Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chaper 29 Workbook
Hochgeladen von
Jenny HongOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chaper 29 Workbook
Hochgeladen von
Jenny HongCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chaper 29 Workbook Section 29.1 1. F 2. F 3. F 4. T 1. B 2. A 3. B 4. C 5. C 6. A 1.
The standard definition of a recession is a decrease in real GDP that lasts for at least two quarters or 6 months 2.
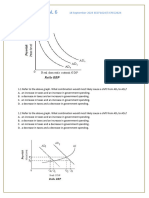
3. The economy experiences recession at the 3rd quarter of 2004 to the 2nd quarter of 2005 and also the 1st quarter of 2006 to the 3rd quarter of 2006. Section 29.2 1. F 2. F 3. T 4. T 1. C 2. A 3. E 4. A 5. C 1. A) a fall in the money wage rate and E) an increase in productivity increase aggregate supply and shift the AS curve rightward. D) A rise in the price of oil and H) Government regulations severely restrict the amount of pollution firms decrease aggregate supply and shift the AS curve leftward. The remaining letters b, c, f, and g doesnt shift the AS.
2a.
2b. If there was a fall in the money wage rate, then it would have no effect on potential GDP therefore the potential GDP line does not change, but the aggregate supply increases so the AS curve shifts rightward. 2c.
2d. Both the potential GDP line and the aggregate supply curve would both shift rightward by $2 trillion. 1. The AS curve would slope upward and brings a change in the real wage rate therefore if the price level rises, the real wage rate falls. 2. The aggregate supply shifts because an increase in the money wage rate increases firms costs. Also, aggregate supply decreases and the AS curve shifts leftward resulting that changes in the money wage rate does not change potential GDP 3. The effect on aggregate supply if the money price of oil rises is that if the money price of oil rises, firms cost increases, Aggregate supply decreases and the aggregate supply curve shifts leftward.
Section 29.3 1. T 2. F 3. F 4. F 1. D 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. A 6. A 1. B) and C) would increase aggregate demand and shift the AD curve rightward. F) and G) would decrease aggregate demand and shift the AD curve leftward. A) D) E) and H) would not shift the AD curve. 2a. 2b.
1. An increase in the price level decreases the quantity of real GDP demanded because an increase in the price level lowers the buying power of money, which decreases consumption expenditure. 2. The effect of this is that there would be an increase in expected future profit increasing the investment therefore would increase aggregate demand. 3. If the government increases its taxes, the effect of aggregate demand and consumers disposable income is that they both decrease. 4. The aggregate demand multiplier is an effect that magnifies changes in expenditure and increases fluctuations in aggregate demand. Section 29.4 1. T 2. F 3. T 4. F
1. D 2. B 3. C 4. B 5. E 6. B 7. C 8. A 9. A 1. Stagflation is a combination of recession and inflation and stagflation can be created by a decrease in aggregate supply. 2. If a government decreases its taxes, it increases aggregate demand and the price level would rise as well as the real GDP increasing. 3. If the government decreases its expenditure, it decreases aggregate demand and shifts the AD curve leftward resulting in the price level falling and real GDP decreasing. 4. A fall in the money wage rate increases aggregate supply and shifts the AS curve rightward. Also, the price level rises and the real GDP would also increase. 1a. 1b.
