Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Assignment 1 - Chapter 3 Answer
Hochgeladen von
Harryzam MartelCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignment 1 - Chapter 3 Answer
Hochgeladen von
Harryzam MartelCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ASSIGNMENT 1 CHAPTER 3 1.
. Define the following terms: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Crystal Structure: 3D pattern of atoms or ions in space Space Lattice: 3D array of points each of which has the same geometric environment Lattice Point: One point in the array in a space lattice Unit Cell: A smallest repeating unit of a space lattice Lattice Constants: Length dimensions or angles that characterize geometry of a unit cell
2. What are the 14 Bravais unit cells? Simple cubic, body-centered cubic, face-centered cubic, simple tetragonal, body-centered tetragonal, simple orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, face-centered orthorhombic, simple rhombohedral, simple hexagonal, simple monoclinic, base-centered monoclinic, and simple triclinic 3. What are the 3 most common metal crystal structures? Give an example of the metal that have each of these crystal structures. Three common crystal structures: Body-centered cubic (BCC), Face-centered cubic (FCC), and Hexagonal close packed (HCP). BCC: iron, tungsten, chromium FCC: copper, aluminum, nickel, silver HCP: magnesium, zinc, cadmium 4. Molybdenum at 20 C is BCC and has an atomic radius of 0.140 nm. Calculate a value for its lattice constant, a in nm.
5. Lithium at 20 C is BCC and has a lattice constant of 0.35092 nm. Calculate a value for the atomic radius of a lithium in nm.
6. Gold is FCC and has a lattice constant of 0.40788 nm. Calculate a value for the atomic radius of a gold atom in nm.
7. Palladium is FCC and has an atomic radius of 0.137 nm. Calculate a value for its lattice constant, a in nm.
8. Calculate the volume in nm3 of the titanium crystal structure unit cell. Titanium is HCP at 20 C with a = 0.29504 nm and c = 0.46833 nm. V = = = = = Area of base x Height (1/2) x a x (3/4)a x 6 x c 2.59809a2 x c 2.59809(0.29504)2 x (0.46833) 0.106 nm3
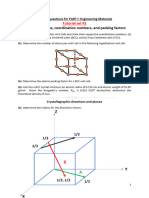
9. Draw the following directions in a BCC unit cell: (a) [100], (b) [110], (c) [111]
10. Draw direction vectors in unit cells for the following cubic directions: (a) [111], (b) [110], (c) [121], (d) [113]
11. A direction vector passes through a unit cube from the (3/4, 0, 1/4) to the (1/2, 1, 0) positions. What are its direction indices?
12. A direction vector passes through a unit cube from the (1, 0, 3/4) to the (1/4, 1, 1/4) positions. What are its direction indices?
13. Draw in unit cubes the crystal planes that have the following Miller indices: (a) (111), (b) (102), (c) (121), (d) (213)
14. Determine the Miller indices of the cubic crystal plane that intersects the following position coordinates: (1, 1/2, 1); (1/2, 0, 3/4); (1, 0, 1/2)
15. The lattice constant for BCC tantalum at 20 C is 0.33026 nm and its density is 16.6 g/cm3. Calculate a value for its relative atomic mass.
16. Calculate the planar atomic density in atoms/mm2 for the following crystal planes in BCC chromium, which has a lattice constant of 0.28846 nm: (a) (100), (b) (110), (c) (111)
17. Calculate the linear atomic density in atoms/mm for the following directions in FCC iridium, which has a lattice constant of 0.38389 nm: (a) [100], (b) [110], (c) [111]
18. Do you expect gold and silver to have the same (a) atomic packing factor, (b) volume of unit cell, (c) number of atoms per unit cell, and (d) coordination number? Verify your answers. We expect gold and silver, both are FCC. These materials have the same: Atomic packing factor = 0.74 Atoms per unit cell = 4 Coordination number = 12 The volume of the cell will be larger for the atom with the larger atomic radius.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Assignment 1 - Chapter 3Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1 - Chapter 3Harryzam MartelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapt 03 Sect 1 To 6Dokument18 SeitenChapt 03 Sect 1 To 6Jesse McClureNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMEN 120 - Crystal Structures Practice QuestionsDokument4 SeitenMMEN 120 - Crystal Structures Practice QuestionsnattydreadfathelahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating unit cell volume and density from atomic radiusDokument7 SeitenCalculating unit cell volume and density from atomic radiusks kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Sheet 2Dokument4 SeitenProblem Sheet 2Siddharth SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 03 - Crystal StructureDokument2 SeitenTutorial 03 - Crystal StructuremarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-27.2 Crystalline Materials - Detects in Crystalline MaterialsDokument92 SeitenCh-27.2 Crystalline Materials - Detects in Crystalline MaterialsManojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-27.2 Crystalline Materials - Detects in Crystalline MaterialsDokument102 SeitenCh-27.2 Crystalline Materials - Detects in Crystalline MaterialsasjfgauojfgfNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetE 227 study questions on materials science conceptsDokument3 SeitenMetE 227 study questions on materials science conceptsCaner AkkuşNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal HandoutsDokument23 SeitenCrystal HandoutsArup DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-27.2 Crystalline Materials & Detects in Crystalline MaterialsDokument93 SeitenCh-27.2 Crystalline Materials & Detects in Crystalline MaterialsSmruti Ranjan PattanayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Problems 2: Crystal Structures and PropertiesDokument3 SeitenTutorial Problems 2: Crystal Structures and PropertiesMajak MarialNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 2Dokument1 SeiteHW 2azizieh5701Noch keine Bewertungen
