Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Answer Key: (Jee Mains)
Hochgeladen von
ssjatav128Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Answer Key: (Jee Mains)
Hochgeladen von
ssjatav128Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
12
th
(Date: 23-09-2012) ReviewTest-5
(JEEMAINS)
Code-B
ANSWER KEY
PHYSICS
SECTION-1
PART-A
Q.1 C
Q.2 D
Q.3 B
Q.4
8
A
Q.5
9
A
Q.6
10
C
Q.7
4
A
Q.8
5
A
Q.9
6
B
Q.10
7
A
Q.11 C
Q.12 A
Q.13 B
Q.14
16
B
Q.15
17
C
Q.16
18
A
Q.17
19
C
Q.18
14
D
Q.19
15
B
Q.20 D
Q.21 B
Q.22
24
B
Q.23
25
D
Q.24
26
B
Q.25
22
C
Q.26
23
D
Q.27 D
Q.28
32
C
Q.29
33
C
Q.30
28
D
Q.31
29
A
Q.32
30
A
Q.33
31
B
CHEMISTRY
SECTION-2
PART-A
Q.1
11
D
Q.2
12
D
Q.3
13
A
Q.4
14
B
Q.5
15
B
Q.6
16
A
Q.7
17
B
Q.8
18
A
Q.9
19
D
Q.10
20
D
Q.11
21
A
Q.12
22
A
Q.13
23
C
Q.14
24
B
Q.15
25
D
Q.16
26
A
Q.17
27
C
Q.18
28
A
Q.19
29
B
Q.20
30
B
Q.21
31
C
Q.22
32
D
Q.23
33
A
Q.24
1
D
Q.25
2
D
Q.26
3
A
Q.27
4
B
Q.28
5
A
Q.29
6
C
Q.30
7
A
Q.31
8
C
Q.32
9
B
Q.33
10
C
MATHS
SECTION-3
PART-A
Q.1 B
Q.2 C
Q.3 B
Q.4
7
A
Q.5
8
B
Q.6
9
C
Q.7
4
D
Q.8
5
B
Q.9
6
D
Q.10
13
A
Q.11
14
C
Q.12
15
A
Q.13
10
B
Q.14
11
C
Q.15
12
B
Q.16
19
A
Q.17
20
C
Q.18
21
B
Q.19
16
A
Q.20
17
A
Q.21
18
A
Q.22
25
D
Q.23
2
C or D
Q.24
27
B
Q.25
22
C
Q.26
23
D
Q.27
24
B
Q.28
31
D
Q.29
32
D
Q.30
33
C
Q.31
28
D
Q.32
29
D
Q.33
30
D
Code-B Page # 1
PHYSICS
PART-A
Q.1
[Sol. Violates newton's 3
rd
law ]
Q.2
[Sol. v
0
= 12
2 . 1
2t
= 20t
32 =
2
2
) 20 (
x 10
2
1
t
10
400 64
2
t
= x
2
8 20 = 160 m ]
Q.3
[Sol. Perpendicular vector cannot give sumequal to zero. ]
Q.4
[Sol.
PO
V m P D H
= ]
Q.5
[Sol. F =mg sin 30
FR=
2
1
mR
2
o
R
30 sin g 2
]
Q.6
[Sol. gh 2 v = = 4 10 2 = 5 2 2
5 4 v =
]
Q.7
[Sol.
) i
2 . 0 ( 6 ) i
8 . 1 ( 4 +
=
) i
4 . 1 ( 6 ) i
6 . 0 ( 4 +
velocity of approach = 1.8 + 0.2 = 2
velocityof separation = 1.4 + 0.6 = 2 ]
Q.9
[Sol. k 0.06 =
1
2 3 . 0
2
k = 20 ]
Q.11
[Sol. Q = nC
p
AT
= 9
6 . 1
25 R 6 . 1
200 = 40000 ]
Code-B Page # 2
PHYSICS
Q.12
[Sol. C
3
become short after closing S
1
and S
2
. ]
Q.13
[Sol. t = pE = 10
12
2
10
8
]
Q.14
[Sol. W = qEx = 8 10 10 10
2
]
Q.15
[Sol. Fromrarer to denser, rayshould bend towards normal ]
Q.16
[Sol. This question is most easilyanswered if you have a picture of second harmonic motion in your head.
Most of these standing wave problems, here and sound waves , are best solved byknowing what they
look like. The string vibrates the most at a distance of L/4 fromeither end the string. ]
Q.17
[Sol.
dt
dQ
= mc |
dt
dT
+ ]
Q.18
[Sol. C=
v
Q
= k
|
.
|
\
|e
d
A
0
, slope heigher k heigher ]
Q.19
[Sol. Animportant point toremember about electricfields is that theyemanate
frompositive charges and point towards negative charges. With this in
mind, we knowchoicesAand Care incorrect. The next question is to
judge the straightness or curvature of the lines between the plates.
