Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Electrochemistry principles
Hochgeladen von
MAk KhanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electrochemistry principles
Hochgeladen von
MAk KhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Written by: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-7891989, 0333-5319544 e-mail: shahzad2sunny@hotmail.com website: www.eservicespakistan.
com CHEMISTRY FOR 9TH CLASS (UNIT # 8) ============================================================ Read Instructions before study: Bullet means you have to write the answer in paragraph shape and you could not change the sequence. Bullets are used only for your ease. i) Roman numbered, question may be written as it is. However sequence can be changed. *** This item should not be written in answer. It is just a hint for you. Pay more attention on the bold text in answers. =*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=*=
THEORY
Question: Define Electrochemistry? The branch of chemistry in which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy or electrical energy is converted into chemical energy is called electrochemistry. Question: Define conductor and insulator? i) The substances through which electric current can pass are called conductors i.e. Copper, Aluminium, Iron etc. ii) The substances through which electric current cannot pass are called insulators or non-conductors. i.e. rubber, plastic, wood etc. Question: Define a Cell? A vessel in which oxidation-reduction reaction takes place at electrodes is called cell. Question: Define Electrolysis? When electricity is passed through fused ionic compounds or their aqueous solutions, they are decomposed into their constituents. Such compounds are called Electrolytes and the process is called Electrolysis. Question: Define Electrolyte and also write its types? The compounds in molten state or in aqueous solution through which electricity can pass are called electrolyte. And the compounds through which electricity cannot pass are called non-electrolyte. Strong Electrolyte: Ionization is complete in these electrolytes. For example, in a dilute solution of NaCl there will no formula unit present. Their examples of strong electrolytes are mineral acids, caustic alkalies and their salts. Weak Electrolyte: Ionization is incomplete in these electrolytes. Their examples are ammonium hydroxide, tartaric acid, citric acid and carbonic acid. Question: Define Electrodes? Electrodes are the terminals of the battery at which ions are deposited during the process of electrolysis. They are: Anode: It is a positive electrode through which electrons enter the external circuit. Cathode: It is a negative electrode through which electrons leave the external circuit.
============================================================
Visit www.eservicespakistan.com for Notes, Syllabus, Old Papers, Home Tuitions, Jobs & much more (Page 1 of 6)
Written by: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-7891989, 0333-5319544 e-mail: shahzad2sunny@hotmail.com website: www.eservicespakistan.com CHEMISTRY FOR 9TH CLASS (UNIT # 8) ============================================================
Question: On which factors substances librated at electrodes? During electrolysis the quantities of substances librated at electrodes depend upon the following factors: i) The quantity of current passed. ii) Time duration of passing the current at a uniform rate. iii) Charge on the ions being deposited. Question: Define oxidation and reduction? Oxidation: - A chemical reaction in which: i) Oxygen is added ii) Hydrogen is removed iii) Electrons are lost. Reduction: - A chemical reaction in which: i) Oxygen is removed. ii) Hydrogen is added. iii) Electrons are absorbed. Question: Define Ionization? An electrolyte splits up into charged particles upon heating or in its aqueous solution. This process is called ionization. Question: Describe in detail the Ionic Theory to explain electrolysis? OR Arrhenius theory of ionization? In 1887, Arrhenius, a Swedish chemist, put forward his ionic theory to explain the process of electrolysis. According to this theory: i) When electrolyte are fused or dissolved in water, they are split into positive and negative ions. This process is called ionization. ii) The total positive charge is equal to the total negative charge and the solution is electrically neutral. iii) Metallic ions, ammonium ions and hydrogen ions carry positive charge while on metallic ions and hydroxide ions carry negative charge. iv) The number of electrical charges present on any ion is equal to the valency of the atom or the radical. v) The properties of ions are different from the properties of the related atoms. vi) Ions move in all possible directions in fused salts or in aqueous solutions of salts. vii) When an electric current is passed through an electrolyte, the positive ions are attracted towards the cathode while the negative ions tend to move towards the anode. Question: Define Degree of ionization? The level to which an electrolyte can ionize in water is called its degree of ionization. Degree of Ionization = Number of molecules which ionize Total number of molecules
============================================================
Visit www.eservicespakistan.com for Notes, Syllabus, Old Papers, Home Tuitions, Jobs & much more (Page 2 of 6)
Written by: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-7891989, 0333-5319544 e-mail: shahzad2sunny@hotmail.com website: www.eservicespakistan.com CHEMISTRY FOR 9TH CLASS (UNIT # 8) ============================================================
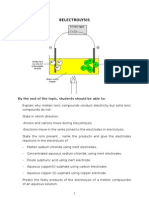
Question: Explain the process of electrolysis of water? i) Water is weak electrolyte. It ionizes in the following way: H2O <----------------> H+ + OHii) In pure water, out of 6x108 molecules only one molecule is ionized. iii) If hydrogen or hydroxide ions are removed from the above reaction, more water molecules are ionized. iv) A few drops of sulphuric acid are added in water to increase its conduction. (***Draw fig here). v) Both the electrodes used in this cell are made of platinum. vi) On passing the electric current, hydrogen ions move towards the cathode, where they pick up electrons and are converted into hydrogen atoms. Reaction at cathode: H+ + e-------------> H H+H -------------> H2 Reaction at Anode: OH-------------> OH + e2OH -------------> H2O + O O+O -------------> O2 Question: Explain the process of electrolysis of aqueous solution of Sodium Chloride (NaCl)? i) In this process cathode is used of plantium while anode is used of carbon. ii) Carbon anode is used to avoid the reaction with chlorine gas. iii) Following ions are present in solution a. Na+, Cl- (From sodium chloride) b. H+, OH- (From Water) + iv) Na and H+ ions both migrate towards cathode. Reaction at Cathode: H+ + e-------------> H H+H -------------> H2 Reaction at Anode: Cl-------------> Cl + eCl + Cl -------------> Cl2 Question: Explain the process of electrolysis of Fused Sodium Chloride (NaCl)? i) A reactive metal sodium is obtained by the electrolysis of fused sodium chloride. ii) The cell used for this process is called Downs Cell. (***Draw Fig here) iii) A graphite anode and steel cathode is used in this process. iv) The electrolysis gives sodium metal and chlorine gas as products. v) It is necessary to keep these products separate, otherwise they will react again to give sodium chloride. vi) For this purpose cathode and anode are separated by a steel gauze.
============================================================
Visit www.eservicespakistan.com for Notes, Syllabus, Old Papers, Home Tuitions, Jobs & much more (Page 3 of 6)
Written by: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-7891989, 0333-5319544 e-mail: shahzad2sunny@hotmail.com website: www.eservicespakistan.com CHEMISTRY FOR 9TH CLASS (UNIT # 8) ============================================================
Reaction at Cathode: 2Cl----------------> Cl2 + 2eReaction at Anode: 2Na+ + 2e- ----------------> 2Na Question: Describe the laws of Faraday regarding Electrolysis? Faradays First law of Electrolysis: i) The mass of an element, which is deposited, on an electrode during electrolysis, is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity Q, which passes through the electrolyte. ii) The unit of the quantity of electricity is called coulomb. One coulomb is the quantity of electricity passed when one ampere current passes for one second. One Faraday = 96,500 coulombs. And Q = Ixt I is the current, t is time in seconds and Q is the quantity of electricity passing through electrolyte. iii) According to this law: m Ixt m = ZxIxt Z is constant and m is mass of substance deposited. Here m is expressed in grams. iv) The quantity of substance, which is deposited when one Faraday of electricity is passed through an electrolyte, is called One Gram Chemical Equivalent of that substance. Faradays Second law of Electrolysis: i) When the same quantity of electricity is passed, for the same time, through different electrolytes connected in series, the substances deposited at the electrodes will be in the ratio of their chemical equivalents. ii) Faradays laws are very useful for determination of electrochemical equivalents of different substances. The following equation is used for this purpose. Electrochemical Equivalent (Z) = Quantity of Substance Deposited (W) Quantity of electricity Passed (Q) Z = W/Q. Question: Explain Electrochemical Series? i) When an aqueous solution containing Copper and Zinc ions is electrolyzed, zinc ions will remain in the solution while copper ions are reduced and discharged. ii) Cations (positive ions) can be arranged in the order of increasing ease of discharge at the cathode similarly anions (negative ions) can also be arranged in the order of increasing ease of discharge at the cathode. iii) The list of ions arranged in the order of their ease of discharge at the electrodes is called electrochemical series.
============================================================
Visit www.eservicespakistan.com for Notes, Syllabus, Old Papers, Home Tuitions, Jobs & much more (Page 4 of 6)
Written by: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-7891989, 0333-5319544 e-mail: shahzad2sunny@hotmail.com website: www.eservicespakistan.com CHEMISTRY FOR 9TH CLASS (UNIT # 8) ============================================================
iv)
Electrochemical series also throw light on the reactivity of metals, which form ions in aqueous solutions.
Question: Define Electroplating and describe its objectives? It is the process in which a metal is deposited on another metal electrolytically. There are three main objectives of electroplating: Decoration: We deposit noble metals (like Gold & Silver) on inferior metals to enhance their beauty. Protection: Electroplating protect the inferior metals from rusting and reaction of organic salts. Repair: To weld the broken parts of the machinery by electro-deposition of metals. Question: Describe the Procedure of Electroplating? i) The article to be electroplated is first cleaned with sand and then washed with caustic soda solution and then with plenty of water. ii) This article is then made a cathode, while the metal to be deposited is made anode. iii) The electrolyte is a salt of the metal being deposited and the electroplating is carried out in a tank made of cement, glass or wood. It is called electrolytic tank. iv) The electrolyte chosen should have following properties: a. Very soluble in water. b. Good conductor c. Not easily oxidized or reduced or hydrolyzed. d. Cheap. v) Electrodes are dipped in the electrolytic tank and current is passed through it. vi) A thin layer of the noble metal is deposited on the article to be electroplated. vii) The following conditions should be fulfilled to get good deposits. a. High current density. b. Low temperature. c. Higher concentration of the metal in its electrolyte. Question: What is difference between Chemical Reaction and Electrochemical Reaction? The chemical changes taking place in the substance is called chemical reaction. Electrochemical reactions are always oxidation-reduction reaction. Transfer of electrons takes place through the external circuit. Question: Differentiate between the following? Gram equivalent and electrochemical equivalent: Equivalent weight of substance expressed in gram is called gram equivalent. While Electrochemical equivalent is the amount of a substance produced at the electrode when one coulomb of electric current is passed through electrolyte for one second. Electrolytic dissociation and thermal dissociation:
============================================================
Visit www.eservicespakistan.com for Notes, Syllabus, Old Papers, Home Tuitions, Jobs & much more (Page 5 of 6)
Written by: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-7891989, 0333-5319544 e-mail: shahzad2sunny@hotmail.com website: www.eservicespakistan.com CHEMISTRY FOR 9TH CLASS (UNIT # 8) ============================================================
Decomposition of a substance into its ions by electric current is called electrolytic dissociation. Decomposition of a substance into its ions by heating in the absence of air is called thermal dissociation. Question: Why Gold, Silver and platinum are used for making ornaments? They are used to make ornaments because i) They do not rust. ii) They are lustrous. iii) They are not oxidized by environment. iv) They are hard and elastic and can be moulded to any shape. Question: What happens when electricity is passed through a solution? The ions of electrolyte migrate towards respective electrode. Question: Define Electrolytic Cell and Voltaic Cell? Electrolytic Cell: - In this cell a non-spontaneous oxidation-reduction reaction takes place with the help of electrical energy. Voltaic Cell: - In this cell a spontaneous oxidation-reduction reaction is used to produce electric current.
=*=*=*=*= More works/Tasks: Do Exercise from your Book. Do Objectives from book & from any other objective book. Do Numerical with the help of your teacher. Do Interesting Information from book. Do Scientific Reasons with the help of teacher.
============================================================
Visit www.eservicespakistan.com for Notes, Syllabus, Old Papers, Home Tuitions, Jobs & much more (Page 6 of 6)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Atomic StructureDokument6 SeitenAtomic StructureMushtaqAnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation ElectrochemistryDokument12 SeitenSimulation Electrochemistryain kasbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.8 ElectrolysisDokument18 Seiten5.8 Electrolysishafizhapni67% (3)
- G10 worksheet for ElectrolysisDokument17 SeitenG10 worksheet for Electrolysismuaz0% (2)
- Electrochemistry E WADokument92 SeitenElectrochemistry E WAlol7755330Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Effect of Electric Current-5 (2021-22)Dokument24 SeitenChemical Effect of Electric Current-5 (2021-22)Avyam SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Naultha (Panipat) : Electrochemical CellDokument12 SeitenJawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Naultha (Panipat) : Electrochemical CellAkshay Indora100% (1)
- Local Media74401850953142935Dokument4 SeitenLocal Media74401850953142935Albert MariquitNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrolysisDokument17 SeitenElectrolysisAdil Yaqub - 74665/TCHR/CNTBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochemistry Is The Study of The Relationship Between Chemical Reactions and ElectricalDokument7 SeitenElectrochemistry Is The Study of The Relationship Between Chemical Reactions and ElectricalTudio GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 6 - Exp 5Dokument23 SeitenGroup 6 - Exp 5Arrianna PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galvanic Cells IntroDokument3 SeitenGalvanic Cells IntroSana SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Electrolysis With Instructional LessonDokument15 SeitenLesson Plan Electrolysis With Instructional LessonMichael Harris100% (1)
- Class 12 Chemistry ProjectDokument16 SeitenClass 12 Chemistry Projectdhaundiyalshriyansh048Noch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument15 SeitenChemistryTGC NINJANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project - Class 12 - DerrickDokument18 SeitenChemistry Project - Class 12 - Derricksuperheroanush2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- 185_638283988626517543Dokument3 Seiten185_638283988626517543pqvrc6q25mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry ProjectDokument24 SeitenChemistry ProjectNidhi PorwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Voltaic Cells (Chemical CellsDokument22 SeitenUnderstanding Voltaic Cells (Chemical CellsGuru temp id-03 for KPM-Guru-TempNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry BgmiDokument12 SeitenChemistry Bgmisayam jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project: AIM: To Study Electrochemical Principles On Any Electrochemical CellDokument15 SeitenChemistry Project: AIM: To Study Electrochemical Principles On Any Electrochemical CellR.MANJULA pillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class X ElectrolysisDokument4 SeitenClass X ElectrolysisvartikasinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Inestigatory ProjectDokument16 SeitenChemistry: Inestigatory ProjectAnshulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project Report On Finding EMF of Electrochemical Cell PDFDokument15 SeitenChemistry Project Report On Finding EMF of Electrochemical Cell PDFAditya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project Report On Finding EMF of Electrochemical CellDokument15 SeitenChemistry Project Report On Finding EMF of Electrochemical CellAnant Chaturvedi80% (51)
- Electrochemical Cell LabDokument9 SeitenElectrochemical Cell Labribots0% (1)
- TaniDokument14 SeitenTanitanishqpanwar9Noch keine Bewertungen
- LaksDokument14 SeitenLakstanishqpanwar9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Relationship Between Standard Electrode Potential & Rate of ElectrolysisDokument3 SeitenRelationship Between Standard Electrode Potential & Rate of ElectrolysisAbbey HeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science MODEL TEST PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - 2Dokument10 SeitenScience MODEL TEST PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - 2Apex InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 8 - Science - Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentDokument7 SeitenClass 8 - Science - Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentSougrakpam SNoch keine Bewertungen
- DHRITIDokument13 SeitenDHRITIrekha raniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5: What Are Electrochemical Cells?Dokument29 SeitenUnit 5: What Are Electrochemical Cells?Elena SalvatoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolysis and Electroplating QuestionsDokument6 SeitenElectrolysis and Electroplating QuestionsManash SinghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project On Electrochemical Cell 1Dokument12 SeitenChemistry Project On Electrochemical Cell 1Nitin100% (1)
- Name-Devender Kumar Singh Class - Xii - C School - Cambridge School YEAR - 2009-2010Dokument9 SeitenName-Devender Kumar Singh Class - Xii - C School - Cambridge School YEAR - 2009-2010Aditya KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochemical Cell Project ReportDokument13 SeitenElectrochemical Cell Project ReportMIRACULOUS MATHSNoch keine Bewertungen
- SarveDokument22 SeitenSarveAditya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Year Chemistry Notes Electrochemistry ExercisesDokument31 Seiten1st Year Chemistry Notes Electrochemistry ExercisesshahidkakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AkashchemoDokument29 SeitenAkashchemoakash ojhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMISTRY Project RISHIDokument13 SeitenCHEMISTRY Project RISHIRishi AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Chapter Electrochemistry Short Question With Answers PDFDokument11 Seiten10 Chapter Electrochemistry Short Question With Answers PDFMARITIM GEOFFREY KIPLANGATNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Voltaic CellsDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To Voltaic CellsFlash MobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Project.Dokument17 SeitenChem Project.Shresth TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project On Electrochemical CellDokument12 SeitenChemistry Project On Electrochemical Cell11th commerceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shivalik School student's 39-char EMF cell report titleDokument13 SeitenShivalik School student's 39-char EMF cell report titleBRIJESH DWIVEDINoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi Public School Bangalore - East Chemistry Chemical Effects of Electric Current (Notes) NAME: - Class: Viii SecDokument3 SeitenDelhi Public School Bangalore - East Chemistry Chemical Effects of Electric Current (Notes) NAME: - Class: Viii SecSkanda EnterprisesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved QuestionsDokument3 Seiten8th Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved QuestionsKavitha KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finding of Emf of Electrochemical CellDokument20 SeitenFinding of Emf of Electrochemical CellVaibhav Shankar100% (1)
- Electrochemistry Textbook ChapterDokument11 SeitenElectrochemistry Textbook ChapterSam FisherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 2Dokument15 SeitenChem 2CR7STUDIO 70% (1)
- Chemistry Project....Dokument15 SeitenChemistry Project....Ravindra SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project On Electrochemical CellDokument12 SeitenChemistry Project On Electrochemical CellSatyam Giri84% (138)
- CBSE PHYSICS - 8th Chemical Effects of Electric Current PDFDokument8 SeitenCBSE PHYSICS - 8th Chemical Effects of Electric Current PDFginga7160% (1)
- Electroplating for Amateurs: Classic Reference for Small WorkshopsVon EverandElectroplating for Amateurs: Classic Reference for Small WorkshopsNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Install Electric Bells, Annunciators, and AlarmsVon EverandHow to Install Electric Bells, Annunciators, and AlarmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wood Supply and Demand Analysis in Pakistan - Key IssuesDokument12 SeitenWood Supply and Demand Analysis in Pakistan - Key IssuesMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personality& ITS DISORDERDokument48 SeitenPersonality& ITS DISORDERMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Original 1051542 3Dokument2 SeitenOriginal 1051542 3MAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTO Test PaperDokument3 SeitenMTO Test PaperMAk Khan50% (2)
- Poisonous' Economic CombinationsDokument1 SeitePoisonous' Economic CombinationsMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suzuki Annual Report 2016Dokument105 SeitenSuzuki Annual Report 2016waleedjuttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Metals Pay Slip TitleDokument1 SeiteDynamic Metals Pay Slip TitleMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagmentDokument12 SeitenFinancial ManagmentMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay PSL 3 2018Dokument1 SeiteEssay PSL 3 2018MAk Khan100% (4)
- Finance Thesis TopicDokument9 SeitenFinance Thesis TopicMAk Khan33% (3)
- Business Statistics & Mathematics Past Paper 2009 B.com 1Dokument12 SeitenBusiness Statistics & Mathematics Past Paper 2009 B.com 1MAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidated2013 FinalDokument100 SeitenConsolidated2013 FinalMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Yrs Per OGDCLDokument2 SeitenSix Yrs Per OGDCLMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LN OptionsDokument29 SeitenLN OptionsMrutunjay PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost AccountingDokument5 SeitenCost AccountingMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResearchDokument29 SeitenResearchMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAT Practice Test 2010-2011Dokument48 SeitenSAT Practice Test 2010-2011Elvir CrncevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th GW BasicDokument9 Seiten9th GW BasicMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product LaunchDokument33 SeitenProduct LaunchMAk Khan100% (1)
