Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ramin Shamshiri Risk Analysis Exam2 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Redmond R. ShamshiriOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ramin Shamshiri Risk Analysis Exam2 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Redmond R. ShamshiriCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Page 1 of 8 EMM5622, RISK ANALYSIS IN ENGINEERING EXAM II
Ramin Shamshiri
Ramin Shamshiri
EMM5622, EXAM II
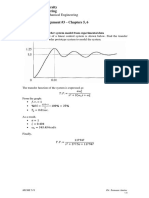
Page 2 of 8 Question 1 A project schedule network has two paths of tasks needed to compute the total time to complete the project. They are either or as shown by the following time functions
Compute the probability of (
) by calculating the reliability index ( ) using
a. First-order reliability method b. Advanced second-moment method The noncorrelated random variables are assumed to have the following probabilistic characteristics:
Random Variable Mean Value Coefficient of Variation Distribution Type
1 5 4 3 10
0.25 0. 50 0.05 0.20 0.25
Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal
Solution a:
( (
) )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
Coefficient of Variation:
( ( ( ( ( Also ; ( )
)( ) )( ) )( ) )( ) )( ( ) ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
Ramin Shamshiri
EMM5622, EXAM II
Page 3 of 8
It can be seen than
Random Variable
Mean Value
Coefficient of Variation
Standard Deviation
1 5 4 3 10
0.25 0. 50 0.05 0.20 0.25
0.25 2.5 0.2 0.6 2.5
Ramin Shamshiri
EMM5622, EXAM II
Page 4 of 8 Solution b:
) (
Solving Solving Random Variable
( ) ( )
Mean Value
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
yields yields
Standard Deviation Directional Cosines for T1 ( ) Directional Cosines for T2 ( )
Coefficient of Variation
1 5 4 3 10 ( ( ( (
0.25 0. 50 0.05 0.20 0.25 )( )( )( )) ( )( )( )( (
0.25 2.5 0.2 0.6 2.5 ) ) ) )( )(
0.09919 0.697139 0.079352 0.9919 0.167313 0.697139
)(
)(
))
)(
)(
))
5.951394
( ( ( (
)( )( )( )) (
)( )( )( (
) ) ) )( )( )) ( ( )( )( ))
)(
)(
5.019404
It can be seen than
Ramin Shamshiri
EMM5622, EXAM II
Page 5 of 8 Question 2 Describe four engineering systems that can be modeled using the black-box method. What are the inputs and outputs for each system? Solution: Input X SYSTEM Output Y
A schematic of the black-box system model is shown in the above figure. A structural engineer might observe the deflection of a bridge as an output of a input such as load at the middle of its span. By varying the intensity of the load, the deflection chances, hence by producing a relationship such as y=f(x) where x is an input variable, y is an input variable and f is a function that relates input to output. Example 1: Probable maximum load Input: Meteorological and Hydrological conditions Output: Flood runoff System: River Catchment Basin Example 2: Greenhouse Environmental Control Input: Heating and cooling load System: Relevant actuators Output: Environment temperature and relative humidity
Example 3: DC motor speed control Input: Variable voltage to the system Output: Speed of the motor shaft in rpm System: DC motor Example 4: Vehicle Input: Amount of gas provided to the engine Output: Speed or performance of the vehicle System: Engine and other components
Ramin Shamshiri
EMM5622, EXAM II
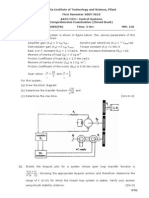
Page 6 of 8 Question 3 An engineer inspects a piece of equipment and estimates the probability of the equipment running at peak efficiency to be 80%. She/he then receives a report that the operating temperature of the machine has exceeded an 80C critical level. Past records of operating performance suggest that the probability of exceeding the 80C temperature when the machine is working at peak efficiency is 0.4. Also, the probability of the temperature being exceeded if the machine is not working at peak efficiency is 0.85. a. Revise the engineers initial probability estimate based on this additional information from past records b. Draw a probability tree for this situation Solution a: Event A: Exceeding 80C Event B: Running at peak efficiency ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) => ( ) => ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ( ) ( ) ) ) has occurred
Posterior probability of variables B after variable ( ( )
( )
) ( ) ( ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ) ( )
Total= ( ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ) ( )
Total= (
Ramin Shamshiri
EMM5622, EXAM II
Page 7 of 8 Solution b:
Ramin Shamshiri
EMM5622, EXAM II
Page 8 of 8 Question 4 Using the data of example 4.21 as provided in Table 4.23 (from the textbook), and assuming five identical components connected in series, compute ( ) ( ), and ( ) function for a system in series. The component hazard function is given by the following equation:
( ) Solution: ( ) ( ) ( )
Ramin Shamshiri
EMM5622, EXAM II