+ + + + + + +
Imagine a point placed directlybetween two parallel plates (see the diagramto the right). It will have a
net electric field determined byall the individual electric fields generated byeverycharge on the two
plates. For clarity, onlyfive electric field lines are shown in the diagram. If these field lines are added
vectorially, all the horizontal components will cancel each other out; a net field oriented vertically
downward will remain (the field lines shown in the choices are the possible net electric fields). The
cancellation is due to the symmetry of the point in space with respect to the charges on the plates.
However, this horizontal component cancellation continues onlyuntil one approaches the left andright
edges of the plates. Here, thefield lines bowout, muchlike those arounda dipole (the parallel plates are
like several dipoles positioned next to each other). Remember, between parallel plates of opposite
charge, the field lines are straight. Theyare also constant in strength throughout the interplate region.
Thus, a parallel plate arrangement is agooddesignfor capacitors, electrophoresis equipment, andcharge
accelerators. The correct choice is B. ]
Code-B Page # 3
PHYSICS
Q.22
[Sol.
2
gh
1
=
2
gh
2
12
=
5
20
500
h
h
1
2
2
=
1
= 2000 kg/m
3
]
Q.23
[Sol. Phase change in first reflection shouldchange byt. ]
Q.24
[Sol. E R
(
+ +
CR
Q
CR
Q
dt
dQ
C
Q
= 0
E
C
Q 3
=
dt
RdQ
( ) 3 / RC
Q
3
EC
(
=
dt
dQ
]
Q.26
[Sol.
F
]
Q.27
Sol. W =
2
r
GMm
2
r
1
]
Q.31
[Sol. 1.98 R
S
= 0.02 25 = 0.5 ]
Q.32
[Sol.
2
1
E
E
=
2
1
]
Q.33
[Sol. K
i
= W = k
f
K
i
= 300 eV
w = e(1500) 1.2 = 1800 eV ]
CHEMISTRY
Code-B Page # 1
PART-A
Q.1
[Sol. Due to back - donation, all would have longer CO length than free CO molecule. ]
Q.2
Sol.
O
HCl . conc
Hg Zn
N H /EtO
2 4
LiAlH
4
OH
H
/ KMnO
4
/ A is oxidising agent, it will not reduce cyclohexanone.
Q.3
Sol. BCl C = 0.01 M
B
+
+ H
2
O BOH + H
+
K
h
=
x c
x
K
K
2
b
w
=
c
cx x x
x 01 . 0
x
10
10
2
6
14
x
2
= 10
8
0.01
x
2
= 10
10
; x = 10
5
Q.4
[Sol. AlF
3
is ionic. AlBr
3
and AlI
3
exist as dimer. ]
Q.5
Sol. Carbonyl compounds containing
O
| |
C CH
3
unit will give iodoform test.
Q.6
Sol. X X X
B
C C
B
(g) X
(g)
+ X X
B
C C
B
(g)
A A = A
t tan reac f product f reaction
H H H
AH = [100 + 300] [200] kJ / mole
AH = 400 kJ
AH
reaction
=
product reactant
BE BE
= BE
XX
= 400 kJ
CHEMISTRY
Code-B Page # 2
Q.7
[Sol.
6
7 2
O Si
is Pyrosilicate
O
O
O
O
O
]
Q.8
Sol. Rate of reaction o electrophilicity of C= O group.
