Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Artificial Vegetative Propagation
Hochgeladen von
RainZZaKCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Artificial Vegetative Propagation
Hochgeladen von
RainZZaKCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
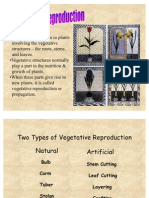
ARTIFICIAL VEGETATIVE PROPAGATION
Layering: In layering a shoot of a parent plant is bent until it can be covered by soil. The tip of the shoot remains above ground. New roots and eventually a new plant will grow. These plants can be seperated. In mound layering the stem is pruned and the base of the plant is covered with soil. From the base, new shoots develop, which are separated from the parent plant, ad grown into a new plant. Many types of apples and gooseberries are grown using this method. Air layering is another type of layering in which branches of the plants cannot be bent to the ground. A piece of the branch is scraped (girdled) in this method and polythene or plastic sheet is used as cover to preserve moisture. Roots arise from the scraped part after a few weeks. This branch is then detached from the parent plant which grows into a new plant after plantation. Layering differs from cutting in that the developments of adventitious buds are induced before the stem is cut to form the new plant.
2. CUTTING In rose, sugar-cane, Coleus,
Bougainvillea, etc., this method is used to produce new plants. In this process stem cuttings with some nodes and internodes are placed in moist soil which gives rise to adventitious roots and a new plant subsequently. It is a very common method of vegetative propagation. Farmers divide up the rhizomes, tubers or roots stocks at the end of flowering or growing season. Each part grows into a separate plant in the following year. Root cuttings propagate some plants like dahlia.
3. GRAFTING
In horticultural practices this method is commonly used. In this method the cutting of a plant (scion) is attached to the stem of another rooted plant (stock). After some time the attached cutting becomes an integrated part of the rooted plant. The scion and stock are placed in such a way that no gap remains between them. Finally they become joined in such a way that their vascular systems are united. Usually the scion is of a plant having desirable characters like large sized fruits and the stock has good absorbing capacity. Because of the arrangement of their vascular bundles, grafting experiments are successful only in dicots and not in monocots. This method is commonly
applied to improve the variety of fruits like mango. Wax is used to cover the
place where grafting is being done. This is to avoid infection.
Tissue culture: this is the growth of a new plant in a cultured medium containing all the substances necessary for growth. This is done in a sterile medium and often in a laboratory. A cell tissue or organ may be used in propagation and is very advantageous in producing healthy clones. Small part of this tissue is put in another medium, which induces the formation of plantlets. The plantlets can be transplanted in soil or pots foe developing to maturity. This technique is also called micro propagation. This method is used in propagating plants like Asparagus, orchids, Chrysanthemum. This method allows us to grow whole plant from cells taken from various parts of the plant body.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Principles of Vegetative PropagationDokument5 SeitenPrinciples of Vegetative PropagationJensenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vegetative PropogationDokument4 SeitenVegetative PropogationkzrdurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method of Plant Breeding in Cross Pollinated PlantsDokument2 SeitenMethod of Plant Breeding in Cross Pollinated PlantsAdita Nur FaoziyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- GymnospermsDokument16 SeitenGymnospermsMahnoor Farooq100% (2)
- Vegetative ReproductionDokument19 SeitenVegetative ReproductionJane Sandra LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asexual Reproduction in Plants SEREDDYDokument34 SeitenAsexual Reproduction in Plants SEREDDYJovs StreamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gardening - Planning The GardenDokument4 SeitenGardening - Planning The Gardencontadino_impazzitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anther or Pollen CultureDokument15 SeitenAnther or Pollen Culturej131089Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11th Morphology of Flowering Plants SolutionsDokument13 SeitenClass 11th Morphology of Flowering Plants SolutionsMufeedAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vegetative PropagationDokument23 SeitenVegetative PropagationAaron DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Propagation in Plants: Most Higher Plants Start Their Life As Vegetative Prop UnitDokument41 SeitenSexual Propagation in Plants: Most Higher Plants Start Their Life As Vegetative Prop UnitDoni DarimastNoch keine Bewertungen
- A LEVEL Crop Science Mcqs 6049-1Dokument90 SeitenA LEVEL Crop Science Mcqs 6049-1tapiwa nzvatu100% (3)
- SpermatophytesDokument26 SeitenSpermatophytesNaomi Deirdre ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Plant Growth Regulators For Seed Germination CapacityDokument16 SeitenEffect of Plant Growth Regulators For Seed Germination Capacitysalma sabilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Germination of SeedDokument18 SeitenGermination of SeedHafiZa RoZikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cucurbitaceae: (Assignment # 02 Semester Spring-2020) Submission Date (April 27, 2020) BY Group #04Dokument14 SeitenCucurbitaceae: (Assignment # 02 Semester Spring-2020) Submission Date (April 27, 2020) BY Group #04Aqib ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seed Viabillty TestDokument13 SeitenSeed Viabillty TestJitendra YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsDokument16 Seiten4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsYu HasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asexual PropagationDokument25 SeitenAsexual PropagationchacharancharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ORGAN CULTURE, Anther & Pollen CultureDokument72 SeitenORGAN CULTURE, Anther & Pollen CultureSanthiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionDokument14 SeitenIGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-Plant Structure and FunctionDokument7 Seiten4-Plant Structure and FunctionfebrimetrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- AngiospermDokument14 SeitenAngiospermJoy EscamillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant MorphologyDokument34 SeitenPlant Morphologyapi-262572717100% (2)
- Seed GerminationDokument12 SeitenSeed GerminationDima33% (3)
- Biofertilizer Part 2Dokument20 SeitenBiofertilizer Part 2Garima BartariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water LilyDokument9 SeitenWater LilyChairunnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Exercise 2. Plant CellDokument2 SeitenLaboratory Exercise 2. Plant CellJC SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Symbionts InteractionDokument13 SeitenPlant Symbionts InteractionIram TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On INFLUENCE OF PRE-HARVEST FACTORS ON POST HARVEST HANDLING OF FLORICULTURAL CROPsDokument68 SeitenSeminar On INFLUENCE OF PRE-HARVEST FACTORS ON POST HARVEST HANDLING OF FLORICULTURAL CROPsAnand Singh RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Nutrition PowerpointDokument10 SeitenPlant Nutrition PowerpointYoshitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Plant?Dokument35 SeitenWhat Is A Plant?Precious UdoadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and History of HorticultureDokument44 SeitenIntroduction and History of HorticulturenavinnaithaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydroponics Mechanism in Growing PetchayDokument2 SeitenHydroponics Mechanism in Growing PetchayChedelle Fatima Cajayon FloridoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asexual ReproductionDokument11 SeitenAsexual ReproductionKoushik KanjilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptation in PlantsDokument19 SeitenAdaptation in PlantsRACHIT MOHAN GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Types of Tissue CultureDokument129 SeitenChapter 6 Types of Tissue Culturerajiv pathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canopy Mamagement 1Dokument30 SeitenCanopy Mamagement 1Nitesh PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 - Distribution of Soil Microorganisms PDFDokument7 Seiten14 - Distribution of Soil Microorganisms PDFshubham100% (1)
- Mineral Nutrition Lab ReportDokument12 SeitenMineral Nutrition Lab Reportapi-381645920100% (2)
- Biofertilizer 141031013427 Conversion Gate01Dokument39 SeitenBiofertilizer 141031013427 Conversion Gate01Sajid HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDokument25 SeitenReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSanthiya MadhavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pteridophytes IntroductionDokument4 SeitenPteridophytes IntroductionSanchita Kulshrestha100% (1)
- Physiology of Flowering by AnjaliDokument46 SeitenPhysiology of Flowering by Anjalianjali khatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Reproduction - Sexual and Asexual Worksheet For Form 5Dokument52 SeitenPlant Reproduction - Sexual and Asexual Worksheet For Form 5api-262572717100% (7)
- Fruits and Fruit Types PDFDokument41 SeitenFruits and Fruit Types PDFSidraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chrysanthemum ClassificationsDokument2 SeitenChrysanthemum ClassificationsSamar Karemore100% (1)
- Orchard GardeningDokument16 SeitenOrchard GardeningMaribeth Tangco FrondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Transport and Translocation of Nutrients and WaterDokument93 SeitenPlant Transport and Translocation of Nutrients and Waterrinlacer100% (13)
- Plants Reproduction and DevelopmentDokument6 SeitenPlants Reproduction and DevelopmentAlwìn GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vegetative PropagationDokument12 SeitenVegetative PropagationNikilsha K100% (1)
- 3 Plant Protection II PDFDokument129 Seiten3 Plant Protection II PDFAvijitSinharoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-2) System Approach For Representing Soil-plant-Atmospheric ContinuumDokument31 Seiten1-2) System Approach For Representing Soil-plant-Atmospheric ContinuumDhanaji Sawant100% (1)
