Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter3 - Ideal Gas
Hochgeladen von
Shafiq HafizullahCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter3 - Ideal Gas
Hochgeladen von
Shafiq HafizullahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances
Duty, Honor and Integrity
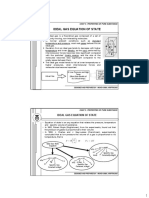
Interpolation Method (kaedah tentu dalaman)
if required data is in between 2 given data. Using linear function y=f(x) Properties 1 Example: x1
Properties 2
y1 yt
(yt y1) (xt x1) (y2 y1) = (x2 x1)
(xt x1) yt = (x2 x1) (y2 y1) + y1
xt
x2
y2
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
What is gas?
gas molecules move about random, continually colliding with each other and the walls of container they are in.
Vgas Vcontainer gas Tgas, P
Properties which can compressible. ie oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen Pgas lower pressure Tgas higher temp. ( 2 time critical point)
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Differences between Fluids and gasses
A liquid will take the shape of its container but exhibits a free surface.
A gas will fill its container completely and does not exhibit a free surface.
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Ideal Gas (gas unggul)
a properties that can easily compressed in the gas phase. Such as nitrogen, oxygen & hydrogen
Note: oxygen - 164.4K Hydrogen 33.3K Nitrogen 126 K
Di anggap gas unggul pada suhu dan tekanan atmosphere.
Wap air >748 C pada tekanan rendah boleh di anggap sebagai gas unggul
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
The ideal gas equation of state
a state that related with pressure, temp., and specific volume of a substance.
pv
where
RT
kJ/kg
This implies: (1) very little molecular interaction (p <<0),and (2) molecules are point masses, i.e., zero volume.
v = V/m
where n no of molecular &
m = nM (kg)
M molecular weight
(1)
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
R - gas constant (pemalar gas tentu)
Universal gas constant
Molecular weight
Note: the ideal gas equation of state can be derived from basic principle if one assume i. ii. Intermolecular force are small Volume occupied by the particles is small
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Gas
Formula Kimia
Berat Molekul, M (kg/kmol)
Pemalar gas tentu R, (kJ/kgK)
Argon Helium Hidrogen Karbon dioksida Nitrogen Oksigen Udara Wap Air
A He H2 CO2 N2 O2 H2O
39.948 4.003 2.016 44.010 8.013 31.999 28.970 18.015
0.2081 2.0770 4.1242 0.1889 0.2968 0.2598 0.2870 0.4615
Jisim molekul dan pemalar gas tentu beberapa gas pada tekanan atmosfera dan suhu 23 C. Refer Table A-1 page 910.
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Is water vapor an ideal gas?
Answer cannot say Yes or No
Under pressure below 10kPa water vapor called ideal gas. However, at high pressure gas assumption yields unacceptable error, particularly at critical point and at saturated vapor line (over 100%). Example: air conditioning water vapor is treated as ideal gas since water vapor is very low.
But steam power plant involved higher pressure ideal gas relation should not be used.
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
FIGURE 2-49 Percentage of error involved in assuming steam to be an ideal gas, and the region where steam can be treated as an ideal gas with less than 1 percent error. 2-12
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Enthalpy of an ideal gas
pv u (T ) RT
h(T )
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Compressibility Factor
(Faktor kebolehmampatan)
-Ideal gas equation use to analysis simple and easy gas state and suitable to be used if the gas are at low density or at low pressure at high temperature.
-We also known that gases deviate from ideal-gas and have the problem to derive the limit of low density states and to interfered how far behaviors of the gases can go.
-To avoid the uncertain situation and to get the accurate measurements, the compressibility factor is introduced.
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Compressibility Factor
(Faktor kebolehmampatan) - Used to identify ideal gas behavior or a measure of deviation from gas behavior.
pv
Z pv RT
ZR T
Where if Z = 1 for ideal gas Z > 1 or Z < 1 for real gas
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
FIGURE 2-49 Percentage of error involved in assuming steam to be an ideal gas, and the region where steam can be treated as an ideal gas with less than 1 percent error. 2-12
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
To measure Z value, we need : 1. Generalized compressibility Factor Chart 2. Reduce pressure ratio Pr = P/Pcritical 3. Reduce temperature ratio Tr = T/Tcritical
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
2-13
FIGURE 2-51 Comparison of Z factors for various gases. Page 141
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Reduced pressure and temperature
Generalized Compressibility Chart
Z
Tr1 Tr2 Pr = P/Pcritical Tr = T/Tcritical
(14.6)
Pr
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Real Gases
Z
T1 T2 T3
pv RT
1
Ideal Gas
T1 < T2 < T3
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
From the generalized compressibility chart, we can observed that:
low pressure PR < 1 ideal gas regardless of the temperature. High temperature TR > 2 good ideal gas behavior regardless of pressure. The deviation of a gas from the ideal gas behavior is greater in the vicinity of the critical point.