Q.9
Sol. K
C
=0.98 at 300 K
K
C
= 1.2 at 400 K
(
A
=
(
(
2 1 C
C
T
1
T
1
R
H
K
K
ln
1
2
(A) With increase in temperature K
C
increases so reaction is endothermic
(B) AG = RT ln K
C
AG < 0 at standard condition
K
C
> 1 so reaction is non spontaneous at 300 K spontaneous at 400 K
(C)
(
A
=
(
120000
100
R
H
98 . 0
2 . 1
ln
AH = 1200 R
(
98 . 0
2 . 1
ln
(D) AG = AH TAS
as AG
=
0
So, AS
=
T
H
A
AS
=
. eq at T
H A
Q.10
[Sol. B
2
H
6
, Fe
2
Cl
6
and FeCl
4
are non-planar
H
H
B B
H
H
H
H
Cl
Fe
Cl
Fe
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Fe
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
]
CHEMISTRY
Code-B Page # 3
Q.11
Sol. Cross aldol condensation take place product(s) will be B, C and D [o,|-unsaturated carbonyl
compounds]
Q.12
Sol. x mole x mole
Na
2
C
2
O
4
KHC
2
O
4
. 3H
2
C
2
O
4
with KMnO
4
m
eq
KMnO
4
= m
eq
of salts
0.1 V
1
5 = [x 2 + x 8] 1000
with NaOH
m
eq
NaOH = m
eq
of acid
0.2 V
2
1 = x 7 1000
=
7
4
35
20
2 . 0
1000 x 7
1000
5 . 0
x 10
V
V
2
1
= =
=
Q.13
[Sol. Ligand field strength follows the order Cl
< H
2
O < NH
3
< CN
]
Q.14
Sol. Carboxylic acid + Optically active alcohol
H
Mixture of Diastereomers
( or d/l or racemic mixture )
Q.15
Sol. (A)
10
40 05 . 0
10
40 M
v
w
%
=
=
= 0.2
(B) n
NaOH
= 0.05 mole
66 . 55
18
002 . 1 1000
n
O H
2
=
=
X
NaOH
=
66 . 55 05 . 0
05 . 0
+
(C)
% 2 . 0
v
w
% =
%
02 . 10
2
002 . 1
2 . v / w %
v
w
% =
0
=
=
(D) ppm =
pm 2000 10
1000
40 05 . 0
6
~
CHEMISTRY
Code-B Page # 4
Q.16
[Sol.
F
F
Br
F F
F
]
Q.17
Sol. Acid-base reaction take place
Q.18
Sol. (I)
8
32
M
M
r
r
A
B
B
A
= =
2
r
r
B
A
=
r
A
= 2r
B
(II) H
2(g)
+
2
1
O
2(g)
H
2
O
(g)
o
f
S A
(H
2
O, gas) < 0
as An
g
< 0
(III) 90 ml of HCl (pH = 3)
3
H
10 C
=
+
10 ml of NaOH (pH = 11)
3
OH
10 C
=
60 ml of H
2
O
3
H
10 90 mole m
=
+
3
OH
10 10 mole m
=
3
H
10 80 left mole m
=
+
3
3
H
10
2
1
160
10 80
left C
=
+
pH = log
(
3
10
2
1
= 3 + log 2
pH = 3.3010
Q.19
[Sol. ClO
2
and NO
2
are odd-electron species and O
2
has two unpaired electrons in
*
p 2
x
t and
*
p 2
y
t
molecular
orbitals.]
CHEMISTRY
Code-B Page # 5
Q.20
Sol. Me
O
para
meta
+I
+H
O
O
Me
COH
CNH
2
Q.21
Sol. R = 8.314 JK
1
mole
1
; T = 115.4 K ; M =
mole / kg
1000
32
M
RT 3
U
rms
=
U
avg
=
M
RT 8
t
U
MP
=
M
RT 2
(A) All molecule will have different speed.
(B) U
avg
=
. sec / m 38 . 276
M
RT 8
=
t
(C) U
MP
= 300
. sec / m
3
2
(D) U
rms
=
32
1000 4 . 115 314 . 8 3
M
RT 3
=
PV = nRT
3 1 =
T 08314 . 0
32
10
; T = 115.4 K
U
rms
= 300 m/sec.
Q.22
[Sol. SCl
6
does not exist due to steric crowding.]
Q.23
Sol. PhOMe
partial
double bond
) excess (
HI
PhOH + MeI
Q.24
Sol. At radial node
(r)
= 0
| | 0 e ) 12 8 )( 1 (
2 / 2
= + o o o
o
o 1 =0 , o
2
8o + 12 = 0 , 0 e
2 /
=
o
Hence o = 1,o = 6, 2 and o =
Subtituting the value of o in o =
0
a
r 2
Thus r =
2
a
0
, r = 3a
0
, r = a
0
and r = will have node
Thus there will be No radial node at r = 2a
0
CHEMISTRY
Code-B Page # 6
Q.25
[Sol. Reaction (C) is involved in smelting (Pyrometallurgy)]
Q.26
Sol. CH
3
CH
2
Cl
KCN
CH
3
CH
2
CN
K C N
Ionic bond
This is more
nucleophilic
than N
N C
Q.27
Sol. P
(g)
Q
(g)
+ R
(g)
t = 0 1.5 atm
t =20 1.5 x x x 1.5 + x = 2 atm
x = 0.5 atm
t =40 1.5 x' x' x' 1.5 + x' =
atm
3
7
x' =
6
5
2
3
3
7
=
at t = 20 min
K =
(
=
(
2
3
ln
20
1
x 5 . 1
5 . 1
ln
20
1
at t= 40 min
K =
(
' x 5 . 1
5 . 1
ln
40
1
K =
(
=
(
=
(
(
(
2
3
ln
20
1
4
9
ln
40
1
6
5
5 . 1
5 . 1
ln
40
1
Q.28
[Sol. Ligands are named in alphabetical order. ]
Q.29
Sol. Rate of S
N
1 o stability of carbocation formed
CHEMISTRY
Code-B Page # 7
Q.30
Sol. H
2(g)
+ S
(s)
H
2
S
(g)
K
c
= 8 10
2
0.3 mole 2 mole 0
l 2
x 3 . 0
l 2
x
K
C
=
2
x 3 . 0
2
x
= 8 10
2
x 3 . 0
x
= 8 10
2
x = 0.024 0.08 x
1.08 x = 0.024
x = 0.0222
litre 2 P
S H
2
= 0.0222 0.08 360
atm 319 . 0 P
O H
2
~
Q.31
[Sol. Square planar complex having monodentate ligands does not show optical isomerism due to presence of
plane of symmetry.
