Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
LMCC Part 2 - Shoulder Exam
Hochgeladen von
psandrew1_88338763Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
LMCC Part 2 - Shoulder Exam
Hochgeladen von
psandrew1_88338763Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
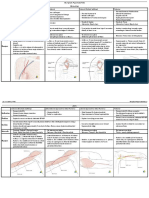
Shoulder pain Communication introduces self to patient describe what is happening to the patient it tends to patient comfort during
ring the physical exam appropriately drapes patient
Inspection SEADS: swelling, erythema or ecchymosis, atrophy, deformity, skin changes clearly states comparison with contralateral joint
Palpation TEST CAA: tenderness, effusion, swelling, temperature, crepitus, atrophy, asymmetry palpate the sternoclavicular joint palpate the acromioclavicular joint palpate the thoracoscapular articulation palpate the acromion, spine, and body of the scapula palpate the greater tubercle of the humerus and the humeral head palpate the tendon of the long head of the biceps in the groove medial to the greater tuberosity
Range of motion active range of motion o looks for pain and limitation of movement throughout
palpates during active movement and comments on the presence of crepitus raise arms forward straight over the head - flexion extend arms backward - extension lift arms laterally over head - abduction swing arm across the chest adduction put hands behind the head - internal rotation put hands behind the back - external rotation
o o o o o o
passive range of motion o guides the shoulder through the same ROM as above - flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal rotation, external rotation
Power repeats above ROM but with the application of an opposing force; muscle power may be graded according to the Oxford scale acknowledges that reduced strength, particularly for abduction (arm across the chest) and external rotation (hand behind the back), is common with acute and chronic injuries of the rotator cuff
Special Tests Yergensons test o Bicepital tendonitis
Painful arc o Subacromial impingement
Apley scratch test o o Internal and external rotation
Empty can test o o Supraspinatus tendonitis
Hawkins test o o Rotator cuff tendonitis
Neers test o Rotator cuff tendons impingement
Cross-arm test o o Acromioclavicular joint disorder
Additional testing o o o X-ray from the group Ultrasound MRI
Diagnosis
defines most likely problem to the examiner and the patient summarizes findings for the patient
Joint assessment above and below shoulder joint Neck o Rules out referred pain by Spurlings sign
Palpates cervical vertebra to elicit cervical root impingement or radiculopathy
Elbow
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoulder ExaminationDokument4 SeitenShoulder ExaminationYS NateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Exam GuideDokument22 SeitenAbdominal Exam GuideSamuel Sebastian SirapanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment MusculoskeletalDokument6 SeitenAssessment Musculoskeletaldd marshall100% (1)
- Respiratory Examination OSCE GuideDokument14 SeitenRespiratory Examination OSCE GuideSam James100% (1)
- Hip Examination - OSCE Guide - Geeky MedicsDokument6 SeitenHip Examination - OSCE Guide - Geeky MedicsAmcDelhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procrastinotes: Rehabilitation Medicione Osce Reviewer 1Dokument14 SeitenProcrastinotes: Rehabilitation Medicione Osce Reviewer 1Edwin Elgar CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Exam 2020Dokument6 SeitenAbdominal Exam 2020InhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme 4 - HTN in The OSCEDokument1 SeiteTheme 4 - HTN in The OSCEShannon RamsumairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osce Abdominal ExaminationDokument1 SeiteOsce Abdominal ExaminationNairobipaeds Madakitari WatotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSCE Note 1Dokument2 SeitenOSCE Note 1Presley Omorodion100% (1)
- List of OSCE Neurology StationsDokument10 SeitenList of OSCE Neurology StationsHamo Refaat100% (1)
- History Taking Physical ExamininationDokument41 SeitenHistory Taking Physical ExamininationAya AmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE Mark SchemeDokument1 SeiteLower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE Mark Schemefkunpad.tutorial10100% (1)
- FGE Report August/September 2002Dokument12 SeitenFGE Report August/September 2002mnigam64Noch keine Bewertungen
- CVS Nac-Osce BlocksDokument35 SeitenCVS Nac-Osce BlocksRoop SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Exam OSCEDokument4 SeitenThyroid Exam OSCEJon Mark LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOPS Revision - Orthopaedic TestingDokument38 SeitenDOPS Revision - Orthopaedic TestingDr-Syed Hammad Hussain-GilaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exam: Https://learnuw - Wisc.edu/ (Requires Log In) 2. Practice OSCE Scenarios (Below)Dokument20 SeitenPractice Exam: Https://learnuw - Wisc.edu/ (Requires Log In) 2. Practice OSCE Scenarios (Below)chioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proper Vital Signs AssessmentDokument51 SeitenProper Vital Signs Assessmentpelly3190100% (2)
- HPI For History and Physical ExamDokument2 SeitenHPI For History and Physical Examv-santNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pelvic Exam PDFDokument2 SeitenPelvic Exam PDFRosu GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typhon Cases 2Dokument7 SeitenTyphon Cases 2api-483865455Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPECIAL TESTS FOR ANKLE, KNEE, HIP AND SHOULDERDokument6 SeitenSPECIAL TESTS FOR ANKLE, KNEE, HIP AND SHOULDERHeather UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurological Examination of The Limbs TextDokument8 SeitenNeurological Examination of The Limbs Textvidur_talrejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction History and ExaminationDokument43 SeitenIntroduction History and ExaminationDanyal Hassan100% (1)
- Comprehensive H&P Note Template For Phase 1 Spring Assessment 2016Dokument5 SeitenComprehensive H&P Note Template For Phase 1 Spring Assessment 2016Derek JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hopkins History Taking ArtDokument5 SeitenHopkins History Taking ArtAnastasia TjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- History Taking - Chief Complaint, HPI, PMH, FH, SHDokument52 SeitenHistory Taking - Chief Complaint, HPI, PMH, FH, SHGurpreet CharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examining the Cardiovascular SystemDokument3 SeitenExamining the Cardiovascular SystemPalwasha MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bates Physical Exam Video NotesDokument3 SeitenBates Physical Exam Video Notesdulcedeleche12359Noch keine Bewertungen
- Free Crack The Nac GuideDokument10 SeitenFree Crack The Nac GuideEmad MerganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imperial College Medical Finals Notes SummaryDokument138 SeitenImperial College Medical Finals Notes SummaryThistell ThistleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical MnemonicsDokument15 SeitenMedical MnemonicsPrashantVedwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Episodic 3Dokument2 SeitenEpisodic 3AlexanderWarrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquifer InternalMedicine09 - 55Dokument7 SeitenAquifer InternalMedicine09 - 55JulieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric History TakingDokument11 SeitenPaediatric History TakingIlyas SaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Exam (RCT)Dokument8 SeitenRespiratory Exam (RCT)kenners100% (31)
- Assessing Thorax & Lungs Physical ExamDokument3 SeitenAssessing Thorax & Lungs Physical ExamZJ GarcianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spine Exam ChecklistDokument1 SeiteSpine Exam ChecklistqmajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ten-Minute History-Taking and Physical Examination Station ExampleDokument2 SeitenTen-Minute History-Taking and Physical Examination Station ExampleMin MawNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSCE Communication Skills ReviewDokument45 SeitenOSCE Communication Skills ReviewKay BristolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Examination: Preparation of The PatientDokument4 SeitenCardiovascular Examination: Preparation of The PatientLolla SinwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whole Patient EncounterDokument6 SeitenWhole Patient EncounterAchwani SantoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Schemes 1Dokument27 SeitenMark Schemes 1crampuppy100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Examination - OSCE Guide - Geeky MedicsDokument6 SeitenCardiovascular Examination - OSCE Guide - Geeky MedicsJahangir AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birthing Options Wipe + IceDokument3 SeitenBirthing Options Wipe + IcerangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Log 111713Dokument3 SeitenClinical Log 111713api-242065432Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical ExaminationDokument11 SeitenClinical ExaminationLaura GranadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- OsceDokument11 SeitenOscedocali11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Orthopaedic Test TablesDokument5 SeitenOrthopaedic Test Tablesapi-461267075Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASCM 2 2010 Clinical Skills Handbook PORTALDokument134 SeitenASCM 2 2010 Clinical Skills Handbook PORTALMatias Cammisa100% (1)
