Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Guide To Drug Dose Adjustment in Renal Impairment: (Based On Cockcroft-Gault Equation, Adapted From BNF)
Hochgeladen von
vi_wiviaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Guide To Drug Dose Adjustment in Renal Impairment: (Based On Cockcroft-Gault Equation, Adapted From BNF)
Hochgeladen von
vi_wiviaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
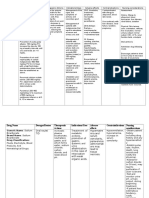
Guide to drug dose adjustment in Renal Impairment
(Based on Cockcroft-Gault equation, Adapted from BNF1)
Degree of renal impairment as per GFR Drug or class of drug Allopurinol Dose adjustment based on creatinine clearance
1020 mL/min; 100200 mg daily <10 ml/min; 100 mg on alternate days (max 100 mg daily) Start low and go slow. Start with very low doses and titrate to maximum
ACE inhibitors
tolerated dose. Proceed cautiously at doses above enalapril 10 mg or equivalent, i.e. captopril 75 mg or cilazapril 2.5 mg daily
Bezafibrate 400 mg (Bezalip retard) -blockers Cotrimoxazole Colchicine (from Prescriber Update, Nov 2005) Digoxin Lithium Metformin* (from bpacnz Diabetes POEMs, Oct 2004) Nitrofurantoin
< 60 mL/min; Avoid (For 200 mg tablets see product data sheet) Dose reduction of some -blockers required, especially atenolol, sotalol and nadolol. Refer to individual drug datasheets < 15 mL/min; Avoid 1530 ml/min; Use half normal dose < 10 mL/min; avoid < 50 mL/min; reduce dose by half Dose adjustment required in renal impairment (including age related). Adjust according to plasma concentrations Dose adjustment required in renal impairment (including age related). Adjust according to plasma concentrations < 30 mL/min; avoid 3060 mL/min; max 1000 mg/day 6090 mL/min; max 2000 mg/day Avoid in mild, moderate and severe impairment Mild impairment; Use lowest effective dose and monitor renal function, sodium
NSAIDs
and water retention Moderate and Severe; avoid if possible
Ranitidine Simvastatin Venlafaxine
< 20 mL/min; use half the normal dose < 30 mL/min; Doses above 10 mg daily should be used with caution < 10 mL/min; avoid 1030 mL/min; use half normal dose
* Some references recommend avoiding metformin even in mild renal impairment but metformin can be used with caution if the dose is reduced. All patients should be advised to withhold treatment and seek medical advice if they experience vomiting and diarrhoea and if they have planned medical, surgical or radiological procedures.
bpacnz
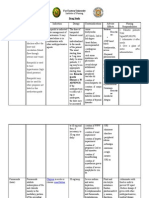
Action plan for Chronic Kidney Disease (Based on eGFR)
eGFR mL/min/1.73 m2 Description No kidney damage OR Stage 1 CKD (Kidney damage with normal or kidney function) proteinuria OR Stage 2 CKD (Kidney damage with mild kidney function) Clinical action plan Further investigation for CKD may be indicated in those at increased risk (smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, age over 50 years, family history, Mori or Pacific Island or Asian heritage: ---Assessment of proteinuria Urinalysis Blood pressure
60
Cardiovascular risk reduction (blood pressure, lipids, blood glucose, smoking, obesity, physical activity) Blood pressure targets 130/80; 122/76 if protein > 1 g/24 hours As for Stage 2 plus: -- Blood pressure control -- Monitor eGFR 3 monthly -- Avoid nephrotoxic drugs (e.g. NSAIDS, colchicine) -- Prescribe antiproteinuric drugs (ACE inhibitors and/or angiotensin receptor blockers) if appropriate -- Address anaemia, acidosis and hyperparathyroidism -- Ensure drug dosages appropriate for level of kidney function (adjust according to Cockcroft-Gault equation) Consider referral to nephrologist As for Stage 3 plus: -- Referral to nephrologist is usually indicated for preparation for dialysis (including access surgery, education) or transplantation As for Stage 4 plus referral to nephrologist
30 - 59
Stage 3 CKD Moderate kidney function
15 - 29
Stage 4 CKD Severe kidney function Stage 5 CKD End-stage kidney failure
< 15
Cockcroft-Gault equation for calculating creatinine clearance Creatinine Clearance mL/min = (140 age) x weight (kg) 815 x serum creatinine (mmol/L)
The MDRD equation for eGFR GFR = 186 (SCR 88.4)-1.154 age-0.203 (Female: multiply result by 0.742; African-Caribbeans: multiply result by 1.212) Note: Ethnicity factors have not yet been calculated for other ethnic groups.