2. A rise in the price of oil, the aggregate supply decreases and the AS curve shifts leftward from AS to AS1. Therefore, the real GDP would decrease and the price level would rise. 3. An inflationary gap is a gap that exists when real GDP exceeds potential GDP. Inflationary gap is eliminated when eventually real GDP returns to the potential GDP and therefore eliminating the inflationary gap.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CH 29Dokument4 SeitenCH 29Prashant Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 2Dokument6 SeitenHW 2Mansi ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aggregate Demand & Aggregate SupplyDokument4 SeitenAggregate Demand & Aggregate Supplymahimrashidulhasan008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 & 10 - : Solutions To Problem Set # 8Dokument11 SeitenChapter 9 & 10 - : Solutions To Problem Set # 8rashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Lecture Notes Chapter 33Dokument8 SeitenReview Lecture Notes Chapter 33- OriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infaltion & Unemployment NotesDokument11 SeitenInfaltion & Unemployment Notesjoebloggs1888Noch keine Bewertungen
- WKSHT Macro Unit3 Lesson3 Act23 KeyDokument10 SeitenWKSHT Macro Unit3 Lesson3 Act23 KeyCarl WeinfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 5Dokument6 SeitenProblem Set 5bus242Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aggregate DemandDokument4 SeitenAggregate Demandjaz2423Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 08 Aggregate Demand and Supply HW Attempt 1Dokument5 SeitenChapter 08 Aggregate Demand and Supply HW Attempt 1Pat100% (1)
- FINAL Econ ReportDokument13 SeitenFINAL Econ ReportTsum Lok TungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Aggregate Demand and SupplyDokument5 SeitenChapter 11 Aggregate Demand and SupplyPinaki MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muntasir Ahmmed - Tutorial 3Dokument3 SeitenMuntasir Ahmmed - Tutorial 3Muntasir AhmmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation (Parkin)Dokument2 SeitenInflation (Parkin)tauhidult100% (1)
- MCQ Inflation Page 261 270Dokument10 SeitenMCQ Inflation Page 261 270Hoàng Lê KiênNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 Spring Bpea HamiltonDokument70 Seiten2009 Spring Bpea HamiltonrandebenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hkcee Economics - 8.8 GDP at Current and Constant Market Prices - P.1Dokument3 SeitenHkcee Economics - 8.8 GDP at Current and Constant Market Prices - P.1林衍諾Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument8 SeitenAssignment 2Hà ChiếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 011 NotesDokument10 SeitenChap 011 Notesfree50Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 6Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 6scarletmbalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Assignment - ECO 104Dokument10 SeitenFinal Assignment - ECO 104Md. Rezwan Hossain Sakib 1711977630Noch keine Bewertungen
- Level 2 Eco InflationDokument3 SeitenLevel 2 Eco InflationVadim FongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment II - Solution by Elias AbboudDokument6 SeitenAssignment II - Solution by Elias AbboudHarout KeshishianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Push InflationDokument3 SeitenCost Push InflationObaidullah Al Mahmud RefatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 541Dokument11 SeitenQuiz 541Haris NoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions EcoDokument3 SeitenQuestions EcocapoojamalooNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CorrectionDokument8 SeitenThe CorrectionDiamante GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco 101 HW & Class Test Quizz PDFDokument7 SeitenEco 101 HW & Class Test Quizz PDFMehadi Hasan RoxyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggested Answers Exercise Question Beeb3023 Intmd Macro A221Dokument15 SeitenSuggested Answers Exercise Question Beeb3023 Intmd Macro A221Amirul AimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid19 Submission TemplateDokument9 SeitenCovid19 Submission TemplateASISH SABATNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument3 Seiten2dinauy88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Ch5Dokument10 SeitenPractice Ch5Ali_Asad_1932Noch keine Bewertungen
- FIN201 - Quiz - 2 - FA - 2022 - Nguyễn Đức Minh-HS173138Dokument12 SeitenFIN201 - Quiz - 2 - FA - 2022 - Nguyễn Đức Minh-HS17313828- Nguyễn Đức Minh - Chíp PơNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 OdlDokument10 SeitenTopic 4 OdlNur NabilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)Dokument6 Seiten1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)Haifa Al-humayydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Solutions To Rec ProbsDokument4 SeitenChapter 10 Solutions To Rec ProbsAnonymous O5asZmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aggregate Demand and Supply-MacroDokument13 SeitenAggregate Demand and Supply-MacroFaryal ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man Kiw Chapter 06 Solutions ProblemsDokument9 SeitenMan Kiw Chapter 06 Solutions ProblemsJosemariaSaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CB2402 Week 7Dokument5 SeitenCB2402 Week 7RoyChungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation Unemployment 90Dokument10 SeitenInflation Unemployment 90Segun OgunleyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Principles and Practice Asia Pacific 1st Edition Littleboy Test BankDokument38 SeitenMacroeconomics Principles and Practice Asia Pacific 1st Edition Littleboy Test Bankcharleshoansgb3y100% (32)
- Macroeconomics Principles and Practice Asia Pacific 1st Edition Littleboy Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument59 SeitenMacroeconomics Principles and Practice Asia Pacific 1st Edition Littleboy Test Bank Full Chapter PDFStevenCookexjrp100% (11)
