Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cell Parts and Functions Table
Hochgeladen von
Nyk KhowOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cell Parts and Functions Table
Hochgeladen von
Nyk KhowCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
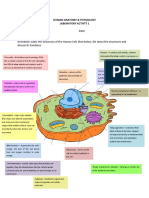
Cell Parts and Functions Table Cell Organelle Nucleus Nuclear Envelope (Membrane) Cytoplasm Golgi Body (Apparatus)
Cell Function Directs all cell activities "Brain or Control Center of cell" Controls what passes in and out of the nucleus Jelly-like substance found inside cell that acts as a medium for chemical reactions within the cell Packages the proteins made by the ribosomes so they can be sent out of the cell. The UPS store of the cell "powerhouse of the cell" breaks down sugar molecules to release energy, site of cellular respiration, double membrane, self-replicating, contains own DNA, cristae "Storage tanks" Can hold food, water or waste for the cell Makes proteins for the cell, can be found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or free in the cytoplasm Transportation network for the cell, moves materials around in the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)endoplasmic reticulum that has ribosomes attached. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)- does not have ribosomes attached
Mitochondrion
Vacuole Ribosome
Lysosome Nucleolus
"Stomach of the cell" Helps the cell digest food, waste and worn out cell parts Produces ribosomes and rRNA( stuff ribosomes are made of)
"Gatekeeper" Separates the cell from the rest of the environment Cell Membrane and helps control what passes in and (plasma membrane) out of the cell. Semi-permeable: allows some materials to pass through but not all Chloroplast A special plastid that contains chlorophyll a pigment that captures the sun's energy to produce glucose in a process called photosynthesis Rigid outer layer made of cellulose that supports and protects the cell (plant, fungi, and bacterial cells) Stores and Transports substances from the Golgi Body to the cell membrane for export. "The UPS truck of the cell" gives support and shape to the cell, made of proteins Organizes special parts of the cytoskeleton called microtubules for cell division, migrates to opposite ends (poles) of the cell to assist with cell division
Cell Wall
Vesicle
Cytoskeleton
Centriole
Cell theory -some organisms are unicellular only one cell -some organisms are multicellular countless cell *the life of even the most complicated multicellular organism still starts from a cell a fertilized egg or so-called zygote. Zygote divides into two , and each newly formed cell subdivides. Cell theory - Further divisions of cells occur continuously until a multitude of cells organize into tissues, tissues into organs, and organs into organ systems of a multicellular organism. - The complex life processes which occur in each organ system are the same life-sustaining reactions which the single cell of a unicellular organism performs. 1. All living things are structurally made up of cells. 2. The cell is the fundamental unit of life. 3. Cells come from the division of pre-existing cells.
Biologists: 1. Robert Hooke Englishman ; coined the term cell and was responsible for the beginnings of cytology as a subdiscipline in biology. 2. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek Dutch naturalist ; discovered bacteria and other microscopic organisms in rainwater and studied the structure of plant and animal cells. 3. Francesco Redi & Lazzaro Spallanzani Italian physician and biologist respectively ; disproved the Theory of Spontaneous Generation. 4. Robert Brown Scottish botanist ; discovered the presence of nuclei within cells.
5. Felix Dujardin a French man ; noted that all living things contain a thick jelly fluid which he called sarcode that time. 6. Matthias SChleiden & Theodor Schwann German botanist and zoologist respectively ; introduced the concept that all plants and animals are made up of cells. 7. Johannes Purkinje Czechoslovakian ; coined the terms protoplasm to refer to the living matter of the cell. 8. Rudolf Virchow German physician ; found that cells divide to form new cells. He concluded that omnis cellula e cellula or cells come from pre-existing cells. 9. Louis Pasteur French chemist ; supplied the proof for Virchows Theory of Biogenesis.
