Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Basics of Fluid Rheology
Hochgeladen von
dougCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Basics of Fluid Rheology
Hochgeladen von
dougCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Basics of Fluid Basics of Fluid Rheology Rheology BasicsofFluid BasicsofFluidRheology Rheology
RayFernando,Ph.D.
Rheology Rheology
Science concerned with the Science concerned with the Scienceconcernedwiththe Scienceconcernedwiththe
flowanddeformationof flowanddeformationof
materials materials
2
Overview Overview
Rheology Rheology
Science concerned with the flow and deformation of Science concerned with the flow and deformation of Scienceconcernedwiththeflowanddeformationof Scienceconcernedwiththeflowanddeformationof
materials materials
Rheology Rheology includes includes gy gy
Viscosity,Shear Viscosity,Shearthinning& thinning&thickening, thickening,Thixotropy Thixotropy, ,
Viscoelasticity Viscoelasticity
EffectofFormulationAspectsonRheology EffectofFormulationAspectsonRheology
Latex,Pigments,Additives,etc.,andtheirInteractions Latex,Pigments,Additives,etc.,andtheirInteractions
Impactof ImpactofRheology Rheology onProcesses onProcesses
3
Process Overview Process Overview ProcessOverview ProcessOverview
RawMaterials
Mixing/Blending
Storage(Shelf/Pot)
DeliverytoApplicator
Application
Flow&Leveling
Drying/Curing
4
Vi it Vi it R i t t fl R i t t fl Viscosity Viscosity Resistancetoflow Resistancetoflow
5
Viscosity Quantitative Definition Viscosity QuantitativeDefinition
Velocity=V
Velocity=0
Shear Stress = F/A [N cm
2
]
ShearRate=(V 0)/d[s
1
]
ShearStress=F/A[Ncm ]
6
Vi it Vi it Q tit ti D fi iti Q tit ti D fi iti Viscosity Viscosity QuantitativeDefinition QuantitativeDefinition
A Area
d
V l it V
A Area
F Force
2
Velocity=V
2
Velocity=V
1
ShearRate=(V
1
V
2
)/d[s
1
]
ShearStress=F/A[Ncm
2
]
Viscosity=ShearStress/ShearRate[Pas]
7
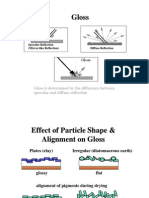
Whichismoreviscous? Whichismoreviscous?
Wateroroliveoil?
Olive oil or honey? Oliveoilorhoney?
Honey or mayonnaise? Honeyormayonnaise?
8
Typical Viscosity Values Typical Viscosity Values TypicalViscosityValues TypicalViscosityValues
Viscosity
cps mPa.s Pa.s
Water 1 1 0.001
Olive Oil 100 100 0.01
Glycerol 1000 1000 1
Honey 5000 5000 5 Honey 5000 5000 5
Polymer Melt 1,000,000 1,000,000 1000
9
CommonViscosity y
MeasuringDevices
CupMethods
[e.g.Zahn]
PaddleMethods
[e g Stormer]
SpindleMethods
[e.g.,Brookfield]
[e.g.,Stormer]
10
Stormer Viscosities(KU)ofCommercialLatex
P i t Paints
Paint Sample
Unstirred
(KU)
Stirred
(KU)
PaintSample
(KU) (KU)
Commercial
SatinBase
119 117
Commercial
SatinWhite
109 108
BYKInstrumentsProductCatalog
11
Sag CommercialLatexPaints g
119/117KU
CommercialSatinBase
/
CommercialSatinWhite
109/108KU
BYKInstrumentsProductCatalog
12
Leveling Commercial Latex Paints Leveling CommercialLatexPaints
119/117 KU
Commercial Satin Base
119/117KU
Commercial Satin White
CommercialSatinBase
109/108KU
CommercialSatinWhite
BYKInstrumentsProductCatalog
13
IfViscosityisIndependentofShear IfViscosityisIndependentofShearRate, Rate,
Fl id Fl id i N t i i N t i Fluid FluidisNewtonian isNewtonian
