Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
,.
Hochgeladen von
Nyk KhowCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
,.
Hochgeladen von
Nyk KhowCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CELLULAR ORAGANIZATION - UNICELLULAR - COLONIAL - MULTICELLULAR EVOLUTION OF LIFE INORGANIC COMPOUNDS - WATER most abundant - ACID - BASES - SALTS
S ORGANIC COMPOUNDS - CARBOHYDRATES contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen o SIMPLE SUGARS OR MONOSACCHARIDES cannot be broken down into smaller pieces(C6H12O6) Glucose Fructose Galactose Most important simple sugars 5 carbon sugars, deoxyribose or ribose
o DOUBLE SUGARS OR DISACCHARIDES - formed out of two simple sugars (C12H21O11) o Maltose = glucose + glucose o Lactose = glucose + galactose o Sucrose = glucose + fructose Sucrose most common table sugar o POLYSACCHARIDES long chain of simple sugars linked together by dehydration synthesis Polymer molecule made up of many similar units called monomers Starch main stored food in plants Glycogen counterpart of starch in animals LIPIDS Constitute a class of large organic molecules that have little or no affinity for water. Not soluble in water. Soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol. Cholesterol common constituent of the brain. Phospholipids similar to fat molecule Fat molecule synthesized out of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecule by the process of dehydration synthesis.
PROTEINS - Macromolecules that contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. - Some also contain sulphur and phosphorus. - Amino acid is the building blocks of protein.
A polymer consisting of similar units called amino acid. Upon hydrolysis , a protein molecule liberates many amino acid molecules. Amino acid are necessary for protein synthesis Nonessential amino acid synthesized by cells. Essential amino acid must be supplied with diet.
- The kinds of proteins found in organisms are enormously varied. The reason for this is that each kind of protein molecule is characterized by: The number of amino acid it contain The kinds of amino acid it contain The sequence of amino acid The structural orientation, such as the kind of folding and coiling which may be assumed by the protein molecule.
NUCLEIC ACID - Organic compounds - Polymers formed out of nucleotides that serve as their building blocks. - A nucleotide is an organic molecule made up of three components namely, 5-carbon sugar, an organic base, and a phosphate group. - The organic base may be a purine or pyrimidine.
- The purine, which consists of a double ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms o Adenine o Guanine - The pyrimidine, which consists of a single ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms. o Thymine o Cytosine o Uracil - (PO4)-3 phosphate group - When a 5-carbon sugar is linked to an organic base , a bigger molecule called a nucleoside is formed. - When a phosphate group is attached to a nucleoside , a still bigger molecule called a nucleotide is formed. - RNA & DNA DIFFERENCES - The 5-carbon sugar found in the RNA is ribose whereas in DNA is deoxyribose. - The organic base found in DNA are adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. In RNA organic base, adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
REQUIREMENTS OF A CELL - Genetic material such as deoxyribonucleic acid that permits the reproduction of new cells of the same type as well as the control of all cellular activity. - A metabolic machinery for the maintenance of life-sustaining activities - Cell membrane that establishes the boundary and allows the exchange of materials. METABOLISM Sum total of all chemical reactions ANABOLISM constructive phase of metabolism, energy storing or endergonic reactions. PHOTOSYNTHESIS food making process CATABOLISM destructive phase of metabolism ; cellular respiration
ENTRANCE & EXIT - PASSIVE TRANSPORT less concentrated, follows concentration is gradient - ACTIVE TRANSPORT against concentration gradient ; exocytosis & endocytosis.
DIFFUSION - Spontaneous and random movement of molecule from one place to another. - Direction of greater movement of molecules NET DIFFUSION - Difference in concentration between two regions CONCENTRATION GRADIENT OSMOSIS - DIVISION OF SOLVENT MOLECULES THROUGH A DIFFERENT PERMEABLE MEMBRANE - Occurs when two solutions are separated by a differentially permeable membrane.
HYPTONIC SOLUTION - Contains lower concentration of dissolved materials (solutes) than the cell. - Concentration of water in the solution is greater than in the cell.
