Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lesson Planning Sheet Title: Regular Polygons Learning Objectives
Hochgeladen von
Jonathan RobinsonOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson Planning Sheet Title: Regular Polygons Learning Objectives
Hochgeladen von
Jonathan RobinsonCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
mr-mathematics.
com
Lesson Planning Sheet Title: Regular Polygons Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson: All students should be able to construct a regular polygon using a pair of compasses and a straight edge. Most students should be able to discover the sum of the exterior angles around a polygon. Some students should be able to discover the sum of interior and exterior angles around a polygon Keywords: Polygon, Regular, Construct, Edges Learning Activities Starter/Introduction To introduce the idea of regular polygons the class can work in pairs or small groups to categorise a collection of shapes. To promote a variety of approaches pose the task simply as it is with little to no additional guidance. Have the groups present their categories to the class for discussion. If needed, review the activity using the categories regular polygons, polygons and non-polygons. At this point define the term regular as all sides equal in length and polygon as any shape with straight edges. Development The development phase is intended as an investigation into the interior and exterior angles by having the class construct regular polygons inscribed within a circle. This typically takes a two hour lesson to complete. To begin, students construct a circle and its radius. For an equilateral triangle, the circle is split into three (since a triangle has three sides) equal sectors with points marked along the circumference of the circle. The points along the circumference of the circle are joined together with chords to create the triangle. Students measure and make note of the interior and exterior angles. To construct the exterior angles each edge of the triangle is extended in a clockwise direction. Repeat this process for all the regular polygons up to a decagon if time allows. The Geogebra file in additional resources could be used to illustrate construction. Plenary The plenary is used to review the findings of the lesson. Use the Excel Spread sheet or the table on slide four to input the measured interior and exterior angles for each polygon. Have the class consider the exterior angles of each shape by calculating their totals. They will find that all the sum of all the exteriors for each polygon is 360 degrees since they rotate around a circle. Therefore, given a number of sides a single exterior angle can be calculated. The class then considers the relationship between the interior and exterior angle and how they join to make a straight line and therefore have a sum of 180 degrees. From this, the total interior angles for any polygon can be calculated. Differentiation More able: Students could work in pairs to help the less able for peer support. Less Able Students may need support to accurately construct the polygons. Resources: Mini-whiteboards Card Pairs of Compasses Protractor Pencil Interactive Geogebra File Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lesson Planning Sheet Title: Interior and Exterior Angles Learning ObjectivesDokument1 SeiteLesson Planning Sheet Title: Interior and Exterior Angles Learning ObjectivesJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan AnglesDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Anglesapi-321289595100% (1)
- CPA Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenCPA Lesson Planrcohen425Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cmp2 Geometry StorylineDokument48 SeitenCmp2 Geometry StorylinenomoretwistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Planning Sheet Title: Angles in Triangles Learning ObjectivesDokument2 SeitenLesson Planning Sheet Title: Angles in Triangles Learning ObjectivesJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Format (Generic) : The Following Is A Sample of The Lesson Plan Format Used by The UniversityDokument2 SeitenLesson Plan Format (Generic) : The Following Is A Sample of The Lesson Plan Format Used by The Universityapi-318813104Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Planning Drawing AnglesDokument1 SeiteLesson Planning Drawing AnglesJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: Self-Learning Module 12Dokument13 SeitenMathematics: Self-Learning Module 12jan lawrence panganibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: Relationships of Exterior and Interior Angles of A Convex Polygon Week 6 Content StandardDokument19 SeitenTopic: Relationships of Exterior and Interior Angles of A Convex Polygon Week 6 Content StandardAldwin Jake SantillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Planning Sheet Title: Angle, Side, Angle Constructions Learning ObjectivesDokument1 SeiteLesson Planning Sheet Title: Angle, Side, Angle Constructions Learning ObjectivesJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Planning Angles PointDokument1 SeiteLesson Planning Angles PointJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 Parent TipsDokument2 SeitenModule 4 Parent Tipsapi-298601310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Innovative Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenInnovative Lesson PlanAnonymous 4cVWwg4HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan QuadrilateralsDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan QuadrilateralsJonathan Robinson100% (3)
- Common Core State StandardsDokument7 SeitenCommon Core State Standardsapi-343459926Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Planning Sheet BisectorsDokument1 SeiteLesson Planning Sheet BisectorsJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade7 MathematicsDokument3 SeitenA Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade7 MathematicsAngela Mariz Penuela ForroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sptve - Techdrwg2 - Q2 - M2Dokument9 SeitenSptve - Techdrwg2 - Q2 - M2Jeannettee ParrochaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polygon Homework Year 4Dokument5 SeitenPolygon Homework Year 4afmtibboa100% (1)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Three 2013Dokument15 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Three 2013Nur BainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry and Measurement in A 5th Grade Class!Dokument24 SeitenGeometry and Measurement in A 5th Grade Class!api-405714668Noch keine Bewertungen