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignVon EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Islamabad Campus Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDokument3 SeitenIslamabad Campus Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringLabeeb KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedback Control Systems: Dr. Basil Hamed Electrical Engineering Islamic University of GazaDokument43 SeitenFeedback Control Systems: Dr. Basil Hamed Electrical Engineering Islamic University of GazaSalmaanCadeXaajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual - EEE 402 - Exp01 July2014Dokument7 SeitenLab Manual - EEE 402 - Exp01 July2014AhammadSifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aim of The Experiment: System Identification of DC Motor Using Matlab/Labview. Equipments RequiredDokument10 SeitenAim of The Experiment: System Identification of DC Motor Using Matlab/Labview. Equipments Requiredpriyatosh dashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Lab All Exp and Reports in Single PDF (Abdullah Ibn Mahmud) PDFDokument183 SeitenControl Lab All Exp and Reports in Single PDF (Abdullah Ibn Mahmud) PDFShakil Ahmed100% (1)
- Control Lab All Exp and Reports in Single PDF (Abdullah Ibn Mahmud)Dokument183 SeitenControl Lab All Exp and Reports in Single PDF (Abdullah Ibn Mahmud)Anik PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna Azimuth Position Control System Modelling, AnalysisDokument30 SeitenAntenna Azimuth Position Control System Modelling, AnalysisMbongeni Maxwell100% (3)
- 8 EE5 CBPS LabDokument68 Seiten8 EE5 CBPS Labkuldeep singh50% (2)
- Gandhinagar Institute of Technology: Question BankDokument5 SeitenGandhinagar Institute of Technology: Question BankvineetanishadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenAssignment 3 - SolutionsHussein BasmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab:05 Transient Analysis of First Order Systems: ObjectiveDokument3 SeitenLab:05 Transient Analysis of First Order Systems: ObjectiveTajdar HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A02503 Control SystemsDokument4 Seiten9A02503 Control SystemssivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Stability Analysis and Enhancement of Ieee-9 Bus SystemDokument11 SeitenTransient Stability Analysis and Enhancement of Ieee-9 Bus SystemNirmal mehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RegelTechniek1 2014Dokument3 SeitenRegelTechniek1 2014John AppleseedNoch keine Bewertungen
- UFMFV7-15-2 Control (2017 November)Dokument6 SeitenUFMFV7-15-2 Control (2017 November)Nuwan AsankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 5Dokument6 SeitenProblem Set 5PeaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp01 EEE318Dokument7 SeitenExp01 EEE318Abid AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC602 Control Q Bank 2023Dokument9 SeitenEC602 Control Q Bank 2023ROHAN CHOWDHURYNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENG3104 Assignment3Dokument8 SeitenENG3104 Assignment3Nayim MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Machine DriveDokument15 SeitenDC Machine DriveMridul MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiments - RC Circuit Sheet PDFDokument5 SeitenExperiments - RC Circuit Sheet PDFĂkŕăm LôKâNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Problem 4Dokument12 SeitenMachine Problem 4JERUELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Speed 1Dokument22 SeitenMotor Speed 1Narciso VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptive Control Theory: Model Reference Adaptive SystemsDokument16 SeitenAdaptive Control Theory: Model Reference Adaptive SystemsThanh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 1 SolutionDokument8 SeitenExam 1 SolutionAdam Moody0% (1)
- Lab 2: Quanser Hardware and Proportional Control: I. ObjectiveDokument7 SeitenLab 2: Quanser Hardware and Proportional Control: I. ObjectiveAndré LeopoldinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techteach - No Simview DC Motor IndexDokument3 SeitenTechteach - No Simview DC Motor IndexDiabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code: 55336: B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOV./DEC. 2011 Regulations 2008Dokument4 SeitenQuestion Paper Code: 55336: B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, NOV./DEC. 2011 Regulations 2008Sarika VadivelanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robust Iterative PID Controller Based On Linear Matrix Inequality For A Sample Power SystemDokument9 SeitenRobust Iterative PID Controller Based On Linear Matrix Inequality For A Sample Power Systemsjo05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concentration Changes in A CSTR (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor)Dokument10 SeitenConcentration Changes in A CSTR (Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor)pekanselandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Unit 6 1Dokument7 SeitenMCQ Unit 6 1gsg682205Noch keine Bewertungen
- IES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Dokument28 SeitenIES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Srujan BobbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC6405-Control Systems EngineeringDokument12 SeitenEC6405-Control Systems EngineeringAnonymous XhmybK0% (1)
