Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Awareness To I MDG Code
Hochgeladen von
Abd ZouhierOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Awareness To I MDG Code
Hochgeladen von
Abd ZouhierCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IMDG Code- What is it?
International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code The International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code was developed as a uniform international code for the transport of dangerous goods by sea covering such matters as packing, container traffic and stowage, with particular reference to the segregation of incompatible substances.
Development of the IMDG Code The development of the IMDG Code dates back to the 1960 Safety of Life at Sea Conference, which recommended that Governments should adopt a uniform international code for the transport of dangerous goods by sea to supplement the regulations contained in the 1960 International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS). A resolution adopted by the 1960 Conference said the proposed code should cover such matters as packing, container traffic and stowage, with particular reference to the segregation of incompatible substances. A working group of IMO's Maritime Safety Committee (MSC) began preparing the Code in 1961, in close co-operation with the United Nations Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, which in a 1956 report had established minimum requirements for the transport of dangerous goods by all modes of transport. Since its adoption by the fourth IMO Assembly in 1965, the IMDG Code has undergone many changes, both in appearance and content to keep pace with the ever-changing needs of industry. Amendments which do not affect the principles upon which the Code is based may be adopted by the MSC, allowing IMO to respond to transport developments in reasonable time. Amendments to the IMDG Code originate from two sources; proposals submitted directly to IMO by Member States and amendments required to take account of changes to the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods which sets the basic requirements for all the transport modes. Amendments to the provisions of the United Nations Recommendations are made on a two-yearly cycle and approximately two years after their adoption, they are adopted by the authorities responsible for regulating the various transport modes. In that way a basic set of requirements applicable to all modes of transport is established and implemented, thus ensuring that difficulties are not encountered at inter-modal interfaces. IMDG Code to be made mandatory Amendments to SOLAS chapter VII (Carriage of Dangerous Goods) adopted in May 2002 make the IMDG Code mandatory from 1 January 2004. Also in May 2002, IMO adopted the IMDG Code in a mandatory form - known as Amendment 31. In practice, this means that from the legal point of view, the whole of the IMDG Code is made mandatory.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- International Maritime Dangerous Good CodesDokument5 SeitenInternational Maritime Dangerous Good CodesDennis BurgherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imdg CodeDokument7 SeitenImdg CodeMarverick Solmoro-Caraig Evangelista0% (1)
- International Maritime Dangerous Goods CodeDokument2 SeitenInternational Maritime Dangerous Goods CodeIrdam JonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG)Dokument6 SeitenInternational Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG)joeven64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment: Public International LAWDokument6 SeitenAssignment: Public International LAWMayank YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMO HistoryDokument7 SeitenIMO HistoryBurduja IonNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Maritime Organization or IMO What It Is, What It Does and How It WorksDokument12 SeitenInternational Maritime Organization or IMO What It Is, What It Does and How It WorksGiorgi KandelakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imo HistoryDokument3 SeitenImo HistoryPaul AbonitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Maritime Dangerous Goods (Imdg) : Notes By: Capt. Parvinder Singh BhatiaDokument133 SeitenInternational Maritime Dangerous Goods (Imdg) : Notes By: Capt. Parvinder Singh BhatiaHdhdhdbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1: Imo & International ConventionsDokument144 SeitenUnit 1: Imo & International Conventions8396.Nandhu Krishna pNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 SOLAS CH - VII - Chanachai 1-65 PDFDokument29 Seiten11 SOLAS CH - VII - Chanachai 1-65 PDF18-กันต์ธีภพ น้องดีNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-7-11 DG Participants Manual-RevFS FinalDokument45 Seiten1-7-11 DG Participants Manual-RevFS FinalzairisnickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bulk Carrier Safety: International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes Code (IMSBC Code)Dokument2 SeitenBulk Carrier Safety: International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes Code (IMSBC Code)BuzamatAdrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imdg Code 2001Dokument26 SeitenImdg Code 2001Zitouni FodhilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 88th Session (24th Nov To 3rd Dec)Dokument3 Seiten88th Session (24th Nov To 3rd Dec)Vivek GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- BF 03195083Dokument20 SeitenBF 03195083Takele Tesfaye BelayNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Maritime Dangerous GoodsDokument18 SeitenInternational Maritime Dangerous GoodsI Made Yogi Agastya100% (1)
