Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chemistry
Hochgeladen von
Anilkmar P MCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry
Hochgeladen von
Anilkmar P MCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CHEMISTRY-1 S BLOCK ELEMENTS-ALKALI AND ALKALINE EARTH METALS The alkali metals are Li,Na,K,Rb,Cs,Fr *Why the elements
in group 1 is called alkali metals? They form hydroxides with water which are strongly alkaline in nature #Physical properties 1. Occurance -they are silverly white soft metals ,stored in kerosene (because they will react with water )but Li stored in paraffin wax due to low density 2. Size of elements- Li<Na<K<Rb<Cs<Fr 3. Density-Li<K<Na<R<Cs<Fr 4. Melting and boiling point-Low due to weak metallic bonding Li>Na>K>Rb>Cs 5 Electro positivity-strong electropositive due to low IE 6.Oxidation state-Allways = +1 (Alkali metals are paramagnetic) 7.Hydration energy- Li+ > Na+> K+> Rb+> Cs+ 8.Ionic mobility &Conductance-Li+ <Na+ <K+ <Rb+<Cs+ 9.Reducing powerA) in free state- Li<Na<K<Rb<Cs B) in aq.solution Li>Na>K>Rb>Cs 10. Flame coloration- they show colour in flame due to exitation of outer most eThis property makes Cs, K useful electrodes in photoelectric cells #Chemical properties their reactivity increases down the group 1.Reaction with air Li forms monoxides, Na forms peroxides, other elements will form superoxides 4Li + O2 2Li2O (monoxide) 2Na +O2 Na2O2 (peroxides) M +O2 MO2 (superoxides) M=K,Rb,Cs *Oxidation state of oxygen in KO2? ---- Ans = +1 NOTE **Li will form Li3N in reaction with N2 in air ** 2. Reaction with water 2M + 2H2O 2MOH +H2 (M=Alkali metals) Li will react vigorously with water, due to small size and high hydration energy 3. Reactivity towards di hydrogen 2M +H2 2MH (at 673 K) (M= Alkali metal) 4.Reactivity towards halogens 2M + X2 2MX (M=Alkali metals, X=Halogen F,Cl,Br,I )
5.Reaction with ammonia M + (x+y)NH3 [M(NH3)x] +[e(NH3)y] Dilute solution is blue coloured, paramaganetic ,conducting, reducing Conc.. solution is bronze color dia magnetic Characteristics of compounds 1.HYDRIDES (MH) Ionic solids , with high MP,BP ,They are good reducing agent Order of stabilityLiH >NaH >KH >RBH >CsH 2. OXIDES 3 Types M2O, M2O2 , MO2 M2O M2O+H2O 2MOH M2O2 M2O2+H2O H2O2+2MOH MO2 MO2+ H2OMOH+H2O2+O2 Na2O2, K2O are used as air purifier 3.HYDROXIDES(MOH) White crystalline solids ,strong bases order of basicity &solubility -LiOH<NaOH<KOH<RbOH<CsOH 4.HALIDES(MX) Halides have high ve Hf value MP- Flurides> Chlorides> Bromides> Iodides LiF has high lattice energy, CsI has low hydration energy , therfore they are insoluble in water 5.CARBONATES(M2CO3 ) Order of thermal stability&solubility Li2CO3<Na2CO3<K2CO3<Rb2CO3<Cs2CO3 6.BYCARBONATES(MHCO3) All except LiHCO3 exist as solids ,LiHCO3 exist only in solution 2MHCO3 M2CO3+H2O+CO2 7.NITRATES(MNO3) LiNO3 Li2O+H2O+O2 MNO3MNO2+O2 (M=Na,K,Rb,Cs)
SOME IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS OF SODIUM 1Sodium carbonate(Washing soda) Na2CO3.10H2O Prepared by solvay process solvay process Raw meterials are lime stone ,sodium chloride,ammonia Steps 1. generation of CO2 --- CaCO3CO2+CaO 2. recovery of NH3 CaO+H2OCa(OH)2 Ca(OH)2+NH4ClNH3+CaCl2+H2O 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Morphing of Multistable Variable-Stiffness Laminates Using MFC ActuatorsDokument48 SeitenMorphing of Multistable Variable-Stiffness Laminates Using MFC ActuatorsAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- AM5360: Composite Structures Assignment 2: Submitted By, Anilkumar P M Reg. No: CE18D755Dokument9 SeitenAM5360: Composite Structures Assignment 2: Submitted By, Anilkumar P M Reg. No: CE18D755Anilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Morphing of Multistable Variable Stiffness Laminates Using MFC ActuatorsDokument6 SeitenMorphing of Multistable Variable Stiffness Laminates Using MFC ActuatorsAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- SpiceJet - E-Ticket - PNR MC5QMD - 16 Aug 2018 Chennai-Delhi For MR. PMDokument2 SeitenSpiceJet - E-Ticket - PNR MC5QMD - 16 Aug 2018 Chennai-Delhi For MR. PMAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Approximate MethodsDokument15 SeitenApproximate MethodsAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMS ProjectDokument10 SeitenAMS ProjectAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anilkumar P. M., M.Tech (Civil-Structural Engg.) : EducationDokument3 SeitenAnilkumar P. M., M.Tech (Civil-Structural Engg.) : EducationAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Mu/bd 2Dokument14 SeitenMu/bd 2Anilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Calculation For Single Angle Section Load (P) Dial Gauge Reading Deflection (D) in MM KG N Face 1 Face 2 Face 1 Face 2Dokument8 SeitenCalculation For Single Angle Section Load (P) Dial Gauge Reading Deflection (D) in MM KG N Face 1 Face 2 Face 1 Face 2Anilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Natural Time Period (S) Mode 1 0.576 Mode Shape Roof 1 Middle Floor 0.802 First Floor 0.445Dokument3 SeitenNatural Time Period (S) Mode 1 0.576 Mode Shape Roof 1 Middle Floor 0.802 First Floor 0.445Anilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Deterioration of Concrete Structures: Causes and Preventive Measures: An OverviewDokument41 SeitenDeterioration of Concrete Structures: Causes and Preventive Measures: An OverviewAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICRM 2014 PPT FinalDokument19 SeitenICRM 2014 PPT FinalAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Aqueduct and Canal RegulatorDokument26 SeitenAqueduct and Canal RegulatorAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
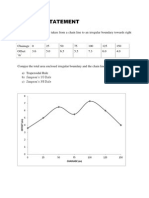
- Problem Statement: Chainage (M)Dokument7 SeitenProblem Statement: Chainage (M)Anilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- How To Reach NITCDokument1 SeiteHow To Reach NITCAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Studies On Durability of Reinforced Concrete: Department of Civil EngineeringDokument48 SeitenStudies On Durability of Reinforced Concrete: Department of Civil EngineeringAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
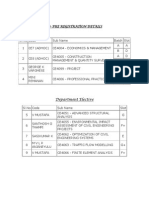
- S8-Pre RegDokument1 SeiteS8-Pre RegAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Noiseless Pavements: by Jestin John B110286CEDokument26 SeitenNoiseless Pavements: by Jestin John B110286CEAnilkmar P M80% (5)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- High WayDokument4 SeitenHigh WayAnilkmar P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Topic 7 - D BlockDokument47 SeitenTopic 7 - D Blockizz isalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Refinery Gas AnalysisDokument92 SeitenRefinery Gas AnalysiscxmzswNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plante Ca Antioxidanți Naturali Pentru Produsele Din Carne 1 PDFDokument10 SeitenPlante Ca Antioxidanți Naturali Pentru Produsele Din Carne 1 PDFFlorentina LucanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aromatic Compounds (13th)Dokument24 SeitenAromatic Compounds (13th)Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Total Ion Concentration Using Ion Exchange ChromatographyDokument3 SeitenDetermination of Total Ion Concentration Using Ion Exchange ChromatographyBulawan LaNeref OremseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2003 - Fukuoka - A Novel Non-Phosgene Polycarbonate Production Process Using By-Product CO2 As Starting MaterialDokument11 Seiten2003 - Fukuoka - A Novel Non-Phosgene Polycarbonate Production Process Using By-Product CO2 As Starting MaterialViraj EdirisingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion Protection of Steel Offshore Units and InstallationsDokument36 SeitenCorrosion Protection of Steel Offshore Units and Installationsdamnamyte100% (1)