- Measure Angles with PrecisionDokument18 SeitenMeasure Angles with PrecisionallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4-Angles of PolygonsDokument4 SeitenLesson 4-Angles of Polygonsapi-269787508100% (1)
- m4 Parent LetterDokument2 Seitenm4 Parent Letterapi-299639200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Convex Polygon Lesson PlanDokument12 SeitenConvex Polygon Lesson PlanJeffrey HallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc Length Lesson PlanDokument1 SeiteArc Length Lesson PlanJonathan Robinson100% (3)
- Unit Overview and Lesson Plan SeriesDokument31 SeitenUnit Overview and Lesson Plan SeriesKendallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real-life examples and properties of polygonsDokument19 SeitenReal-life examples and properties of polygonsAdam ShukorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: Introduction To Theorem 19 Year Group: 3 Year HLDokument23 SeitenTopic: Introduction To Theorem 19 Year Group: 3 Year HLJAYSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angles Unit PlannerDokument9 SeitenAngles Unit Plannerapi-427559206Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Rotational SymmetryDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Rotational SymmetryJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- m201 Math Lesson Plan 4 1Dokument4 Seitenm201 Math Lesson Plan 4 1api-384966224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Overview and Lesson PlanDokument31 SeitenUnit Overview and Lesson PlanKendall100% (1)
- Rectangles Lesson PlanDokument1 SeiteRectangles Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angles Week 1Dokument4 SeitenAngles Week 1api-288880257Noch keine Bewertungen
- Goal(s) :: LESSON PLAN Lesson # - 7 - Name: Sarah Fadness Content Area: Math Date: 4/27/16 Grade Level: 5thDokument11 SeitenGoal(s) :: LESSON PLAN Lesson # - 7 - Name: Sarah Fadness Content Area: Math Date: 4/27/16 Grade Level: 5thapi-334958359Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Pie ChartsDokument2 SeitenLesson Plan Pie ChartsJonathan Robinson100% (9)
- Rectangle DeconstructionDokument3 SeitenRectangle Deconstructionapi-373177454Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volume Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenVolume Lesson Planccreeb150% (2)
- Problems Involving Circumference of Circles Lesson PlanDokument1 SeiteProblems Involving Circumference of Circles Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Popcorn CylindersDokument4 SeitenPopcorn Cylindersapi-309050107Noch keine Bewertungen
- Perimeter Lesson PlanDokument1 SeitePerimeter Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit PlanDokument10 SeitenUnit Planapi-249419897Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mefb 460 Lesson PlanDokument6 SeitenMefb 460 Lesson Planapi-378350740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 4 Rhombi and SquaresDokument5 SeitenHomework 4 Rhombi and Squaresegx124k2100% (1)
- Angles and ProtractorsDokument5 SeitenAngles and Protractorsapi-340307917Noch keine Bewertungen
- Social Skills Standards That Will Also Be Addressed in LessonDokument4 SeitenSocial Skills Standards That Will Also Be Addressed in LessonAnonymous RnIiiQkrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flip Class Room Model MathDokument11 SeitenFlip Class Room Model MathAwais KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polygons: Learning OutcomesDokument4 SeitenPolygons: Learning OutcomesShrim MasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- CurriculumDokument12 SeitenCurriculumapi-379793479Noch keine Bewertungen
- Agu 3 ParentletterDokument2 SeitenAgu 3 Parentletterapi-208514376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan EnlargementsDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan EnlargementsJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angles - Lesson Plan - CsvilansDokument4 SeitenAngles - Lesson Plan - Csvilansapi-359286252Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 - Angles and PolygonsDokument5 SeitenUnit 4 - Angles and Polygonsapi-251666799Noch keine Bewertungen
- Social Skills Standards That Will Also Be Addressed in LessonDokument4 SeitenSocial Skills Standards That Will Also Be Addressed in LessonAnonymous cLlK4lbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Udl Lesson Plan - Ed 4702Dokument6 SeitenUdl Lesson Plan - Ed 4702api-242345831Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instructional Software Lesson Idea AllisoncheekDokument3 SeitenInstructional Software Lesson Idea Allisoncheekapi-618424404Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Pin GeoboardDokument7 Seiten9 Pin GeoboardGrace Melissa ChoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Reverse PercentagesDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Reverse PercentagesJonathan Robinson100% (1)
- Tables of Functions Lesson PlanDokument1 SeiteTables of Functions Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Ordering NegativesDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Ordering NegativesJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan SpeedDokument2 SeitenLesson Plan SpeedJonathan Robinson100% (8)
- Lesson Plan MetricDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan MetricJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Venn Diagrams StarterDokument1 SeiteVenn Diagrams StarterJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Lesson PlanDokument1 SeiteTime Lesson PlanJonathan Robinson100% (4)
- Lesson Plan Travel GraphsDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Travel GraphsJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Trig WorksheetDokument4 Seiten3D Trig WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Simlar LengthsDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Simlar LengthsJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Conversion GraphsDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Conversion GraphsJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel TrigDokument3 SeitenExcel TrigJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Similar VolumesDokument2 SeitenLesson Plan Similar VolumesJonathan Robinson100% (1)
