Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
14 DETEMINANTS & MATRICES PART 3 of 6 PDF
Hochgeladen von
sabhari_ramOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
14 DETEMINANTS & MATRICES PART 3 of 6 PDF
Hochgeladen von
sabhari_ramCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
2
1
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
SHORT REVISION
1. The symbol
a b
a b
1 1
2 2
is called the determinant of order two .
Its value is given by : D = a
1
b
2
a
2
b
1
2. The symbol
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
is called the determinant of order three .
Its value can be found as : D = a
1
b c
b c
2 2
3 3
a
2
b c
b c
1 1
3 3
+ a
3
b c
b c
1 1
2 2
OR
D = a
1
b c
b c
2 2
3 3
b
1
a c
a c
2 2
3 3
+ c
1
a b
a b
2 2
3 3
....... and so on .
In this manner we can expand a determinant in 6 ways using elements of ; R
1
, R
2
, R
3
or C
1
, C
2
, C
3
.
3. Following examples of short hand writing large expressions are :
(i) The lines : a
1
x + b
1
y + c
1
= 0........ (1)
a
2
x + b
2
y + c
2
= 0........ (2)
a
3
x + b
3
y + c
3
= 0........ (3)
are concurrent if ,
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
= 0 .
Condition for the consistency of three simultaneous linear equations in 2 variables.
(ii) ax + 2
hxy + by + 2
gx + 2
fy + c = 0 represents a pair of straight lines if :
abc + 2
fgh af bg ch = 0 =
a h g
h b f
g f c
(iii) Area of a triangle whose vertices are (x
r
, y
r
) ; r = 1 , 2 , 3 is :
D =
1
2
x y
x y
x y
1 1
2 2
3 3
1
1
1
If D = 0 then the three points are collinear .
(iv) Equation of a straight line passsing through (x
1
, y
1
) & (x
2
, y
2
) is
1 y x
1 y x
1 y x
2 2
1 1
= 0
4. MINORS : The minor of a given element of a determinant is the determinant of the elements
which remain after deleting the row & the column in which the given element stands . For example,
the minor of a
1
in (Key Concept 2) is
b c
b c
2 2
3 3
& the minor of b
2
is
a c
a c
1 1
3 3
.
Hence a determinant of order two will have 4 minors & a determinant of order three will
have 9 minors .
5. COFACTOR :If M
ij
represents the minor of some typical element then the cofactor is defined as :
C
ij
= (1)
i+j
. M
ij
; Where i & j denotes the row & column in which the particular element lies.
Note that the value of a determinant of order three in terms of Minor & Cofactor can be
written as : D = a
11
M
11
a
12
M
12
+ a
13
M
13
OR D = a
11
C
11
+ a
12
C
12
+ a
13
C
13
& so on .......
6. PROPERTIES OF DETERMINANTS : P
1 :The value of a determinant remains unaltered , if the
rows & columns are inter changed . e.g. if D =
a b c
a b c
a b c
a a a
b b b
c c c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
1 2 3
1 2 3
1 2 3
=
= D
D & D are transpose of each other . If D =
D then it is SKEW SYMMETRIC
determinant but D = D 2
D = 0 D = 0 Skew symmetric determinant of
third order has the value zero .
P
2 : If any two rows (or columns) of a determinant be interchanged , the value
of determinant is changed in sign only . e.g.
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
2
2
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
Let D =
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
& D =
a b c
a b c
a b c
2 2 2
1 1 1
3 3 3
Then D =
D .
P
3 : If a determinant has any two
rows (or columns)
identical , then its value is
zero . e.g. Let D =
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
1 1 1
3 3 3
then it can be verified that D = 0.
P
4 : If all the elements of any row (or column) be multiplied by the same number ,
then the determinant is multiplied by that number.
e.g. If D =
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2
3 3 3
2
and D =
Ka Kb Kc
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2
3 3 3
2
Then D= KD
P 5 : If each element of any row (or column) can be expressed as a sum of two terms
then the determinant can be expressed as the sum of two determinants . e.g.
a x b y c z
a b c
a b c
a b c
a b c
a b c
x y z
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
2 2 2
3 3 3
+ + +
= +
P 6 : The value of a determinant is not altered by adding to the elements of any
row (or column) the same multiples of the corresponding elements of any
other row (or column). e.g. Let D =
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
and
D =
a ma b mb c mc
a b c
a na b n b c n c
1 2 1 2 1 2
2 2 2
3 1 3 1 3 1
+ + +
+ + +
. Then D = D .
Note : that while applying this property ATLEAST ONE ROW (OR COLUMN)
must remain unchanged .
P 7 : If by putting x = a the value of a determinant vanishes then (x
a) is a factor
of the determinant .
7. MULTIPLICATION OF TWO DETERMINANTS :
(i)
a b
a b
x
l m
l m
a l b l a m b m
a l b l a m b m
1 1
2 2
1 1
2 2
1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2
2 1 2 2 2 1 2 2
=
+ +
+ +
Similarly two determinants of order three are multiplied.