- Gr9 OSSD Chemistry RevisionDokument4 SeitenGr9 OSSD Chemistry RevisionocNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAC Hyperfluid Plus (H2) : Superplasticiser For Low Grades Concrete Based On Poly-Carboxylic EtherDokument2 SeitenCAC Hyperfluid Plus (H2) : Superplasticiser For Low Grades Concrete Based On Poly-Carboxylic Ethersmkrishnan89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bel Ray Industrial Gear Oil PDSDokument1 SeiteBel Ray Industrial Gear Oil PDSDaniel Salazar CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- MATSCI 210 - Lecture 5 - PolyelectrolytesDokument22 SeitenMATSCI 210 - Lecture 5 - PolyelectrolytesSamanoske AkechiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idoc - Pub - Astm A570 Steel Grade 50 PDFDokument1 SeiteIdoc - Pub - Astm A570 Steel Grade 50 PDFFrancisco Javier Torres AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Assessment Result For Grades 1-10 Learning Area: - (English/Filipino/Mtb/Ap/Esp)Dokument18 SeitenClass Assessment Result For Grades 1-10 Learning Area: - (English/Filipino/Mtb/Ap/Esp)Joe TitularNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulating Clear Type Beverage Q-NATURALE® White PaperDokument4 SeitenFormulating Clear Type Beverage Q-NATURALE® White PaperIngredion Knowledge Bank100% (1)
- USP-NF Tribasic Calcium PhosphateDokument3 SeitenUSP-NF Tribasic Calcium PhosphateVõ Đức TrọngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Wax and OilDokument26 SeitenDifference Between Wax and OilJessa Mae Malinao100% (2)
- Module 2 Gen Bio CellsDokument59 SeitenModule 2 Gen Bio CellsSophia Joy A. FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- % Recovery of B Mass of B Recovered Mass of B Used Initially X 100Dokument4 Seiten% Recovery of B Mass of B Recovered Mass of B Used Initially X 100Ayle NakamuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Problem of Corrosion in Orthopaedic ImplantDokument5 SeitenThe Problem of Corrosion in Orthopaedic ImplantSoreh AminiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production of Perfumes .Dokument13 SeitenProduction of Perfumes .tariq fareedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Class Xii Chemistry Students Support MaterialDokument95 SeitenClass Xii Chemistry Students Support MaterialDivyam GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDS 8127-Eng PDFDokument2 SeitenTDS 8127-Eng PDFadammzjinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro-Chemistry 2020 2022Dokument28 SeitenElectro-Chemistry 2020 2022Vincent AnzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of An Oil Analysis ReportDokument8 SeitenAnatomy of An Oil Analysis ReportRuben_3115Noch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Perspectives For (Microbial) BiosurfactantsDokument15 SeitenIndustrial Perspectives For (Microbial) BiosurfactantslaucyzhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical Characterization of Immobilized Tannase From Aspergillus AwamoriDokument19 SeitenBiochemical Characterization of Immobilized Tannase From Aspergillus AwamoriKatherine GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet Baymag 30: Industrial Grade Magnesium OxideDokument1 SeiteData Sheet Baymag 30: Industrial Grade Magnesium OxideKiko NobreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19Dokument26 SeitenChapter 19tyobertsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 304H Buttweld FittingsDokument4 Seiten304H Buttweld FittingsPetromat Oil and Gas Equipment Pvt. Ltd.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 Powerpoint - Student VersionDokument141 SeitenChapter 16 Powerpoint - Student Versionroshni rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarVon EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (19)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonVon EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (103)
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureVon EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (125)