bpacnz
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CKD Pocket GuideDokument2 SeitenCKD Pocket GuideLutfi MalefoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesVon EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus Drug ChartDokument3 SeitenDiabetes Mellitus Drug Chartlui.stephanie1751100% (1)
- Identification of CKD: Algorithm ADokument3 SeitenIdentification of CKD: Algorithm ArawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 1Dokument6 SeitenCase Study 1rajambal_ayyasamy0% (1)
- Julia R. Nunley, Edgar V. Lerma (Eds.) - Dermatological Manifestations of Kidney Disease-Springer-Verlag New York (2015)Dokument273 SeitenJulia R. Nunley, Edgar V. Lerma (Eds.) - Dermatological Manifestations of Kidney Disease-Springer-Verlag New York (2015)Shantanu DixitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianDokument54 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease: For The Primary Care PhysicianFlavia PolodeanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digoxin Drug CardDokument1 SeiteDigoxin Drug CardMahsa Ahmadzadeh100% (2)
- Chemo MedsDokument17 SeitenChemo MedsSophia Smartz100% (1)
- DialysisDokument5 SeitenDialysisAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- ACE Inhibitors PrintDokument5 SeitenACE Inhibitors PrintBernard TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dosage Adjustment of Cytotoxics in Renal ImpairmentDokument24 SeitenDosage Adjustment of Cytotoxics in Renal ImpairmenthamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetic Kidney Disease - DynaMedDokument117 SeitenDiabetic Kidney Disease - DynaMedElisa ChinchillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enalapril: Indications and DosageDokument18 SeitenEnalapril: Indications and Dosageshahera rosdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aki and CKD Therapy 2021Dokument46 SeitenAki and CKD Therapy 2021Alfathri YunediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs and Kidney DiseasesDokument46 SeitenDrugs and Kidney Diseasesمرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of GoutDokument6 SeitenManagement of GoutSeanHong TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apo Captopril TabDokument19 SeitenApo Captopril TabansenoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Erlieza Roosdhania, SP - PD (CKD)Dokument38 SeitenDr. Erlieza Roosdhania, SP - PD (CKD)Pon PondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qtern 84413Dokument19 SeitenQtern 84413Manoj KaluvakotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Woodell2018 (Jurnal Asli)Dokument13 SeitenWoodell2018 (Jurnal Asli)Fatah Jati PNoch keine Bewertungen
- CaptoprilDokument3 SeitenCaptoprilNovi YulianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jardiance Epar Product Information - enDokument47 SeitenJardiance Epar Product Information - enSaad MasoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Prescribing in Renal Impairment Information. Patient PatientDokument13 SeitenDrug Prescribing in Renal Impairment Information. Patient PatientEffy AngeLi LomocsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATORVASTATINDokument4 SeitenATORVASTATINeshikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Impairment: Appendix-4Dokument9 SeitenRenal Impairment: Appendix-4CLICK & WATCHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prescribing Opioids in Renal PatientsDokument5 SeitenPrescribing Opioids in Renal PatientsAnonymous 9dVZCnTXSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Prescribing in Renal Failure: 37.1 General PrinciplesDokument9 SeitenGuidelines For Prescribing in Renal Failure: 37.1 General PrinciplesArshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotik For Renal FailureDokument6 SeitenAntibiotik For Renal FailureWidhy Joss BangetzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension: Increase in Blood PressureDokument29 SeitenHypertension: Increase in Blood PressureKeesha Mae AnteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationDokument6 SeitenLisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationCliff by the seaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKD PocketGuideDokument2 SeitenCKD PocketGuidelayzierainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : Provider's Guide To Diagnose and Code CKDDokument2 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : Provider's Guide To Diagnose and Code CKDAry Rio PambudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akt RenalDokument4 SeitenAkt Renaldzidek7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDokument9 SeitenAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ify Drug StudiesDokument15 SeitenIfy Drug StudiesifyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAQ - FinerenoneDokument9 SeitenFAQ - Finerenoneraea.dobsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CapotrilDokument2 SeitenCapotrilmahgadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharma ProjectDokument9 SeitenPharma Projectfarah.abd97Noch keine Bewertungen
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDokument30 SeitenAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsPharmaEducationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coxib 2Dokument4 SeitenCoxib 2ras emil sazuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etoricoxib 120 MG Film-Coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - (Emc)Dokument1 SeiteEtoricoxib 120 MG Film-Coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - (Emc)vikasjha12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Core Safety ProfileDokument6 SeitenCore Safety ProfilexepayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drus Study AaaaaaDokument6 SeitenDrus Study AaaaaamarkharoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metformin 1 METFORMIN (500mg, 850mg and 1000mg Tablets) : New Zealand Data SheetDokument11 SeitenMetformin 1 METFORMIN (500mg, 850mg and 1000mg Tablets) : New Zealand Data SheetAfifa ZainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nootropil: Qualitative and Quantitative CompositionDokument12 SeitenNootropil: Qualitative and Quantitative CompositionMuhammad TalhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cad Sihd 2Dokument67 SeitenCad Sihd 2mohammedghassan53Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilDokument3 