- 03 - Crystal Structures of MetalsDokument8 Seiten03 - Crystal Structures of MetalsJant Erbert GarbosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Physical Metallurgy: Density: 19.05 G/CM Atomic Weight: 238.03 Amu or G/mol Atomic Radius: 0.1385 NMDokument4 SeitenModern Physical Metallurgy: Density: 19.05 G/CM Atomic Weight: 238.03 Amu or G/mol Atomic Radius: 0.1385 NM哭哭麻頭Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 1Dokument23 SeitenChem 1Adi SoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common unit cells and crystal structuresDokument99 SeitenCommon unit cells and crystal structuresasjfgauojfgfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 E FDokument2 SeitenAssignment 1 E FSudhananda MallickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Materials (UES012) School of Physics and Materials Science Tutorial Sheet No 3-4Dokument2 SeitenEngineering Materials (UES012) School of Physics and Materials Science Tutorial Sheet No 3-4dareghost ytNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 03 AnnotDokument4 SeitenChapter 03 AnnotNur Amira Mardiana ZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unmatchable Material Science Quiz AnswersDokument11 SeitenUnmatchable Material Science Quiz AnswersApurva RakeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 3Abood AtiyatNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure of Crystalline SolidDokument32 SeitenThe Structure of Crystalline SolidRakesh Lingayat100% (2)
- MSE 101 Sample Problems - Crystal StructuresDokument1 SeiteMSE 101 Sample Problems - Crystal StructuresKate Lynn PabelicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- McsDokument13 SeitenMcsRodneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal StructureDokument16 SeitenCrystal StructureᎽᎪsh ᏒᎪj sᎥᏁᎶhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Assignment - Solid StatesDokument5 SeitenPhysics Assignment - Solid Statesanshaggarwal7491Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State Physics MCQsDokument7 SeitenSolid State Physics MCQsAhsan MoinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spheres - Na)Dokument6 SeitenSpheres - Na)amarnath_b5986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State & Surface Chemistry & Colloids - FDokument4 SeitenSolid State & Surface Chemistry & Colloids - FAshwin BalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deber 2. Redes Cristalinas Aragon CMBDokument14 SeitenDeber 2. Redes Cristalinas Aragon CMBYajaira AragonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Tutorial 3Dokument29 SeitenAnswer Tutorial 3Sofea IzyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Problems For Chapter3Dokument11 SeitenReview Problems For Chapter3johandreher100% (1)
- Organizacion AtomicaDokument99 SeitenOrganizacion AtomicaJoel ParrNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCC Crystal Structure and PropertiesDokument4 SeitenFCC Crystal Structure and PropertiespewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2. Structure of Crystalline SolidsDokument20 SeitenModule 2. Structure of Crystalline SolidsPearl Alexandra FabitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Solid State: Unit-1Dokument7 SeitenThe Solid State: Unit-1Rams ChanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Academy: Exercise - IDokument11 SeitenChem Academy: Exercise - IHamit RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm P2800 2008 SolutionsDokument6 SeitenMidterm P2800 2008 Solutionskhalil alhatabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument86 SeitenChapter 3Jose L. Rosado100% (1)
- 295 4 Solid State Practice ProblemsDokument11 Seiten295 4 Solid State Practice ProblemsArijit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal StructureDokument10 SeitenCrystal StructureMorena EmorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Questions For Part 1Dokument5 SeitenTutorial Questions For Part 1Ng Yan XiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04_1_Solid_State_15_4_2023_pdf_Margdarshan_2_0_Solid_St_JindalJi247Dokument5 Seiten04_1_Solid_State_15_4_2023_pdf_Margdarshan_2_0_Solid_St_JindalJi24735 Pranay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic and Ionic Arrangements CalculationsDokument19 SeitenAtomic and Ionic Arrangements CalculationsRafael AraújoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems On STMDokument4 SeitenProblems On STMshanthakumargc0% (1)
