Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Effect of Concentration On Initial Rate of Reaction of An Enzyme
Hochgeladen von
science_ASs_are_funOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Effect of Concentration On Initial Rate of Reaction of An Enzyme
Hochgeladen von
science_ASs_are_funCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Measuring the effect of concentration on initial rate of reaction This experiment uses the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into
oxygen and water. The rate of this reaction is increased by the addition of the enzyme catalase and this fact can be used to investigate the concentration of an enzyme on the rate of initial reaction. Method: 1) Make up six different concentrations of the enzyme or potato extract (made using pH buffer) by diluting with water 2) Set up equipment as shown in figure 1 3) Place 10cm3 of the enzyme in the conical flask 4) Measure 10cm3 of hydrogen peroxide into the syringe and add to the enzyme solution 5) Using the gas collection tube measure the volume of oxygen produced in 60s 6) Plot the volume of oxygen produced (cm3) against concentration (%) of enzyme on a graph 5) Repeat with the different concentrations of enzyme
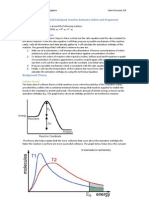
Figure 1 Explanation: Increased concentration means more enzyme molecules to collide with substrate so more enzyme-substrates complexes form, meaning increased rate of reaction. However: there is a limited amount of substrate so there will be a point where there are more enzyme molecules than substrate and at this point increasing the concentration will have no further effect. Control variables: PH buffer, temperature water bath, time of reaction stopwatch, volume of enzyme measuring cylinder/syringe, type of enzyme same batch of enzyme and concentration of hydrogen peroxide same batch/bottle.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Investigating An Enzyme Controlled Reaction - Catalase and Hydrogen PeroxideDokument4 SeitenInvestigating An Enzyme Controlled Reaction - Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxidevictoria.crausazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Catalase Experiment DesignDokument6 SeitenBiology Catalase Experiment DesignLata SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Catalase Experiment DesignDokument6 SeitenBiology Catalase Experiment DesignNimisha SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Activity of The Enzyme CatalaseDokument7 SeitenThe Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Activity of The Enzyme CatalaseSmith PennanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substrate Substrate Substrate Substrate SubstrateDokument3 SeitenSubstrate Substrate Substrate Substrate Substratecondoleeza smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes WriteupDokument3 SeitenEnzymes WriteupJay WalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Lab 6 EnzymesDokument5 SeitenBiology Lab 6 EnzymesMarc MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Laboratory Report Enzyme Concentration and Rate of ReactionDokument11 SeitenBiology Laboratory Report Enzyme Concentration and Rate of ReactionTaslim Haji MunshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Practical 4 Enzyme Concentration For BiologyDokument7 SeitenCore Practical 4 Enzyme Concentration For BiologyMitullesh EngarshalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpac 12Dokument3 SeitenCpac 12mohammed kibriahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment To Investigate How Enzyme Concentration Can Affect The Initial Rate of ReactionDokument4 SeitenExperiment To Investigate How Enzyme Concentration Can Affect The Initial Rate of ReactionJan StankiewiczNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Enzyme Concentration of Rate of ReactionDokument18 SeitenEffect of Enzyme Concentration of Rate of ReactionAbdul Rahman Mohamed75% (8)
- Lab 3 KineticsDokument6 SeitenLab 3 KineticsMichelle SamayoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Activity of EnzymesDokument7 SeitenThe Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Activity of Enzymesjosephine100% (1)
- Botany Lab Report 2 How Does The PH Affect The Rate of Catalase ActivityDokument8 SeitenBotany Lab Report 2 How Does The PH Affect The Rate of Catalase ActivityCatherineNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCI B Investigation PHDokument12 SeitenSCI B Investigation PHgeneva conventionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Lab 8 (Submit)Dokument6 SeitenBio Lab 8 (Submit)Nor Ashikin IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Running Head The Effect of Peroxidase Concentration On Reaction Rate 1Dokument7 SeitenRunning Head The Effect of Peroxidase Concentration On Reaction Rate 1migire kennedyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aim: Summary:: To Observe How Enzyme Concentration Can Affect The Initial Rate of ReactionDokument4 SeitenAim: Summary:: To Observe How Enzyme Concentration Can Affect The Initial Rate of ReactionormattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme Reaction LabDokument13 SeitenEnzyme Reaction LabAakash ParikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beano LabDokument12 SeitenBeano Labapi-284496286Noch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes Report Biology AS Core Practical Write Up EdexcelDokument7 SeitenEnzymes Report Biology AS Core Practical Write Up EdexcelthariniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: Biological CatalystsDokument9 SeitenEnzymes: Biological CatalystsChamzelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme LabDokument4 SeitenEnzyme LabvincentmdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme ConcentrationDokument16 SeitenEnzyme ConcentrationSya Subi100% (1)
