Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sinus
Hochgeladen von
fakrulnersmudaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sinus
Hochgeladen von
fakrulnersmudaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SINUS INFECTION
(Sinusitis)
BASIC INFORMATION DESCRIPTION Inflammation of the sinuses (air-filled cavities) adjacent to the nose. Sinusitis commonly affects the ethmoidal sinuses, located between the eyes; and the maxillary sinuses, located in the cheekbone. Germs that cause sinusitis are contagious. FREQUENT SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Early stages: Nasal congestion with green-yellow (sometimes bloodtinged) discharge. Feeling of pressure inside the head. Eye pain. Headache that is worse in the morning or when bending forward. Cheek pain that may resemble a toothache. Post-nasal drip. Cough (sometimes) that is usually non-productive. Disturbed sleep (sometimes). Fever (sometimes). Late stages: Complete blockage of the sinus openings, blocking the discharge and increasing pain. CAUSES Infection (usually initiated by a cold or other upperrespiratory infection). The infection may be complicated by a bacterial invasion of organisms that normally inhabit the nose and throat. Irritation of the nasal passages from allergies, smoking, harsh sneezes with the mouth closed, chilling, swimming (especially jumping into the water without holding the nose) and fatigue. RISK INCREASES WITH Illness that has lowered resistance. Smoking. Exposure to cold, damp weather outdoors and dry heat indoors. Exposure to others in public places. Immunosuppression due to illness or drugs. Swimming in contaminated water. PREVENTIVE MEASURES Prompt treatment of respiratory infections. EXPECTED OUTCOMES Usually curable with intense treatment. Recurrence is common. POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS Meningitis or brain abscess (rare). Infection of bone or bone marrow (rare). TREATMENT GENERAL MEASURES Diagnostic tests (depending on severity of infection and chronicity) may include laboratory blood studies, culture of mucus, endoscopy, x-rays or CT scan of the sinuses. Treatment at home is aimed at improving drainage and control of infection. Use a cool-mist, ultrasonic humidifier to help thin secretions so they will drain more easily. Clean humidifier daily. For infants and young children who cannot blow the nose, use a nasal aspirator to suction each nostril gently before applying nose drops. Suction again 10 minutes after using nose drops. Apply moist heat to relieve pain in the sinuses and nose. Dont allow other persons to use your nose drops. They will be contaminated by the infection. Discard them after treatment. Avoid non-prescription nose drops or sprays. Use prescribed drops only for the recommended time. They can interfere with normal nasal and sinus function and become addictive, causing a rebound phenomenon. Sinusitis not responding to other treatment may require surgery to drain blocked sinuses. Numerous techniques are available depending on the site of the infection. If the infection is severe, stay indoors in an even temperature. MEDICATIONS Nasal sprays, nose drops or decongestant medicine to reduce congestion may be prescribed. Antibiotics to fight infection. For minor pain, you may use non-prescription drugs such as acetaminophen. ACTIVITY Resume your normal activities gradually. Exercise can help to clear your head. DIET No special diet, but drink extra fluids to help thin secretions. NOTIFY OUR OFFICE IF You or a family member has symptoms of sinusitis. The following occur during treatment: Fever; bleeding from the nose; severe headache. Swelling of the face (forehead, eyes, side of the nose or cheek).