- OSCE Reasoning and ConditionsDokument111 SeitenOSCE Reasoning and ConditionsWiCKieWiCKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoulder Examination Mark SchemeDokument1 SeiteShoulder Examination Mark SchemeGeorge GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification and Surgical Treatment of Thumb-in-Palm DeformitiesDokument4 SeitenClassification and Surgical Treatment of Thumb-in-Palm DeformitiesAbdelhakim MareiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bill Kazmaier & The Bench PressDokument14 SeitenBill Kazmaier & The Bench PressBrock Dulaney100% (20)
- Injuries Around The ElbowDokument82 SeitenInjuries Around The ElbowNitisha SethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fingerprint 101Dokument10 SeitenFingerprint 101Revier NasgadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arm and Back - TabulatedDokument5 SeitenArm and Back - TabulatedandiedeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comprehensive Treatment Guide For de Quervains SyndromeDokument12 SeitenA Comprehensive Treatment Guide For de Quervains SyndromeHoan TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMT ReviewDokument12 SeitenOMT ReviewKyle Derouen100% (6)
- Upper Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideDokument15 SeitenUpper Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideLeen abusarhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractures Radial Head & Neck. JBJS. 2013Dokument10 SeitenFractures Radial Head & Neck. JBJS. 2013C Martin TraumatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. A. Samy TAG Surgical Approaches - 1Dokument7 SeitenDr. A. Samy TAG Surgical Approaches - 1gehadbeddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Takagi Yoshin Ryu Jutaijutsu techniquesDokument25 SeitenTakagi Yoshin Ryu Jutaijutsu techniquesmoon100% (3)
- Jiu Jitsu Complete ManualDokument56 SeitenJiu Jitsu Complete ManualMarcello Arias Cano100% (3)
- PBL 15Dokument27 SeitenPBL 15AndiMuhYasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiography Technique and Anatomy GuideDokument684 SeitenRadiography Technique and Anatomy Guidesami xNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cinahl Rotator Cuff InjuriesDokument11 SeitenCinahl Rotator Cuff InjurieslizardbeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction, Deep ReflexesDokument10 SeitenIntroduction, Deep ReflexesQairul AzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Range of MotionDokument6 SeitenSelf-Range of MotionKath100% (1)
- Muscle Stretching in Manual Therapy I - The Extremities (Team Nanban) (TPB)Dokument177 SeitenMuscle Stretching in Manual Therapy I - The Extremities (Team Nanban) (TPB)CNPOULIS100% (22)
- SHOULDER PAIN AND INJURY GUIDEDokument7 SeitenSHOULDER PAIN AND INJURY GUIDEJohnpeter EsporlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Examination of The ElbowDokument9 SeitenPhysical Examination of The ElbowpuchioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Therapy Protocol Shoulder Rotator Cuff Repair 26dec17Dokument2 SeitenPhysical Therapy Protocol Shoulder Rotator Cuff Repair 26dec17LeonardoValenzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDokument22 SeitenCarpal Tunnel SyndromeNUR ZAMZAM AZIZAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff RepairDokument13 SeitenArthroscopic Rotator Cuff RepairmogosadrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoulder JointDokument2 SeitenShoulder JointGeorge FogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ue TestDokument3 SeitenUe TestRhaegar TargaryenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Supply of The Upper LimbDokument12 SeitenBlood Supply of The Upper LimbMnashinatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Humerus (Bone and Attachments) Flow ChartDokument4 SeitenHumerus (Bone and Attachments) Flow ChartLove GuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoulder DislocationDokument6 SeitenShoulder DislocationRizki IrwansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoulder and Lower Limb Muscle TestsDokument1 SeiteShoulder and Lower Limb Muscle TestsDadaboo UaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Tool Project Requirements: The Case of Banana Cultivation and Its Physical Demands (OWAS)Dokument13 SeitenHand Tool Project Requirements: The Case of Banana Cultivation and Its Physical Demands (OWAS)melbe5jane5quiamcoNoch keine Bewertungen