(ii) If D =
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
0 then , D =
A B C
A B C
A B C
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
where A
i
, B
i
, C
i
are cofactors
PROOF : Consider
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
A A A
B B B
C C C
1 2 3
1 2 3
1 2 3
=
D
D
D
0 0
0 0
0 0
Note : a
1
A
2
+ b
1
B
2
+ c
1
C
2
= 0 etc.
therefore , D x
A A A
B B B
C C C
1 2 3
1 2 3
1 2 3
= D
3
A A A
B B B
C C C
1 2 3
1 2 3
1 2 3
= D OR
A B C
A B C
CA B C
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
= D
8. SYSTEM OF LINEAR EQUATION (IN TWO VARIABLES) :
(i) Consistent Equations : Definite & unique solution . [ intersecting lines ]
(ii) Inconsistent Equation : No solution . [ Parallel line ]
(iii) Dependent equation : Infinite solutions . [ Identical lines ]
Let a
1
x + b
1
y + c
1
= 0 & a
2
x + b
2
y + c
2
= 0 then :
a
a
b
b
c
c
1
2
1
2
1
2
= Given equations are inconsistent &
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
2
3
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
a
a
b
b
c
c
1
2
1
2
1
2
= = Given equations are dependent
9. CRAMER'S RULE : [ SIMULTANEOUS EQUATIONS INVOLVING THREE UNKNOWNS ]
Let ,a
1
x + b
1
y + c
1
z = d
1
...(I) ; a
2
x + b
2
y + c
2
z = d
2
...(II) ; a
3
x + b
3
y + c
3
z = d
3
...(III)
Then , x =
D
D
1
, Y =
D
D
2
, Z =
D
D
3
.
Where D =
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
; D
1
=
d b c
d b c
d b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
; D
2
=
a d c
a d c
a d c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
& D
3
=
a b d
a b d
a b d
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
NOTE : (a) If D 0 and alteast one of D
1
, D
2
, D
3
0 , then the given system of
equations are consistent and have unique non trivial solution .
(b) If D 0 & D
1
= D
2
= D
3
= 0
, then the given system of equations are
consistent and have trivial solution only .
(c) If D = D
1
= D
2
= D
3
= 0
, then the given system of equations are
consistent and have infinite solutions
.
In case
= + +
= + +
= + +
3 3 3 3
2 2 2 2
1 1 1 1
d z c y b x a
d z c y b x a
d z c y b x a
represents these parallel planes then also
D = D
1
= D
2
= D
3
= 0 but the system is inconsistent.
(d) If D = 0
but atleast one of D
1
, D
2
, D
3
is not zero then the equations are inconsistent and have no
solution .
10. If x
, y
, z are
not
all zero
,
the
condition for a
1
x + b
1
y + c
1
z = 0 ; a
2
x + b
2
y + c
2
z = 0 &
a
3
x + b
3
y + c
3
z = 0 to be consistent in x
, y
, z is that
a b c
a b c
a b c
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
= 0.
Remember that if a given system of linear equations have Only Zero Solution for all its
variables
then
the
given
equations are said to have TRIVIAL SOLUTION.
EXERCISE-1
Q 1. Without expanding the determinant prove that :
(a)
0
0
0
b c
b a
c a
= 0 (b)
0
0
0
p q p r
q p q r
r p r q
= 0 (c)
9 i 5 4 i 4
3
2
i 5 4 8 i 3 5
i 4
3
2
i 3 5 7
+
+
+
is real
(d)
a x by cz
x y z
2 2 2
1 1 1
=
a b c
x y z
y z zx xy
(e)
1
1
1
2
2
2
a a bc
b b ca
c c a b
= 0
Q 2. Without expanding as far as possible , prove that :
(a)
a a a
a a
2
2 2 1 1
2 1 2 1
3 3 1
+ +
+ + = (a 1)
3
(b)
1 1 1
3 3 3
x y z
x y z
= [(xy)
(yz)
(zx)
(x+y+z)]
Q 3. If
x x x
y y y
z z z
3 2
3 2
3 2
1
1
1
+
+
+
= 0 and x
, y
, z are all different then , prove that xyz =
1 .
Q 4. Using properties of determinants or otherwise evaluate
18 40 89
40 89 198
89 198 440
.
Q 5. Prove that
a b c a a
b b c a b
c c c a b
2 2
2 2
2 2
= (a + b + c)
3
.
Q 6. If D =
a b c
c a b
b c a
and D =
b c c a a b
a b b c c a
c a a b b c
+ + +
+ + +
+ + +
then prove that D = 2
D .
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
2
4
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
Q 7. Prove that
+ +
+ +
+ +
2
2
2
a a b a c
b a b b c
c a c b c
= 4 [(a+b)
(b+c)
(c+a)]
Q 8. Prove that
1 2 2
2 1 2
2 2 1
2 2
2 2
2 2
+
+
a b ab b
ab a b a
b a a b
= (1 + a + b)
3
.
Q 9. Prove that
a b c c b
a c b c a
a b b a c
+
+
+
= (a + b + c)
(a + b + c) .
Q 10. Show that the value of the determinant
tan( ) tan( ) tan( )
tan( ) tan( ) tan( )
tan( ) tan( ) tan( )
A P B P C P
A Q B Q C Q
A R B R C R
+ + +
+ + +
+ + +
vanishes for all values
of A, B, C, P, Q & R where A + B + C + P + Q + R = 0
Q 11. Factorise the determinant
b c b c b c b c
ca ca c a c a
a b a b a b a b
+
+
+
.
Q 12. Prove that
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
+ +
+ +
+ +
4 2
4 2
4 2
1
1
1
=
64(
)
(
)(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
Q 13. For a fixed positive integer n , if D =
n n n
n n n
n n n
! ( )! ( )!
( )! ( )! ( )!
( )! ( )! ( )!
+ +
+ + +
+ + +
1 2
1 2 3
2 3 4
then show that
D
n ( !)
3
4
(
(
is divisible by n .
Q 14. Solve for
x
x x x
x x x
x x x
+ + +
+ + +
+ + +
2 2 3 3 4
2 3 3 4 4 5
3 5 5 8 10 17
= 0 .
Q 15. If a
+
b
+
c = 0 , solve for x :
a x c b
c b x a
b a c x
= 0 .
Q 16. If a
2
+ b
2
+ c
2
= 1 then show that the value of the determinant
+ +
+ +
+ +
cos ) b a ( c ) cos 1 ( bc ) cos 1 ( ac
) cos 1 ( cb cos ) a c ( b ) cos 1 ( ab
) cos 1 ( ca ) cos 1 ( ba cos ) c b ( a
2 2 2
2 2 2
2 2 2
simplifies to cos
2
.
Q 17. If p
+
q
+
r = 0 , prove that
pa q b r c
q c r a p b
r b p c qa
= pqr
a b c
c a b
b c a
.
Q 18. If a
, b
, c are all different &
a a a
b b b
c c c
3 4
3 4
3 4
1
1
1
= 0 , then prove that :
abc (ab
+
bc
+
ca) = a
+
b
+
c .
Q 19. Show that
a ab ac
ab b bc
ac bc c
2
2
2
+
+
+
is divisible by
2
and find the other factor..
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
2
5
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
Q 20. (a) Without expanding prove that
b c a a
ca b b
a b c c
a a
b b
c c
2
2
2
2 3
2 3
2 3
1
1
1
= .
(b)
a b c
a b c
a b c
a b c
a b c
2 2 2
2 2 2
2 2 2
2 2 2
1 1 1
1 1 1
4
1 1 1
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( )
+ + +
= .
Q 21. Without expanding a determinant at any stage, show that
x x x x
x x x x
x x x x
2
2
2
1 2
2 3 1 3 3 3
2 3 2 1 2 1
+ +
+
+ +
=
Ax
+
B where
A & B are determinants of order 3 not involving x .
Q 22. Prove that
+ +
+ +
+ +
b c b b c c b c
a a c a c c a c
a a b b a b a b
2 2
2 2
2 2
= (ab + bc + ca)
3
.
Q 23. Solve
x a x b x c
x a x b x c
x a x b x c
2 2 2 2 2 2
3 3 3
3 3 3
+ + +
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( )
= 0 where a
, b
, c are non zero and distinct .
Q 24. Solve for x :
x x x
x x x
x x x
2 2 3 3 4
4 2 9 3 16
8 2 27 3 64
= 0 .
Q 25. If
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
a x
b x
c x
a y
b y
c y
a z
b z
c z
P
Q
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
= where Q
is the product of the denominator , prove that
P = (a
b) (b
c) (c
a) (x
y) (y
z) (z
x)
Q 26. If D
r
=
( ) ( )
2 2 3 4 5
2 1 3 1 5 1
1 1 1 r r r
n n n
x y z
then prove that
r
n
=
1
D
r
= 0 .
Q 27. If 2
s = a
+
b
+
c then prove that
a s a s a
s b b s b
s c s c c
2 2 2
2 2 2
2 2 2
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
= 2
s
3
(s
a)
(s
b)
(s
c) .
Q 28. In a ABC,
determine condition under which
cot cot cot
tan tan tan tan tan tan
A B C
B C C A A B
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2
1 1 1
+ + + = 0
Q 29. Show that
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
+ +
+ +
+ +
b c a b c a a c a b
ba b c c a b c a b
ca b c cb c a a b
2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2
= (ab + bc + ca)
3
.
Q 30. Prove that
b c a ca b a b c
b c ca a b b c ca a b b c ca a b
a b a c b c b a c a c b
+ + + +
+ + + + + +
2 2 2
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
= 3
.
(b
c) (c
a) (a
b) (a
+
b
+
c) (ab
+
bc
+
ca)
Q 31. For
all
values of A
, B
, C & P
, Q
, R show that
cos ( ) cos( ) cos( )
cos( ) cos( ) cos( )
cos( ) cos( ) cos( )
A P A Q A R
B P B Q B R
C P C Q C R
= 0.
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
2
6
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
Q 32. Show that
a l b m a l b m a l b m
a l b m a l b m a l b m
a l b m a l b m a l b m
1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 3 1 3
2 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 3
3 1 3 1 3 2 3 2 3 3 3 3
+ + +
+ + +
+ + +
= 0 .
Q 33. Prove that
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( )
a b a b a b
a b a b a b
a b a b a b
1 1
2
1 2
2
1 3
2
2 1
2
2 2
2
2 3
2
3 1
2
3 2
2
3 3
2
= 2 (a
1
a
2
)
(a
2
a
3
)
(a
3
a
1
)
(b
1
b
2
)
(b
2
b
3
)
(b
3
b
1
)
Q 34. Prove that
2
2
2
+ + + +
+ + + + + + + +
+ + + +
( )( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( )
= 0 .
Q 35. If ax + 2 hxy + by + 2 gx + 2 fy + c (l
1
x + m
1
y + n
1
) (l
2
x + m
2
y + n
2
) , then prove that
a h g
h b f
g f c
= 0 .
Q 36. Prove that
1
1
1
2 2
2 2
2 2
cos ( ) cos ( )
cos ( ) cos ( )
cos ( ) cos ( )
A B A C
B A B C
C A C B
= 2sin
2
(A B)sin
2
(B C)sin
2
(C A)
Q 37. If ax
1
+ by
1
+ cz
1
2
= ax
2
2
+ by
2
2
+ cz
2
2
= ax
3
2
+ by
3
2
+ cz
3
2
= d and
ax
2
x
3
+ by
2
y
3
+ cz
2
z
3
= ax
3
x
1
+ by
3
y
1
+ cz
3
z
1
= ax
1
x
2
+ by
1
y
2
+ cz
1
z
2
= f , then prove that
x y z
x y z
x y z
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
= (d
f)
d f
abc
+
(
2
1 2 /
(a , b , c 0)
Q 38. If (x
1
x
2
)
2
+ (y
1
y
2
)
2
= a
2
, (x
2
x
3
)
2
+ (y
2
y
3
)
2
= b
2
and (x
3
x
1
)
2
+ (y
3
y
1
)
2
= c
2
prove that 4
1
1
1
1 1
2 2
3 3
2
x y
x y
x y
= (a + b + c)
(b + c
a)
(c + a
b)
(a + b c) .
Q 39. If S
r
=
r
+
r
+
r
then show that
S S S
S S S
S S S
0 1 2
1 2 3
2 3 4
= ( )
2
( )
2
( )
2
.
Q 40. If u = ax
2
+ 2
bxy
+
cy
2
, u = ax
2
+ 2
bxy
+
cy
2
. Prove that
y xy x
a b c
a b c
ax by bx cy
a x b y b x c y y
u u
ax by a x b y
2 2
1
=
+ +
+ +
=
+ +
.
EXERCISE-2
Q 1. Solve using Cramers rule :
4
5
3
7 x y +
+
+
=
1 &
6
5
6
7 x y +
+
=
5 .
Q 2. Solve the following using Cramers rule and state whether consistent or not.
(a)
x y z
x y z
x y
+ + =
+ + =
+ =
2 1
3 6
2 0
(b)
x y z
x y z
x y z
+ =
+ + =
+ + =
3 2
3 6
5 3 3
(c)
5 z 5 y 3 x 2
7 z 5 y x 3
3 z 5 y 7 x 7
= + +
= + +
= +
Q 3. Solve the system of equations ;
z a y a x a
z by b x b
z cy c x c
+ + + =
+ + + =
+ + + =
(
(
(
(
2 3
2 3
2 3
0
0
0
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
2
7
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
Q 4. For what value of K do the following system of equations possess a non trivial
(i.e. not all zero) solution over the set of rationals Q ?
x
+
K
y + 3
z = 0 , 3
x
+
K
y
2
z = 0 , 2
x
+
3
y
4
z = 0 .
For that value of K , find all the solutions of the system .
Q 5. Given
x = cy
+
bz ; y = az + cx
; z = bx
+
ay where x
, y
, z are
not
all
zero ,
prove
that
a + b + c + 2
abc = 1 .
Q 6. Given a =
x
y z
; b =
y
z x
; c =
z
x y
where x
, y
, z are not
all zero , prove that :
1 + ab + bc + ca = 0 .
Q 7. If sin q cos q and x, y, z satisfy the equations
x cos p y sin p + z = cos q + 1
x sin p + y cos p + z = 1 sin q
x cos(p + q) y sin (p + q) + z = 2 then find the value of x
2
+ y
2
+ z
2
.
Q 8. If A, B and C are the angles of a triangle then show that
sin 2A x + sin C y + sin B z = 0
sin C x + sin 2B y + sin A z = 0
sin B x + sin Ay + sin 2C z = 0 possess non-trivial solution.
Q 9. Investigate for what values of , the simultaneous equations x + y + z = 6 ;
x
+
2
y
+ 3
z = 10 & x
+
2
y
+ z = have ; (a) A unique solution .
(b) An infinite number of solutions . (c) No solution .
Q 10. For what values of p , the equations : x
+
y
+
z = 1 ; x
+
2
y
+
4
z = p &
x
+
4
y
+
10
z = p have a solution ? Solve them completely in each case .
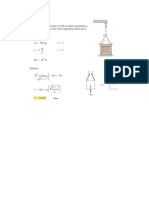
Q 11. Solve the equations : K
x
+
2
y
2
z = 1 , 4
x
+
2
K
y z = 2 , 6
x
+
6
y
+
K
z = 3
considering specially the case when K = 2 .
Q 12. Solve the system of equations :
x + y + z = m , x + y + z = n and x + y + z = p
Q 13. Find all the values of t for which the system of equations ;
(t
1)
x + (3
t
+
1)
y + 2
t
z = 0
(t
1)
x + (4
t
2)
y + (t
+
3)
z = 0
2
x
+ (3
t
+
1)
y + 3
(t
1)
z = 0 has non trivial solutions and in this context find the ratios
of x : y : z , when t
has the smallest of these values.
Q 14. Solve : (b
+
c)
(y
+
z)
ax = b c , (c
+
a)
(z
+
x)
by = c a and
(a
+
b)
(x
+
y)
cz = a b where a
+
b
+
c
0.
Q 15. If bc
+
qr = ca
+
rp = ab
+
pq =
1 show that
a p a p
bq b q
cr c r
= 0 .
Q 16. If x, y, z are not all
zero & if
ax
+
by
+ cz = 0, bx
+ cy + az = 0 & cx + ay + bz = 0, then prove
that x
: y: z = 1 : 1 : 1 OR 1
: : OR 1
:
: ,
where is one of the complex cube root of unity.
Q 17. If the following system of equations (a
t)x
+
by
+
cz = 0
, bx
+
(c
t)y
+
az = 0
and
cx
+
ay
+
(b
t)z = 0 has nontrivial solutions for different values of
t
, then show that we can
express product of these values of t in the form of determinant .
Q18. Show that the system of equations
3x y + 4z = 3 , x + 2y 3z = 2 and 6x + 5y + z = 3
has atleast one solution for any real number . Find the set of solutions of = 5.
EXERCISE-3
Q.1 For what values of p & q, the system of equations 2
x
+ p
y
+ 6
z = 8 ; x
+
2
y
+
q
z = 5 &
x
+
y
+
3
z = 4 has ; (i) no solution (ii) a unique solution (iii) infinitely many solutions
Q.2 (i) Let a
, b
, c positive numbers . The following system of equations in x
, y & z.
x
a
y
b
z
c
2
2
2
2
2
2
+ = 1 ;
2
2
2
2
2
2
c
z
b
y
a
x
+ = 1 ; + +
x
a
y
b
z
c
2
2
2
2
2
2
= 1 has:
(A) no solution (B) unique solution
(C) infinitely many solutions (D) finitely many solutions
(ii) If (
1) is a cube root of unity , then
1 1
1 1 1
1 1
2 2
2
+ +
+
i
i
i i
equals :
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) i (D) [ IIT '95 , 1 + 1 ]
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
2
8
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
Q.3 Let a > 0, d > 0 . Find the value of determinant
1 1 1
2
1 1
2
1
2 3
1
2
1
2 3
1
3 4
a
a a d a d a d
a d a d a d a d a d
a d a d a d a d a d
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
+ + +
+ + + + +
+ + + + +
. [ IIT 96 , 5 ]
Q.4 Find those values of c for which the equations :
2
x
+
3
y = 3
(c
+
2)
x
+ (c
+
4)
y = c
+
6
(c
+
2)
x + (c
+
4)
y = (c
+
6) are consistent .
Also solve above equations for these values of c . [ REE 96 , 6 ]
Q.5 For what real values of k , the system of equations x + 2y + z = 1 ; x + 3y + 4z = k ;
x + 5y + 10z = k
2
has solution ? Find the solution in each case. [ REE ' 97, 6 ]
Q.6 The parameter, on which the value of the determinant
1
2
a a
p d x px p d x
p d x px p d x
cos( ) cos cos( )
sin( ) sin sin( )
+
+
does not
depend upon is :
(A) a (B) p (C) d (D) x
Q.7 If
6 3 1
4 3 1
20 3
i i
i
i
= x + iy , then :
(A) x = 3 , y = 1 (B) x = 1 , y = 3 (C) x = 0 , y = 3 (D) x = 0 , y = 0
Q.8 (i) If f(x) =
( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
1 1
2 1 1
3 1 1 2 1 1
x x
x x x x x
x x x x x x x x
+
+
+
then f(100) is equal to :
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 100 (D)
100
(ii) Let a, b, c, d be real numbers in G.P. If u, v, w satisfy the system of equations,
u + 2v + 3w = 6
4u + 5v + 6w = 12
6u + 9v = 4 then show that the roots of the equation,
1 1 1
u v w
+ +
|
\
|
x
2
+ [(b c)
2
+ (c a)
2
+ (d b)
2
]
x + u + v + w = 0 and
20
x
2
+ 10
(a d)
2
x 9 = 0 are reciprocals of each other .
Q.9 If the system of equations x Ky z = 0, Kx y z = 0 and x + y z = 0 has a non zero solution,
then the possible values of K are
(A) 1, 2 (B) 1, 2 (C) 0, 1 (D) 1, 1
Q.10 Prove that for all values of ,
sin cos sin
sin cos sin
sin cos sin
2
2
2
2
3
2
3
4
3
2
3
2
3
4
3
+
|
\
| +
|
\
| +
|
\
|
\
|
|
\
|
|
\
|
= 0
Q.11 Find the real values of r for which the following system of linear equations has a non-trivial solution
. Also find the non-trivial solutions :
2 r
x 2
y + 3
z
=
0
x + r
y + 2
z
=
0
2
x + r
z
=
0
Q.12 Solve for x the equation
a a
n x nx n x
n x nx n x
2
1
1 1
1 1
sin( ) sin sin( )
cos( ) cos cos( )
+
+
= 0
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
2
9
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
Q.13 Test the consistency and solve them when consistent, the following system of equations for all
values of :
x + y + z = 1
x + 3y 2z =
3x + ( + 2)y 3z = 2 + 1 [ REE 2001 (Mains) , 5 out of 100 ]
Q.14 Let a, b, c be real numbers with a
2
+ b
2
+ c
2
= 1 . Show that the equation
ax by c bx ay cx a
bx ay ax by c cy b
cx a cy b ax by c
+ +
+ + +
+ + +
= 0 represents a straight line.
Q.15 The number of values of k for which the system of equations
(k + 1)x + 8y = 4k
kx + (k + 3)y = 3k 1
has infinitely many solutions is
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) inifinite
Q . 1 6 Q . 1 6 Q . 1 6 Q . 1 6 T h e v a l u e o f T h e v a l u e o f T h e v a l u e o f T h e v a l u e o f for which the system of equations 2x y z = 12, x 2y + z = 4, x + y + z = 4
has no solution is
(A) 3 (B) 3 (C) 2 (D) 2
ANSWER KEY [EXERCISE-1]
Q 4.
1 Q 11. (ab
ab)
(bc
bc)
(ca
ca) Q 14. x =
1 or x
=
2
Q 15. x = 0 or x =
( )
3
2
2 2 2
a b c + +
Q19.
2
( a
2
+ b
2
+ c
2
+ )
Q 23. If ab + bc + ca 0 , then x = 0 is the only real
root ; If ab + bc + ca > 0
,
then x = 0 or x =
+ + ab bc ca
3
Q 24. x = 4 Q 28. Triangle ABC is isosceles .
EXERCISE-2
Q 1. x =
7 , y =
4
Q 2. (a) x = 2 , y =
1 , z = 1 ; consistent
(b) x =
13
3
, y =
7
6
, z =
35
6
; consistent (c) inconsistent
Q 3. x = (a + b + c) , y = ab + bc + ca , z = abc
Q 4. K =
33
2
, x
: y
: z =
15
2
: 1 :
3 Q7. 2
Q 9. (a) 3 (b) = 3, =10 (c) = 3, 10
Q 10. x = 1
+
2
K
, y =
3
K , z = K
, when p = 1
; x = 2
K
, y = 1
3
K
, z =
K
when p = 2 ;
where K R
Q 11. If K
2 ,
( )
x
K
y
K
z
K
K K
2 6 2 3 6 2
1
2 2 15
2
( ) ( ) +
=
+
=
=
+ +
If K= 2 ,
then x = , y =
2
2 1
and z = 0 where R
Q 12. If 1 or 2 , unique solution ;
If = 2 & m + n + p = 0 , infinite solution ;
If = 2 & m + n + p
0 , no solution ;
If = 1 , infinite solution if m = n = p ;
D
E
T
.
&
M
A
T
.
/
P
a
g
e
:
3
0
o
f
5
4
T
E
K
O
C
L
A
S
S
E
S
,
H
.
O
.
D
.
M
A
T
H
S
:
S
U
H
A
G
R
.
K
A
R
I
Y
A
(
S
.
R
.
K
.
S
i
r
)
P
H
:
(
0
7
5
5
)
-
3
2
0
0
0
0
0
,
0
9
8
9
3
0
5
8
8
8
1
,
B
H
O
P
A
L
F
R
E
E
D
o
w
n
l
o
a
d
S
t
u
d
y
P
a
c
k
a
g
e
f
r
o
m
w
e
b
s
i
t
e
:
w
w
w
.
t
e
k
o
c
l
a
s
s
e
s
.
c
o
m
If = 1 , no solution if m n or n p or p m
Q 13. t = 0 or 3
; x : y : z = 1 : 1 : 1 Q 14. x =
c b
a b c
+ +
, y =
a c
a b c
+ +
, z =
b a
a b c
+ +
Q 17.
a b c
b c a
c a b
Q18. If 5 then x =
7
4
; y =
9
7
and z = 0 ;
If = 5 then x =
4 5
7
K
; y =
7
9 K 13
and z = K where K R
EXERCISE-3
Q 1. (i) p
2 , q = 3 (ii) p
2 & q
3 (iii) p = 2
Q 2. (i) d (ii) a
Q 3.
4
2 3 4
4
2 3 2
d
a a d a d a d a d ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) + + + +
Q 4. for c = 0 , x =
3 , y = 3 ; for c =
10
,
x =
1
2
, y =
4
3
Q 5. k = 1 : ( 5t+1, 3t, t) ; k = 2 : (5t
1, 1
3
t, t) for t R ; no solution
Q 6. B Q 7. D Q 8. (i) A Q9. D
Q 11. r = 2 ; x = k ; y =
k
2
; z = k where k R {0} Q 12. x = n, n I
Q 13. If = 5, system is consistent with infinite solution given by z = K, y =
1
2
(3K + 4) and
x =
1
2
(5K + 2) where K R
If 5, system is consistent with unique solution given by x =
1
3
(1 ); x =
1
3
( + 2) and y =
0.
Q15. B Q.16 D
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- FE Math PracticeDokument8 SeitenFE Math PracticeAdam Wilkins71% (7)
- Notes and Formulae MathematicsDokument9 SeitenNotes and Formulae MathematicsNurAinKhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gyan-Sutra-Physics-Formula-Booklet IIT JEE, AIEEEDokument60 SeitenGyan-Sutra-Physics-Formula-Booklet IIT JEE, AIEEEHemant Yadav94% (84)
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsVon EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- CompressorsDokument30 SeitenCompressorssabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aieee Paper 2008Dokument30 SeitenAieee Paper 2008Ravi LorventNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit Jee 2004 Screening MathsDokument10 SeitenIit Jee 2004 Screening MathsRahul BadwaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Additional Maths NoteDokument10 SeitenForm 5 Additional Maths NoteEric WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Space Frame StructuresDokument96 SeitenDynamic Space Frame Structuresg1n2100% (2)
- Steel Tables by R Agor, Birla Publications PDFDokument97 SeitenSteel Tables by R Agor, Birla Publications PDFankitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesVon EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesBewertung: 1.5 von 5 Sternen1.5/5 (2)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Von EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Maths Exam Paper (2008-2012) FinalDokument430 Seiten12th Maths Exam Paper (2008-2012) FinalAdityas AravindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageVon EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newnes Mathematics Pocket Book for EngineersVon EverandNewnes Mathematics Pocket Book for EngineersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Chapter 13 - Kinetics of Particles - 1Dokument55 SeitenChapter 13 - Kinetics of Particles - 1Zizhen JiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathsDokument29 SeitenMathsKarunamoorthy PeriasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Formulas: 1. Set IdentitiesDokument20 SeitenAlgebra Formulas: 1. Set IdentitiesHiren Mistry100% (1)
- Mathematics As A Study of PatternsDokument31 SeitenMathematics As A Study of PatternsRainelda C. CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- S. No Questions Solutions Sol: 1 (B) : Poornima University. For Any Query, Contact Us At: 8875666617,18Dokument6 SeitenS. No Questions Solutions Sol: 1 (B) : Poornima University. For Any Query, Contact Us At: 8875666617,18Vaibhav SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- DeterminantsDokument125 SeitenDeterminantsajay2gNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE X MathematicsDokument8 SeitenCBSE X MathematicsmicrodotcdmNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEM1833 Topic 3 State Space Realizations HANDOUTDokument27 SeitenMEM1833 Topic 3 State Space Realizations HANDOUTHasrulnizam HashimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narayana Institute Iit Jee 2008 Paper 1 2Dokument53 SeitenNarayana Institute Iit Jee 2008 Paper 1 2Pranjal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 Paper 1Dokument53 Seiten2008 Paper 1Aashray KothaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typical Questions & AnswersDokument93 SeitenTypical Questions & AnswersAjeet GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KVPY Maths (Part 1)Dokument3 SeitenKVPY Maths (Part 1)Adas30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Studymate Solutions To CBSE Board Examination 2013-2014: MathematicsDokument13 SeitenStudymate Solutions To CBSE Board Examination 2013-2014: MathematicsRajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business MathematicsDokument14 SeitenBusiness MathematicsamityscribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3A. Double Integrals in Rectangular CoordinatesDokument8 Seiten3A. Double Integrals in Rectangular Coordinatesjuan perez lunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Laplace TransformDokument20 SeitenChapter 3 Laplace TransformKathryn Jing LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kvpy Paper XiiDokument25 SeitenKvpy Paper XiiVishank RustagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week12 Lect2 HandoutsDokument3 SeitenWeek12 Lect2 HandoutsManuel Xavier RajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR Nisar PDF XI Akueb McqsDokument10 SeitenSR Nisar PDF XI Akueb McqsMuqadas HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 3Dokument6 SeitenMathematical Programming Solutions To Examples 3Ng Chun HiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Aberdeen Department of Mathematical Sciences: Author IC Date 3.11.04 CodeDokument5 SeitenUniversity of Aberdeen Department of Mathematical Sciences: Author IC Date 3.11.04 CodeAlhilali ZiyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsDokument6 SeitenIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsSayan Kumar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leep 214Dokument23 SeitenLeep 214Koyal Gupta100% (1)
- GATE Mathematics Paper-2006Dokument11 SeitenGATE Mathematics Paper-2006RajkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnDokument8 Seiten2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim Solnfocuscharade_8247490Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Guidelines For Board Exams PDFDokument11 SeitenMaths Guidelines For Board Exams PDFheenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE Mathematics Paper 2011Dokument8 SeitenGATE Mathematics Paper 2011RajkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT JEE 2006 MathsDokument14 SeitenIIT JEE 2006 MathsKainshk GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 265 - Final - 2012Dokument9 SeitenMATH 265 - Final - 2012examkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths QE Teacher NotesDokument19 SeitenMaths QE Teacher NotessashaankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Structure Chapter 3 Mathematical Induction-68Dokument70 SeitenDiscrete Structure Chapter 3 Mathematical Induction-68rockers910% (1)
- Narayana Grand Test - 8Dokument12 SeitenNarayana Grand Test - 8Meet ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)Dokument4 SeitenFormula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)naedkcinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Dokument13 SeitenMaths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Apex InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estabilidad Interna y Entrada-Salida de Sistemas Continuos: Udec - DieDokument10 SeitenEstabilidad Interna y Entrada-Salida de Sistemas Continuos: Udec - DieagustinpinochetNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCI 2008 Promo W SolutionDokument12 SeitenHCI 2008 Promo W SolutionMichael CheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- JNU-2008 PaperDokument9 SeitenJNU-2008 PaperVivek SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 (Techniques of Integration)Dokument8 SeitenChapter 3 (Techniques of Integration)S M AkashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover Letter Boston Children's Hospital PDFDokument1 SeiteCover Letter Boston Children's Hospital PDFsabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCE Mid TermDokument9 SeitenSCE Mid Termsabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework1 HANYDokument6 SeitenHomework1 HANYsabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover Letter Bristol-Myers Squibb PDFDokument1 SeiteCover Letter Bristol-Myers Squibb PDFsabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Fabrication of Spur Gear by Using Palm Fiber, Aluminium Powder With EpoxyDokument21 SeitenDesign and Fabrication of Spur Gear by Using Palm Fiber, Aluminium Powder With Epoxysabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agro Machine Drawing PDFDokument1 SeiteAgro Machine Drawing PDFsabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Failure List-1 PDFDokument21 SeitenThe Failure List-1 PDFsabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anudeep 1.45 CR GoogleDokument6 SeitenAnudeep 1.45 CR Googlesabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal 1Dokument37 SeitenInternal 1sabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec3 Iit Engg Mech.Dokument24 SeitenLec3 Iit Engg Mech.sabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Best Book On Mit Grad School Admissions SampleDokument13 SeitenThe Best Book On Mit Grad School Admissions Samplesabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec8 PDFDokument25 SeitenLec8 PDFsabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of Arts: Exercise #1Dokument4 SeitenElements of Arts: Exercise #1Balbin JenNy Joy V.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Differentiation 1. Tangents and NormalsDokument13 SeitenApplications of Differentiation 1. Tangents and NormalsronnieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration - MTH0002 - Lecture Notes (4) - Spring 2023 - Dr. Fayad GalalDokument22 SeitenIntegration - MTH0002 - Lecture Notes (4) - Spring 2023 - Dr. Fayad Galalziad abdelkadrNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sun, The Moon, and ConvexityDokument5 SeitenThe Sun, The Moon, and ConvexityAnonymous e8BzOGqlaw100% (1)
- Lecture # 11: Chapter 4: Forces Due To Static FluidsDokument9 SeitenLecture # 11: Chapter 4: Forces Due To Static FluidsJohn GriffenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paraxial Eoe 03Dokument12 SeitenParaxial Eoe 03Arkapravo ChaudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symmetry (Planes Of)Dokument37 SeitenSymmetry (Planes Of)Ibrahim NasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT 3 Grade 9 Set A 17 JanDokument2 SeitenPT 3 Grade 9 Set A 17 Jansoul ninjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KEB 2018: Work Hard in Silence, Let Success Be Your NoiseDokument6 SeitenKEB 2018: Work Hard in Silence, Let Success Be Your NoiseTumusiime osagyefo Johnbosco AdyeeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 7 Crystal SystemsDokument9 SeitenThe 7 Crystal SystemsJuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prova 1 - Cinemática - Parte IDokument6 SeitenProva 1 - Cinemática - Parte IVinícius GonçalvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigid Motion and Homogeneous Transformation PDFDokument9 SeitenRigid Motion and Homogeneous Transformation PDFabcNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4037 s05 QP 2Dokument8 Seiten4037 s05 QP 2mstudy123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025 Curriculum - 2004 B.E. Electronics and Communication Engineering Semester I Code No. Course Title L T P M TheoryDokument36 SeitenAnna University:: Chennai - 600 025 Curriculum - 2004 B.E. Electronics and Communication Engineering Semester I Code No. Course Title L T P M TheorySiva Lrn SivalrnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 12 Mean Value TheoremsDokument20 SeitenUnit 12 Mean Value TheoremsChandradeep Reddy TeegalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 1 of 21 Designing Parametric Bevel Gears With Catia V5Dokument21 SeitenPage 1 of 21 Designing Parametric Bevel Gears With Catia V53pherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iygb Gce: Core Mathematics C2 Advanced SubsidiaryDokument7 SeitenIygb Gce: Core Mathematics C2 Advanced SubsidiaryssmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-14 Abs Value Notes PDFDokument24 Seiten10-14 Abs Value Notes PDFParadox ParadoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- MENSURATIONDokument7 SeitenMENSURATIONnbhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics Module: User's GuideDokument164 SeitenRay Optics Module: User's GuideValerioApicellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Vector Algebra (Ch-7) Multivariate CalculusDokument14 SeitenReview of Vector Algebra (Ch-7) Multivariate CalculusSubrat BarikNoch keine Bewertungen
- XIX - Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesDokument3 SeitenXIX - Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesDaniel PardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Restriction (Mathematics) PDFDokument4 SeitenRestriction (Mathematics) PDFmarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roane James B. The Balanced Force Concept JOE 11 5 May 1985Dokument12 SeitenRoane James B. The Balanced Force Concept JOE 11 5 May 1985Anderson ChiguanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- International - Competitions CentroAmerican 2015 30 PDFDokument2 SeitenInternational - Competitions CentroAmerican 2015 30 PDFferrousweiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying MCQDokument63 SeitenSurveying MCQPriya Nagargoje100% (1)