Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
List of Area Moments of Inertia - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Hochgeladen von
alvia3Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
List of Area Moments of Inertia - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Hochgeladen von
alvia3Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
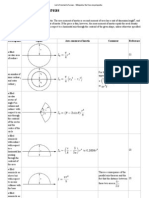
List of area moments of inertia - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_area_moments_of_inertia
Description
Figure
Area moment of inertia
Comment
Reference
a filled circular area of radius r
or
[1]
an annulus of inner radiusr 1 and outer radiusr 2
For thin tubes, this is approximately equal to: or
r3t .
a filled circular sector of angle in radians and radius r with respect to an axis through the centroid of the sector and the centre of the circle a filled semicircle with radius r with respect to a horizontal line passing through the centroid of the area a filled semicircle as above but with respect to an axis collinear with the base a filled semicircle as
1 sur 3 2012-02-22 10:38
[2]
This is a consequence of the parallel axis theorem and the fact that the distance between these two axes is [2]
List of area moments of inertia - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_area_moments_of_inertia
a filled semicircle as above but with respect to a vertical axis through the centroid a filled quarter circle with radius r entirely in the 1st quadrant of the Cartesian coordinate system a filled quarter circle as above but with respect to a horizontal or vertical axis through the centroid a filled ellipse whose radius along the x-axis is a and whose radius along the y-axis is b a filled rectangular area with a base width of b and height h a filled rectangular area as above but with respect to an axis collinear with the base a filled rectangular area as above but with respect to an
2 sur 3
[2]
[3]
This is a consequence of the parallel axis theorem and the fact that the distance between these two axes is [3]
[4]
This is a result from the parallel axis [4] theorem
2012-02-22 10:38
List of area moments of inertia - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_area_moments_of_inertia
with respect to an axis collinear, where r is the perpendicular distance from the centroid of the rectangle to the axis of interest a filled triangular area with a base width of b and height h with respect to an axis through the centroid
This is a result from the parallel axis [4] theorem
[5]
a filled triangular area as above but with respect to an axis collinear with the base
This is a consequence of the parallel [5] axis theorem
a filled regular hexagon with a side length of a
The result is valid for both a horizontal and a vertical axis through the centroid, and therefore is also valid for an axis with arbitrary direction that passes through the origin.
3 sur 3
2012-02-22 10:38
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Modern Electromagnetic Scattering Theory with ApplicationsVon EverandModern Electromagnetic Scattering Theory with ApplicationsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- List of Moment of AreasDokument3 SeitenList of Moment of AreasTk Kendrick LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lighting Fittings Performance and Design: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringVon EverandLighting Fittings Performance and Design: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of InertiaDokument4 SeitenMoment of Inertiabansal123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of Inertia FundamentalsDokument4 SeitenMoment of Inertia FundamentalsSam ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area Moment of Inertia Basic ShapesDokument3 SeitenArea Moment of Inertia Basic ShapeswilliaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Angle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument8 SeitenSolid Angle - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediayerlis21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Euler Polyhedron Formula & Solids FormulasDokument6 SeitenEuler Polyhedron Formula & Solids FormulasRara Rahma AuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular Segment: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument2 SeitenCircular Segment: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPeter TothNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual DraftDokument5 SeitenUser Manual Draftjohn-john castañedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle Equations and PropertiesDokument8 SeitenCircle Equations and PropertiesSofiyah Sitorus PaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument9 SeitenCircle - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMahaveerprasad GotarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AreaDokument13 SeitenAreaamitjustamitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area Formulas for Polygons and CirclesDokument7 SeitenArea Formulas for Polygons and CirclesRojan MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Mechanical Fact SheetDokument3 SeitenStructural Mechanical Fact SheetKerri-Lyn LordeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Moment of AreaDokument3 SeitenSecond Moment of AreaArvind SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- r h V = πr h h r x A (x) : right circular cylinder having a finite height with circular endsDokument2 Seitenr h V = πr h h r x A (x) : right circular cylinder having a finite height with circular endsdwarika2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Area Wiki PDFDokument6 SeitenArea Wiki PDFgooglepleckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 103 Lecture Notes: Leah Keshet January 9, 2005Dokument28 SeitenMath 103 Lecture Notes: Leah Keshet January 9, 2005nagaraj108Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fred Richman: The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 24, No. 2. (Mar., 1993), Pp. 160-162Dokument4 SeitenFred Richman: The College Mathematics Journal, Vol. 24, No. 2. (Mar., 1993), Pp. 160-162David SumnersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume of A Sphere FormulaDokument7 SeitenVolume of A Sphere Formulaapi-126876773Noch keine Bewertungen