H N
3
Br
Pt
Py Cl
H N
3
H N
3
Br Br
Pt Pt
Py
Py Cl
Cl
and
are geometrical isomers.]
Q.32
Sol. (A) CH
3
CH = CH CH
3
O H / Zn
O
2
3
O
| |
H C CH
3
(B) CH
3
CH
2
CH = CH
2
O H / Zn
O
2
3
O
| |
H C CH CH
2 3
+
O
| |
H C H
(C) CH
2
= CH CH = CH
2
O H / Zn
O
2
3
O
| |
H C H 2
+
CHO
|
CHO
(D)
O H / Zn
O
2
3
CHO
|
CHO 3
CHEMISTRY
Code-B Page # 8
Q.33
Sol.
A
100
B
800
50 400
200
100
50
25
50 min 10 min
10 min
10 min
10 min
10 min
t = 50 min
MATHEMATICS
Code-B Page # 1
PART-A
Q.1
[Sol. UsingSinelaw,
C sin
B sin A sin
c = 2 a = 4
b = 5
C A
B
=
c
b a
=
2
5 4
=
2
1
. Ans.]
Q.2
[Sol. Number of ways is 2 4 4 = 32.
2 4 4
]
Q.3
[Sol. Let f(x) = x
2
+ (1 b)x + (b 5)
x = 0
x = |
f(x)
x
x = o
f(0) < 0
b 5 < 0 b < 5
b
Largest integer
= 0004. Ans. ]
Q.4
[Sol.
2
) 1 n ( n +
= 45 n =9 Ans.]
Q.5
[Sol. Given
}
1
0
dx ) x ( f = 4 and
}
2
0
dx ) x ( f = 6
Now
}
2
1
dx ) x ( f =
} }
+
2
1
1
1
dx ) x ( f dx ) x ( f = 8 + 2 = 10. Ans. ]
Q.6
[Sol. When y =
2
5
We have,
3 x 5
2 x 3
+
=
2
5
x = 1;
dx
dy
=
2
) 3 x 5 (
19
g ' (x) =
19
) 3 x 5 (
2
g ' (1) =
19
4
Ans.]
Q.7
[Sol.
dx
dy
=
dx
dv
dv
du
du
dy
= sec
2
u
|
.
|
\
| 1
|
.
|
\
|
+
x v
1
1
2
e x
dx
dy
=
= 1 (1 + 1)
e
1
=
e
2
. Ans.]
MATHEMATICS
Code-B Page # 2
Q.8
[Sol. x eR, tan
1
x e |
.
|
\
| t t
2
,
2
. So cos(tan
1
x) e(0, 1]. Ans.]
Q.9
[Sol. A+ A
T
= O
(
u
u
sin 2 0
0 sin 2
= O
sin u = 0 u = nt, n eI
u = t e (0, 6). Ans.]
Q.10
[Sol. t
r+1
=
14
C
r
( )
r
r 14
2
x
1
x
=
14
C
r
x
28 3r
28 3r = 1 r = 9
Coefficient is =
14
C
9
=
14
C
5
Ans. Ans.]
Q.11
[Sol. | B | =
r c z
q b y
p a x
8
=
r c z
q b y
p a x
8
=
r q p
c b a
z y x
8 = 8 | A| = 16 Ans. ]
Q.12
[Sol.
p
dx
dy
=
1
1
y
x
=
4
3
y
1
=
3
x 4
1
(
x
,
y
)
1
1
P
Y
X
(0,0)
Also x
1
2
+ y
1
2
= 4
9
x 16
x
2
1
2
1
+ = 4
25x
1
2
= 36 x
1
=
5
6
y
1
=
5
8
Ans.]
Q.13
[Sol. We have, f (x) = dt ) 12 t t ( ) 4 t ( e
2
2
x
3
2 t
}
+
f '(x) = 2x
4
x
e
(x
2
4) (x
4
x
2
+ 12)
= 2x
4
x
e
(x 2) (x + 2) (x
4
x
2
+ 12)
0 2 2
+ +
Sign of f '(x)
f(x) + on ( , 2) (0, 2). Ans.]
MATHEMATICS
Code-B Page # 3
Q.14
[Sol. S =
r 1
a
= 20
2
2
r 1
a
= 80 r =
3
2
a =
3
20
=
q
p
(p + q) = 23. Ans.]
Q.15
[Sol.
=
|
.
|
\
|
n
1 r
2
n n
r
1
n
1
Lim
=
}
1
0
2
dx x 1
=
}
t
u u
2
0
2
d cos =
4
t
Ans.]
Q.16
[Sol. Since Lis the tangent tothe hyperbola,
we knowthat its slope is given by
m =
dx
dy
=
2
x
6
at x = 3, that is m =
3
2
.
An Equation for this line is y 2 =
3
2
(x 3).
A
(0,4)
(6,0)
Fromthis equation we get that B=4 and
A=6 which implies that the area is 12. ]
Q.17
[Sol. f '(x) =
3
4
x
3
x
4
f "(x) = 4x
2
4x
3
= 4x
2
(1 x) = 0
x = 1
f "'(x) = 8x 12x
2
f '''(1) = 4 < 0. Ans.]
Q.18
[Sol.
M A
=
4
25
4
1
1 + +
=
2
30
A(1,1,1)
B(2,3,4) C(2,0,3)
\14 \14
M
|
.
|
\
|
2
7
,
2
3
, 0
Ans. ]
Q.19
[Sol. sin x (1 + 2 cos x) > 0
0 2
3
t t 4
3
t 2t
+ +
. Ans. ]
MATHEMATICS
Code-B Page # 4
Q.20
[Sol. f(x)
}
x
0
dt t sin =C(given)
f(x) (1 cos x) = C
put x = t
2(2) = C C = 4
f(x) =
x cos 1
4
|
.
|
\
| t
2
f = 4. Ans. ]
Q.21
[Sol. Slope of OC = tan (u + 45) where tan u =
4
1
=
4
1
1
1
4
1
+
=
3
5
Ans.]
45
u
1/4
B
C
D
O
4
Y
X
Q.22
[Sol.
(A) For f(x) = 3x
2
2, f(2) = f(3)
(B) For f(x) = | x 1|, f '(1) does not exist.
(C) For f(x) =| sgn x|, f(x) is discontinuous at x = 0 e[ 1, 1]
(D) For f(x) =
x
1
x + , |
.
|
\
|
3
1
f =f(3), continuous in
(
3 ,
3
1
and differentiable in
|
.
|
\
|
3 ,
3
1
. Ans.]
Q.23
[Sol. MC = 3 sin 60 =
2
3 3
MC = j
2
3 3
Now MB CB MC = +
C
A
M B
X
Y
60
x
3
2
3
i
i
3
2
,
3 3
2
O
B C j
2
3 3
+ =
i
2
3
( ) j
3 i
2
3
CB = . Ans.]
MATHEMATICS
Code-B Page # 5
Q.24
[Sol. Draw graph of y = p and y = 3x
2
2x
3
y
1
y = p
O
x
Hence, for three roots p e[0, 1]. Ans.
Aliter: Let f(x) = 2x
3
3x
2
+ p
f '(x) = 6x (x 1)
f '(x) = 0
0
1
Now, f (0) f(1) s 0 p (p 1) s 0 p e [0, 1]. Ans.]
Q.25
[Sol. f ( 1
) = f ( 1
+
) p + q = p 1 + 2q q = 1.
Also, f ' ( 1
) = f ' ( 1
+
) p = 3p + 1 p =
2
1
. Ans.]
Q.26
[Sol. f(u) =
u + u
2
cos 2 2 sin 3
1
=
1 2 cos 2 sin 3
1
+ u + u
f (u)|
min
=
1 2
1
+
=
3
1
. Ans.]
Q.27
[Sol. I = dx x sec x tan e e
4
0
2 x tan
2
}
t
Put tan x = t
=
}
1
0
t
dt t e e
2
=
1
0
t
2
e
2
e
(
(
=
] 1 e [
2
e
=
2
e e
2
Ans. ]
Q.28
[Sol.
3
cos
t
=
3
k h
2 2
+
h
2
+ k
2
=
4
9
C (0, 0)
r = 3
A B
P
(h, k)
t
/
3
. Ans. ]
MATHEMATICS
Code-B Page # 6
Q.29
[Sol. We have x cos x ) x ( ' f = ,
|
.
|
\
| t
e
2
5
, 0 x
0
2
t
2
3t
2
5t
+ +
sign of f ' (x)
f (x) has local maximumat
2
t
andlocal minimumat
2
3t
Ans.]