- Z Sample DataDokument12 SeitenZ Sample DataMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Yrs Per OGDCLDokument2 SeitenSix Yrs Per OGDCLMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF FlashFilledDokument15 SeitenPDF FlashFilledMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Financial Functions IDokument18 SeitenExcel Financial Functions IElie YabroudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResearchDokument29 SeitenResearchMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Training Application TampletsDokument10 SeitenPersonal Training Application TampletsMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridgwater: Staff Satisfaction QuestionnaireDokument3 SeitenBridgwater: Staff Satisfaction QuestionnairehasandalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business FinanceDokument4 SeitenBusiness FinanceMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Subject QuizDokument34 SeitenResearch Subject QuizMAk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Satisfaction Survey Detailed Version PDFDokument5 SeitenEmployee Satisfaction Survey Detailed Version PDFAleeza KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Report 2012Dokument66 SeitenAnnual Report 2012Mashgool AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 29541-2010 Solid Mineral Fuels - Determination Total Carbon Hydrogen NitrogDokument18 SeitenISO 29541-2010 Solid Mineral Fuels - Determination Total Carbon Hydrogen NitrogWinnjone YinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Price For Water Treatment Chemicals by The Following 3 VendorDokument1 SeiteComparison of Price For Water Treatment Chemicals by The Following 3 VendorAK TRIPATHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Treatment TechnologyDokument10 SeitenWater Treatment TechnologynickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheology Study of LiquidsDokument9 SeitenRheology Study of LiquidsQi YingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes 2Dokument5 SeitenEnzymes 2Ema Arroyo LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic TrendsDokument31 SeitenPeriodic TrendsAndrew Bondad100% (1)
- Introduction to MEMS Etching TechniquesDokument16 SeitenIntroduction to MEMS Etching TechniquesArjit GoswamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making A Standrad SolutionDokument2 SeitenMaking A Standrad SolutionFaridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPA Corrosion ManualDokument141 SeitenEPA Corrosion Manualnert100% (1)
- Mock Test 4 Paper Neet SolDokument16 SeitenMock Test 4 Paper Neet Solspamhater566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project Polymers Synthesis and Property AnalysisDokument19 SeitenChemistry Project Polymers Synthesis and Property AnalysisMohitRastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapor Phase Soldering TechniqueDokument5 SeitenVapor Phase Soldering TechniquealisakeerpkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrophilic AdditionDokument15 SeitenElectrophilic AdditionShiyi YauNoch keine Bewertungen
- DJH PresentationDokument20 SeitenDJH PresentationThanh Dung LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- New VARTA Power Trio batteries for commercial vehiclesDokument68 SeitenNew VARTA Power Trio batteries for commercial vehiclesJosh DuplooyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Class Science Mid-Term AssessmentDokument6 Seiten9th Class Science Mid-Term AssessmentAshish GambhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Characterization of Commercial Liquid Smoke ProductsDokument14 SeitenChemical Characterization of Commercial Liquid Smoke ProductsLuciano EscobarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science ReportDokument9 SeitenPhysical Science ReportRoschelle ValleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Austenitic Cast Iron Welding Detailsfrequently Aske-WPS OfficeDokument17 SeitenAustenitic Cast Iron Welding Detailsfrequently Aske-WPS Officearjun prajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Training Presentation on Thermal Power Plant ComponentsDokument26 SeitenPractical Training Presentation on Thermal Power Plant ComponentsDivyansh ChaturvediNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument396 SeitenPhysicsIndroneil KanungoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 - EnergeticsDokument2 SeitenTopic 4 - EnergeticsKajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Metallurgy and CorrosionDokument2 SeitenApplied Metallurgy and Corrosiongetavijit.asheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Questions in Engineering MechanicsDokument2 SeitenTest Questions in Engineering Mechanicsbasanth babuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mollis Range Catalogue 1577960812Dokument6 SeitenMollis Range Catalogue 1577960812Ug1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Camphor MAR CAS No 76-22-2: Material Safety Data Sheet Sds/MsdsDokument7 SeitenCamphor MAR CAS No 76-22-2: Material Safety Data Sheet Sds/MsdsArlan ZulkarnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Expansion Valve ElectronicDokument2 SeitenElectronic Expansion Valve ElectronicIEA.BOD.I2 - Sơn, Vũ Văn - Giám đốc E&A - INTECH GROUPNoch keine Bewertungen
- LPG PropertiesDokument2 SeitenLPG Propertiesvvk557Noch keine Bewertungen
- GED Physics Note4 (Electricity and Magnetism)Dokument6 SeitenGED Physics Note4 (Electricity and Magnetism)Shahadat Hussain ParvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUB: Heat & Mass Transfer (EME 504) : Assignment-IDokument2 SeitenSUB: Heat & Mass Transfer (EME 504) : Assignment-IdearsaswatNoch keine Bewertungen