Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Testing by Numero Uno Technologies
Hochgeladen von
Hitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Testing by Numero Uno Technologies
Hochgeladen von
Hitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TYPES OF TESTS:
UNIT TESTING: Unit testing involves the design of test cases that validate that the internal program logic is functioning properly, and that program inputs produce valid outputs. All decision branches and internal code flow should be validated. It is the testing of individual software units of the application .it is done after the completion of an individual unit before integration. This is a structural testing, that relies on knowledge of its construction and is invasive. Unit tests perform basic tests at component level and test a specific business process, application, and/or system configuration. Unit tests ensure that each unique path of a business process performs accurately to the documented specifications and contains clearly defined inputs and expected results.
INTEGRATION TESTING: Integration tests are designed to test integrated software components to determine if they actually run as one program. Testing is event driven and is more concerned with the basic outcome of screens or fields. Integration tests demonstrate that although the components were individually satisfaction, as shown by successfully unit testing, the combination of components is correct and consistent. Integration testing is specifically aimed at exposing the problems that arise from the combination of components.
FUNCTIONAL TESTING: Functional tests provide systematic demonstrations that functions tested are available as specified by the business and technical requirements, system documentation and user manuals.
Functional testing is centered on the following items: Valid Input Invalid Input Functions Output exercised. Systems/Procedures: interfacing systems or procedures must be invoked. : identified classes of valid input must be accepted. : identified classes of invalid input must be rejected. : identified functions must be exercised. : identified classes of application outputs must be
Organization and preparation of functional tests is focused on requirements, key functions, or special test cases. In addition, systematic coverage pertaining to identify Business process flows; data fields, predefined processes, and successive processes must be considered for testing. Before functional testing is complete, additional tests are identified and the effective value of current tests is determined.
SYSTEM TESTING: System testing ensures that the entire integrated software system meets requirements. It tests a configuration to ensure known and predictable results. An example of system testing is the configuration oriented system integration test. System testing is based on process descriptions and flows, emphasizing pre-driven process links and integration points.
WHITE BOX TESTING:
White Box Testing is a testing in which in which the software tester has knowledge of the inner workings, structure and language of the software, or at least its purpose. It is purpose. It is used to test areas that cannot be reached from a black box level .
BLACK BOX TESTING: Black Box Testing is testing the software without any knowledge of the inner workings, structure or language of the module being tested . Black box tests, as most other kinds of tests, must be written from a definitive source document, such as specification or requirements document, such as specification or requirements document. It is a testing in which the software under test is treated, as a black box .you cannot see into it. The test provides inputs and responds to outputs without considering how the software works.
6.1 Unit Testing:
Unit testing is usually conducted as part of a combined code and unit test phase of the software lifecycle, although it is not uncommon for coding and unit testing to be conducted as two distinct phases.
Test strategy and approach Field testing will be performed manually and functional tests will be written in detail.
Test objectives All field entries must work properly.
Pages must be activated from the identified link. The entry screen, messages and responses must not be delayed. Features to be tested Verify that the entries are of the correct format No duplicate entries should be allowed All links should take the user to the correct page.
6.2 Integration Testing:
Software integration testing is the incremental integration testing of two or more integrated software components on a single platform to produce failures caused by interface defects. The task of the integration test is to check that components or software applications, e.g. components in a software system or one step up software applications at the company level interact without error.
Test Results: All the test cases mentioned above passed successfully. No defects encountered.
6.3 Acceptance Testing:
User Acceptance Testing is a critical phase of any project and requires significant participation by the end user. It also ensures that the system meets the functional requirements.
Test Results: All the test cases mentioned above passed successfully. No defects encountered.
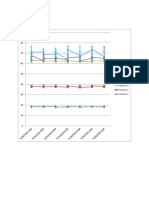
Screen Shots
IMPLEMENTATION: Implementation is the stage of the project when the theoretical design is turned out into a working system. Thus it can be considered to be the most critical stage in achieving a successful new system and in giving the user, confidence that the new system will work and be effective.