- Engineering Metallurgy Homework # 2Dokument3 SeitenEngineering Metallurgy Homework # 2Ahmed Hamdy KhattabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Lattice, Space LatticeDokument6 SeitenCrystal Lattice, Space LatticeSelemon AssefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4.0 Basic Concepts of Crystalline StructureDokument11 SeitenLesson 4.0 Basic Concepts of Crystalline StructureyoureqtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 - Egm 241Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 3 - Egm 241king100% (1)
- Solid State Made BY KeshavPandey EngineerDokument6 SeitenSolid State Made BY KeshavPandey EngineerVibhansh BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises - ReciprocalSpaces and XRDDokument2 SeitenExercises - ReciprocalSpaces and XRDtackyjc0% (1)
- JR IitDokument3 SeitenJR IitGowri ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State Revision SheetDokument6 SeitenSolid State Revision SheetRumaysa -Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solved Problem SheetDokument2 SeitenSolved Problem SheetAbdla DoskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW3Dokument1 SeiteHW3Christian PetersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computational Liquid Crystal Photonics: Fundamentals, Modelling and ApplicationsVon EverandComputational Liquid Crystal Photonics: Fundamentals, Modelling and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesVon EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wigner-Seitz Cell - WikipediaDokument28 SeitenWigner-Seitz Cell - Wikipediaafzaal malikNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCEE5210 2023F L5 CrystallizationDokument72 SeitenMCEE5210 2023F L5 Crystallizationtc1992423Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Physics (PH22101) : ObjectivesDokument59 SeitenEngineering Physics (PH22101) : ObjectivesSK crushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 6th Edition Groover Solutions ManualDokument3 SeitenFundamentals of Modern Manufacturing 6th Edition Groover Solutions ManualJacobTorresbipkz100% (14)
- Crystal Structure and Defects GuideDokument14 SeitenCrystal Structure and Defects GuideLogesh GovindNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Crystal Symmetries and BindingsDokument38 Seiten2 - Crystal Symmetries and Bindingsdtqphuong1001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 6 Study Material emDokument28 SeitenNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 6 Study Material emÂshwin ÂshwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Crystal DefectsDokument47 Seiten3 Crystal DefectsLahiru JananjayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 3Dokument15 SeitenActivity 3emjay100% (1)
- Chemical Element Atoms Crystalline MoleculesDokument3 SeitenChemical Element Atoms Crystalline MoleculesReign AckermannNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoogleDokument10 SeitenGoogleVatsal ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 3Dokument5 SeitenProblem Set 3Catarina MascarenhasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Science Problem Sets and AnswersDokument18 SeitenMaterial Science Problem Sets and AnswersMajeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial On Powder X Ray Diffraction For Characterizing Nanoscale MaterialsDokument7 SeitenTutorial On Powder X Ray Diffraction For Characterizing Nanoscale MaterialsJaymin RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2 Crystal StructuresDokument5 SeitenExperiment 2 Crystal StructuresPhamAnhKhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Crystallography Problems and Question BankDokument7 Seiten02 Crystallography Problems and Question BankBhavesh Mhatre100% (2)
- Part 8 The Triclinic SystemDokument2 SeitenPart 8 The Triclinic SystemstephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bai TapDokument3 SeitenBai TapHai NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mms Module 1 NotesDokument19 SeitenMms Module 1 NotesArvidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reciprocal Lattice ConstructionDokument21 SeitenReciprocal Lattice ConstructionP Em ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Miller Indices ClassDokument35 SeitenMiller Indices ClassDhiyaAldeenAl-SerhanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - Electron DiffractionDokument12 SeitenLecture - Electron DiffractionOlivia WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jorn H KruhlDokument20 SeitenJorn H KruhlSumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 3 MineralogyDokument36 SeitenGroup 3 MineralogyLenoj OlarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Deformation of Single Crystals ExplainedDokument42 SeitenPlastic Deformation of Single Crystals ExplainedNaresh DeshpandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficient creation and convergence of surface slabsDokument13 SeitenEfficient creation and convergence of surface slabsHoàng Thu ThuỷNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Solid State Chemistry To Catalysis - Svetlana IvanovaDokument320 SeitenFrom Solid State Chemistry To Catalysis - Svetlana IvanovaaersaaagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3b Miller IndicesDokument53 SeitenChapter 3b Miller Indicesshian ervin lopezNoch keine Bewertungen