e
s
s
,
P
a
P
a
s
S
h
e
a
r
S
t
r
e
V
i
s
c
o
s
i
t
y
,
P
Shear Rate, s
-1
Shear Rate, s
-1
Stress Rate
Viscosity
q t
=
y
14
Non NonNewtonianViscosityBehavior NewtonianViscosityBehavior
BrookfieldViscosities@DifferentRPMs
WaterborneCoating
RPM Viscosity (cps) Spindle #
0.5 8000 4
1 5000 "
2.5 2560 "
5 1520 " 5 1520
10 1000 "
20 550 2
50 316 "
100 227 "
15
Shear ShearThinningBehavior ThinningBehavior
4
"
"
"
ViscosityMeasuredwith
Brookfield
10000
"
"
2
"
"
1000
i
t
y
(
c
p
s
)
1000
V
i
s
c
o
s
i
100
0.1 1 10 100
RPM
As RPM(Shear Rate)
Coating is Shear Thinning
Viscosity
Coating is Shear-Thinning
16
ShearThinningBehavior ShearThinningBehavior
Viscosity Measured with ARES
10000
100000
p
s
)
1000
c
o
s
i
t
y
(
c
p
10
100
0.01 0.10 1.00 10.00 100.00 1000.00
V
i
s
Shear Rate (s-1)
Cone and
Plate Plate
17
Shear Thinning & Thickening Behavior Shear Thinning & Thickening Behavior ShearThinning&ThickeningBehavior ShearThinning&ThickeningBehavior
) ( 1 >
n
q t
) ( 1 > = n
n
K t
r
e
s
s
,
P
a
q t =
) ( 1 <
n
K
S
h
e
a
r
S
t
r
) ( 1 < = n
n
K t
Shear Rate, s
-1
18
What makes a Latex Formulation What makes a Latex Formulation WhatmakesaLatexFormulation WhatmakesaLatexFormulation
Non NonNewtonian? Newtonian?
ContinuousPhaseComposition ContinuousPhaseComposition
Thickener Other Thickener Other Thickener,Other Thickener,Other
HydrodynamicVolume HydrodynamicVolume
ChainEntanglements ChainEntanglements
VolumeFractionandNatureof VolumeFractionandNatureof
DispersedComponents DispersedComponents
Binder,Pigment,Filler Binder,Pigment,Filler
19
PolymerConformationHydrodynamic PolymerConformationHydrodynamic
V l Rh l V l Rh l VolumeRheology VolumeRheology
IntrinsicViscosity, |q| = KM
v
a
M
v
- Viscosity average molecular weight
K - Huggins Constant
a - Mark-HouwinkConstant
a = 0.5 at theta(u) conditions
(e.g., polyisobutylene in benzene
at 24
o
C)
a > 05 in a good solvent a > 0.5 in a good solvent
20
Polymer Concentration Polymer Concentration Rheology Rheology PolymerConcentration PolymerConcentrationRheology Rheology
C t t d
Dilute Critical
(Overlapping)
Concentrated
(Entanglements)
Viscosity dependence on shear-rate increases
Viscosity dependence on time increases
21
PolymerMolecularWeightEffecton PolymerMolecularWeightEffecton
Viscosity Viscosity Viscosity Viscosity
Polymer Critical MW
Polyethylene 4,000
Polystyrene 30,000
3.4
Polystyrene 30,000
Polymethyl methacrylate 28,000
Polycarbonate 13,000
s
c
o
s
i
t
y
Cis-polyisoprene 10,000
Polyisobutylene 15,000
1 0
LogM
c
L
o
g
V
i
s
1,4 polybutadiene 5,000
Polyvinyl acetate 23,000
P l di th l il 24 000
1.0
LogM.W.
Polydimethyl siloxane 24,000
Chain entanglements above a critical polymer chain length
Ferry,Viscoelastic PropertiesofPolymers,3
rd
ed,Wiley,NewYork,1980
22
Hi h h b k Hi h h b k Highshearcanbreakup Highshearcanbreakup
entanglements entanglements
LSV
V
i
s
c
o
s
i
t
y
HSV
o
s
i
t
y
Molecular Weight
V
i
s
c
Shear Rate
23
P l MWD i h P l MWD i h hi i hi i PolymerMWDimpactsshear PolymerMWDimpactsshear thinning thinning
Narrow
c
o
s
i
t
y
Broad
V
i
s
c
Broad
Shear Rate
24
EffectofMolecularWeightonThickening
10.00
1.000
a
.