- Macro On TapDokument43 SeitenMacro On Tap20070433 Nguyễn Lê Thùy DươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syed Talha Ahmad Eco AssignmentDokument10 SeitenSyed Talha Ahmad Eco AssignmentSyed Talha AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Practice Exam: FIGURE 24-1Dokument13 SeitenMacroeconomics Practice Exam: FIGURE 24-1adam jamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 16Dokument8 SeitenChap 16Humaid SaifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa Ec0n2 W QP Jun09Dokument16 SeitenAqa Ec0n2 W QP Jun09api-247036342Noch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Tutorial Answers 1Dokument3 SeitenMacroeconomics Tutorial Answers 1Puja TulsyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 SolutionsDokument9 SeitenChapter 12 Solutionsehab_ghazallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Materials To Topic3Dokument4 SeitenExtra Materials To Topic3КатеринаNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre AP Economics - FinalDokument6 SeitenPre AP Economics - FinalRebecca NiezenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mls 2f Grp2 InflationDokument35 SeitenMls 2f Grp2 InflationAntoinette Macayan MonsaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Dokument8 SeitenStudy Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Kiran KachhawahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AD AS Headline ActivityDokument16 SeitenAD AS Headline ActivitysaragakannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problem Set 1 With AnswersDokument7 SeitenPractice Problem Set 1 With AnswersJoy colabNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Practice Midterm 2Dokument8 Seiten1 Practice Midterm 2Krishna ArjunNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAP 33 - Group3Dokument15 SeitenCHAP 33 - Group3thaothuvg2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- StudyGuide PDFDokument36 SeitenStudyGuide PDFSamihaSaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- STAS 111 - Information AgeDokument20 SeitenSTAS 111 - Information AgeMayeee GayosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wavoo Wajeeha Women's College - Annual Report - 2013-14Dokument29 SeitenWavoo Wajeeha Women's College - Annual Report - 2013-14kayalonthewebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contractions 29.01Dokument1 SeiteContractions 29.01Katita la OriginalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature ReviewDokument7 SeitenLiterature Reviewapi-353923446Noch keine Bewertungen
- Settlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Dokument11 SeitenSettlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Arindam RoulNoch keine Bewertungen
- WearebecausewebelongDokument3 SeitenWearebecausewebelongapi-269453634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oral ComDokument2 SeitenOral ComChristian OwlzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crim 2 Module 2 Atty A.D.G.Dokument7 SeitenCrim 2 Module 2 Atty A.D.G.Badens DgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bob Dylan Diskografija Prevodi PesamaDokument175 SeitenBob Dylan Diskografija Prevodi PesamaJolanda NešovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Assignment 10 (Prac)Dokument3 SeitenClass 11 Assignment 10 (Prac)9crollno14bhewensagarsahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Magical Diaries of Ethel ArcherDokument7 SeitenThe Magical Diaries of Ethel Archerleeghancock100% (1)
- Optical CamouflageDokument27 SeitenOptical CamouflageAlliluddin ShaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibullying Presentation 1Dokument23 SeitenAntibullying Presentation 1Martin Ceazar HermocillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denso HP4Dokument87 SeitenDenso HP4Abraham Janco Janco100% (2)
- Q&A FractureDokument13 SeitenQ&A FractureRed JimenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPE 166182 Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Leads The Way in The Quest For Intervention Free Upper Completion InstallationDokument9 SeitenSPE 166182 Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Leads The Way in The Quest For Intervention Free Upper Completion InstallationjangolovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4 Creating Graphic OrganizerDokument1 Seite1.4 Creating Graphic OrganizerTrixie Roselle Y. MesiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Priya - Rachna Kumari PrasadDokument17 SeitenPriya - Rachna Kumari PrasadSumant priyadarshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write Effective Sex ScenesDokument4 SeitenHow To Write Effective Sex ScenesAria DiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Semiology Reading NotesDokument6 SeitenIntro To Semiology Reading NotesRyan DrakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- English ExercisesDokument2 SeitenEnglish ExercisesLiceth HuertasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Brain in Your Pocket Evidence - That - SDokument8 SeitenThe Brain in Your Pocket Evidence - That - Sanwaarft123Noch keine Bewertungen
- US of GIT of CattleDokument13 SeitenUS of GIT of CattlesangeetsamratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Strategies in TeachingDokument12 SeitenDifferent Strategies in TeachingCris MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Test 1Dokument3 SeitenMidterm Test 1Hùng Trường NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Founders' ShareDokument2 SeitenFounders' ShareHenry BerlangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mutants Genetic Gladiators Hack PDFDokument2 SeitenMutants Genetic Gladiators Hack PDFFercho GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uber Eats Business Model CanvasDokument1 SeiteUber Eats Business Model Canvass MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report End of Chapter 1Dokument4 SeitenReport End of Chapter 1Amellia MaizanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Short Summary of English and American GeographyDokument2 Seiten2 Short Summary of English and American GeographyDonna Mendoza ComiaNoch keine Bewertungen