Q.30
[Sol. Clearly, (x, x) eR x eW,
So, Ris reflexive.
Let (x, y) eR then (y, x) eR as x and y have atleast one letter in common.
So Ris also symmetric.
But Ris not transitive
e.g. let x = M I LK
y = L I M E
and z =ENERGY
then (x, y) eR and (y, z) eR but (x, z) eR. Ans.]
Q.31
[Hint: The equation will be satisfied for everypoint lyingonthe x-axis or anypoint lyingon the y-axis.]
Q.32
[Sol. Put log
3
x = a and log
2
y = b
Now a + b = 1 .....(1)
and 2
a
= 2 3
b
.....(2)
On putting b = (1 a) from(1) in (2),
we get
2
a
= 2 3
1 a
6
a
= 6
a = 1 and b = 0
x = 3 and y = 1
Hence, (x
0
3
+ y
0
3
) = (3)
3
+ (1)
3
= 28 Ans.]
Q.33
[Sol. L
1
and L
2
are intersectinglines.
The position vector of their point of intersection is k
6 j
7 i
5 + (For =2 or =1).
Also, angle between L
1
and L
2
=
42 11
70
. Ans.]
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesVon EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesBewertung: 1.5 von 5 Sternen1.5/5 (2)
- Answer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 13-11-2011) Review Test-4 Paper-1Dokument20 SeitenAnswer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 13-11-2011) Review Test-4 Paper-1vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: Paper-1Dokument15 SeitenAnswer Key: Paper-1vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 11 PQRS (Date: 07-08-2011) Review Test-3 Paper-1Dokument11 SeitenAnswer Key: 11 PQRS (Date: 07-08-2011) Review Test-3 Paper-1vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 18-12-2011) Review Test-5 Paper-2Dokument15 SeitenAnswer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 18-12-2011) Review Test-5 Paper-2vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 12 ABCD (Date: 06-11-2011) Review Test-6Dokument19 SeitenAnswer Key: 12 ABCD (Date: 06-11-2011) Review Test-6vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: Paper-1Dokument15 SeitenAnswer Key: Paper-1vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-21!08!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code ADokument12 SeitenRT Solutions-21!08!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code Avishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: Full Syllabus TestDokument12 SeitenAnswer Key: Full Syllabus TestchakshuishanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit Jee 2012 Paper2-Final SolnDokument8 SeitenIit Jee 2012 Paper2-Final Solnvarun303gr8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry: Answer KeyDokument15 SeitenPhysical Chemistry: Answer Keyvishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-18!12!2011 XIII VXY Paper I Code ADokument17 SeitenRT Solutions-18!12!2011 XIII VXY Paper I Code Avishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iit-Jee 2012 Fst1 p1 SolnsDokument18 SeitenIit-Jee 2012 Fst1 p1 Solnssanskarid94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 11 (J7 & J8) (Date: 07-08-2011) Review Test-1Dokument11 SeitenAnswer Key: 11 (J7 & J8) (Date: 07-08-2011) Review Test-1vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 12 ABCD (Date: 06-11-2011) Review Test-6Dokument17 SeitenAnswer Key: 12 ABCD (Date: 06-11-2011) Review Test-6vishal27042233Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: Special TEST-2 1 5 - 0 1 - 2 0 1 2Dokument15 SeitenAnswer Key: Special TEST-2 1 5 - 0 1 - 2 0 1 2vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 13-11-2011) Review Test-4 Paper-2Dokument16 SeitenAnswer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 13-11-2011) Review Test-4 Paper-2vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-IITJEE 2012-05-06 XII A Paper II Code BDokument16 SeitenRT Solutions-IITJEE 2012-05-06 XII A Paper II Code Bvishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- IIT-JEE-2011 Chemistry Paper Ii Solution Paper Code 4: Detailed AnswersDokument10 SeitenIIT-JEE-2011 Chemistry Paper Ii Solution Paper Code 4: Detailed Answerssanits591Noch keine Bewertungen
- Target Iit-Jee: All India Test SeriesDokument8 SeitenTarget Iit-Jee: All India Test SeriesasuhassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 11 PQRS (Date: 25-12-2011) Review Test-7 Paper-1Dokument13 SeitenAnswer Key: 11 PQRS (Date: 25-12-2011) Review Test-7 Paper-1vishal27042233Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 11 J-BATCH (Date: 16-10-2011) Review Test-4 Paper-1Dokument13 SeitenAnswer Key: 11 J-BATCH (Date: 16-10-2011) Review Test-4 Paper-1vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-25!09!2011 XII ABCD Paper I Code ADokument17 SeitenRT Solutions-25!09!2011 XII ABCD Paper I Code Avishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Due Mar 7Dokument14 SeitenDue Mar 7Keith Joseph JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 11 J-BATCH (Date: 16-10-2011) Review Test-4 Paper-2Dokument14 SeitenAnswer Key: 11 J-BATCH (Date: 16-10-2011) Review Test-4 Paper-2vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- IIT-JEE Paper 1 SolutionsDokument9 SeitenIIT-JEE Paper 1 SolutionsSrinivasulu KonetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 11 (J) (Date: 03-07-2011) Review Test-1Dokument11 SeitenAnswer Key: 11 (J) (Date: 03-07-2011) Review Test-1vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: 11 J (Date: 25-12-2011) Review Test-6 Paper-1Dokument13 SeitenAnswer Key: 11 J (Date: 25-12-2011) Review Test-6 Paper-1vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Academy: MOCK GATE (2012) - 2Dokument12 SeitenEngineering Academy: MOCK GATE (2012) - 2shrish9999Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-25!09!2011 XII ABCD Paper I Code BDokument17 SeitenRT Solutions-25!09!2011 XII ABCD Paper I Code Bvishal27042233Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: Paper-2Dokument14 SeitenAnswer Key: Paper-2vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Jee Mains Ts 8 2013Dokument10 SeitenSolutions Jee Mains Ts 8 2013krishnabagariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derive The Integrated Rate Equation Half-LifeDokument7 SeitenDerive The Integrated Rate Equation Half-Lifeumut2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: Paper-2Dokument18 SeitenAnswer Key: Paper-2vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- PostingsDokument7 SeitenPostingsSarath BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Problems, Capitulo 2 LevenspielDokument6 SeitenSolutions To Problems, Capitulo 2 LevenspielAlexander Gonzalez Romero75% (4)
- Solutions HWT ElectrostaticsDokument11 SeitenSolutions HWT ElectrostaticsShubhamKhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSEJS Solution (Code-578) .Dokument6 SeitenNSEJS Solution (Code-578) .Yatish GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit Jee 2012 Pet4 Solns p2Dokument22 SeitenIit Jee 2012 Pet4 Solns p2Ishita AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 06 2011 Xii Abcd Paper II Code BDokument14 Seiten12 06 2011 Xii Abcd Paper II Code Bvishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: (Jee Advance) Paper-2Dokument14 SeitenAnswer Key: (Jee Advance) Paper-2DrManoj Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brilliant'S Progressive Test: Our One/Two-Year Postal Courses All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2012Dokument11 SeitenBrilliant'S Progressive Test: Our One/Two-Year Postal Courses All India Engineering Entrance Examination, 2012sanskarid94Noch keine Bewertungen
- 08-JEE-Adv Grand Test 08 Solutions (P 2)Dokument13 Seiten08-JEE-Adv Grand Test 08 Solutions (P 2)Ranjan PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Homework SolutionDokument27 SeitenChapter 9 Homework Solutionjoe100% (3)
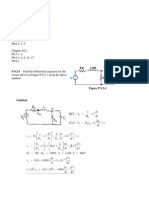
- Leader Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning ProgrammeDokument7 SeitenLeader Test Series / Joint Package Course: Distance Learning Programmefamily_lifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCP-06-02-2011 Paper-1 11th (PQRS & JK) Code ADokument16 SeitenMCP-06-02-2011 Paper-1 11th (PQRS & JK) Code AYash SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Villa Asynch SCI115Dokument3 SeitenVilla Asynch SCI115Christine Lomeda VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key: Paper-1Dokument16 SeitenAnswer Key: Paper-1vishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-25!09!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code ADokument17 SeitenRT Solutions-25!09!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code Avishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-08!05!2011 XII ABCD Paper I Code BDokument15 SeitenRT Solutions-08!05!2011 XII ABCD Paper I Code Bvishal27042233Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fiitjee 37 38Dokument4 SeitenFiitjee 37 38BHAAJI0001Noch keine Bewertungen
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 1)Dokument22 SeitenJEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 1)Ranjan PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Kinetics1Dokument59 SeitenChemical Kinetics1farooq_bagbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-25!09!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code BDokument17 SeitenRT Solutions-25!09!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code Bvishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iit Jee 2012 Paper1-Final SolnDokument9 SeitenIit Jee 2012 Paper1-Final SolnPedamallu SrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-08!05!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code ADokument13 SeitenRT Solutions-08!05!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code Avishal27042233Noch keine Bewertungen
- 01-IIT11 C+M+P Combined Test - Solutions Version ADokument16 Seiten01-IIT11 C+M+P Combined Test - Solutions Version ADeepa LakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportVon EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-04!09!2011 XIII VXY Paper I Code BDokument18 SeitenRT Solutions-04!09!2011 XIII VXY Paper I Code Bssjatav128Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-04!03!2012 XIII VXY Paper I Final Test Code ADokument32 SeitenRT Solutions-04!03!2012 XIII VXY Paper I Final Test Code Assjatav128Noch keine Bewertungen
