Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Building The E-Column
Hochgeladen von
gcpasambaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Building The E-Column
Hochgeladen von
gcpasambaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Ecocolumn
Terrestrial chamber
Filtration Layer Soil/potting soil Seeds/plant
Decomposition chamber Leaf/grass material
Potting soil Fruit, potato Fruit fly/worms
Aquatic chamber
Substrate material (sand/gravel, aquarium rock) Guppy, other organisms aquatic plant
Activity: Building the Ecocolumn
Part A. The Terrestrial Chamber
Terrestrial chamber
Sand, gravel, stones Soil/potting soil Seeds/plant
1. Germinate the seeds. a. Measure the mass of 5 seeds. Find the average. b. Place the seeds in a bed of moist cotton spread out in a petri dish. Note: Mark the area first with 2. Prepare the terrestrial chamber.
the desired height before you start cutting the bottle
a. Have a layer of gravel, stone, and sand at the bottom. This will serve as a filtration layer. Measure the mass of each material before placing these into the chamber. b. Place soil on top of your filtration layer. Measure the mass of the soil. Use pH paper to determine its acidity. c. Plant your germinated seeds. d. Make small holes in the cap and a bigger hole to insert a piece of plastic straw. This will allow water to pass through and will connect this chamber with the decomposing chamber.
Activity: Building the Ecocolumn
Part B. The Aquatic Chamber 1. Decide on what organisms you plan to include in your aquatic chamber. 2. Mark and cut the bottle to the desired height.
Aquatic chamber
Substrate material (sand/gravel, aquarium rock) Guppy (optional) Snail aquatic plant
3. Make a port hole for easy access. This should be above the water level. 4. Measure the mass of the substrate material you plan to use. Place your substrate material at the bottom of the bottle. 5. Add water. Make sure to measure the volume of water before this is added.
6. Measure the temperature and pH of the water.
7. Add your organism/s.
Activity: Building the Ecocolumn
Part C. The Decomposition Chamber 1. Mark and cut the bottle to the desired height. 2. Make small holes in the cap to allow water to pass through.
Decomposition Chamber
Leaf/grass material Potting soil Fruit, potato Fruit fly/worms
3. Make a small port hole enough for a thermometer to pass through.
4. Measure the mass of an empty zip loc bag. 5. Collect the desired amount of decayed material and place in the zip loc bag. Measure its mass. 6. Place the decayed material in the chamber. 7. Measure the temperature of the decayed material.
In their notebook, answer the following: Create a list of biotic and abiotic factors Draw a labeled diagram of the chamber.
What is present in your chamber that will help sustain life? Absent? What must be done for organisms in your system to survive?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 7th Grade Science: International School ManilaDokument2 Seiten7th Grade Science: International School ManilagcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper HelicopterDokument8 SeitenPaper HelicoptergcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - Block - Lab: Which Heats Up Fastest: Soil, Sand or Water?Dokument4 SeitenName: - Block - Lab: Which Heats Up Fastest: Soil, Sand or Water?gcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Machines Slide PresentationDokument51 SeitenSimple Machines Slide PresentationgcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Density Quiz GlossaryDokument1 SeiteDensity Quiz GlossarygcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poster Rescue MachinesDokument6 SeitenPoster Rescue MachinesgcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Javier" Liquid Drop TestDokument8 Seiten"Javier" Liquid Drop TestgcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rockets Performance TaskDokument20 SeitenRockets Performance TaskgcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pendulum Lab-Conclusion GuideDokument3 SeitenPendulum Lab-Conclusion GuidegcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONCLUSION GUIDE: Evidence OrganizerDokument1 SeiteCONCLUSION GUIDE: Evidence OrganizergcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - Summary and Performance TaskDokument39 SeitenChemistry - Summary and Performance TaskgcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONCLUSION GUIDE: Explaining The Science: (Question 2 of Summary)Dokument1 SeiteCONCLUSION GUIDE: Explaining The Science: (Question 2 of Summary)gcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
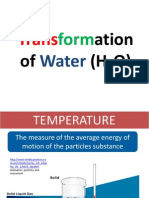
- Transformations of WaterDokument12 SeitenTransformations of WatergcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces and First Law C Notes 2012Dokument3 SeitenForces and First Law C Notes 2012gcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Revision List - CirculationDokument1 SeiteGrade 8 Revision List - CirculationgcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Task - System DisordersDokument2 SeitenPerformance Task - System Disordersgcpasamba100% (1)