- EVOLUTION AND EFFECTIVENESS OF THE INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION (IMODokument9 SeitenEVOLUTION AND EFFECTIVENESS OF THE INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION (IMOMayank YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 IMO & Its FunctionsDokument23 Seiten2019 IMO & Its FunctionsramkidhayanithiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carriage of Dangerous Goods RegulationsDokument110 SeitenCarriage of Dangerous Goods RegulationsBorgy JalopNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMO What It IsDokument6 SeitenIMO What It IsRathinavel001Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMO ConventionDokument95 SeitenIMO ConventionJoselito Ramos Cawagas Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMO StructureDokument24 SeitenIMO StructurePhilip Joshua CapeNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMO codes for chemical tankers safety and pollution preventionDokument2 SeitenIMO codes for chemical tankers safety and pollution preventionIndraSenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Facts About ImoDokument11 SeitenBasic Facts About ImoTambe Chalomine AgborNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Maritime Organization: HistoryDokument4 SeitenInternational Maritime Organization: HistoryKenneth JasminNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMO ConventionDokument95 SeitenIMO ConventionPhilip Joshua CapeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mgn159 - Marine PollutantsDokument12 SeitenMgn159 - Marine Pollutantsaakash9090Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMO AmendmentsDokument3 SeitenIMO Amendmentsbhupendra singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5 International Maritime ConventionsDokument28 SeitenWeek 5 International Maritime ConventionsZhean GreenwoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Promoting Maritime Treaty RatificationDokument6 SeitenPromoting Maritime Treaty RatificationHarel Santos RosaciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imdg - AmsaDokument32 SeitenImdg - AmsaardinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law DocumentsDokument10 SeitenLaw DocumentsSamarinerSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Goverment, Imo and Other Regulatory Bodies in Effecting World Maritime SafetyDokument41 SeitenThe Role of Goverment, Imo and Other Regulatory Bodies in Effecting World Maritime SafetyRe No BolivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImoDokument5 SeitenImoAnoyaj YamNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To The IMDG CodeDokument31 SeitenAn Introduction To The IMDG Codej_hergeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Safety at Sea Through The Compliance With The International Maritime Safety CodesDokument14 SeitenImproving Safety at Sea Through The Compliance With The International Maritime Safety Codestatjana djikanovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolasDokument46 SeitenSolasAmirhosein60533467% (9)
- 7th Edition: Australian Dangerous Goods Code Information GuideDokument62 Seiten7th Edition: Australian Dangerous Goods Code Information Guidefuransu777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Seam 4 Sir Guevara (Mt-Petition)Dokument42 SeitenSeam 4 Sir Guevara (Mt-Petition)Christian Felix Guevarra33% (3)
- IMO Instruments - Summary - ReportDokument4 SeitenIMO Instruments - Summary - ReportMithran DirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amendment 1 To The Code of Safe Working Practices For Merchant SeamenDokument21 SeitenAmendment 1 To The Code of Safe Working Practices For Merchant Seamenjunniel derlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Convention For The Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), 1974Dokument24 SeitenInternational Convention For The Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), 1974Rohit MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to IMO - the UN agency for global shipping standardsDokument70 SeitenIntroduction to IMO - the UN agency for global shipping standardsjohndmariner123100% (2)
- INTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION LEGISLATIONDokument11 SeitenINTERNATIONAL MARITIME ORGANIZATION LEGISLATIONAnoop Anandan PayyappillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teoria de Buque Mejorado1Dokument6 SeitenTeoria de Buque Mejorado1Javier Wayne Samaniego SaenzNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMO-IACS Training Rev 2.0 02082010Dokument46 SeitenIMO-IACS Training Rev 2.0 02082010Suresh GoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solas Convention 1974Dokument35 SeitenSolas Convention 1974wolf4853Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Maritime Organization Adopts ISPS CodeDokument111 SeitenInternational Maritime Organization Adopts ISPS Codeclaudio.jc.lima100% (2)