- 04 03 2012 XIII VXY Paper II Final Test Code ADokument32 Seiten04 03 2012 XIII VXY Paper II Final Test Code Avishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review TEST-1: Class: Date: TimeDokument29 SeitenReview TEST-1: Class: Date: Timessjatav128Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-Practice Test Papers XIII VXY 1 To 6 SolDokument40 SeitenRT Solutions-Practice Test Papers XIII VXY 1 To 6 Solvishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test Papers 1 To 14 EDokument35 SeitenPractice Test Papers 1 To 14 Essjatav128Noch keine Bewertungen
- Body Care - Premium: Whole Foods Market - Quality StandardsDokument8 SeitenBody Care - Premium: Whole Foods Market - Quality StandardshrithenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0147723 A1Dokument20 SeitenPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0147723 A1AtulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sika® ViscoCrete®-4100Dokument3 SeitenSika® ViscoCrete®-4100eduardi7720Noch keine Bewertungen
- Covalent BondDokument12 SeitenCovalent BondCristine Joy AbantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13415Dokument94 Seiten13415Prakash WarrierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recycling and Filament Extruder For 3D Printer PresentationDokument30 SeitenRecycling and Filament Extruder For 3D Printer PresentationRJ Munn100% (1)
- Stabilizing Sensitive Shales With Inhibited, Potassium-Based Drilling FluidsDokument12 SeitenStabilizing Sensitive Shales With Inhibited, Potassium-Based Drilling Fluidstaufiq01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table PtableDokument1 SeitePeriodic Table Ptableapi-239694539Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Periodicity: Richard Parsons, (Richardp) Therese Forsythe, (Theresef) Ck12 EditorDokument30 SeitenChemical Periodicity: Richard Parsons, (Richardp) Therese Forsythe, (Theresef) Ck12 EditoracmcNoch keine Bewertungen
- MgO Effect TGDokument3 SeitenMgO Effect TGBiswanath senNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of ElementsDokument17 SeitenClassification of Elementsaaranyaka shobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partial DataDokument2 SeitenPartial DataKarla CeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnswersDokument30 SeitenAnswersTravel UnlimitedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer Nanocomposite Materials Applications in Integrated Electronic Devices Ye Zhou Download 2024 Full ChapterDokument47 SeitenPolymer Nanocomposite Materials Applications in Integrated Electronic Devices Ye Zhou Download 2024 Full Chapterwanda.miller526100% (8)
- Using CO2 For PH ControlDokument7 SeitenUsing CO2 For PH ControlstreamtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis RevisedDokument60 SeitenNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Revisedemanuel coatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic SynthesisDokument6 SeitenOrganic Synthesiszarfan sabriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Matter: Class 9th ScienceDokument11 SeitenMeasurement of Matter: Class 9th ScienceKushal Kholgade100% (12)
- Cargo Tank CoatingsDokument96 SeitenCargo Tank Coatingsvamsiarangi75% (4)
- Super Absorbent PolymerDokument10 SeitenSuper Absorbent PolymerReply choiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Micro Organisms (I)Dokument28 SeitenIndustrial Micro Organisms (I)पतञ्जलि पण्डितNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem - June 2022 (R) QPDokument36 SeitenChem - June 2022 (R) QPLing JaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface CoatingDokument11 SeitenSurface Coatingdu.maximeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Misra 1972 Chem SOD Activity AssayDokument6 SeitenMisra 1972 Chem SOD Activity AssayIgnacio PaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institute For Excellence in Higher Education (IEHE), Bhopal: TitleDokument2 SeitenInstitute For Excellence in Higher Education (IEHE), Bhopal: TitleRhythemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural StrengtheningDokument94 SeitenStructural Strengtheningdidit kennia100% (1)
- ASTM E716-94 (2002) : Standard Practices For Sampling Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys For Spectrochemical AnalysisDokument4 SeitenASTM E716-94 (2002) : Standard Practices For Sampling Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys For Spectrochemical AnalysisAnonymous 7ZTcBnNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certifi Cate of Secondary EducationDokument12 SeitenUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certifi Cate of Secondary EducationCris. PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soils wk-3-4Dokument28 SeitenSoils wk-3-4Wynnie RondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tds Aquaec3000Dokument2 SeitenTds Aquaec3000REFİKNoch keine Bewertungen