SeitenBrand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilPoinsithia OrlandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candesartan + Hydrochloroziazide PDFDokument25 SeitenCandesartan + Hydrochloroziazide PDFddandan_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Gout in AdultsDokument3 SeitenManagement of Gout in AdultsZubair Mahmood KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azathioprine: Class: IndicationsDokument3 SeitenAzathioprine: Class: IndicationsAnna GozaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- BenazeprilDokument2 SeitenBenazeprilFeliciaDorghamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPC Pramipexole 0.7 MGDokument14 SeitenSPC Pramipexole 0.7 MGJehan SarahdiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of The Medicinal Product: AdultsDokument9 SeitenName of The Medicinal Product: Adultsddandan_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prinsip Terapi Pada GG Ginjal Dan Hepar - DR Tri Murti Andayani, SP - FrsDokument58 SeitenPrinsip Terapi Pada GG Ginjal Dan Hepar - DR Tri Murti Andayani, SP - FrsJinan RanasaninahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDokument65 SeitenAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsMikro BatomouroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gout Treatment Medications and Lifestyle Adjustments To Lower Uric AcidDokument16 SeitenGout Treatment Medications and Lifestyle Adjustments To Lower Uric AcidnellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- See Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningDokument26 SeitenSee Full Prescribing Information For Complete Boxed WarningMauricio UmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmlodipineDokument2 SeitenAmlodipineAnonymous QqyLDoW1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysiaDokument1 SeiteMefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysianuruladyanisaifuzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prescribing Information Abiratred Abiraterone Acetate Tablets 250 MGDokument9 SeitenPrescribing Information Abiratred Abiraterone Acetate Tablets 250 MGChrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obat CaptoprilDokument3 SeitenObat CaptoprilSyifa HurulNoch keine Bewertungen
- DaVitaHealthCarePartnersInc 10K 20140221Dokument212 SeitenDaVitaHealthCarePartnersInc 10K 20140221Wallace Min0% (1)
- National Kidney FoundationDokument16 SeitenNational Kidney Foundationajeng puspitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition of Aging DogsDokument19 SeitenNutrition of Aging DogsBrisbany AlcibarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Isn WCN - Credence Symposium - FinalDokument86 Seiten2019 Isn WCN - Credence Symposium - FinalChristian Acosta VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument18 SeitenPDFGene AngcaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrology Midt 20 MCQ For StudDokument3 SeitenNephrology Midt 20 MCQ For StudMrunal DiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aglis Marselina-Revisi Resume Keperawatan Hemodialisa Umb SMT 7.id - enDokument8 SeitenAglis Marselina-Revisi Resume Keperawatan Hemodialisa Umb SMT 7.id - enLaila FahrezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuberculosis and The Kidney: Disease of The MonthDokument8 SeitenTuberculosis and The Kidney: Disease of The Monthkiki_beNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Chronic Kidney Disease by Using Orange ToolDokument8 SeitenAnalysis of Chronic Kidney Disease by Using Orange ToolSantosh PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviews: The Global Epidemiology of HypertensionDokument15 SeitenReviews: The Global Epidemiology of Hypertensionrifa iNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Algorithm For Prescribing SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor AgonistsDokument11 SeitenDecision Algorithm For Prescribing SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor AgonistsNati BocciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cronic Kidney Disease: Prof. Dr. Agus Tessy SP - PD KGH Systema UrologiDokument39 SeitenCronic Kidney Disease: Prof. Dr. Agus Tessy SP - PD KGH Systema UrologifauziyahabidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKD PDFDokument26 SeitenCKD PDFNogra CarlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Tribune January 2012 HKDokument72 SeitenMedical Tribune January 2012 HKKarena SabadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKD Treated With Dialysis Case Study 18 MNT 409 - 2Dokument3 SeitenCKD Treated With Dialysis Case Study 18 MNT 409 - 2api-240419901Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10.1007@s11886 019 1213 XDokument13 Seiten10.1007@s11886 019 1213 XИлија РадосављевићNoch keine Bewertungen
- More Accurate Than Ever: Vcheck Product Catalog - 5.1Dokument36 SeitenMore Accurate Than Ever: Vcheck Product Catalog - 5.1dmantsioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sleep and The Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Cohort StudyDokument8 SeitenSleep and The Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Cohort StudyEtaursaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKPDDokument9 SeitenCKPDShay Patrick CormacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney Health PDFDokument77 SeitenKidney Health PDFAnonymous CQSNUSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Renal Failure: Lecture Speaker Dr. V. Lakshmi Prasanna MariseDokument23 SeitenChronic Renal Failure: Lecture Speaker Dr. V. Lakshmi Prasanna MariseManjunath ArunachalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DebateDokument3 SeitenDebateTulbanos KenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serum Interleukin - 6 Level Among Sudanese Patients With Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument3 SeitenSerum Interleukin - 6 Level Among Sudanese Patients With Chronic Kidney DiseaseBIOMEDSCIDIRECT PUBLICATIONSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal OsteodystrophyDokument4 SeitenRenal OsteodystrophyLuigiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nej MR A 1206793Dokument13 SeitenNej MR A 1206793David LeónNoch keine Bewertungen
- BNP in CKDDokument6 SeitenBNP in CKDDedy ShauqiNoch keine Bewertungen