- Imperial Lesson PlanDokument1 SeiteImperial Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Similar AreasDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Similar AreasJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
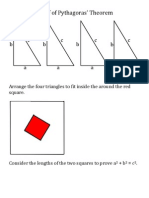
- Proof of Pythagoras' TheoremDokument1 SeiteProof of Pythagoras' TheoremJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Similar CalculationsDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Similar CalculationsJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Trig LengthsDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Trig LengthsJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Rotation WorksheetDokument4 SeitenBasic Rotation WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Trig AnglesDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Trig AnglesJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan HypotenuseDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan HypotenuseJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Basic EnlargementsDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Basic EnlargementsJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Pythag IntroDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Pythag IntroJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 3D TrigDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan 3D TrigJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Pythagoras 3Dokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Pythagoras 3Jonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Trig IntroDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Trig IntroJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet For Basic EnlargementDokument3 SeitenWorksheet For Basic EnlargementJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotation WorksheetDokument3 SeitenRotation WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational Symmetry WorksheetDokument4 SeitenRotational Symmetry WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Grid WorksheetDokument4 SeitenReflection Grid WorksheetJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blocked threads jstack analysisDokument69 SeitenBlocked threads jstack analysisMike TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Machine Learning Top-Down Approach - Towards Data ScienceDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Machine Learning Top-Down Approach - Towards Data ScienceKashaf BakaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Is OkDokument84 SeitenBase Is OkajaydevmalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gr.10 Music History ModuleDokument45 SeitenGr.10 Music History ModuleKyle du PreezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DesignWS P1 PDFDokument673 SeitenDesignWS P1 PDFcaubehamchoi6328Noch keine Bewertungen
- CM - Scope of ServicesDokument3 SeitenCM - Scope of ServicesMelvin MagbanuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cursos Link 2Dokument3 SeitenCursos Link 2Diego Alves100% (7)
- UM Routing L3P 15 01 UsDokument102 SeitenUM Routing L3P 15 01 UsmiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ListDokument4 SeitenListgeralda pierrelusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeDokument4 SeitenMicroscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeLouie Jane EleccionNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Heart Journal Supplements Pathophysiology ArticleDokument8 SeitenEuropean Heart Journal Supplements Pathophysiology Articleal jaynNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Lift Cylinder Drift (Bulldozer) - CheckDokument2 Seiten09 Lift Cylinder Drift (Bulldozer) - CheckFredy Manrique AstoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards ColgateDokument15 SeitenA Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour Towards Colgatebbhaya427Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8510C - 15, - 50, - 100 Piezoresistive Pressure Transducer: Features DescriptionDokument3 Seiten8510C - 15, - 50, - 100 Piezoresistive Pressure Transducer: Features Descriptionedward3600Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Refinery Sulfur Recovery ProjectsDokument8 SeitenSummary Refinery Sulfur Recovery ProjectsAli MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colorimetric Determination of ManganeseDokument16 SeitenColorimetric Determination of ManganeseidaayudwitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Borang JPK CA 01 Tahap 2Dokument2 SeitenBorang JPK CA 01 Tahap 2ajai1010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental ScienceDokument5 SeitenEnvironmental Sciencearijit_ghosh_18Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2016-08-03 Iot Global Forecast Analysis 2015-2025Dokument65 Seiten2016-08-03 Iot Global Forecast Analysis 2015-2025Hoang ThanhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Indian Airlines Industry On Social Media, Mar 2015Dokument9 SeitenReport On Indian Airlines Industry On Social Media, Mar 2015Vang LianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lehman BrothersDokument10 SeitenLehman BrothersJaikishin RuprajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Bloom Gardner Matrix Example 2009Dokument2 Seiten09 Bloom Gardner Matrix Example 2009Ellen Jaye BensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wall Street Expose: Monkey Business Reveals Investment Banking RealitiesDokument2 SeitenWall Street Expose: Monkey Business Reveals Investment Banking Realitiestorquewip100% (1)
- FloridaSharkman ProtocolsDokument14 SeitenFloridaSharkman ProtocolsgurwaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement Pressure TestingDokument15 SeitenMethod Statement Pressure TestingAkmaldeen AhamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines To MAS Notice 626 April 2015Dokument62 SeitenGuidelines To MAS Notice 626 April 2015Wr OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Sound Gateway - Installation - EngDokument9 SeitenActive Sound Gateway - Installation - EngDanut TrifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Dokument2 SeitenEcma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Anil JindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nistha Tamrakar Chicago Newa VIIDokument2 SeitenNistha Tamrakar Chicago Newa VIIKeshar Man Tamrakar (केशरमान ताम्राकार )Noch keine Bewertungen
- High Volume InstrumentDokument15 SeitenHigh Volume Instrumentcario galleryNoch keine Bewertungen