- Evolution and Natural Selection C Notes 2012Dokument2 SeitenEvolution and Natural Selection C Notes 2012gcpasambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Bio TAXONOMYDokument5 SeitenBio TAXONOMYSheila DominguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grow Tomatoes in Six StepsDokument16 SeitenGrow Tomatoes in Six Stepsmichael angelo0% (1)
- Tissues MCQDokument9 SeitenTissues MCQtraptisharma3342Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practocal Manual On Plant Tissue CultureDokument130 SeitenPractocal Manual On Plant Tissue CultureĐương Anh CaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Video Seminar On Rice Seed Production - Organized by CARD SecretariatDokument37 SeitenVideo Seminar On Rice Seed Production - Organized by CARD SecretariatArgus EyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agriculture Statistics Balochistan 2019 20Dokument220 SeitenAgriculture Statistics Balochistan 2019 20Muhamamd Zahid Ullah Khan50% (2)
- SCIENCE AyaDokument8 SeitenSCIENCE AyaHannah Jessa AngobNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Use of Vermicompost PDFDokument23 SeitenThe Use of Vermicompost PDFVon Carlo Tabuan LptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Project Wood ScienceDokument17 SeitenMini Project Wood ScienceFARHANIZAH BINTI ALIP BS20160587Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4. (14pp) Direct Planting and TransplantingDokument14 SeitenModule 4. (14pp) Direct Planting and TransplantingDimasalang Perez88% (8)
- E - Book A Manual On Orchid Education: Siddhartha Sankar BiswasDokument76 SeitenE - Book A Manual On Orchid Education: Siddhartha Sankar BiswasYuliana Nina YuanitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agrinome For Breeding - Glossary List For Mutual Understandings v0.3 - 040319Dokument7 SeitenAgrinome For Breeding - Glossary List For Mutual Understandings v0.3 - 040319mustakim mohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asexual Plant PropagationDokument10 SeitenAsexual Plant PropagationSonia Revilla ObligadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MarchantiaDokument25 SeitenMarchantiaSanchita KulshresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lycopodium Clavatum Is A: Diphasiastrum Digitatum Is Known As Groundcedar, Running Cedar or Crowsfoot, Along WithDokument3 SeitenLycopodium Clavatum Is A: Diphasiastrum Digitatum Is Known As Groundcedar, Running Cedar or Crowsfoot, Along WithEarlyn Joy Villaruel EniolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Language of FlowersDokument36 SeitenLanguage of Flowerscristina_bartlebyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botany HorsetailDokument3 SeitenBotany HorsetailJohn Kevin NocheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crooked-Stem Aster: Symphyotrichum Prenanthoides (Muhl. Ex Willd.) G.L. Nesom - Plant Fact Sheet - Plant Materials Center, Beltsville, MDDokument2 SeitenCrooked-Stem Aster: Symphyotrichum Prenanthoides (Muhl. Ex Willd.) G.L. Nesom - Plant Fact Sheet - Plant Materials Center, Beltsville, MDMaryland Native Plant ResourcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yamadori ARTS 344Dokument5 SeitenYamadori ARTS 344Ron GermanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poplar Tree Farming Information Guide - Agri Farming PDFDokument6 SeitenPoplar Tree Farming Information Guide - Agri Farming PDFfaraz zeeshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevalence and Management of Rice ROOT-KNOT NEMATODE (MeloidogyneDokument81 SeitenPrevalence and Management of Rice ROOT-KNOT NEMATODE (MeloidogynePraveen GoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcatchment: NegarimDokument11 SeitenMicrocatchment: Negarimhaithamelramlawi7503Noch keine Bewertungen
- Morphology Practical-1 - 220624 - 093751Dokument4 SeitenMorphology Practical-1 - 220624 - 093751Kritika KadiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Tissue Culture TrainingDokument2 SeitenPlant Tissue Culture TrainingreddygonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity of Shrubs On Tropical Lowland Forest Pangandaran Preservation, West JavaDokument6 SeitenBiodiversity of Shrubs On Tropical Lowland Forest Pangandaran Preservation, West JavaLyla PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ornamental Bulbous Plants of Brazil: Zephyranthes. Alliaceae Has Few Species in Brazil, Some Nothoscordum and IpheionDokument6 SeitenOrnamental Bulbous Plants of Brazil: Zephyranthes. Alliaceae Has Few Species in Brazil, Some Nothoscordum and Ipheionmarcus456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test in EPPDokument7 SeitenTest in EPPNexus KrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Please Eat The FlowersDokument12 SeitenPlease Eat The FlowersDave_SadvertfileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strawberry FarmingDokument45 SeitenStrawberry Farmingc_chesho100% (1)
- Hor 211 KabiDokument6 SeitenHor 211 Kabik5b55Noch keine Bewertungen