Pseudo reduce specific volume
VR =
V actual RTcr / Pcr
Thermodynamics I (EMM2503) Chapter 3 Properties of Pure Substances (Ideal gas)
Duty, Honor and Integrity
Other equation of state
Van der waals equation of state Beattie-bridgeman equation of state Benedict-webb-rubin equation of state Virial equation of state.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsVon EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Ideal Gas Equation of StateDokument18 SeitenIdeal Gas Equation of StateAditya SuryawanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic Models for Chemical Engineering: Design, Develop, Analyse and OptimizeVon EverandThermodynamic Models for Chemical Engineering: Design, Develop, Analyse and OptimizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Exergy AnalysisDokument22 SeitenChapter 3: Exergy AnalysisAnamikaSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PV RT: Equations of StateDokument11 SeitenPV RT: Equations of StateJeff HardyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generalized CompressibilityDokument17 SeitenGeneralized CompressibilityappealmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry Establishes and Develops The: Pchem I 1.1Dokument26 SeitenPhysical Chemistry Establishes and Develops The: Pchem I 1.1Kaaya GodfreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 3 - TgaDokument7 SeitenExp 3 - TgailknurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3 Perfect Gas: Thermal Equation of StateDokument4 Seiten1.3 Perfect Gas: Thermal Equation of Statespeciala102Noch keine Bewertungen
- 03-ch3 2015 EngDokument77 Seiten03-ch3 2015 EngRyanKelinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PVT (Properties of Petroleum Fluids)Dokument32 SeitenPVT (Properties of Petroleum Fluids)Oscar Mauricio TellezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument10 SeitenChapter 1Shreyas ShenoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ideal Gas EquationDokument10 SeitenThe Ideal Gas EquationBilly Jake CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week4 - Chapter3-Ideal Gas ModelDokument28 SeitenWeek4 - Chapter3-Ideal Gas ModelNadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE1101 Aero 1Dokument54 SeitenAE1101 Aero 1KrasakKrusuk Si MaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Two-Temperature Thermodynamic and Transport Properties For Argon, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Air Plasmas at Atmospheric PressureDokument4 SeitenCalculation of Two-Temperature Thermodynamic and Transport Properties For Argon, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Air Plasmas at Atmospheric PressureSujay BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mol. Gas Const.Dokument4 SeitenMol. Gas Const.Shiju Kp.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument13 SeitenUnit 2pedro_erguetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 181 Chemistry of GasesDokument15 SeitenChem 181 Chemistry of GasesJoey PooleNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGSC 2333 - ThermodynamicsDokument47 SeitenENGSC 2333 - ThermodynamicsDan McNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Thermodynamics (Lecture#01) : Course OutlineDokument16 SeitenApplied Thermodynamics (Lecture#01) : Course Outlinevaratharajan g rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Reacting MixturesDokument6 SeitenNon Reacting MixturesLalo RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech Engineering 2 - BIS 154 - 2021.ppsxDokument36 SeitenMech Engineering 2 - BIS 154 - 2021.ppsxMohamed NadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGSC 2333 - ThermodynamicsDokument47 SeitenENGSC 2333 - ThermodynamicsPravallika KolliparaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cinetica 2 InglesDokument9 SeitenCinetica 2 InglesEdward GuevaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 GasesDokument17 Seiten11 Gasespuja ritongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14: The Behavior of GasesDokument3 SeitenChapter 14: The Behavior of GasesKM10 khalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clouds: Stephan de Roode September 7, 2004Dokument84 SeitenClouds: Stephan de Roode September 7, 2004Dardo Melgar RocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Some Experimental Parameters On TPR ProfilesDokument5 SeitenEffect of Some Experimental Parameters On TPR ProfilesJoaquim Paulo SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument35 SeitenModule 1Shinichi KudoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo 1Dokument20 SeitenThermo 1MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics and Its Applications CompressDokument29 SeitenThermodynamics and Its Applications Compress莊凱軒Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compressor Handbook 2Dokument7 SeitenCompressor Handbook 2mssj87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problems and SolutionsDokument37 SeitenProblems and Solutionsalfrinjarj100% (2)