- HW 5Dokument2 SeitenHW 5Mahir MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 ControlDokument3 Seiten2008 ControlPujan NarjinaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9) Submissions Will Close at 9am On Tuesday, 19Th January 2021Dokument3 Seiten9) Submissions Will Close at 9am On Tuesday, 19Th January 2021Thembelihle HadebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A19401 Contol SystemsDokument7 Seiten9A19401 Contol SystemssivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bekc3643 - Control System Engineering: SEM 1 - 2021/2022 Assignment (15%)Dokument3 SeitenBekc3643 - Control System Engineering: SEM 1 - 2021/2022 Assignment (15%)Hui ShanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSR 1Dokument11 SeitenPSR 1Poornima TadikondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 06Dokument7 SeitenLab 06Andy MeyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives:: Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenObjectives:: Lab Reportraheel buttNoch keine Bewertungen
- MST Nov12Dokument2 SeitenMST Nov12aaditya24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Problem Matlab Project TFDokument19 SeitenDesign Problem Matlab Project TFhumayun azizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controls Infosheet and Sample Problems 0Dokument11 SeitenControls Infosheet and Sample Problems 0Md Nur-A-Adam DonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SystemDokument4 SeitenControl Systemsumanta.kundu318020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aaoc C321 642 C 2009 1Dokument2 SeitenAaoc C321 642 C 2009 1Tushar GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 402 Exp1Dokument5 SeitenEEE 402 Exp1Sunil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR 2303Dokument4 SeitenPR 2303Karthik Srinivas0% (1)
- AAOC C321 Control Systems Compre PaperDokument5 SeitenAAOC C321 Control Systems Compre PaperTushar GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDPN372 PS4 Spring 2021Dokument5 SeitenMDPN372 PS4 Spring 2021akhbar elyoum academyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument24 SeitenPDFOlga Joy Labajo GerastaNoch keine Bewertungen
- l24 PDFDokument27 Seitenl24 PDFAshok KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- (FL Challenge C8) M Frequency Domain Response: AtlabDokument6 Seiten(FL Challenge C8) M Frequency Domain Response: AtlabCent SecurityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme - I Sample Question PaperDokument4 SeitenScheme - I Sample Question PaperYogesh ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Question Paper Sixth Semester B.Tech Electrical and Electronics Engineering Ee 010 603 Control SystemsDokument2 SeitenModel Question Paper Sixth Semester B.Tech Electrical and Electronics Engineering Ee 010 603 Control SystemsBaisil K BabyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IES - Electronics Engineering - Control System PDFDokument66 SeitenIES - Electronics Engineering - Control System PDFRod S Pangantihon Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods for Simulation and Optimization of Piecewise Deterministic Markov Processes: Application to ReliabilityVon EverandNumerical Methods for Simulation and Optimization of Piecewise Deterministic Markov Processes: Application to ReliabilityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soft Computing in the Design and Manufacturing of Composite Materials: Applications to Brake Friction and Thermoset Matrix CompositesVon EverandSoft Computing in the Design and Manufacturing of Composite Materials: Applications to Brake Friction and Thermoset Matrix CompositesNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Presentation By: Ramin Shamshiri: PH.D Candidate, Ag & Bio Engineering University of FloridaDokument41 SeitenA Presentation By: Ramin Shamshiri: PH.D Candidate, Ag & Bio Engineering University of FloridaRedmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA6166 HW6 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionDokument18 SeitenSTA6166 HW6 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionRedmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Recycle Materials For Sustainable Design of Interior SpacesDokument15 SeitenThe Role of Recycle Materials For Sustainable Design of Interior SpacesRedmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning and Eural EtworkDokument21 SeitenMachine Learning and Eural EtworkRedmond R. Shamshiri100% (1)
- STA6166 HW1 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionDokument9 SeitenSTA6166 HW1 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionRedmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA6166 HW2 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionDokument14 SeitenSTA6166 HW2 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionRedmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam: STA 6166, Section 8489, Fall 2007Dokument8 SeitenFinal Exam: STA 6166, Section 8489, Fall 2007Redmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA6167 Project 3 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionDokument12 SeitenSTA6167 Project 3 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionRedmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA6167 Project 2 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionDokument10 SeitenSTA6167 Project 2 Ramin Shamshiri SolutionRedmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA5328 Ramin Shamshiri HW3Dokument6 SeitenSTA5328 Ramin Shamshiri HW3Redmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA 5325 HW 3 Ramin ShamshiriDokument20 SeitenSTA 5325 HW 3 Ramin ShamshiriRedmond R. Shamshiri93% (15)
