Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture 1: Introduction To Immunology
Hochgeladen von
Mohit ModyOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture 1: Introduction To Immunology
Hochgeladen von
Mohit ModyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
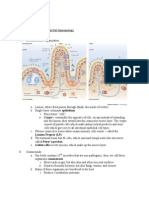
Lecture 1: Introduction to Immunology 1. The first thing on the page is the Hematopoiesis chart, know it. 2.
The immune system is split up into innate and adaptive immunity. a. Innate immunity i. Rapid protection ii. No memory or specificity 1. Use a primitive receptor unlike adaptive immunity iii. Two principle cell types 1. Phagocytes (macrophages and neutrophils) 2. Natural Killer (NK) cells iv. Complement system b. Adaptive immunity i. Takes longer to respond ii. Has memory and specificity 1. Lymphocytes have restricted recognition a. They can only recognize one antigen because of their unique epitope. b. Once the epitope recognizes the antigen it is imperative that it undergoes clonal expansion. 3. The adaptive immune system must discriminate self from non-self. This is known as tolerance. a. Tolerance can occur in two areas i. Central occurs during the development of lymphocytes. ii. Peripheral occurs outside the tissue of development. b. When tolerance is lost it leads to autoimmune disorders. The body recognizes self-antigen as foreign. c. Tolerance induction is the process of deleting or inactivating cells that express receptors that recognize self. 4. The immune system is divided not only by innate and adaptive but also upon where lymphocytes develop. a. Primary lymphoid tissue i. Here lymphocytes develop ii. Two examples are the bone marrow and thymus b. Secondary lymphoid tissue i. Here lymphocytes are activated ii. Some examples are the lymph nodes, tonsils and adenoids, spleen, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. 5. Primary lymphoid tissue: Bone marrow a. Contains self-renewing pluripotent stem cells that replace a large variety of blood cells (eosinophils, basophils, erythrocytes, and platelets) using hematopoeis. i. To see the molecules that affect bone marrow see the chart b. Site of B cell development and maturation. i. Occurs prior to antigen exposure, referred to as antigenindependent B cell maturation. 6. Primary lymphoid tissue: Thymus
a. Site of T cell maturation b. Undergoes tolerance induction but with a special name i. Death by neglect ii. Negative selection iii. Both are used to inactivate/destroy cells with self-recognizing or useless receptors. c. After the initial selection cells that have been positively selected (i.e. not destroyed) undergo lineage commitment. i. Lineage commitment is the process of changing phenotype. Tcells can become either: 1. CD4 2. CD8 d. Once T-cells migrate from the cortex to the medulla they undergo a second screening process. 7. Secondary lymphoid tissue: Lymph nodes a. The outer cortex of a lymph node contains follicles. These can be either primary or secondary depending on whether they have germinal centers. i. Primary contain mature resting B cells and no germinal centers ii. Secondary contain germinal centers and antigen-activated Bcells. 8. Secondary lymphoid tissue: Spleen a. Contains red and white pulp i. White pulp contains majority of lymphoid cells b. Periarterial lymphatic sheath (PALS) is the predominant T-cell region 9. Secondary Lymphoid tissue: Mucosa-Associated-Lymphoid-Tissue (MALT) a. General term for the unencapsulated lymphoid tissue present underlying the mucosal areas. i. (G)astrointestinal (ALT), (B)ronchus (ALT), etc. b. In some areas these areas are organized i. Peyers patches organized follicles present in GALT ii. Microbes enter MALT and are presented to M-cells 10. There is a lot of Histology review in this lecture that is beyond the scope of what youre going to be tested on. While it may be interesting dont get bogged down in it. 11. Soluble mediators of the immune system a. Cytokines and Chemokines i. Cytokines are small peptides secreted by activated leukocytes ii. Chemokines are chemoattractants. They attract different kind of lymphocytes. 1. Like Yogi bear to a pie in the woods b. Antibodies i. Also known as Immunoglobulins (Igs) ii. Contains an antigen binding site (Fb) and a site that carries out biological activity (Fc)
iii. Five Immunoglobuins 1. IgA, IgG, IgM, IgE, IgD iv. B-cells encounter antigen and for plasma cells that secrete Igs c. Complement i. A family of proteins used to facilitate microorganism elimination ii. You will learn these in more detail in another lecture 12. Activators of lymphocytes a. Monoclonal activate a single clone b. Polyclonal activate most or all clones c. Oligoclonal activate some clones d. Carrier effect: When a small molecule (hapten) couples with a large protein (carrier) to form an immunogenic compound.
