Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
WWII Study Guide
Hochgeladen von
Julian Barcelon SorianoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
WWII Study Guide
Hochgeladen von
Julian Barcelon SorianoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Julian Soriano US History Mr. Thompson March 20, 2013 WWII Study Guide Terms: 1.
Lend-Lease: Act passed in 1941 that allowed President Roosevelt to sell or lend what supplies to any country whose defense he considered vital to the safety of the United States. 2. Munich Pact: Agreement made between Germany, Italy, Great Britain, and France in 1938 that sacrificed the Sudetenland to preserve peace. 3. Nonaggression Pact: Agreement between 2 or more countries, in this case, that Germany and Soviets wont attack each other. 4. Manhattan Project: Code name of the project that developed the atomic bomb. 5. Mein Kampf: Diary that Adolf Hitler wrote during his time in jail. 6. Internment: Temporary imprisonment of members of a specific group. 7. Erwin Rommel: Known as the Desert Fox wanted to push back the Allies to the sea as they landed. 8. Isolationism: A policy that a country or countries isolate themselves from joining any alliances. 9. National Socialist Party: Nazi party lead by Adolf Hitler during WWII and was disbanded in 1945 10. Munich Pact: Agreement made between Germany, Italy, Great Britain, and France in 1939 that sacrificed the Sudetenland to preserve peace. 11. Neville Chamberlain: British prime minister who was at the Munich Conference with Hitler in 1938. 12. Appeasement: Policy of granting concessions in order to keep the peace. 13. Winston Churchill: Prime minister of the UK during WWII. 14. Concentration Camps: Camps used by the Nazis to imprison undesirable members of society. 15. Day of Infamy: 16. General Dwight D. Eisenhower: Supreme Commander of Allies Forces that planned the invasion on Normandy. 17. D-Day: June 6, 1944, the day Allies landed on the beaches of Normandy, France. 18. Yalta Conference (what was it and date): 19. Executive Order 8802: World War II measure that assured fair hiring practices in any job funded by their government. 20. Selective Service Act: Act passed by Congress in May in 1917 authorizing draft of young men for military service. 21. Bracero Program: Plan that brought laborers from Mexico to work on American farms. Questions: 1. What event started World War II in Europe?
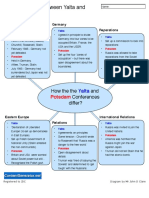
- The event that started World War II in Europe was when Germany attacked Poland on September 1939. 2. What was the most effective factor in slowing the Nazi drive into the Soviet Union in 1941? - The most effective factor in showing the Nazi drive into the Soviet Union in 1941 was the Russian Winter. 3. What was Hitlers greatest military blunder? - Hitlers greatest military blunder was declaring war on the U.S.S.R. (Russia). 4. What nations did Germany fail to conquer? - Germany failed to conquer the nations of Russia, Britain, and the Soviet Union. 5. What was Trumans major justification for using the atomic bomb against Japan? - Trumans major justification for using the atomic bomb against Japan was to keep the Americans safe from further attacks and also to save American soldiers to end war between the United States and Japan. 6. When did Roosevelt die? - Roosevelt died on April 12, 1945. 7. When did Germany surrender? When did Japan surrender? - Germany surrendered on May 7, 1945 and Japan surrendered on September 2, 1945. 8. What were the effects of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? - The creation of a better radar system, immediate declaration of war on Japan and US get out of neutrality and enter the war. 9. What was the point of the Neutrality Acts? -The point of Neutrality Acts was to keep the US out of overseas wars from different countries. 10. Who made the final decision to drop the atomic bombs? - President Truman made the final decision to drop the atomic bombs. 11. What were the major battles in the Pacific theater of WWII? - Major battles in the Pacific theater of WWII were Pearl Harbor, Coral Sea, Midway, Iwo Jima, Okinawa, and Doolittle Raid.