s
)
1.3M
1.0M
0.1000
v
i
s
c
o
s
i
t
y
(
P
a
HHR
Natrosol 250
1%inwater
720K
0.01000
v
HR
MR
GR
LR
300K
90K
0.01000 0.1000 1.000 10.00 100.0 1000
shear rate (1/s)
1.000E-3
25
EffectofSolidsLevelonViscositiesat EffectofSolidsLevelonViscositiesat
VariousShearRates VariousShearRates
Low Low--Shear Shear Medium Medium- -Shear Shear
High High--Shear Shear
s
i
t
y
)
gg
l
o
g
(
V
i
s
c
o
Solids Solids
Increases Increases
Low Low--Shear Shear
Medium Medium- -Shear Shear High High- -Shear Shear
l
log (Shear Rate)
o
s
i
t
y
V
i
s
c
o
%Volume Solids
26
TypesofViscosityBehavior TypesofViscosityBehavior
s
s
Plastic
S
t
r
e
Plastic
Shearthinning(Pseudoplastic)
Newtonian
Dilatant(Shearthickening)
Yield
Stress Stress
Rate
2 / 1 2 / 1 2 / 1
0
2 / 1
q t t
+ =
Casson
Approximation
27
Viscosity Viscosity vs vs Shear Rate Curves Shear Rate Curves Viscosity Viscosityvs vs ShearRateCurves ShearRateCurves
Shearthinning
Shearthinning(YieldStress)
t
y
t
y
V
i
s
c
o
s
i
V
i
s
c
o
s
i
t
ShearRate ShearRate
28
Thixotropy Thixotropy Thixotropy Thixotropy
y
V
i
s
c
o
s
i
t
Time
c
o
s
i
t
y
a
r
S
t
r
e
s
s
V
i
s
c
S
h
e
ShearRate
ShearRate
29
ViscosityBehaviorofHEAT/SurfactantMixtures
Shearthickening
ViscositydependenceonshearrateofTritonX45surfactant(1.5Wt.%)andOptifloL100
(1.0Wt.%)aqueousblend.Datapointequilibrationtime 30&90secondsrepresented
bycircleandsquaresymbols,respectively.
Manion,Johnson,andFernando,JCTRes2011
30
ShearRateDependenceof ShearRateDependenceof Viscosifying Viscosifying Mechanisms Mechanisms
Brownian Motion Brownian Motion
Flocculation
Aggregation
Chain Entanglements
Intermolecular Associations Intermolecular Associations
Hydrodynamic Volume
Adsorption
V
i
s
c
o
s
i
t
y
) Aggregation
Intermolecular Associations
Hydrodynamic Volume
Adsorption
l
o
g
(
V
10
-2
10
-1
10
0
10
+1
10
+2
10
+3
10
+4
10
+5
10
+6
log (Shear Rate (s
1
)) log (Shear Rate (s
-1
))
31
What is the Ideal Viscosity Profile? What is the Ideal Viscosity Profile? What is the Ideal Viscosity Profile? What is the Ideal Viscosity Profile?
y
)
Shear-Thinning
s
c
o
s
i
t
y
Newtonian
l
o
g
(
V
i
10
-2
10
-1
10
0
10
+1
10
+2
10
+3
10
+4
10
+5
10
+6
log (Shear Rate (s
-1
))
32
ShearRatesforVariousSub ShearRatesforVariousSubProcesses Processes
Settling
Sag & Leveling
o
s
i
t
y
)
Settling
Wicking
Mixing
R ll S
Brush/Roll
PickUp
(
V
i
s
c
o
(Slurries)
Roll
Coating
Spray
Coating
Pick Up
10
-2
10
-1
10
0
10
+1
10
+2
10
+3
10
+4
10
+5
10
+6
l
o
g
10
2
10
1
10
0
10
+1
10
+2
10
+3
10
+4
10
+5
10
+6
log (Shear Rate (s
-1
))
33
ShearRatesforCoatingSag ShearRatesforCoatingSag
gt
=
Shear Rate
t - film thickness
density
2
- density
- viscosity
Fora1.1gcm
3
density,
3mil(0.0076cm)thick ( )
1Pas(10poise)coating,
sagshearrateis0.4s
1
34
Shear Rates for Reverse Shear Rates for ReverseRoll Application Roll Application ShearRatesforReverse ShearRatesforReverse RollApplication RollApplication
ReverseRoll Coater NipRegion Reverse Roll Coater Nip Region
V =100 F/min
d =2 mil
v
d/2
Shear Rate =
___________
200x12x10
3
60x2
v
60x2
Shear Rate = 2.0x10
4
s
-1
35
AreCommonViscosityMeasurement AreCommonViscosityMeasurement
MethodsAdequate? MethodsAdequate?
CupMethods[Zahn]
SpindleMethods
[Brookfield]
P ddl M h d PaddleMethods
[Stormer]
36
LimitationinSingle LimitationinSinglePointViscosity PointViscosity
MMMeasurements Measurements
o
s
i
t
y
)
BrookfieldSingleRPMViscosity
g
(
V
i
s
c
o
l
o
g
log (Shear Rate) log(ShearRate)
InFormulaDevelopmentthisbehaviormustbeknown InFormulaDevelopmentthisbehaviormustbeknown
beforedefiningproductionviscosityspecs beforedefiningproductionviscosityspecs
37
Stormer Viscosity(KU)ofCommercial
LatexPaints
PaintSample
Unstirred
(KU)
Stirred
(KU)
p
(KU) (KU)
Commercial
SatinBase
119 117
Commercial
SatinWhite
109 108
BYKInstrumentsProduct
Catalog
38
ViscosityDependenceonShear
RateCommercial Latex Paints Rate CommercialLatexPaints
100.0
1000
s
)
CommercialSatinWhite
109/108KU
10.00
o
s
i
t
y
(
P
a
.
s
Commercial Satin Base
1.000
v
i
s
c
o CommercialSatinBase
119/117KU
0.01000 0.1000 1.000 10.00 100.0 1000
shearrate(1/s)
0.1000
shear rate (1/s)
39
StressDependenceonRate
CommercialLatexPaints
6000 600.0
a
)
CommercialSatinBase
119/117KU
r
s
t
r
e
s
s
(
P
a
s
h
e
a
r
CommercialSatinWhite
109/108KU
0 1000 shear rate (1/s)
0
40
StressDependenceonRate
l CommercialLatexPaints
10.00
CommercialSatinWhite
P
a
)
109/108KU
e
a
r
s
t
r
e
s
s
(
P
s
h
e
CommercialSatinBase
119/117KU
0 2.000 shear rate (1/s)
0
YieldStress
41
Honey&Mayonnaise? Honey&Mayonnaise?
10000
1000
P
a
.
s
)
Honey
Mayonnaise
100.0
v
i
s
c
o
s
i
t
y
(
P
10.00
0.01000 0.1000 1.000 10.00 100.0 1000
shear rate (1/s)
1.000
42
Honey&Mayonnaise? Honey&Mayonnaise?
90.00
100.0
70.00
80.00
P
a
)
40.00
50.00
60.00
e
a
r
s
t
r
e
s
s
(
P
Honey
M i
20.00
30.00
s
h Mayonnaise
0 1.000 shear rate (1/s)
0
10.00
43
OptimumFlow
Behavior Behavior
Performance
Rheology
FormulationFeatures
Structure
Property
44
SecondGroupExercise SecondGroupExercise
ArchitecturalCoating
20PVC
28%NVV
62nmAcrylicLatex
SprayConditions
25 psi Fluid Pressure 25psiFluidPressure
55psiAirPressure
Flow Rate 22 ml/s FlowRate 22ml/s
ShearRate(s
1
) Viscosity
(mPa.s)
Fluid Tube (Diameter 2 cm) FluidTube(Diameter 2cm)
Nozzle(Diameter 0.20mm)
45
Shear Rate (s-1) Viscosity (cps)
SecondGroupExercise SecondGroupExercise
0.02 16802.4
0.03 15280.8
0.05 11713.5
0.08 8323.11
Viscosity Measured with ARES
0.13 5649.32
0.20 3938.28
0.32 2833.88
0.50 2026.3
10000
100000
p
s
)
0.80 1463.92
1.26 1064.13
2.00 780.768
3.17 577.941
100
1000
V
i
s
c
o
s
i
t
y
(
c
5.02 430.816
7.96 324.244
12.62 246.411
20.00 189.604
10
0.01 0.10 1.00 10.00 100.00 1000.00
V
Shear Rate (s-1)
31.70 148.027
50.24 117.209
79.62 94.5705
126.19 77.4144
200.00 64.328
46
SecondGroupExercise SecondGroupExercise Solution Solution
Noslip
Linear velocity profile Linearvelocityprofile
2Q
-
3
2
r
Q
H
=
-
FlowRate 22ml/s
ShearRate(s
1
) Viscosity(mPa s)
FluidTube(Diameter 2cm) 14 ~300
Nozzle(Diameter 0.20
mm)
14x10
6
???