- Introduction and History: After Consideration Within IMODokument23 SeitenIntroduction and History: After Consideration Within IMOdavidyalin_resusNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of IMO: International body promoting maritime safetyDokument37 SeitenHistory of IMO: International body promoting maritime safetyReynante P. Consul50% (2)
- 0002international Maritime Organization (IMO)Dokument21 Seiten0002international Maritime Organization (IMO)Zin Maung Tun100% (1)
- ISPS - Code 2003 EditionDokument131 SeitenISPS - Code 2003 EditionJasper AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISPS Code 2003Dokument137 SeitenISPS Code 2003Condulimazi Paul100% (2)
- History of SOLASDokument9 SeitenHistory of SOLASTambe Chalomine AgborNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Legislative Requirements - Introduction To Maritime LawDokument84 Seiten1 Legislative Requirements - Introduction To Maritime LawJade EspirituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rid, Adr, Iata-Dgr, Imdg-CodeDokument1 SeiteRid, Adr, Iata-Dgr, Imdg-CodeShirishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maritime Labour ConventionVon EverandMaritime Labour ConventionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Security of Radioactive Material in Transport: Implementing GuideVon EverandSecurity of Radioactive Material in Transport: Implementing GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing the Interface between Safety and Security for Normal Commercial Shipments of Radioactive MaterialVon EverandManaging the Interface between Safety and Security for Normal Commercial Shipments of Radioactive MaterialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ann Carruthers Event Presentation Notes RemovedDokument65 SeitenAnn Carruthers Event Presentation Notes RemovedAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ann Carruthers Event Presentation Notes RemovedDokument13 SeitenAnn Carruthers Event Presentation Notes RemovedAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ann Carruthers Event Presentation Notes RemovedDokument13 SeitenAnn Carruthers Event Presentation Notes RemovedAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Analgesia - SJH PowerpointDokument29 SeitenObstructive Sleep Apnea and Analgesia - SJH PowerpointAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Key Performance Indicator System of Process Control As A Basis For Relocation PlanningDokument8 SeitenA Key Performance Indicator System of Process Control As A Basis For Relocation PlanningAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of ISO 37500 With OPBOK PDFDokument4 SeitenRole of ISO 37500 With OPBOK PDFAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing PlanDokument11 SeitenMarketing PlanMritunjay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Need For Perioperative Screening in Sleep Apnea PatientsDokument62 SeitenThe Need For Perioperative Screening in Sleep Apnea PatientsAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Get Your ISO 45001 2018 Training Materials NowDokument3 SeitenGet Your ISO 45001 2018 Training Materials NowAbd Zouhier0% (1)
- AITC 1411 Obstructive Sleep ApneaDokument31 SeitenAITC 1411 Obstructive Sleep ApneaAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Analgesia - SJH PowerpointDokument29 SeitenObstructive Sleep Apnea and Analgesia - SJH PowerpointAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obesity and Risk FactorDokument61 SeitenObesity and Risk FactorSaad MotawéaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Event Schedule Planner 2015Dokument3 SeitenEvent Schedule Planner 2015viller_lpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benchmarking Manual Part 2Dokument14 SeitenBenchmarking Manual Part 2Abd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behavior Based SafetyDokument51 SeitenBehavior Based SafetysixejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE806 Hazop JUN KULDokument8 SeitenPE806 Hazop JUN KULAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developing Meaningful Key Performance Indicators V5Dokument39 SeitenDeveloping Meaningful Key Performance Indicators V5Abd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2193 1801 3 28Dokument13 Seiten2193 1801 3 28Abd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead MeetDokument4 SeitenLead MeetilkerkozturkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monthly Business Budget1Dokument1 SeiteMonthly Business Budget1Mohamad RofiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 16192:2010-06 (E) : Space Systems - Experience Gained in Space Projects (Lessons Learned) - Principles and GuidelinesDokument1 SeiteISO 16192:2010-06 (E) : Space Systems - Experience Gained in Space Projects (Lessons Learned) - Principles and GuidelinesAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Timeline Milestones VisualDokument1 SeiteProject Timeline Milestones VisualAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Management Basic ISO 31000Dokument17 SeitenRisk Management Basic ISO 31000Carlos Escobar100% (5)