Dont forget those synonyms when you come across them! CD4 T cells = Helper T cells CD8 T cells = pCTL/CTL = Cytotoxic T-Cells/Lymphoctytes
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CH 15 PT 1Dokument28 SeitenCH 15 PT 1Kathleen Anne JoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVB Immune SystemDokument11 SeitenIVB Immune Systembarathkumar amidalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A.Ince - Lab 3 (Immunology Review Quiz)Dokument8 SeitenA.Ince - Lab 3 (Immunology Review Quiz)ameeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune response worksheetDokument4 SeitenImmune response worksheetlina atyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune SystemDokument21 SeitenImmune SystemNarasimha MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11Dokument12 SeitenChapter 11ingridvirginia2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- III. Immunology Review: M L A B 2 4 3 1 1 7Dokument13 SeitenIII. Immunology Review: M L A B 2 4 3 1 1 7Gianna SablanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesDokument70 SeitenLecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesJoe JoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology OutlineDokument43 SeitenImmunology OutlinekudosforkimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune System Part IDokument4 SeitenImmune System Part IljayNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMMUNITYDokument2 SeitenIMMUNITYJuana IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Immune Response (2) ElyDokument7 SeitenWorksheet Immune Response (2) Elylina atyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 112: Care of Client With Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseDokument10 SeitenNCM 112: Care of Client With Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseNikitaCaitlynLeyaleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2: Cells of Innate ImmunityDokument3 SeitenLecture 2: Cells of Innate ImmunityMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cells of The Immune System: Aditya Gupta & Alok Singh S.Y.Bsc (Microbiology) V.E.S. CollegeDokument22 SeitenThe Cells of The Immune System: Aditya Gupta & Alok Singh S.Y.Bsc (Microbiology) V.E.S. CollegevesascNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ih Lec PrelimDokument24 SeitenIh Lec PrelimReann SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityDokument53 SeitenCells & Organs of The Immune System, Cellular ImmunityfrenchaticiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDokument2 SeitenChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Cell Activation StagesDokument2 SeitenB Cell Activation StagesMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 19 Notes - Mucosal ImmunityDokument5 SeitenLecture 19 Notes - Mucosal ImmunityAlbert Mao LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.2 Immunology Adaptive Immunity 17dec2021Dokument37 Seiten7.2 Immunology Adaptive Immunity 17dec20212023406162Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptive ImmunityDokument18 SeitenAdaptive Immunityandrewmaleto155Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoid Immune System OverviewDokument20 SeitenLymphoid Immune System OverviewJayanti Neogi SardarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lymphatic System HandoutDokument4 SeitenThe Lymphatic System HandoutLleana TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Gold Immunology NotesDokument11 SeitenDR - Gold Immunology NotesAaron PhuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunoSerology - Review Questions (Stevens)Dokument14 SeitenImmunoSerology - Review Questions (Stevens)LUALHATI VILLAS0% (1)
- The Immune System: Back To The BasicsDokument37 SeitenThe Immune System: Back To The BasicsHani GowaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ImmunologyDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To Immunologykaiyeol exoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1,2,3 y 4Dokument15 SeitenTopic 1,2,3 y 4Olaya De Dios HuertaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3: MHC and HLADokument2 SeitenLecture 3: MHC and HLAMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- L 4 Cellular Component of the Immune SystemDokument11 SeitenL 4 Cellular Component of the Immune SystemaugustongoviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organization of Immune SystemDokument44 SeitenOrganization of Immune SystemSaubie AslamiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunologyDokument9 SeitenImmunologyRamadhan Dwi AnggoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson # 13 - Specific Immune ResponseDokument7 SeitenLesson # 13 - Specific Immune ResponseSmith PennanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innate and Adaptive Immunity: Cells, Organs and FunctionsDokument17 SeitenInnate and Adaptive Immunity: Cells, Organs and FunctionsBasma RagabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is - StevensDokument49 SeitenIs - StevensALEXANDRA CALANOCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune OutlineDokument5 SeitenImmune OutlineMisterxy_Arep_3988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology and Serology SolutionDokument17 SeitenImmunology and Serology Solutionzakaria hossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the Complement System's Role in ImmunityDokument70 SeitenUnderstanding the Complement System's Role in ImmunitySarvesh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune OrgansDokument49 SeitenImmune OrgansdenyqueronoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3Dokument28 SeitenLecture 3ranaayy11gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunoSero CFU PracticeDokument16 SeitenImmunoSero CFU PracticeReizel GaasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Imunologi Dasar Fast TrackDokument23 SeitenTugas Imunologi Dasar Fast TrackAnditri WeningtyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 40-character title for this document on the immune system is:TITLEImmune System Defenses and Adaptive ImmunityDokument105 SeitenThe 40-character title for this document on the immune system is:TITLEImmune System Defenses and Adaptive ImmunityHåíthãm KhãtïßNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMMUNITYDokument23 SeitenIMMUNITYFlorence Lynn BaisacNoch keine Bewertungen
- WK10 AnswersDokument6 SeitenWK10 AnswersaskldhfdasjkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology Quiz: MHC, Antigens, Adaptive ImmunityDokument2 SeitenImmunology Quiz: MHC, Antigens, Adaptive ImmunityTiff VoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 BioDokument14 SeitenUnit 5 Bioiam SaveMeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Immune FunctionDokument13 SeitenAssessment of Immune FunctionNajmah Saaban100% (5)