)
47
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- HYDRO-FOIL S8 - Silicate SystemDokument40 SeitenHYDRO-FOIL S8 - Silicate SystemAmine MimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pakinstan Glycol PresentationDokument19 SeitenPakinstan Glycol PresentationKaleem UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYDRO-GUARD® Water-Based Drilling Fluid Delivering Stable Wellbore ThroughDokument1 SeiteHYDRO-GUARD® Water-Based Drilling Fluid Delivering Stable Wellbore ThroughFauzan Rahman HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Cementing Additives CL Jun 00 ADokument37 Seiten4 Cementing Additives CL Jun 00 AasdNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Padhaya Hai) Completion & Workover Fluids PDFDokument23 Seiten(Padhaya Hai) Completion & Workover Fluids PDFMahesh sinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCS Brochure PDFDokument28 SeitenCCS Brochure PDFChandra PramanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAW-18W Foaming Additive - Overview - HiresDokument1 SeiteFAW-18W Foaming Additive - Overview - Hirespedro taquichiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling Fluids With AphronDokument7 SeitenDrilling Fluids With Aphronsaa6383Noch keine Bewertungen
- Faze ProDokument8 SeitenFaze ProLoganBohannonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement and Cementing PDFDokument18 SeitenCement and Cementing PDFSadashiw Patil100% (1)
- SAGDrilDokument8 SeitenSAGDrilLoganBohannonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling FluidsDokument20 SeitenDrilling Fluidsdekra abdo100% (1)
- Rheological Models For Drilling FluidDokument16 SeitenRheological Models For Drilling FluidModesty Ekeh100% (1)
- Kla Gard (Amine)Dokument0 SeitenKla Gard (Amine)Kinni ShenoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cesium FormateDokument20 SeitenCesium FormateAxelio MathNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Snapshot of The Drilling and Completio N Practices in High Temperature Geothermal Wells - SarmientoDokument13 SeitenA Snapshot of The Drilling and Completio N Practices in High Temperature Geothermal Wells - SarmientoAdil AytekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mud ContaminationDokument6 SeitenMud ContaminationAnonymous T32l1RNoch keine Bewertungen
- FazeproDokument8 SeitenFazeproMaria Fernanda Zenteno CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composition of Oil-Based Muds PDFDokument0 SeitenComposition of Oil-Based Muds PDFA MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Inhibitive Water-Based Drilling Fluids - Can They Replace Oil-Based MudsDokument8 SeitenAdvances in Inhibitive Water-Based Drilling Fluids - Can They Replace Oil-Based MudsNA NANoch keine Bewertungen
- Shale ProblemsDokument12 SeitenShale ProblemsShirley Hernandez JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Spe 96798 HPWBM - HodderDokument12 Seiten2 Spe 96798 HPWBM - HodderPT100% (1)
- Ultra High Temperature Aqueous and Non Aqueous Drilling FluidsDokument20 SeitenUltra High Temperature Aqueous and Non Aqueous Drilling FluidspostingidsgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scomi Group BHDDokument49 SeitenScomi Group BHDAbigailLim SieEngNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSA-1 Fines Stabilization AgentDokument1 SeiteFSA-1 Fines Stabilization Agentpedro taquichiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part II Functions of A Drilling FluidDokument47 SeitenPart II Functions of A Drilling FluidMoopSaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeffamine D 230 Polyoxyproine 7 PEADokument2 SeitenJeffamine D 230 Polyoxyproine 7 PEAYureski Belly SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geothermal Drilling: A Baseline Study of Nonproductive Time Related To Lost CirculationDokument13 SeitenGeothermal Drilling: A Baseline Study of Nonproductive Time Related To Lost CirculationForloradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe ThermDokument6 SeitenSafe ThermLoganBohannonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part IV Water Based Mud ChemistryDokument184 SeitenPart IV Water Based Mud ChemistrySlim.BNoch keine Bewertungen
- WorldOil Jun2014Dokument234 SeitenWorldOil Jun2014chaeqq100% (1)
- Drilling FluidsDokument8 SeitenDrilling FluidsFakhrul RaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wax Deposition ProblemDokument2 SeitenWax Deposition ProblemDhea SamanthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of An Asphaltene Inhibitor PDFDokument50 SeitenMechanism of An Asphaltene Inhibitor PDFTEXOPED Parsian KishNoch keine Bewertungen