HYPERTONIC SOLUTION - Contains higher concentration of solutes than the cell. - Concentration of water in the solution is lower than in the cell.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- M S H A Z e L V A SDokument2 SeitenM S H A Z e L V A SNyk KhowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chinese SongsDokument3 SeitenChinese SongsNyk KhowNoch keine Bewertungen
- China AGE Leader Philosophy Accomplishment Zhou QIN HAN SUI T'Ang Song/Sung Yuan MingDokument4 SeitenChina AGE Leader Philosophy Accomplishment Zhou QIN HAN SUI T'Ang Song/Sung Yuan MingNyk KhowNoch keine Bewertungen
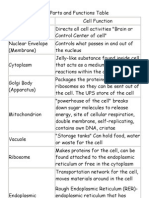
- Cell Parts and Functions TableDokument5 SeitenCell Parts and Functions TableNyk Khow50% (2)
- By: Ralph Lawrence de ClaroDokument6 SeitenBy: Ralph Lawrence de ClaroNyk KhowNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Title - Dating Virtual To Coffee Table Keywords - Dating, Application BlogDokument3 SeitenTitle - Dating Virtual To Coffee Table Keywords - Dating, Application BlogRajni DhimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Archetypal Approach To Macbeth by William ShakespeareDokument9 SeitenArchetypal Approach To Macbeth by William ShakespeareLenka Koutná100% (1)
- American University of Beirut PSPA 210: Intro. To Political ThoughtDokument4 SeitenAmerican University of Beirut PSPA 210: Intro. To Political Thoughtcharles murrNoch keine Bewertungen
- GMDSSDokument1 SeiteGMDSSRahul rajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probset 3 KeyDokument7 SeitenProbset 3 KeyhoneyschuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contemp Module 56Dokument5 SeitenContemp Module 56crisanta pizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benson Ivor - The Zionist FactorDokument234 SeitenBenson Ivor - The Zionist Factorblago simeonov100% (1)
- Review Test 1: Circle The Correct Answers. / 5Dokument4 SeitenReview Test 1: Circle The Correct Answers. / 5XeniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project 2 Analysis of Florida WaterDokument8 SeitenProject 2 Analysis of Florida WaterBeau Beauchamp100% (1)
- Substitution Reactions - PMDokument64 SeitenSubstitution Reactions - PMprasoon jhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Splices LAS 3rd Quarter Week 1Dokument6 SeitenSplices LAS 3rd Quarter Week 1Winnielyn Quarteros BarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintaining Godly Spirituality in The Face of ChallengesDokument3 SeitenMaintaining Godly Spirituality in The Face of ChallengesDavid OmoniyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentDokument19 SeitenModule 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentRoxan Binarao-Bayot60% (5)
- GDCR - Second RevisedDokument290 SeitenGDCR - Second RevisedbhaveshbhoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Dokument75 SeitenIntroduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Teddy HaryadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Chnage at Tata TeaDokument36 SeitenMajor Chnage at Tata Teasheetaltandon100% (1)
- Dadm Assesment #2: Akshat BansalDokument24 SeitenDadm Assesment #2: Akshat BansalAkshatNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On PRT in IndiaDokument21 SeitenA Review On PRT in IndiaChalavadi VasavadattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature Measurement: Temperature Assemblies and Transmitters For The Process IndustryDokument32 SeitenTemperature Measurement: Temperature Assemblies and Transmitters For The Process IndustryfotopredicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips - Dominick Salvatore Microeconomics Wwwpdfsdocuments2comd38dominick SalvatorepdfDokument2 SeitenDokumen - Tips - Dominick Salvatore Microeconomics Wwwpdfsdocuments2comd38dominick SalvatorepdfIshan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontrollers DSPs S10Dokument16 SeitenMicrocontrollers DSPs S10Suom YnonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mywizard For AIOps - Virtual Agent (ChatBOT)Dokument27 SeitenMywizard For AIOps - Virtual Agent (ChatBOT)Darío Aguirre SánchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective-C Succinctly PDFDokument110 SeitenObjective-C Succinctly PDFTKKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jmac TempDokument5 SeitenJmac TempDan GerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saunders & Cornnet Solution Chapter 1 Part 1Dokument5 SeitenSaunders & Cornnet Solution Chapter 1 Part 1Mo AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGN815: Business Models: Ajay ChandelDokument38 SeitenMGN815: Business Models: Ajay ChandelSam RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outbound Idocs Code Error Event Severity Sap MeaningDokument2 SeitenOutbound Idocs Code Error Event Severity Sap MeaningSummit YerawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis SsDokument14 SeitenSynopsis SsJYOTI KATIYAR SVUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Film Interpretation and Reference RadiographsDokument7 SeitenFilm Interpretation and Reference RadiographsEnrique Tavira67% (3)
- 3.1.1 - Nirmaan Annual Report 2018 19Dokument66 Seiten3.1.1 - Nirmaan Annual Report 2018 19Nikhil GampaNoch keine Bewertungen