument1 SeiteTARIKH: 20 MEI 2019 Hari: Isnin Cuti Umum Sempena Hari WesakSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay Title: FriendsDokument3 SeitenEssay Title: FriendsSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly schedule template for September 5-11Dokument1 SeiteWeekly schedule template for September 5-11Syllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule PDFDokument1 SeiteSchedule PDFSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Parlimentary DebateDokument2 SeitenTopic Parlimentary DebateSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Informal Letters For SPMDokument5 SeitenInformal Letters For SPMGomala Sukumaran67% (6)
- Irregular Verb Past Tense Word SearchDokument2 SeitenIrregular Verb Past Tense Word SearchSyllvia Sunniva42% (12)
- Teacher Henley Liew Yun Ye: RehatDokument31 SeitenTeacher Henley Liew Yun Ye: RehatSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jobs Words Search: Chef Programmer Firefighter Musician Nurse Reporter Soldier WaiterDokument1 SeiteJobs Words Search: Chef Programmer Firefighter Musician Nurse Reporter Soldier WaiterSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Scheme Perkampungan PMRDokument7 SeitenAnswer Scheme Perkampungan PMRSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2q 2012 HandoutDokument18 Seiten2q 2012 HandoutKholan Mubarak AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sudoku Variations: Math GamesDokument16 SeitenSudoku Variations: Math GamesSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Beluran Ii. Ujian Bulan Ogos 2012 Kimia Tingkatan 4Dokument4 SeitenSMK Beluran Ii. Ujian Bulan Ogos 2012 Kimia Tingkatan 4Syllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Can Television Be Good For ChildrenDokument22 SeitenCan Television Be Good For Childrencharusat100% (1)
- Band3 DT2Dokument2 SeitenBand3 DT2Syllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Plan (Table of Specifications) TemplateDokument1 SeiteTest Plan (Table of Specifications) TemplateLeo TejanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student EDITION VariationDokument10 SeitenStudent EDITION VariationChepora NorieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Solutions Chapter 07Dokument15 SeitenNotes Solutions Chapter 07Syllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sudoku Variations: Math GamesDokument16 SeitenSudoku Variations: Math GamesSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 14 Inheritance StudentDokument13 SeitenCH 14 Inheritance StudentSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Parlimentary DebateDokument2 SeitenTopic Parlimentary DebateSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student EDITION VariationDokument10 SeitenStudent EDITION VariationChepora NorieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 2 Role of Human Nervous SystemDokument41 Seiten3 2 Role of Human Nervous SystemSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Fighter S Lines PoemDokument14 SeitenA Fighter S Lines PoemIva SivarajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EL Sec Yearly Scheme of Work Form 1 Sample 1 2010Dokument6 SeitenEL Sec Yearly Scheme of Work Form 1 Sample 1 2010ZILAROVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form 4: Cell Structure and FunctionDokument4 SeitenBiology Form 4: Cell Structure and FunctionSyllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dale Experience Cone Model (1969)Dokument2 SeitenDale Experience Cone Model (1969)Syllvia SunnivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Hydroponic Systems and How They WorkDokument13 SeitenBasic Hydroponic Systems and How They WorkJaime HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin D in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis and Its Relationship With Thyroid Function and Inflammatory StatusDokument9 SeitenVitamin D in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis and Its Relationship With Thyroid Function and Inflammatory StatusMedicina UNIDEP T3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Processing Food-Related Toxicants: A Review: Critical Reviews in Food Science and NutritionDokument19 SeitenThermal Processing Food-Related Toxicants: A Review: Critical Reviews in Food Science and NutritionRIFQI FAYYADH ANSARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quirino State University Self-Paced Module on Genetic Trait ModificationsDokument5 SeitenQuirino State University Self-Paced Module on Genetic Trait ModificationsNel McMahon Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology List of BooksDokument3 SeitenMicrobiology List of BooksMoazAdelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Neural Networks For Secondary Structure PredictionDokument21 SeitenArtificial Neural Networks For Secondary Structure PredictionKenen BhandhaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hurdle TechnologyDokument5 SeitenHurdle TechnologyDavid UribeNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Methods in Molecular Medicine) S. Moira Brown, Alasdair R. MacLean - Herpes Simplex Virus Protocols (1998, Humana Press)Dokument406 Seiten(Methods in Molecular Medicine) S. Moira Brown, Alasdair R. MacLean - Herpes Simplex Virus Protocols (1998, Humana Press)Rares TautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rolling NAJSPTDokument13 SeitenRolling NAJSPTDiego LacerdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Neuropsychology of EmotionDokument532 SeitenThe Neuropsychology of EmotionLarisa Ev-a Elena95% (43)
- 2nd PERIODICAL EXAMDokument18 Seiten2nd PERIODICAL EXAMJhuanna Marie CabalteraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Races and Racial ClassificationDokument6 SeitenHuman Races and Racial ClassificationanujNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 BI 602Dokument6 SeitenAssignment 1 BI 602Eneah NaicavacavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthy Weekly Meal Plan Highlights Biomolecule NutritionDokument4 SeitenHealthy Weekly Meal Plan Highlights Biomolecule NutritionAndrie DatulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sticky Trap Monitoring of Insect Pests: Steve H. DreistadtDokument8 SeitenSticky Trap Monitoring of Insect Pests: Steve H. DreistadtBryan AbarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growing Wild MushroomsDokument50 SeitenGrowing Wild Mushroomsviki90% (10)
- Colposcopy, Cervical Screening, and HPV: A Guide to Prevention and ManagementDokument155 SeitenColposcopy, Cervical Screening, and HPV: A Guide to Prevention and ManagementAnnca RoXanna100% (1)
- Trigger Point Therapy Routine For TMJ Massage Techniques To Unlock Your TMJ PDFDokument49 SeitenTrigger Point Therapy Routine For TMJ Massage Techniques To Unlock Your TMJ PDFMilijana D. Delević40% (5)
- Keller & Schoenfeld (1950) - Principles of PsychologyDokument456 SeitenKeller & Schoenfeld (1950) - Principles of PsychologyPablo StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenic FungiDokument65 SeitenPathogenic FungiTamara ElyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Conceptual Framework of Consumer Food Choice Behaviour: CEFAGE-UE Working Paper 2009/06Dokument26 SeitenA Conceptual Framework of Consumer Food Choice Behaviour: CEFAGE-UE Working Paper 2009/06Krishnendu Kizhakedathu SudhakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06-Reframing & Logical LevelsDokument9 Seiten06-Reframing & Logical LevelsJonathan100% (1)
- Modeling mass transfer in fluidized bedsDokument5 SeitenModeling mass transfer in fluidized bedsSmrutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lionex LIOFeronTB LTBIDokument2 SeitenLionex LIOFeronTB LTBIBilgi KurumsalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wbi15 01 Que 20231024Dokument36 SeitenWbi15 01 Que 20231024MuqtasidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timetable LECTURESDokument4 SeitenTimetable LECTURESRebeccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiology Ebook Notes PDFDokument26 SeitenCardiology Ebook Notes PDFsugisweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 Word Puzzle 2023Dokument2 SeitenYear 5 Word Puzzle 2023SJK (CINA) CHUNG WAH-CM4 KPM-SK-PKPNoch keine Bewertungen