Adapted from Instructions for Patients, Sixth Edition, H. Winter Griffith, M.D., W.B Saunders Company.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Acute sinusitis symptoms, causes, treatmentDokument11 SeitenAcute sinusitis symptoms, causes, treatmentEsmael AbubakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- SinusitisDokument23 SeitenSinusitisAhmed Al-IraqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Dokument2 SeitenP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Milanisti22Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 113 Upper Respiratory DiseaseDokument68 SeitenNCM 113 Upper Respiratory DiseaseJerah Aceron SatorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of EarDokument17 SeitenDisorders of EarharpreetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Tract InfectionDokument30 SeitenRespiratory Tract InfectionNaresh JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infection GuideDokument45 SeitenUpper Respiratory Tract Infection GuideFarwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts: Nose Throat Pharynx LarynxDokument47 SeitenParts: Nose Throat Pharynx LarynxRANJIT GOGOINoch keine Bewertungen
- MED SURG OUTLINE Chapter 14 Care of Patients With Disorders of Upper Respiratory SystemDokument6 SeitenMED SURG OUTLINE Chapter 14 Care of Patients With Disorders of Upper Respiratory SystemMichaela LemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MK CoryzaDokument3 SeitenMK CoryzaMoses Jr KazevuNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSC Nursing Guide: Tonsillitis and AdenoiditisDokument41 SeitenBSC Nursing Guide: Tonsillitis and AdenoiditisYAMINIPRIYANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Respiratory JerusalemDokument24 SeitenUpper Respiratory JerusalemAYO NELSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute NasopharyngitisDokument13 SeitenAcute Nasopharyngitisjyoti kunduNoch keine Bewertungen
- What and Where Are The Sinuses?Dokument10 SeitenWhat and Where Are The Sinuses?jercx_trigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Maxillary SinusitisDokument15 SeitenTreatment of Maxillary SinusitisRabina PantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulnus SclopectariumDokument1 SeiteVulnus SclopectariumNurnazila HariviskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinusitis in ChildDokument14 SeitenSinusitis in ChildKin molikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment Plan and Seminar 2Dokument20 SeitenTreatment Plan and Seminar 2alsakar26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sinusitis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDokument5 SeitenSinusitis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDyane VatriciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute SinusitisDokument7 SeitenAcute SinusitisNader SmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDokument73 SeitenUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionsankitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rhinitis and Sinusitis in Guinea PigsDokument3 SeitenRhinitis and Sinusitis in Guinea PigsDivya KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinus Infection Natural Cure: Powerful Home Remedies to Clear a Sinus Infection and Sinus Pain Permanently, Without AntibioticsVon EverandSinus Infection Natural Cure: Powerful Home Remedies to Clear a Sinus Infection and Sinus Pain Permanently, Without AntibioticsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- B.ing PaperDokument15 SeitenB.ing PaperAriph BudiboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsillitis PDFDokument7 SeitenTonsillitis PDFUmar FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do You Get Acute SinusitisDokument4 SeitenHow Do You Get Acute SinusitisPii Lyra RamadatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 - Disaster ManagementDokument40 SeitenLesson 5 - Disaster ManagementHampson MalekanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Sinusitis Types and TreatmentsDokument11 SeitenAcute Sinusitis Types and Treatmentsعبدالله فائز غلامNoch keine Bewertungen
- SINUSDokument16 SeitenSINUSJune Suzete RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- TH THDokument4 SeitenTH THdhen2_kyzluvdenNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPISTAXIS-bleeding From The Nose (Most Common) Etiology (Cause)Dokument34 SeitenEPISTAXIS-bleeding From The Nose (Most Common) Etiology (Cause)Julliza Joy PandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basog - ReportTonsillitis and EpistaxisDokument4 SeitenBasog - ReportTonsillitis and EpistaxisclaribelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDokument93 SeitenManaging Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsErica Clerigo LandichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System (Common Diseases)Dokument23 SeitenRespiratory System (Common Diseases)Philip YansonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NoseDokument37 SeitenNoseDawit workalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Sinusitis: Preferred By: Venida, Joan M. BSN II-B Group 5Dokument22 SeitenPediatric Sinusitis: Preferred By: Venida, Joan M. BSN II-B Group 5Joan VenidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- II. Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDokument98 SeitenII. Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersarielleortuosteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 3 Management of Patients With Problems in Respiratory SystemDokument22 SeitenWeek 1 3 Management of Patients With Problems in Respiratory SystemKIANA LOUISE ROMANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorder of NoseDokument31 SeitenDisorder of NoseSumit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- URTIDokument41 SeitenURTIGetaneh LiknawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alvin M. Hernandez, RN, RM, MSN, Man Faculty, School of NursingDokument37 SeitenAlvin M. Hernandez, RN, RM, MSN, Man Faculty, School of NursingkathnlscNoch keine Bewertungen