Cell Structure and Composition - Cell vary in their sizes and shapes according to the functions which they perform. - Microscopic studies show that a cell has three fundamental parts: Cytoplasm main metabolic activities take place Cell membrane protectively surrounds the cytoplasm Nucleus genetic material is located. = prokaryotic cell lacks nuclear membrane = incipient = ancestors of eukaryotes
= eukaryotic cell has so-called true nucleus
CYTOPLASM Purkinje coined the term protoplasm.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cell Transport Concept Map For NotesDokument2 SeitenCell Transport Concept Map For NotesHaley Osborn67% (3)
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDokument28 SeitenBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Plant & Animal TissueDokument39 SeitenPlant & Animal TissuePrincess Erbie Austria100% (1)
- Cell Organelles Worksheet KEYDokument2 SeitenCell Organelles Worksheet KEYmike_92457% (58)
- Genbio Reviewer 1Dokument8 SeitenGenbio Reviewer 1Franchezkka Mae Belaro100% (1)
- General Biology ReviewerDokument4 SeitenGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and Animal TissuesDokument27 SeitenPlant and Animal TissuesDoods GaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Poly, Many Mer, Unit) Monomers (Mono, One) : Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) PolymersDokument5 Seiten(Poly, Many Mer, Unit) Monomers (Mono, One) : Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) PolymersDaneth Julia TuberaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept MapDokument1 SeiteConcept MapKeith20% (5)
- Homeostasis and Feedback Mechanism PDFDokument3 SeitenHomeostasis and Feedback Mechanism PDFjer montillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDokument21 SeitenCell Parts and Their FunctionsJeff Poi50% (2)
- General Biology ReviewerDokument3 SeitenGeneral Biology ReviewerAngeli Maligalig Ramirez100% (2)
- The Human CellDokument1 SeiteThe Human CellAira Viloria Orbillo100% (1)
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDokument9 SeitenCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of LifeDokument4 SeitenProperties of LifeAndy Bautista De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study This To Ace The Pre-Quarterly Test in Biology!Dokument70 SeitenStudy This To Ace The Pre-Quarterly Test in Biology!Rose MendizabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationDokument1 SeiteCell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationJohn Barry Ibanez80% (15)
- Biology 1st DiscussionDokument52 SeitenBiology 1st DiscussionBea BulasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 Course OutlineDokument2 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 Course OutlineCedrick GenaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Module 14. Genetics - The Study of Inherited Traits2Dokument34 SeitenBiology Module 14. Genetics - The Study of Inherited Traits2Kameshvra92% (12)
- Botany Reviewer For First Quarter PDFDokument6 SeitenBotany Reviewer For First Quarter PDFDale Maristela Peñalosa100% (3)
- Cell DivisionDokument50 SeitenCell Divisionbknishad100% (2)
- Common Laboratory ApparatusDokument5 SeitenCommon Laboratory ApparatusJuan Marcos80% (5)
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDokument4 SeitenNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in General ZoologyDokument12 SeitenReviewer in General ZoologyJasmine Fritz CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell TheoryDokument6 SeitenCell Theoryjanice alquizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell ModificationDokument28 SeitenCell ModificationIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Theory: Lesson 1.1Dokument40 SeitenCell Theory: Lesson 1.1Angel DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Dokument17 SeitenSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Dette Dominic Ballano67% (3)
- Notes For Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDokument18 SeitenNotes For Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationxXxXxXxXxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Cell Organelles WS 2016 KEYDokument2 Seiten1-Cell Organelles WS 2016 KEYElvin Hoyo-a Logroño100% (2)
- Development of Evolutionary ThoughtDokument23 SeitenDevelopment of Evolutionary ThoughtCrow HoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Chapter 1 Cell Notes.Dokument6 SeitenBiology Chapter 1 Cell Notes.Jyoti AmbwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group6 Lab ReportDokument6 SeitenGroup6 Lab ReportAkhu C CeyrranneNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of BiologyDokument36 SeitenHistory of BiologyDaintyKharisma100% (2)
- Lab Equipment Worksheet: Name - PeriodDokument5 SeitenLab Equipment Worksheet: Name - Periodapi-320485715Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationDokument1 SeiteCell Modifications That Lead To AdaptationChris EismaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - ATP-ADP - CycleDokument10 Seiten1 - ATP-ADP - CycleYay SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - Bacterial Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument26 SeitenLecture 3 - Bacterial Anatomy and Physiologyapi-370335280% (5)
- Descent With ModificationDokument40 SeitenDescent With ModificationNanami MumuzunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making A Hay InfusionDokument1 SeiteMaking A Hay InfusionJohn OsborneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of ZoologyDokument2 SeitenFundamentals of ZoologyJeanine Bianca Lastino100% (3)
- Biology Reviewer Notes PDFDokument26 SeitenBiology Reviewer Notes PDFAntonea50% (2)
- Parts of The Cell and FunctionsDokument31 SeitenParts of The Cell and FunctionsMary Joy Llosa Redulla100% (1)
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDokument11 SeitenComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellFatima Reema Gonzales JahariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geologic Time Scale WorksheetDokument2 SeitenGeologic Time Scale WorksheetCharry Cervantes75% (4)