- Photoperiodism Powerpoint EduDokument12 SeitenPhotoperiodism Powerpoint EduAlabi FauziatBulalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HC5E Lesson B1-1 Horticultural Plant ClassificationDokument39 SeitenHC5E Lesson B1-1 Horticultural Plant ClassificationHailey MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.factors Affecting Plant GrowthDokument9 Seiten3.factors Affecting Plant GrowthDalani SinginiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Onion Production Guide PDFDokument4 SeitenOnion Production Guide PDFCyrilJohnDomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layering in PlantsDokument3 SeitenLayering in PlantsS.K. AkhtarzaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS GenBio2 MELC 1 Week 1Dokument14 SeitenLAS GenBio2 MELC 1 Week 1Roland Jacques AlconisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layering, Methods and PrinciplesDokument12 SeitenLayering, Methods and PrinciplesManish M. Ramani100% (2)
- Commercial Private Equity Announces A Three-Level Loan Program and Customized Financing Options, Helping Clients Close Commercial Real Estate Purchases in A Few DaysDokument4 SeitenCommercial Private Equity Announces A Three-Level Loan Program and Customized Financing Options, Helping Clients Close Commercial Real Estate Purchases in A Few DaysPR.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notice: Grant and Cooperative Agreement Awards: Public Housing Neighborhood Networks ProgramDokument3 SeitenNotice: Grant and Cooperative Agreement Awards: Public Housing Neighborhood Networks ProgramJustia.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ahts Ulysse-Dp2Dokument2 SeitenAhts Ulysse-Dp2IgorNoch keine Bewertungen
- AITAS 8th Doctor SourcebookDokument192 SeitenAITAS 8th Doctor SourcebookClaudio Caceres100% (13)
- Human Development IndexDokument17 SeitenHuman Development IndexriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tesmec Catalogue TmeDokument208 SeitenTesmec Catalogue TmeDidier solanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDokument2 SeitenCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationtyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brahm Dutt v. UoiDokument3 SeitenBrahm Dutt v. Uoiswati mohapatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLSQL Day 1Dokument12 SeitenPLSQL Day 1rambabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 10-Dll-Week 3Dokument5 SeitenEnglish 10-Dll-Week 3Alyssa Grace Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- (IME) (Starfinder) (Acc) Wildstorm IndustriesDokument51 Seiten(IME) (Starfinder) (Acc) Wildstorm IndustriesFilipe Galiza79% (14)
- Fix Problems in Windows SearchDokument2 SeitenFix Problems in Windows SearchSabah SalihNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAMILYDokument3 SeitenFAMILYJenecel ZanoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annals of The B Hand 014369 MBPDokument326 SeitenAnnals of The B Hand 014369 MBPPmsakda HemthepNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19-Microendoscopic Lumbar DiscectomyDokument8 Seiten19-Microendoscopic Lumbar DiscectomyNewton IssacNoch keine Bewertungen
- CALIDokument58 SeitenCALIleticia figueroaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hanumaan Bajrang Baan by JDokument104 SeitenHanumaan Bajrang Baan by JAnonymous R8qkzgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key For 1st QaurterDokument5 SeitenAnswer Key For 1st QaurterSteffi89% (9)
- Symptoms: Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)Dokument3 SeitenSymptoms: Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)Nur WahyudiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PsychometricsDokument4 SeitenPsychometricsCor Villanueva33% (3)
- Bodhisattva and Sunyata - in The Early and Developed Buddhist Traditions - Gioi HuongDokument512 SeitenBodhisattva and Sunyata - in The Early and Developed Buddhist Traditions - Gioi Huong101176100% (1)
- Journal Entry EnrepDokument37 SeitenJournal Entry Enreptherese lamelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Questions & Answers For Midterm1: BA 203 - Financial Accounting Fall 2019-2020Dokument11 SeitenReview Questions & Answers For Midterm1: BA 203 - Financial Accounting Fall 2019-2020Ulaş GüllenoğluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7Dokument10 SeitenUnit 7Christopher EddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Adolescence and Education) Tim Urdan, Frank Pajares - Academic Motivation of Adolescents-IAP - Information Age Publishing (2004) PDFDokument384 Seiten(Adolescence and Education) Tim Urdan, Frank Pajares - Academic Motivation of Adolescents-IAP - Information Age Publishing (2004) PDFAllenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob AssignmntDokument4 SeitenOb AssignmntOwais AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)Dokument11 SeitenFoucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)YashinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Past and Past Continuous Notes and ExercisesDokument5 SeitenSimple Past and Past Continuous Notes and ExercisesConstantina KouverianosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hellwalker: "What Terrors Do You Think I Have Not Already Seen?"Dokument2 SeitenHellwalker: "What Terrors Do You Think I Have Not Already Seen?"mpotatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro TeachingDokument3 SeitenMicro Teachingapi-273530753Noch keine Bewertungen