- Immunology PDFDokument70 SeitenImmunology PDFstancy thomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Immunology Lecture 2Dokument53 SeitenClinical Immunology Lecture 2jibril channelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsDokument9 SeitenLeucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsKhant Si ThuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Outline - Intro, Healing and InflammationDokument4 SeitenStudent Outline - Intro, Healing and InflammationmoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology Questions QuizDokument28 SeitenHistology Questions QuizminervamoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immuno - Immunology QnADokument15 SeitenImmuno - Immunology QnANashrah HusnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuis Imun UTSDokument8 SeitenKuis Imun UTSichiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology Flash CardsDokument46 SeitenImmunology Flash CardsRickyNoviantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityVon EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisVon EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unified Quiz practice questions and answers explainedDokument16 SeitenUnified Quiz practice questions and answers explainedMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 11/12: Inflammation and Wrap UpDokument3 SeitenLecture 11/12: Inflammation and Wrap UpMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5: Complement, EtcDokument7 SeitenLecture 5: Complement, EtcMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9: T-Lymphocyte ActivationDokument5 SeitenLecture 9: T-Lymphocyte ActivationMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3: MHC and HLADokument2 SeitenLecture 3: MHC and HLAMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 8: Adaptive ImmunityDokument3 SeitenLecture 8: Adaptive ImmunityMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6: B-Lymphocytes, EtcDokument2 SeitenLecture 6: B-Lymphocytes, EtcMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Cell Activation StagesDokument2 SeitenB Cell Activation StagesMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4: Specific Immunology: Antigen Binding Capacity of The Antibody Will DifferDokument5 SeitenLecture 4: Specific Immunology: Antigen Binding Capacity of The Antibody Will DifferMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2: Cells of Innate ImmunityDokument3 SeitenLecture 2: Cells of Innate ImmunityMohit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian List-Of-HospitalsDokument564 SeitenIndian List-Of-HospitalsPinder BaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Oral Rehydration Therapy in The Treatment of Childhood Diarrhoea in Douala, CameroonDokument5 SeitenUse of Oral Rehydration Therapy in The Treatment of Childhood Diarrhoea in Douala, CameroonKiti AstutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics as First-Line Treatment for Early-Episode SchizophreniaDokument3 SeitenUsing Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics as First-Line Treatment for Early-Episode SchizophreniaFan TomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Blood Circulatory SystemDokument3 SeitenThe Blood Circulatory SystemListiyani IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain: What Is A Subarachnoid Hemorrhage?Dokument4 SeitenBrain: What Is A Subarachnoid Hemorrhage?Rashellya RasyidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1016@j Joen 2019 10 009Dokument8 Seiten10 1016@j Joen 2019 10 009fatimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Anuj Raj BijukchheDokument60 SeitenDR Anuj Raj BijukchheMUHAMMAD JAWAD HASSANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broken Heart Syndrome: DiagnosticsDokument25 SeitenBroken Heart Syndrome: DiagnosticsOlga Goryacheva100% (1)
- 12 OET Sample Referral Letter (Nurse) WritingDokument43 Seiten12 OET Sample Referral Letter (Nurse) WritingAL ' ARIS98% (41)
- Surgery and Post OpDokument96 SeitenSurgery and Post OpNguyễn Nhật HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights PharmaDokument1 SeiteRights PharmaMargaret ArellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saving SightDokument3 SeitenSaving SightSang LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mata Merah Visus TurunDokument27 SeitenMata Merah Visus TurunErinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DermaRoller Consent Form 2011Dokument3 SeitenDermaRoller Consent Form 2011BrianZackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Skill Lab AS PER INDIAN NURSING COUNCILDokument10 SeitenAdvance Skill Lab AS PER INDIAN NURSING COUNCILRahul Kashyap73% (11)
- Fundamentals of hearing impairment and audiological managementDokument4 SeitenFundamentals of hearing impairment and audiological managementsuraj singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism: Principles of Early Clinical ManagementDokument5 SeitenAmniotic Fluid Embolism: Principles of Early Clinical Management16.11Hz MusicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquatic Exercise - Lung Function and Weight LossDokument48 SeitenAquatic Exercise - Lung Function and Weight LossDr Vaishali MathapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the Key Elements of a HemogramDokument53 SeitenUnderstanding the Key Elements of a Hemogramromanas25Noch keine Bewertungen
- AIJ Clasif PRINTO 2019Dokument9 SeitenAIJ Clasif PRINTO 2019Michael ParksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Board ReviewDokument599 SeitenPharmacology Board ReviewMelbhon Fabro RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNS Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenCNS Drug StudyMAHUSAY JOYCE CARINANoch keine Bewertungen
- NSE121 - Care PlanDokument7 SeitenNSE121 - Care Planramyharoon2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ds Pedia WardDokument2 SeitenDs Pedia WardRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing responsibilities for generic medicationsDokument6 SeitenNursing responsibilities for generic medicationsAngelito LeritNoch keine Bewertungen
- AgoraphobiaDokument12 SeitenAgoraphobiaprakharkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atom Electrosurgical SystemDokument40 SeitenAtom Electrosurgical SystemOgut AjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healing Through MusicDokument11 SeitenHealing Through MusicMiguel MacaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest PainDokument13 SeitenChest Paing3murtulu100% (1)
- Snake Bite First AidDokument3 SeitenSnake Bite First AidJoeban R. PazaNoch keine Bewertungen