The implementation stage involves careful planning, investigation of the existing system and its constraints on implementation, designing of methods to achieve changeover and evaluation of changeover methods.
Implementation is the process of converting a new system design into operation. It is the phase that focuses on user training, site preparation and file conversion for installing a candidate system. The important factor that should be considered here is that the conversion should not disrupt the functioning of the organization.
The implementation can be preceded through Socket in java but it will be considered as one to all communication .For proactive broadcasting we need dynamic linking. So java will be more suitable for platform independence and networking concepts. For maintaining route information we go for MSaccess/SQL-server as database back end.
Future Enhancement: It also helps pinpoint the true origin of an attack packet to be within a small number of candidate networks, thus simplifying the reactive IP traceback process.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sai SiddhiDokument11 SeitenSai SiddhiHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Patient or Elder Fall Detection Based On Movement and Sound DataDokument5 SeitenAdvanced Patient or Elder Fall Detection Based On Movement and Sound DataHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affective Text Based Emotion Mining in Social MediaDokument9 SeitenAffective Text Based Emotion Mining in Social MediaHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance EvaluationDokument1 SeitePerformance EvaluationHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposed SystemDokument1 SeiteProposed SystemHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- K Proto TypeDokument2 SeitenK Proto TypeHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Monitoring SysDokument13 SeitenWater Monitoring SysHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRI 12288 Dehradun Kochuveli Weekly SF ExpressDokument1 SeiteIRI 12288 Dehradun Kochuveli Weekly SF ExpressHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gnatt Chart: Page 1 of 1 Exported On November 17, 2013 2:38:08 AM PSTDokument1 SeiteGnatt Chart: Page 1 of 1 Exported On November 17, 2013 2:38:08 AM PSTHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Year ProjectDokument2 SeitenFinal Year ProjectHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- University SynopsiusDokument3 SeitenUniversity SynopsiusHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Text Summarization Based On Sentences Clustering and ExtractionDokument4 SeitenAutomatic Text Summarization Based On Sentences Clustering and ExtractionHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Power Auto Temp Controller With Cooling SystemDokument3 SeitenSolar Power Auto Temp Controller With Cooling SystemHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Context Aware Messaging and Addressing For Emergency ApplicationDokument25 Seiten1 Context Aware Messaging and Addressing For Emergency ApplicationHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jamming Aware Traffic Allocation For Multiple Path Routing Using Portfolio Selection PDFDokument6 SeitenJamming Aware Traffic Allocation For Multiple Path Routing Using Portfolio Selection PDFHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficient and Discovery of Patterns in Sequences DataDokument19 SeitenEfficient and Discovery of Patterns in Sequences DataHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nymble Blocking Misbehaving Users in Anonymizing Networks IEEE Project Base PaperDokument15 SeitenNymble Blocking Misbehaving Users in Anonymizing Networks IEEE Project Base PaperprojectacademyindiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Building Monitoring Using GprsDokument3 SeitenPublic Building Monitoring Using GprsHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors: Hierarchical Leak Detection and Localization Method in Natural Gas Pipeline Monitoring Sensor NetworksDokument26 SeitenSensors: Hierarchical Leak Detection and Localization Method in Natural Gas Pipeline Monitoring Sensor NetworksHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Monitoring SysDokument6 SeitenEnergy Monitoring SysHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShridaDokument1 SeiteShridaHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Based RFID Authentication IEEE 2013 PDFDokument8 SeitenCloud Based RFID Authentication IEEE 2013 PDFHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Information ExtractionDokument7 SeitenWeb Information ExtractionHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mona Secure Multi-Owner Data SharingDokument10 SeitenMona Secure Multi-Owner Data SharingSrujan SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Adaptive Opportunistic Routing SchemeDokument13 SeitenAn Adaptive Opportunistic Routing SchemeMohit SnggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clustering User Preferences Using W-KmeansDokument8 SeitenClustering User Preferences Using W-KmeansHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icwac 1310Dokument7 SeitenIcwac 1310Hitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Integrated Scheme Based On Triple DES, RSA andDokument6 SeitenAn Integrated Scheme Based On Triple DES, RSA andHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Privacy Preservation Model For Facebook-Style Social Network SystemsDokument18 SeitenA Privacy Preservation Model For Facebook-Style Social Network SystemsHitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IJERTV2IS50048Dokument5 SeitenIJERTV2IS50048Hitesh ವಿಟ್ಟಲ್ ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Introduction To PythonDokument27 SeitenIntroduction To PythonRyan ReasNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUDISON BitTune Pro License Activation ENG RevADokument4 SeitenAUDISON BitTune Pro License Activation ENG RevANaeem SamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRSTDokument10 SeitenFRSTLinusChinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSSQL Interview QuestionsDokument32 SeitenMSSQL Interview QuestionsAnonymous 1GAxwUf100% (1)
- IMAGINE UAV 1.7.0. For 2018 Installation GuideDokument10 SeitenIMAGINE UAV 1.7.0. For 2018 Installation GuideAbnan YazdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBPS IT Officer Model Questions Computer MIcroprocessor and Assembly Language MCQ Question BankDokument146 SeitenIBPS IT Officer Model Questions Computer MIcroprocessor and Assembly Language MCQ Question BankNaveen KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec2306 Set2Dokument5 SeitenEc2306 Set2kaliappan45490Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Human Pose Estimation With Deep LearningDokument11 SeitenAn Overview of Human Pose Estimation With Deep LearningAnshu kumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lexical AnalysisDokument13 SeitenLexical Analysisapi-20012397Noch keine Bewertungen
- Frequently Asked Questions VMMDokument18 SeitenFrequently Asked Questions VMMMohinuddin MustaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- FA GenreratorDokument18 SeitenFA Genreratorved.prakash.mehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions in C ProgrammingDokument15 SeitenFunctions in C ProgrammingVignesh Murali100% (1)
- Omiga BattlecardDokument6 SeitenOmiga BattlecardSalman AslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cse & ItreqDokument11 SeitenCse & ItreqVallam RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSARDokument187 SeitenMSARmoaziz2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intel DPDK API ReferenceDokument262 SeitenIntel DPDK API ReferenceGilbedt Zelaya OrtízNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap04C OrthophotoDokument70 SeitenChap04C OrthophotoAnonymous 6yonWEaFuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mediatek Confidential: Linux STA Driver Release History RT5xxxDokument5 SeitenMediatek Confidential: Linux STA Driver Release History RT5xxxAnderson JSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vigers KeDokument321 SeitenVigers KeiazcuzcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Virtual Machine - Wiki.Dokument6 SeitenJava Virtual Machine - Wiki.prasad357Noch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring Italc Management Software For Use With Ncomputing SystemsDokument16 SeitenConfiguring Italc Management Software For Use With Ncomputing SystemsNilson Gongora PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DevOps VLabs Internship JDDokument1 SeiteDevOps VLabs Internship JDPravinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developer's Journal 2007-06Dokument36 SeitenDeveloper's Journal 2007-06PerryShopsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CL Commands XiDokument526 SeitenCL Commands Xiapi-3800226Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bitonic SortDokument3 SeitenBitonic SortPreetesh PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPM Download FilesDokument5 SeitenEPM Download FilesRajendra PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lenteur SSL Palo AltoDokument17 SeitenLenteur SSL Palo AltoVivien PrieurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report Payroll Management SystemDokument18 SeitenProject Report Payroll Management Systemsrilakshmi4466_3309467% (3)
- 6.2 Elements of Transport ProtocolsDokument12 Seiten6.2 Elements of Transport ProtocolsSeptian Rahman Hakim67% (3)
- SrsDokument18 SeitenSrsSaransh DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen