Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pathophysiology (Glioma)
Hochgeladen von
peterjongCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pathophysiology (Glioma)
Hochgeladen von
peterjongCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
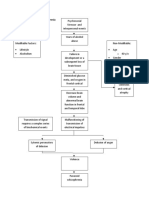
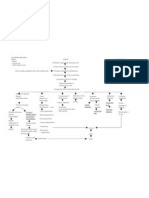
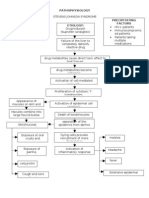
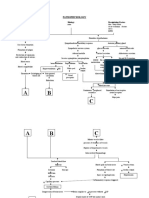
Predisposing Factors 1) 2) Race Gender
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Precipitating Factors Lifestyle: Diet (Carnivorous), No exercise Exposure to radiation (Phone calls) Stress
Mutation of normal cells (Glial cells) Formation of cancer cells
Normal cells affected
Number and growth of abnormal cells
Hypertrophy of gliomal layer
Persistent overgrowth of cells Metastasis to near area(Meninges)
If not treated:
TUMOR formation (GLIOMA)
Intracranial pressure MENINGIOMA Depletion of O2 and Nutrients Hypo perfusion in cerebral circulation Restlessness, Irritability, Anxiety
Lactic acid formation LIR (Local Inflammato ry Response) SIRS (Systemic Inflammat ory Response Syndrome Swelling of cerebral cells Damage to cells
Capillary Refill Permeability Headache, swelling of the affected area, Vomiting, Nausea, Dizziness
Formation of Edema
Stimulation of SNS (Constriction)
Compensatory Mechanism
Persistent depletion of O2 and nutrients Cell starvation
Sustained increase in capillary Cerebral Vasodilation Hypovolemia at cerebral Cell Death level
Acidity in cellular and tissue level Metabolic Acidosis
SHOCK
COMATOSE State
Persistent SIRS
Damage of various vital organs Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndromes (MODS)
DEATH
If treated: Early Detection of Tumor Formation Diagnostic tests: MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) SPECT (Singleproton Emission Computed Tomography EEG (Electroencephal ogram) Angiography ComputerTumor Formation (GLIOMA) Prompt Medical Management/ Treatment Surgical Therapy Radiation Therapy and Radiosurgery Chemotherapy Drug Therapy Neoplastic medications Osmotic Diuresis Corticosteroids
Fair Prognosis
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MyelomeningoceleDokument7 SeitenMyelomeningocelemavefigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology TBIDokument1 SeitePathophysiology TBIChester ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular AberrationDokument14 SeitenCellular AberrationjinahyangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 1 FinalDokument28 SeitenCase Study 1 Finalapi-3905968320% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Brain TumorDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Brain TumorAlinor Abubacar100% (1)
- Electrical Burn PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteElectrical Burn PathophysiologydanicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP and Fdar Wk2 Sarscov-19Dokument4 SeitenNCP and Fdar Wk2 Sarscov-19Jamaica Malicdem0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan On Creutzfeldt-Jakob DiseaseDokument7 SeitenNursing Care Plan On Creutzfeldt-Jakob DiseaseUjean Santos Sagaral100% (1)
- Psychopathology of Schizophrenia (Client)Dokument1 SeitePsychopathology of Schizophrenia (Client)Robert Joseph Sison67% (3)
- Cellular AberrationDokument2 SeitenCellular AberrationFrances Gaviola100% (1)
- Pathophysiology SARSDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology SARSStephanie Joy Escala71% (7)
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP LymphedemaDokument1 SeiteNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- Leadership Roles and Responsibilities of A Nurse in Disaster Risk and Reduction ManagementDokument13 SeitenLeadership Roles and Responsibilities of A Nurse in Disaster Risk and Reduction ManagementIrish Jane GalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of CVD InfarctDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of CVD InfarctIris Caberte86% (7)
- Ovarian Cancer, The NEw PathophyDokument3 SeitenOvarian Cancer, The NEw PathophylieselannjacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Room WriteDokument2 SeitenOperating Room WritemodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJhevilin RM100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic FeverDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Rheumatic FeverGehlatin Tumanan100% (2)
- FINALS ReviewerDokument14 SeitenFINALS ReviewerJustine Simeon lagunzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of Breast CancerDemocrito Louierick Plaza VINoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- NCP Risk For InfectionDokument6 SeitenNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guillain Barre Syndrome PathophysiologyDokument4 SeitenGuillain Barre Syndrome Pathophysiologykathy100% (13)
- A Case Study Presentation On Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Presented byDokument78 SeitenA Case Study Presentation On Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Presented byNina100% (1)
- Rabies PreventionDokument3 SeitenRabies PreventionFrinkaWijaya100% (1)
- 10 Pathophysiology DiagramDokument3 Seiten10 Pathophysiology DiagramDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument1 SeiteNCPTalTal Balcera Beniten100% (1)
- Patho Pleural EffusionDokument2 SeitenPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Dokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Justine Mae Loria0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patho MyomaDokument1 SeitePatho MyomaJurilyne Rose TundagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Papillary Thyroid Ca: Group. 1 B Grand CaseDokument16 SeitenPapillary Thyroid Ca: Group. 1 B Grand CaseAdora Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - ERDokument5 SeitenNCP - ERAnnelore ArcayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychopathophysiology: Psychosocial Stressor and Interpersonal EventsDokument2 SeitenPsychopathophysiology: Psychosocial Stressor and Interpersonal EventsMiyuki Bartolaba MangondatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteNarrative PathophysiologyJemsMei Comparativo MensuradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPArien CaleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map - Colon CancerDokument2 SeitenConcept Map - Colon Cancerbea pegadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Stevens Johnson Syndrome SJSDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Stevens Johnson Syndrome SJSDavid Villanueva50% (2)
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVADokument4 SeitenPathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- A Case Presentation of Cerebrovascular Accident InfarctDokument38 SeitenA Case Presentation of Cerebrovascular Accident InfarctKaycee Toling100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Client With Life Threatening Conditions Acute Ill, Multi-Organ Problems High Acuity and Emergency SituationsDokument43 SeitenNursing Care of Client With Life Threatening Conditions Acute Ill, Multi-Organ Problems High Acuity and Emergency SituationsGlaiza Fabia100% (1)
- Case StudyDokument27 SeitenCase Studyapi-313356122Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 NCM 109 - Pregestational ConditionsDokument6 Seiten2.1 NCM 109 - Pregestational ConditionsSittie Haneen TabaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- No. 10 SANAANI Topic For Esophagogastric Balloon Tamponade Tubes Billroth 1 and 11Dokument12 SeitenNo. 10 SANAANI Topic For Esophagogastric Balloon Tamponade Tubes Billroth 1 and 11Nur SanaaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityDokument1 SeiteBasic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityTechnoShindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology - Brain TumorDokument1 SeitePathophysiology - Brain Tumornories_150% (2)
- Care ModalitiesDokument41 SeitenCare Modalitiesjoyrena ochondra100% (1)
- TAT and TIG Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenTAT and TIG Drug StudyMaria NorilynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDokument1 SeiteBreast Cancer Concept MapKeepItSecret100% (1)
- Group 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeDokument60 SeitenGroup 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeKitz T AnasarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDokument16 SeitenSubarachnoid HemorrhageErika NaingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0828 Introduction and Cellular InjuryDokument74 Seiten0828 Introduction and Cellular Injury李宜芳Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atherosclerosis PresentationDokument90 SeitenAtherosclerosis PresentationAbu SaifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System (S.S)Dokument112 SeitenNervous System (S.S)Suman ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- GMS Thyroid Lect 2011Dokument43 SeitenGMS Thyroid Lect 2011Scott YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia - Ontologies - LabDokument6 SeitenAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia - Ontologies - LabAnusha SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple MyelomaDokument20 SeitenMultiple Myelomaasim badarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Anemia Part2Dokument6 SeitenTypes of Anemia Part2April Mae Magos LabradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ttmik Level 1Dokument80 SeitenTtmik Level 1peterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument27 SeitenDrugspeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level 2 Lesson 1: Future TenseDokument3 SeitenLevel 2 Lesson 1: Future Tensedomon46Noch keine Bewertungen
- TyphoidDokument10 SeitenTyphoidpeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smoking Cessation ProgramDokument5 SeitenSmoking Cessation ProgrampeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntroductionDokument12 SeitenIntroductionpeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Tuberculosis Control ProgramDokument3 SeitenNational Tuberculosis Control ProgrampeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance To Be Paid: First Week of August 2012Dokument1 SeiteBalance To Be Paid: First Week of August 2012peterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis of Typhoid FeverDokument5 SeitenDiagnosis of Typhoid FeverpeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- TyphoidDokument3 SeitenTyphoidpeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument27 SeitenDrugspeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument9 SeitenNCPpeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Smoking CampaignDokument3 SeitenAnti Smoking CampaignpeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Smoking CampaignDokument3 SeitenAnti Smoking CampaignpeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Lung CancerDokument9 SeitenWhat Is Lung CancerpeterjongNoch keine Bewertungen