- FlowSolve 110LN PDFDokument1 SeiteFlowSolve 110LN PDFIrelena RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Halad d413 HT FLCDokument2 SeitenHalad d413 HT FLCMasoudTeimoori100% (1)
- Agglomeration and Accretion of Drill Cuttings in Water-Based Fluids PDFDokument13 SeitenAgglomeration and Accretion of Drill Cuttings in Water-Based Fluids PDFAmlk MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeoFlo 1-58 Datasheet PDFDokument4 SeitenNeoFlo 1-58 Datasheet PDFSteven MarinoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Envirotherm NTDokument6 SeitenEnvirotherm NTErlgabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Driscal-D Polymer QMAXDokument1 SeiteDriscal-D Polymer QMAXAnonymous vSLFJCNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Evaluation of HP WBM Drillin PDFDokument105 SeitenPerformance Evaluation of HP WBM Drillin PDFÃndÿ RøõnęÿNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer Systems For Water Shutoff and Profile Modification: A Review Over The Last DecadeDokument15 SeitenPolymer Systems For Water Shutoff and Profile Modification: A Review Over The Last DecadeLeopold Roj DomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bentone 38 - TDS - eDokument2 SeitenBentone 38 - TDS - eDũng ĐỗNoch keine Bewertungen
- 32 - Carbonates Fluid FormulationsDokument40 Seiten32 - Carbonates Fluid FormulationsAdil KOLLINoch keine Bewertungen
- Pakistan Oil-Based Fluids PresentationDokument42 SeitenPakistan Oil-Based Fluids PresentationKaleem UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supervisor Drilling Fluids Engineer: Familiar Technologies: Hazardous MaterialsDokument4 SeitenSupervisor Drilling Fluids Engineer: Familiar Technologies: Hazardous MaterialsMizi MimihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer Additive Reference StandardsDokument36 SeitenPolymer Additive Reference StandardsvasucristalNoch keine Bewertungen
- KAPL Corporate Presentation Oilfield ChemicalsDokument47 SeitenKAPL Corporate Presentation Oilfield ChemicalsKrishna GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Scale Inhibitors PerformanceDokument14 SeitenEvaluation of Scale Inhibitors PerformanceLaura Natalia SalcedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Aqueous Drilling FluidsDokument8 SeitenNon Aqueous Drilling FluidsEZWANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion Prevention by Use of InhibitorsDokument19 SeitenCorrosion Prevention by Use of InhibitorsSai PradeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Lost CirculationDokument10 SeitenPrinciples of Lost CirculationRod UchytilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clay Nanoparticles Modifed Drilling Fluids For Drilling of Deep Hydrocarcbon Wells PDFDokument7 SeitenClay Nanoparticles Modifed Drilling Fluids For Drilling of Deep Hydrocarcbon Wells PDFJuliana BuelvasNoch keine Bewertungen
- RISERLESS DRILLING - Advances in Riserless Drilling Pushing The Deepwater Surface String Envelope - OffshoreDokument7 SeitenRISERLESS DRILLING - Advances in Riserless Drilling Pushing The Deepwater Surface String Envelope - OffshorebruceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 11B Water Base Drilling FluidsDokument44 SeitenSection 11B Water Base Drilling FluidsLazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPE-116364-Entrance Pressure of Oil Based Mud Into Shale Effect of Shale, WaterDokument19 SeitenSPE-116364-Entrance Pressure of Oil Based Mud Into Shale Effect of Shale, WaterwjawichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Retarder TDSDokument1 SeiteAcid Retarder TDSAmbrish KamdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals and Applications of Bionic Drilling FluidsVon EverandFundamentals and Applications of Bionic Drilling FluidsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diels Alder FoamsDokument7 SeitenDiels Alder FoamsdougNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latex Film FormationDokument26 SeitenLatex Film FormationdougNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additives John Du BYKDokument78 SeitenAdditives John Du BYKdougNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pigments NanocompositesDokument28 SeitenPigments NanocompositesdougNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coating Ingredient Effects On RheologyDokument50 SeitenCoating Ingredient Effects On RheologydougNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pigments TiO2Dokument43 SeitenPigments TiO2dougNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATRP LabDAHLIADokument7 SeitenATRP LabDAHLIAdougNoch keine Bewertungen
- BeautyDokument35 SeitenBeautydougNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0849382459Dokument591 Seiten0849382459dougNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Food Rheology and Its Applications Development in Food Rheology 2Nd Edition Jasim Ahmed Editor Full ChapterDokument52 SeitenAdvances in Food Rheology and Its Applications Development in Food Rheology 2Nd Edition Jasim Ahmed Editor Full Chaptermary.mcallister740100% (16)
- Chap - 05 - RHEALOGY PDFDokument36 SeitenChap - 05 - RHEALOGY PDFKarim WasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Index PropertiesDokument85 SeitenIndex PropertiesprashanthreddyhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Properties of AsphaltDokument8 Seiten4 - Properties of AsphalttunlajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TI 1279 Successful Use of Aerosil Fumed Silica in Liquid SystemDokument11 SeitenTI 1279 Successful Use of Aerosil Fumed Silica in Liquid SystemGrandys PerwiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elaborate Report Field Testing Pit Emptying BlantyreDokument69 SeitenElaborate Report Field Testing Pit Emptying BlantyreAlphonsius WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Mechanics-Lecture Notes With Cover-2Dokument237 SeitenSoil Mechanics-Lecture Notes With Cover-2Khalid AljanabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DP490Dokument6 SeitenDP490transervuk2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- RheoWin Software Features For QC and Routine MeasurementsDokument9 SeitenRheoWin Software Features For QC and Routine Measurements--Noch keine Bewertungen
- Opti FloDokument11 SeitenOpti FloAna QuintanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CaseinDokument3 SeitenCaseinDawn ZichkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Patent: Zy 2X ZZZZZZZZDokument8 SeitenUnited States Patent: Zy 2X ZZZZZZZZVansala GanesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- COLLANTE FCB 130 - Araldite - FT - AV138M-1 - HV998 - ENDokument4 SeitenCOLLANTE FCB 130 - Araldite - FT - AV138M-1 - HV998 - ENMax SalogniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2 RheologyDokument35 SeitenChap 2 RheologyALISHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Clay Systems For Improved PerformanceDokument5 SeitenClay Systems For Improved PerformanceDouglas Franco de Souza100% (1)
- Araldite 2013Dokument6 SeitenAraldite 2013c m tambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roll CoatingDokument6 SeitenRoll CoatingAhmet Rasim BozkurtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wetting and DispersingDokument16 SeitenWetting and DispersingSerhan ÜnverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Plug Placement: January 2020Dokument29 SeitenFundamentals of Plug Placement: January 2020Douadi AbderraoufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Properties of Stirred Yogurt Calculation of The PDFDokument22 SeitenFlow Properties of Stirred Yogurt Calculation of The PDFandres332Noch keine Bewertungen
- Visco-Handbook 2015 2.7-MB PDF-EnglishDokument92 SeitenVisco-Handbook 2015 2.7-MB PDF-EnglishThorieForestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Byk 410Dokument4 SeitenByk 410sudhir5441Noch keine Bewertungen
- Papagiannakis Solutions For Text BookDokument112 SeitenPapagiannakis Solutions For Text BookRishiKaithala100% (2)
- Evaluating Structural Buildup at Rest of Self-Consolidating Concrete Using Workability TestsDokument10 SeitenEvaluating Structural Buildup at Rest of Self-Consolidating Concrete Using Workability TestsHuaman Chavez Jesus AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disparlon GuidelinesDokument6 SeitenDisparlon GuidelinesPratik MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating The Viscosity of KetchupDokument3 SeitenInvestigating The Viscosity of KetchupolliharviekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 - RheologyDokument58 Seiten07 - RheologyPuspa DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rhe OlogyDokument51 SeitenRhe OlogySaifuddin AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pigment & Resin Technology: Article InformationDokument7 SeitenPigment & Resin Technology: Article InformationLaura González SossaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RHEOBYK-410: Product DataDokument4 SeitenRHEOBYK-410: Product DataMostafa BatanyNoch keine Bewertungen