- STA 5325 HW 1 Ramin ShamshiriDokument13 SeitenSTA 5325 HW 1 Ramin ShamshiriRedmond R. Shamshiri100% (2)
- Optimal Control Exam1Dokument5 SeitenOptimal Control Exam1Redmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimal Control Exam1Dokument5 SeitenOptimal Control Exam1Redmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- TakeHome Exam2 PDFDokument6 SeitenTakeHome Exam2 PDFRedmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- EML 6934, Spring 2010 Instructor: Dr. W. Dixon Exam #3: UFID#: 9021-3353Dokument11 SeitenEML 6934, Spring 2010 Instructor: Dr. W. Dixon Exam #3: UFID#: 9021-3353Redmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be & Ca PDFDokument45 SeitenBe & Ca PDFRonimack Trajano de SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Cleveland Ruth 1997 PDFDokument21 Seiten01 Cleveland Ruth 1997 PDFMarianne Zanon ZotinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beyond The Pole-Barn Paradox (Paper 64) PDFDokument7 SeitenBeyond The Pole-Barn Paradox (Paper 64) PDFSambit PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report TextDokument2 SeitenReport Textsusila10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kanako Detailed ManualDokument74 SeitenKanako Detailed ManualastikaprasiddhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Stub For Transmission Line TowersDokument26 SeitenDesign of Stub For Transmission Line Towersdebjyoti_das_685% (13)
- 12V 24V Boost Converter PDFDokument5 Seiten12V 24V Boost Converter PDFIonescu ViorelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PADT TheFocus 35 PDFDokument18 SeitenPADT TheFocus 35 PDFDipak BorsaikiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Bolted Beam Splice Connections According To EC3Dokument11 SeitenDesign of Bolted Beam Splice Connections According To EC3Franklyn Genove100% (2)
- Seminar On Wireless Charging of Mobile DevicesDokument24 SeitenSeminar On Wireless Charging of Mobile DevicesGourish Amonkar100% (1)
- Manual PT90Dokument68 SeitenManual PT90Youssef Sarkis MobarakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration Atmospheric Stability CFD Modeling MeteodynWT For Wind Resource Assessment AEP Validation Real Case Wind FarmDokument1 SeiteIntegration Atmospheric Stability CFD Modeling MeteodynWT For Wind Resource Assessment AEP Validation Real Case Wind FarmMeteodyn_EnergyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 171001Dokument2 Seiten171001vishalsanziraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification and Identification of Soils For General Engineering PurposesDokument10 SeitenClassification and Identification of Soils For General Engineering PurposesAmarendra KeerthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dvp-Es2 Ss2 Sa2 Sx2-Program o en 20110302Dokument14 SeitenDvp-Es2 Ss2 Sa2 Sx2-Program o en 20110302yasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines On Good Laboratory Practice in Pesticide Residue Analysis CAC/GL 40-1993 ContentDokument36 SeitenGuidelines On Good Laboratory Practice in Pesticide Residue Analysis CAC/GL 40-1993 ContentVishal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aeroelastic Tailoring-Theory, Practice, and PromiseDokument13 SeitenAeroelastic Tailoring-Theory, Practice, and Promiservramkumar78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sulpiride MonographieDokument3 SeitenSulpiride MonographieMohamed DahmaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Science: Classification of PedologyDokument24 SeitenSoil Science: Classification of Pedologyekush amar100% (1)
- ELE615 Semiconductor Fabrication Technology: Mini ProjectDokument36 SeitenELE615 Semiconductor Fabrication Technology: Mini ProjectAmir HsmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Chemistry Basic ConceptsDokument12 SeitenAnalytical Chemistry Basic ConceptsNino Jay FabrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demand FactorDokument17 SeitenDemand Factorkatiki216100% (1)
- MDOT Research Report NMB Splice PDFDokument74 SeitenMDOT Research Report NMB Splice PDFRajnikanth GedhadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Process Model For EAF Steelmaking: NtroductionDokument9 SeitenA Process Model For EAF Steelmaking: NtroductionacetilenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fesc 115Dokument8 SeitenFesc 115Sundeep GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental and Theoretical Study of Pool BoilingDokument11 SeitenExperimental and Theoretical Study of Pool Boilingvaibhav pawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safty Switch 3TK2825Dokument46 SeitenSafty Switch 3TK2825Amir KeikavoosnejadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - Curves in Space and Their TangentDokument38 SeitenLecture 3 - Curves in Space and Their TangentNURUL YAHSIFAH SYQELLA BINTI YAHYA BK21110100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Swd-Csa-A23.3-04 (Etabs2013)Dokument81 SeitenSwd-Csa-A23.3-04 (Etabs2013)BJERNoch keine Bewertungen