- Heat Sink Shape and Topology Optimization With Pareto-Vector Length Optimization For Air CoolingDokument15 SeitenHeat Sink Shape and Topology Optimization With Pareto-Vector Length Optimization For Air CoolingRameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2 Ideal Gas Law: Example 2.1 Desity of AirDokument2 Seiten2.2 Ideal Gas Law: Example 2.1 Desity of AirFlorian_AngererNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fa19 Che 020 Thermo (Assignment)Dokument5 SeitenFa19 Che 020 Thermo (Assignment)Minahil AzeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics 1 LectureDokument57 SeitenThermodynamics 1 LecturefabyunaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics 1 LectureDokument57 SeitenThermodynamics 1 LecturefabyunaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gases and The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryDokument54 SeitenGases and The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryCassey ToyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics I Ch3 - NSDokument63 SeitenThermodynamics I Ch3 - NSHassan AzouzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 1 Introduction To Chemical Engg and ThermoDokument10 SeitenLecture - 1 Introduction To Chemical Engg and ThermoShahnawaz AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 303 CH11Dokument45 SeitenMe 303 CH11Osman KutluNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHA 390 Sec 2 ReadyDokument13 SeitenCHA 390 Sec 2 Readymajoxa9560Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Mixtures Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDokument21 SeitenGas Mixtures Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDon HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ideal Gas Equation of StateDokument18 SeitenIdeal Gas Equation of StateOssama BohamdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reacting FoamDokument8 SeitenReacting FoamLuis F. RuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.reservoir Engineering Notes K PDFDokument116 Seiten1.reservoir Engineering Notes K PDFAzaru deen100% (1)
- 1 23 Gas Calculations PDFDokument6 Seiten1 23 Gas Calculations PDFschool adressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - 102MAE ThermofluidsDokument21 SeitenLecture 2 - 102MAE ThermofluidsNafiz Uddin NihalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Kathmandu UniversityDokument38 SeitenIntroduction of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Kathmandu UniversityUrgen TamangNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 203 021 HW 2 SolDokument4 SeitenME 203 021 HW 2 SoleasllerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.23 Gas Calculations: Molar Gas Volume (OCR +EDEXCEL)Dokument7 Seiten1.23 Gas Calculations: Molar Gas Volume (OCR +EDEXCEL)SunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscosity and Thermal Conductivity Equations For N, O, Ar and AirDokument49 SeitenViscosity and Thermal Conductivity Equations For N, O, Ar and Airagbas20026896Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kmk20003 (Chapter 2) Week 3Dokument18 SeitenKmk20003 (Chapter 2) Week 3mr bentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic Theory of Gases Worked ExamplesDokument15 SeitenKinetic Theory of Gases Worked Exampleskiwandaemmanuel21Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Conflict Between 1st and 2nd Law of ThermodynamicsDokument1 SeiteThe Conflict Between 1st and 2nd Law of ThermodynamicsRavi KasaudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 411 Prelim Module 1 - Review of Basic Thermodynamics PDFDokument15 SeitenAE 411 Prelim Module 1 - Review of Basic Thermodynamics PDFKen OracioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument40 SeitenChapter 1Hà Giang NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walkin App Lnform My S Dec 17Dokument2 SeitenWalkin App Lnform My S Dec 17Shafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assimen Tronic 2Dokument23 SeitenAssimen Tronic 2Shafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eel1166 CK1Dokument11 SeitenEel1166 CK1Shafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternating Current CircuitsDokument8 SeitenAlternating Current CircuitsShafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument44 SeitenChapter 2Shafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- When Worlds Collide - The Rise of Social Media For Professional and Personal UseDokument25 SeitenWhen Worlds Collide - The Rise of Social Media For Professional and Personal UseShafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument16 SeitenChapter 5Shafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch03 - The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDokument40 SeitenCh03 - The Structure of Crystalline SolidsShafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Practice Problems SolutionsDokument8 SeitenChapter 5 Practice Problems SolutionsShafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy, Work and Heat: (Tenaga, Kerja & Haba)Dokument63 SeitenEnergy, Work and Heat: (Tenaga, Kerja & Haba)Shafiq HafizullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry Practice Booklet-1Dokument65 SeitenInorganic Chemistry Practice Booklet-1godlanshul32Noch keine Bewertungen