- Lesson 9.2 Biological DiversityDokument25 SeitenLesson 9.2 Biological DiversityJohn Cesar CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 1 - 12 - Q2 - M4Dokument15 SeitenBiology 1 - 12 - Q2 - M4Hera VictrixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kami Export - Cell Cycle ReviewDokument3 SeitenKami Export - Cell Cycle ReviewAchionta Nandy100% (3)
- Worksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleDokument3 SeitenWorksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleLaureen BarbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- TAXONOMYDokument23 SeitenTAXONOMYnavinnaithani100% (1)
- Mendelian GeneticsDokument6 SeitenMendelian GeneticsMaria Danica100% (2)
- Genbio 1 1ST Grading ReviewerDokument11 SeitenGenbio 1 1ST Grading ReviewerTodo Roki100% (1)
- The Calvin CycleDokument4 SeitenThe Calvin CycleVerena Raga100% (1)
- Science General EducDokument24 SeitenScience General EducDESSA EMBER ESPARESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Gen EdDokument17 SeitenScience Gen EdDESSA EMBER ESPARESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio w1 SummaryDokument5 SeitenGen Bio w1 Summaryyxcz.rzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell TheoryDokument13 SeitenCell TheoryDaryll BorjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and The Cell TheoryDokument28 SeitenCells and The Cell TheoryJanin CodillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Function 2012Dokument69 SeitenCell Structure and Function 2012gpranay4100% (1)
- M S H A Z e L V A SDokument2 SeitenM S H A Z e L V A SNyk KhowNoch keine Bewertungen
- ,.Dokument7 Seiten,.Nyk KhowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chinese SongsDokument3 SeitenChinese SongsNyk KhowNoch keine Bewertungen
- China AGE Leader Philosophy Accomplishment Zhou QIN HAN SUI T'Ang Song/Sung Yuan MingDokument4 SeitenChina AGE Leader Philosophy Accomplishment Zhou QIN HAN SUI T'Ang Song/Sung Yuan MingNyk KhowNoch keine Bewertungen
- By: Ralph Lawrence de ClaroDokument6 SeitenBy: Ralph Lawrence de ClaroNyk KhowNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsDokument7 SeitenLAS 4 - Plant and Animal CellsJeanne RanielleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essencial Natural Science Unit 1 TestDokument2 SeitenEssencial Natural Science Unit 1 TestAlvaro Rizzo GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Sheet - Plant CellDokument6 SeitenWork Sheet - Plant CellqazNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHS 201Dokument219 SeitenPHS 201aenesiotoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 9Dokument26 SeitenEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 9Remar Jhon Paine50% (2)
- Cells: USC Messed Up The Following QuestionsDokument119 SeitenCells: USC Messed Up The Following Questionsopeyemi idaeworNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1Dokument4 SeitenCH 1Viraaj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- proeukaryoticADMModule - Grade12 - Quarter1STEM - BIO12-Ia-c-3 DAN SIMON P. AQUINODokument26 SeitenproeukaryoticADMModule - Grade12 - Quarter1STEM - BIO12-Ia-c-3 DAN SIMON P. AQUINOLyka Mae BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology UNIT 1 Revision GuideDokument53 SeitenBiology UNIT 1 Revision GuideChristopher DoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Pelik Part 1Dokument6 SeitenSoalan Pelik Part 1KatherinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology Biochemistry - 4th EdDokument152 SeitenCell Biology Biochemistry - 4th EdBlitzen BusaingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Exemplar ProblemsDokument5 SeitenBiology Exemplar ProblemsAkshatha NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 3.1 The Endomembrane SystemDokument4 SeitenActivity 3.1 The Endomembrane SystemVelasco, Josiah M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guyton & Hall Physiology Review, 3e-2Dokument275 SeitenGuyton & Hall Physiology Review, 3e-2Rawan Chakas100% (13)
- Test 1 BotnyDokument6 SeitenTest 1 BotnyaligrehanakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniDokument3 SeitenCell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniSummer ValliniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument91 SeitenCellviktoria dizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- البيولوجي الجزيئي د نشات 2Dokument542 Seitenالبيولوجي الجزيئي د نشات 2Hasn HsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellsDokument31 SeitenCellsPranav ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationDokument6 SeitenTopic 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationAdeyinka OluyoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology For CAPE Chapter 2 AnswersDokument7 SeitenBiology For CAPE Chapter 2 AnswersFiveLimaRomeo100% (4)
- BIOCELLDokument81 SeitenBIOCELLAchraf RbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDokument39 Seiten2.1 Cell Structure and Functionforyourhonour wongNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Cell Analogy PpointDokument14 SeitenSchool Cell Analogy Ppointapi-265180883Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell OrganellesDokument26 SeitenCell Organellesapi-310725472Noch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Flp-1 1st Half Syllabus (Student Copy)Dokument15 Seiten06 Flp-1 1st Half Syllabus (Student Copy)Saad ArsalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resumen Bio IgcseDokument29 SeitenResumen Bio Igcseolimpia.rojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Biology Revision Spreadsheet - Cell BioDokument8 SeitenIB Biology Revision Spreadsheet - Cell Biopari meharunkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOLIO: Biology Form 4 Chapter 2: Cell Structure and OrganisationDokument51 SeitenFOLIO: Biology Form 4 Chapter 2: Cell Structure and OrganisationSashimi 刺身 Chebby100% (1)
- Module-2 (Without Edits)Dokument27 SeitenModule-2 (Without Edits)Jennie SoloNoch keine Bewertungen