- GCSE Biology 2010 Course WorkDokument11 SeitenGCSE Biology 2010 Course WorkDermot McGuckinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAG4.1 Student The Effect of Substrate CDokument3 SeitenPAG4.1 Student The Effect of Substrate CAmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - Rate of Chemical Reactions 2023Dokument7 SeitenChemistry - Rate of Chemical Reactions 2023witness vurayayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics of The Acid Catalysed Reaction Between Iodine and Propanone Final LolDokument23 SeitenKinetics of The Acid Catalysed Reaction Between Iodine and Propanone Final LolYann Perusset90% (10)
- Biology Lab - Catalase ExperimentDokument8 SeitenBiology Lab - Catalase Experimentapi-253040433Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Lab ReportDokument10 SeitenBio Lab ReportMariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Cellular Processes SOLUTIONSDokument8 Seiten1 Cellular Processes SOLUTIONSLeo LouisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Lab # 6Dokument5 SeitenBio Lab # 6Cris SanchEzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes LabDokument3 SeitenEnzymes LabsergsNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnzymeDokument5 SeitenEnzymeBinnie KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rates of Reaction FactorsDokument19 SeitenRates of Reaction FactorsAhmed MasoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen Peroxide DecompositionDokument17 SeitenHydrogen Peroxide DecompositionChristian Eduardo Fabian50% (2)
- The Effects of PH and Inhibitor Concentration On The Activity of A Phosphatase EnzymeDokument12 SeitenThe Effects of PH and Inhibitor Concentration On The Activity of A Phosphatase EnzymeLucas Man75% (4)
- Applications of Critical Solution TemperatureDokument5 SeitenApplications of Critical Solution TemperatureParveen88% (8)
- AQA As Required Practicals Methods Questions and Mark SchemesDokument29 SeitenAQA As Required Practicals Methods Questions and Mark SchemesbekoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio S5 SBADokument5 SeitenBio S5 SBAWONG EVELYNE JADENoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen From Hydrogen Peroxide: A Safe Molar Volume-Molar Mass ExperimentDokument2 SeitenOxygen From Hydrogen Peroxide: A Safe Molar Volume-Molar Mass ExperimentManuel Curitol PiutrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalase Enzyme LabDokument7 SeitenCatalase Enzyme LabJunhyoung ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 3 Instruction: Answer All QuestionsDokument10 SeitenPaper 3 Instruction: Answer All QuestionsNoor Hafezah Mohd MokhtiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aims:: Experiment: Rates of Enzyme Controlled ReactionsDokument4 SeitenAims:: Experiment: Rates of Enzyme Controlled ReactionsNataRondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Wheat Germ Acid Phosphatase Lab Week 6Dokument5 SeitenAnalysis of Wheat Germ Acid Phosphatase Lab Week 6Jay PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report BCM 3Dokument2 SeitenLab Report BCM 3Siti Nurasnizan ChieNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Biology Internal Assessment 2Dokument12 SeitenIB Biology Internal Assessment 2beslisevval89% (9)
- AP Biology Lab 2 Enzyme CatalysisDokument8 SeitenAP Biology Lab 2 Enzyme CatalysisJessica HughesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4 (Biology)Dokument11 SeitenExperiment 4 (Biology)言爱邦0% (1)
- Investigating The Effect of Temperature & PH On Enzyme ActivityDokument3 SeitenInvestigating The Effect of Temperature & PH On Enzyme Activityjuliakang03Noch keine Bewertungen
- IntoruductionDokument3 SeitenIntoruductionRayya MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sediment Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenSediment Lab ReportMihails Aleksejevs100% (1)
- Enzyme Lab ReportDokument9 SeitenEnzyme Lab ReportSafaa TatouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 2Dokument8 SeitenPractical 2Ibrahim Muhamad0% (1)
- Yeast Catalase ManuscriptDokument6 SeitenYeast Catalase Manuscriptapi-743299736Noch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of EnzymesDokument7 SeitenProperties of Enzymeslcassidy9074Noch keine Bewertungen
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideVon EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsVon EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactVon EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideVon EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (14)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactVon EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingVon EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideVon EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeVon EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsVon EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeVon EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesVon EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (90)