- GeometryDokument12 SeitenGeometryJose Marviel JesoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics 01 00017Dokument42 SeitenAcoustics 01 00017Pluto PlutonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sphere: Not On The Sphere (An Open Ball) - The Distinction Between Ball and Sphere Has Not Always Been MaintainedDokument16 SeitenSphere: Not On The Sphere (An Open Ball) - The Distinction Between Ball and Sphere Has Not Always Been MaintainedAndreGuilhermeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand-Out No.11: (Plane and Solid Mensuration)Dokument2 SeitenHand-Out No.11: (Plane and Solid Mensuration)julius daparNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Hydrulic DiameterDokument6 Seiten7 Hydrulic DiameterAzfarizal MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cylinder Shape Guide: Properties, Formulas & Types in 40 CharactersDokument39 SeitenCylinder Shape Guide: Properties, Formulas & Types in 40 CharactersNaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 02 - TorsionDokument35 SeitenChapter 02 - Torsionsengthai100% (1)
- SphereDokument15 SeitenSpherejolinmartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME3112 Help SheetDokument10 SeitenME3112 Help SheetPS ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CirclesDokument2 SeitenCirclesArie AbdillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume of A Sphere FormulaDokument7 SeitenVolume of A Sphere Formulaapi-126876773Noch keine Bewertungen
- Green's TheoremDokument26 SeitenGreen's Theoremjohn_doe_awesome100% (1)
- Chapter 02 - Torsion and ExceriseDokument59 SeitenChapter 02 - Torsion and ExcerisesengthaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setting Out Circular CurvesDokument14 SeitenSetting Out Circular CurvesRubel HaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle: Tycho Crater, One of Many Examples of Circles That Arise in NatureDokument14 SeitenCircle: Tycho Crater, One of Many Examples of Circles That Arise in NatureZulaika ZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulæ: Formulæ Triangle Equilateral Triangle Triangle Triangle Base Altitude Square Rectangle Rhombus DiagonalsDokument2 SeitenFormulæ: Formulæ Triangle Equilateral Triangle Triangle Triangle Base Altitude Square Rectangle Rhombus Diagonalsk2LAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Toriodal Inductor WikiDokument5 SeitenToriodal Inductor Wikilibrian_30005821Noch keine Bewertungen
- Equivalent Diameter Is Not The Same As Hydraulic Diameter.: List of Hydraulic DiametersDokument5 SeitenEquivalent Diameter Is Not The Same As Hydraulic Diameter.: List of Hydraulic DiametersRinnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung Surface Areas and VolumesDokument32 SeitenLung Surface Areas and VolumesareejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of The Focal Length of An Offset Satellite Dish AntennaDokument9 SeitenCalculation of The Focal Length of An Offset Satellite Dish AntennazaphossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanced Force Charles Et Al IEJ 1998Dokument7 SeitenBalanced Force Charles Et Al IEJ 1998abcder1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kamal Roop Class Ix - CDokument15 SeitenKamal Roop Class Ix - CPuneet SachdevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three-Dimensional Geometric Shape Apex VertexDokument9 SeitenThree-Dimensional Geometric Shape Apex VertexAlí PabónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Mechanics of Buried Pipes: Anderson, Loren Runar Et Al "RING DEFORMATION" Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 2000Dokument9 SeitenStructural Mechanics of Buried Pipes: Anderson, Loren Runar Et Al "RING DEFORMATION" Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 2000Sheikh Mizanur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horizontal and Vertical CurvesDokument29 SeitenHorizontal and Vertical CurvesSandro SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAT Math - Plane and Solid GeometryDokument8 SeitenSAT Math - Plane and Solid GeometryΜάριος Α. ΠαππάςNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Areas and Volumes GuideDokument10 SeitenSurface Areas and Volumes GuideBharani SriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Diameter vs. Equivalent DiameterDokument7 SeitenHydraulic Diameter vs. Equivalent DiameterKaiash M YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wide Band AntennasDokument8 SeitenWide Band AntennasDmk ChaitanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Propellers ExplainedDokument25 SeitenScrew Propellers ExplainedAkashDudi100% (1)
- New WordDokument3 SeitenNew WordAwais YousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curves: Definition and Types - Curves - SurveyingDokument55 SeitenCurves: Definition and Types - Curves - SurveyingAderiyike noahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partially Full Pipe Flow Calculations Using Excel Spreadsheets 7-18-14Dokument28 SeitenPartially Full Pipe Flow Calculations Using Excel Spreadsheets 7-18-14hrol310600% (1)
- REVIEW MATHEMATICS 4B FORMULASDokument2 SeitenREVIEW MATHEMATICS 4B FORMULASLaurence CalpoturaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reciprocal Lattice PDFDokument28 SeitenReciprocal Lattice PDFkamal hameed tayyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharp-crested weirs discharge measurementDokument12 SeitenSharp-crested weirs discharge measurementagnwwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular SegmentDokument2 SeitenCircular SegmentTomy GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CircolDokument12 SeitenCircol202130054Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unistrut GEC17 112011Dokument244 SeitenUnistrut GEC17 112011legendszNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Technical Guide Supplement For HDV Drop-In Anchors Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1544126Dokument4 SeitenProduct Technical Guide Supplement For HDV Drop-In Anchors Technical Information ASSET DOC LOC 1544126alvia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- USEPA Total Dissolved Gas Research PDFDokument90 SeitenUSEPA Total Dissolved Gas Research PDFalvia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- GAS BUBBLE DISEASE INFODokument5 SeitenGAS BUBBLE DISEASE INFOalvia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gimp TutDokument421 SeitenGimp Tutpallavi_chopra_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bushing Materials and PropertiesDokument3 SeitenBushing Materials and Propertiesalvia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dissolved Gas Supersaturation (En)Dokument7 SeitenDissolved Gas Supersaturation (En)alvia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Farr Gold Series Mini - GS4M: For Small Airflow ApplicationsDokument3 SeitenFarr Gold Series Mini - GS4M: For Small Airflow Applicationsalvia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Total Gas Pressure Information SheetDokument5 SeitenTotal Gas Pressure Information Sheetalvia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- NL Superbolt Standard-Range-Brochure 70186ENDokument28 SeitenNL Superbolt Standard-Range-Brochure 70186ENalvia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- USEPA Total Dissolved Gas ResearchDokument90 SeitenUSEPA Total Dissolved Gas Researchalvia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Dimension and WeightDokument24 SeitenSteel Dimension and Weightyaqub19799141Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wire Drawing FormulasDokument17 SeitenWire Drawing Formulasdofan thrimavithanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 (MATH11B)Dokument35 SeitenChapter 2 (MATH11B)Ma. Woodelyn ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 Basic Formulas in Civil EngineeringDokument8 Seiten50 Basic Formulas in Civil Engineeringruwan.smb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Picture Has A Height That IsDokument10 SeitenA Picture Has A Height That IsDhea CapuyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cot Math 6 2020-2021Dokument32 SeitenCot Math 6 2020-2021Ronald Tiongson Parana Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACET Practice Test Booklet: This Is Still in Its Testing PhaseDokument47 SeitenACET Practice Test Booklet: This Is Still in Its Testing PhasehelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi Sci Maths Annual QB 2023-24Dokument9 SeitenXi Sci Maths Annual QB 2023-24yashkhedekar262Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Answer Key Class IxDokument14 SeitenMath Answer Key Class IxLakshay BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC June 2014 Mathematics P1Dokument13 SeitenCSEC June 2014 Mathematics P1Tamera GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 - Integration by Parts PDFDokument2 Seiten05 - Integration by Parts PDFpablo fernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL Analysis Formula Booklet PDFDokument14 SeitenSL Analysis Formula Booklet PDFMATHVISION STUDY MATERIALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter IxDokument5 SeitenChapter IxJames JimenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cadet Colleges Entry Test Sample Papers PDF English Mathematics Intelligence Test UrduDokument5 SeitenCadet Colleges Entry Test Sample Papers PDF English Mathematics Intelligence Test UrduThe Nest Montessori School SystemNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSG English Math FileDokument41 SeitenBSG English Math FileDhiman NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 QuadraticsDokument64 SeitenChapter 3 Quadraticsluong anh thuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/22Dokument20 SeitenCambridge O Level: Mathematics (Syllabus D) 4024/22D.T.CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of the Philippines Third Quarterly Test in Mathematics VIDokument3 SeitenRepublic of the Philippines Third Quarterly Test in Mathematics VILietOts Kinse100% (1)
- 58 D 4 Efcce 4 B 0 F 6 C 0 A 90 CDC 44Dokument163 Seiten58 D 4 Efcce 4 B 0 F 6 C 0 A 90 CDC 44BHAVYA BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perimeter, Area, and Circumference FormulasDokument21 SeitenPerimeter, Area, and Circumference FormulasJLuis LuNaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Physics (4PH1) Paper 1PDokument17 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2020: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Physics (4PH1) Paper 1PNairit60% (5)
- 2022 AMOSeniorDokument12 Seiten2022 AMOSeniorBO5 Yuan Rey M. dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry and Trigonometry - EasyDokument41 SeitenGeometry and Trigonometry - EasyDiệu Anh HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Previous Year Boards Questions: Chapter 6 - TrianglesDokument4 SeitenPrevious Year Boards Questions: Chapter 6 - TrianglesshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taller 4 - Centroides y Centros de GravedadDokument22 SeitenTaller 4 - Centroides y Centros de GravedadHENRY ZAMORA HERNANDEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orca Share Media1579045615008Dokument5 SeitenOrca Share Media1579045615008Teresa Marie Yap CorderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect Bell Nozzle Parametric and Optimization Curves: Nasa Reference Publication 1104Dokument31 SeitenPerfect Bell Nozzle Parametric and Optimization Curves: Nasa Reference Publication 1104djeffal mohammed amineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Questions No. 6Dokument2 SeitenMath Questions No. 6Richard PekitpekitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 1 Solid MensurationDokument71 SeitenGroup 1 Solid MensurationEjay Abante83% (6)
- Revision Assertion & Reason - STD 10Dokument19 SeitenRevision Assertion & Reason - STD 10Vedant BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlanimeterDokument17 SeitenPlanimeterhpss77Noch keine Bewertungen