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 5Dokument6 SeitenChapter 5Julian Barcelon SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Roots and Development of The Federal BureaucracyDokument6 SeitenThe Roots and Development of The Federal BureaucracyJulian Barcelon SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gatsby OrganizerDokument2 SeitenGatsby OrganizerJulian Barcelon SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bibliography HistoryDokument1 SeiteBibliography HistoryJulian Barcelon SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Punnett Square GuideDokument6 SeitenPunnett Square GuideJulian Barcelon SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Faith Kisio - Drones FinalDokument19 SeitenFaith Kisio - Drones FinalfaykissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title To Territory in Int' LawDokument9 SeitenTitle To Territory in Int' LawKELVIN A JOHNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outposts of Empire Korea, Vietnam, and The Origins of The Cold War in Asia, 1949-1954Dokument310 SeitenOutposts of Empire Korea, Vietnam, and The Origins of The Cold War in Asia, 1949-1954Abhijatya100% (1)
- What Is IR Notes: Trevor Taylor (1979)Dokument2 SeitenWhat Is IR Notes: Trevor Taylor (1979)Hareem Zoya WarsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASEAN at 40: Mid-Life Rejuvenation?: Amitav AcharyaDokument7 SeitenASEAN at 40: Mid-Life Rejuvenation?: Amitav AcharyaMursyidatul Azhimah Al-HaniefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Paper TCWDDokument1 SeiteReaction Paper TCWDGabriel MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB History Notes - The BalkansDokument5 SeitenIB History Notes - The BalkansemilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction About Philippine Foreign PolicyDokument18 SeitenAn Introduction About Philippine Foreign PolicyEmmanuel Jimenez-Bacud, CSE-Professional,BA-MA Pol Sci0% (1)
- The Long War in UkraineDokument12 SeitenThe Long War in UkraineCarlos SobreNoch keine Bewertungen
- DeMarco Text PagesDokument36 SeitenDeMarco Text Pagesr ylaplayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Travel AdvisoriesDokument1 SeiteTravel AdvisoriesMoe Thouk OoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 72-74 - 08-4-The Situation in Southern RhodesiaDokument13 Seiten72-74 - 08-4-The Situation in Southern RhodesiaVasilije BlagojevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 10 Coercive Methods: StructureDokument10 SeitenUnit 10 Coercive Methods: StructureGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Treaty of VersaillesDokument3 SeitenThe Treaty of Versailleselava94% (16)
- Uchida PDFDokument12 SeitenUchida PDFAndini NasutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kahin - Subversion As Foreign PolicyDokument2 SeitenKahin - Subversion As Foreign PolicyAndrew S. Terrell0% (1)
- Balancing in Neorealism - 748Dokument37 SeitenBalancing in Neorealism - 748Jahanzaib KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1904 - Financing UN PeacekeepingDokument16 Seiten1904 - Financing UN PeacekeepingBasyir ashrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toogood UnderstandingEmergingRelationship 2016Dokument11 SeitenToogood UnderstandingEmergingRelationship 2016ruth kolajoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaishankar's Speech IFPDokument2 SeitenJaishankar's Speech IFPSarthak MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PB StobdanforeignDokument3 SeitenPB Stobdanforeignrahulshandilya2kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yalta and PotsdamDokument1 SeiteYalta and Potsdamapi-292648573Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Most Secret List of Soe Agents: LDokument84 SeitenThe Most Secret List of Soe Agents: LeliahmeyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled PresentationDokument12 SeitenUntitled Presentationapi-376059354Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis PaperDokument70 SeitenThesis PaperDIVYAN SURESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- INT 312 Introduction To Peace and Conflict Studies Disarmament and Survival Asst. Prof. Dr. Efser Rana Coşkun TürkmenDokument14 SeitenINT 312 Introduction To Peace and Conflict Studies Disarmament and Survival Asst. Prof. Dr. Efser Rana Coşkun Türkmeninahnip inanhnipNoch keine Bewertungen
- A World of RegionsDokument4 SeitenA World of RegionsAngel DuguilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA Pakistan and Muslim WorldDokument2 SeitenCA Pakistan and Muslim WorldMehwish AwaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.S. Jain Subodh Law College: Ms. Palak Vashisht Semester-7 (B) Roll No. - 57Dokument13 SeitenS.S. Jain Subodh Law College: Ms. Palak Vashisht Semester-7 (B) Roll No. - 57Yashvardhan TolaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bismarck's Policies - Austria&France (1862-1871)Dokument1 SeiteBismarck's Policies - Austria&France (1862-1871)AlicjaNoch keine Bewertungen