- Controlled Polymers For Pigment DispersantsDokument9 SeitenControlled Polymers For Pigment Dispersantstrường phạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kolgunda Gerumara Main Road To Mahuvatnahalli Harijana ColonyDokument36 SeitenKolgunda Gerumara Main Road To Mahuvatnahalli Harijana ColonyANIL KUMAR H CNoch keine Bewertungen
- 200319-Final Exam - Machine DesignDokument2 Seiten200319-Final Exam - Machine DesignJoseph RefuerzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROAD DATA 18.11.2016 Uranipuram PDFDokument99 SeitenROAD DATA 18.11.2016 Uranipuram PDFHRS REGIONAL LAB TANJAVURNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm C 1202-97Dokument6 SeitenAstm C 1202-97Vasco Sorte100% (1)
- MTPDF4 - Module 4 Main PDF LessonDokument35 SeitenMTPDF4 - Module 4 Main PDF LessonEunnicePanaliganNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDT Method SummaryDokument3 SeitenNDT Method SummaryNguyen Anh TungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ok 83.28Dokument1 SeiteOk 83.28joe_frangiehNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Golden Book of Chemistry ExperimentsDokument114 SeitenThe Golden Book of Chemistry ExperimentsT4urus-VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deewane: IES & GATE: Material ScienceDokument33 SeitenDeewane: IES & GATE: Material ScienceMayank SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete ClothDokument20 SeitenConcrete ClothShrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enclosure 3512BDokument6 SeitenEnclosure 3512BaguswNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pengaruh Lingkungan Minyak Mentah Terhadap Laju Korosi Pada Pipa Baja Karbon Dan Pipa GalvanisDokument4 SeitenPengaruh Lingkungan Minyak Mentah Terhadap Laju Korosi Pada Pipa Baja Karbon Dan Pipa GalvanisafifahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulare Systems For Conveyor PlantsDokument36 SeitenModulare Systems For Conveyor Plantsado31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qa/Qc Department: ICOM QC Inspector Client QC Inspector Name Signature DateDokument2 SeitenQa/Qc Department: ICOM QC Inspector Client QC Inspector Name Signature Dategopi krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry by PMS: OF Co-Ordination CompoundsDokument15 SeitenInorganic Chemistry by PMS: OF Co-Ordination CompoundsKumar AzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energiron Book 2014 PDFDokument52 SeitenEnergiron Book 2014 PDFNasim100% (2)
- Question:-Piping QuestionsDokument4 SeitenQuestion:-Piping Questionsaimri_cochinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technological Result of Decomposition Sodium Aluminate SolutionDokument10 SeitenTechnological Result of Decomposition Sodium Aluminate SolutionDragana Dragojlović SmiljanicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basf Masterseal Roof 3000 TdsDokument2 SeitenBasf Masterseal Roof 3000 TdsmidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asconium: Technical NoticeDokument14 SeitenAsconium: Technical NoticenanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubber JointDokument1 SeiteRubber JointAymen AyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Mix Design DOE PDFDokument15 SeitenConcrete Mix Design DOE PDFkarthiksamp100% (2)
- Jute Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive ReviewDokument21 SeitenJute Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive ReviewbiniyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packaging Code: GRM31BR73A222KW01 - (1206, X7R:EIA, 2200pF, DC1000V) Reference SheetDokument26 SeitenPackaging Code: GRM31BR73A222KW01 - (1206, X7R:EIA, 2200pF, DC1000V) Reference Sheetakshay rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001Dokument16 SeitenChapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001sunitbhaumikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clarkson - KGVDokument8 SeitenClarkson - KGVbloggerparthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDokument16 SeitenCambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationAnisahNoch keine Bewertungen