- Iso9001 2015 Risk Management LinkedinDokument14 SeitenIso9001 2015 Risk Management LinkedinAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratf FinalDokument194 SeitenRatf FinalAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daf Ipres PaperDokument7 SeitenDaf Ipres PaperAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Project Plan DefinitionDokument30 SeitenNew Project Plan DefinitionVictor AndresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toolkit11 Data To Improve CareDokument6 SeitenToolkit11 Data To Improve CareAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Plan 05 FullDokument9 SeitenLecture Plan 05 FullAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazmat EvaluationDokument28 SeitenHazmat EvaluationAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biogas (Methane) EnglishDokument8 SeitenBiogas (Methane) Englishveluthambi8888100% (1)
- ATMS Software Tracks Surgical Device TraceabilityDokument27 SeitenATMS Software Tracks Surgical Device TraceabilityStenaArapocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleeding and Coagulation Disorders: Dr. Shamshuddin Patel SRDokument17 SeitenBleeding and Coagulation Disorders: Dr. Shamshuddin Patel SRSinta HandayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyclone Shelter Construction Maintenance and Management Policy 2011Dokument21 SeitenCyclone Shelter Construction Maintenance and Management Policy 2011MAHABUBUR RAHAMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN Sample Paper 12 UnsolvedDokument9 SeitenEN Sample Paper 12 Unsolvedguptasubhanjali21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cosmetic BrochureDokument4 SeitenCosmetic BrochureDr. Monika SachdevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tradition With A Future: Solutions For Operative HysterosDokument16 SeitenTradition With A Future: Solutions For Operative Hysterosأحمد قائدNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Core FunctionsDokument106 Seiten12 Core FunctionsEmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leaving Disasters Behind: A Guide To Disaster Risk Reduction in EthiopiaDokument12 SeitenLeaving Disasters Behind: A Guide To Disaster Risk Reduction in EthiopiaOxfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lucas MattoonDokument1 SeiteLucas Mattoonapi-248178524Noch keine Bewertungen
- GIGITAN ULAR BERBISA: GEJALA, PENANGANAN DAN JENIS ULAR PALING BERBISADokument19 SeitenGIGITAN ULAR BERBISA: GEJALA, PENANGANAN DAN JENIS ULAR PALING BERBISAYudhistira ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packaged Drinking Water Project ProfileDokument5 SeitenPackaged Drinking Water Project ProfileArpna BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Investigating Brain and LanguageDokument12 SeitenMethods of Investigating Brain and Languagekiranjit_123100% (2)
- Tugas Parafrase Jurnal MIPKI (Revisi) - Rizka Amalia Hutami - 150510160235Dokument2 SeitenTugas Parafrase Jurnal MIPKI (Revisi) - Rizka Amalia Hutami - 150510160235RizkaNoch keine Bewertungen
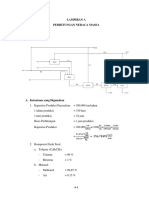
- Perhitungan Neraca Masa Proses Produksi ParaxyleneDokument52 SeitenPerhitungan Neraca Masa Proses Produksi ParaxyleneBayuAjiPratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision in Obstetrics&Gynecology Revision in Obstetrics&GynecologyDokument136 SeitenRevision in Obstetrics&Gynecology Revision in Obstetrics&GynecologySiam Weng Loong100% (3)
- Weeblylp MedicinaDokument18 SeitenWeeblylp Medicinaapi-538325537Noch keine Bewertungen
- Delivery Guide Flood PreparednessDokument23 SeitenDelivery Guide Flood Preparednesshsehamad173Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Plant-Growth Promoting RhizobacteriumDokument7 SeitenA Plant-Growth Promoting RhizobacteriumdanyjorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part A Reading Task Playground Injuries Playground Surface MaterialDokument8 SeitenPart A Reading Task Playground Injuries Playground Surface MaterialMitra NabizadehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report SampleDokument11 SeitenReport SampleArvis ZohoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMI4804 Quiz 5Dokument16 SeitenMMI4804 Quiz 5Ham Mad0% (1)
- Workplace EmergenciesDokument39 SeitenWorkplace EmergenciesUpul Nishantha ThalpawilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perioperative NursingDokument8 SeitenPerioperative NursingGil Platon Soriano100% (3)
- Municipal Ordinance No. 05-2008Dokument5 SeitenMunicipal Ordinance No. 05-2008SBGuinobatan100% (2)
- The Digestive System ExplainedDokument33 SeitenThe Digestive System ExplainedGulAwezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Development and Validation For Estimation of Moxifloxacin HCL in Tablet Dosage Form by RP HPLC Method 2153 2435.1000109Dokument2 SeitenMethod Development and Validation For Estimation of Moxifloxacin HCL in Tablet Dosage Form by RP HPLC Method 2153 2435.1000109David SanabriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Gatekeeping As A Function of Role FidelityDokument2 SeitenProfessional Gatekeeping As A Function of Role FidelityNURSETOPNOTCHER100% (3)
- The Real Paul Thibault: Nothing But The Truth..Dokument20 SeitenThe Real Paul Thibault: Nothing But The Truth..LancasterFirstNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mind Body PDFDokument357 SeitenMind Body PDFAzhari RahmatNoch keine Bewertungen