- NRSG 364 - Respiratory DisordersDokument65 SeitenNRSG 364 - Respiratory DisordersJoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Airway InfectionDokument47 SeitenUpper Airway Infectionjm_john0% (1)
- Emergence of Sinusitis as an Upper Respiratory Tract Disease in Tropical RegionsDokument15 SeitenEmergence of Sinusitis as an Upper Respiratory Tract Disease in Tropical RegionsOlayimika OluwanifemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respi Patho 1Dokument111 SeitenRespi Patho 1Quolette ConstanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinusitis en inDokument2 SeitenSinusitis en inkathirr007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Notes On UrtiDokument9 SeitenLesson Notes On UrtiNeethupaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinusitis Symptoms and TreatmentDokument33 SeitenSinusitis Symptoms and TreatmentshyamashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treat Acute Chronic Ear InfectionsDokument32 SeitenTreat Acute Chronic Ear InfectionsAndrew KaumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 30: Nursing Care of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDokument4 SeitenChapter 30: Nursing Care of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersPaige Nicole GauthreauxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nose Health and DiseasesDokument11 SeitenNose Health and DiseasesLeni fitriani hamdupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary and Respiratory Nursing Assessment GuideDokument48 SeitenPulmonary and Respiratory Nursing Assessment GuideEmjay JapitanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinusitis 2024Dokument39 SeitenSinusitis 2024FrankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barotitis Media (Barotrauma) : DescriptionDokument2 SeitenBarotitis Media (Barotrauma) : DescriptionMeis MalirmaseleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 2 - Common ColdDokument28 SeitenLect 2 - Common ColdRazan diabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of High Risk InfantDokument48 SeitenNursing Care of High Risk InfantDianne Rose AgliamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsillitis and EpistaxisDokument17 SeitenTonsillitis and EpistaxisAllaine Grace CanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sneeze, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandThe Sneeze, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
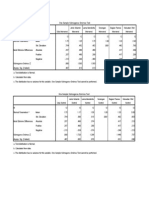
- One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test Results for Gender, Age and Stroke ParametersDokument2 SeitenOne-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test Results for Gender, Age and Stroke ParametersfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument1 SeiteDaftar PustakafakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIA Guidelines 070506 SMDokument37 SeitenTIA Guidelines 070506 SMfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EctopicKidney 508Dokument8 SeitenEctopicKidney 508fakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phenomenology ResearchDokument9 SeitenPhenomenology ResearchfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary Incontinence Guide for Care and ManagementDokument5 SeitenUrinary Incontinence Guide for Care and ManagementfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test Results for Gender, Age and Stroke ParametersDokument2 SeitenOne-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test Results for Gender, Age and Stroke ParametersfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial Profile Associates With AppendicitisDokument8 SeitenBacterial Profile Associates With AppendicitisfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unilateral Ectopic Kidney in the PelvisDokument3 SeitenUnilateral Ectopic Kidney in the PelvisfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urology System Is A System That Process Screening of BloodDokument12 SeitenUrology System Is A System That Process Screening of BloodfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B MJ AppendicitisDokument6 SeitenB MJ AppendicitisXavier QuinteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- PontesDokument1 SeitePontesfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinus Infection Symptoms and TreatmentsDokument1 SeiteSinus Infection Symptoms and TreatmentsfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RM CS - SepDokument14 SeitenRM CS - SepfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DefinitionDokument11 SeitenDefinitionfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Spec Illness AidsDokument12 Seiten6 Spec Illness AidsfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Spec Illness AidsDokument12 Seiten6 Spec Illness AidsfakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinustits FileDokument4 SeitenSinustits FilefakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SinusitisDokument8 SeitenSinusitisAlreisa YulindaNoch keine Bewertungen