Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A1A Standards
Hochgeladen von
Stephanie ClareyCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A1A Standards
Hochgeladen von
Stephanie ClareyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
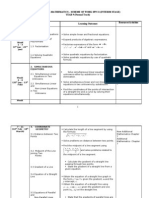
Elementary Algebra Standards
Standard EA-1: The student will understand and utilize the mathematical processes of problem solving, reasoning and proof, communication, connections, and representation. Indicators EA-1.1 EA-1.2 EA-1.3 EA-1.4 EA-1.5 EA-1.6 EA-1.7 Communicate a knowledge of algebraic relationships by using mathematical terminology appropriately. Connect algebra with other branches of mathematics. Apply algebraic methods to solve problems in real-world contexts. Judge the reasonableness of mathematical solutions. Demonstrate an understanding of algebraic relationships by using a variety of representations (including verbal, graphic, numerical, and symbolic). Understand how algebraic relationships can be represented in concrete models, pictorial models, and diagrams. Understand how to represent algebraic relationships by using tools such as handheld computing devices, spreadsheets, and computer algebra systems (CASs).
EA-3.8
Apply proportional reasoning to solve problems.
Standard EA-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the procedures for writing and solving linear equations and inequalities. Indicators EA-4.1 EA-4.2 EA-4.3 EA-4.4 EA-4.5 EA-4.6 EA-4.7 EA-4.8 EA-4.9 EA-4.10 Carry out a procedure to write an equation of a line with a given slope and a y-intercept. Carry out a procedure to write an equation of a line with a given slope passing through a given point. Carry out a procedure to write an equation of a line passing through two given points. Use a procedure to write an equation of a trend line from a given scatterplot. Analyze a scatterplot to make predictions. Represent linear equations in multiple forms (including pt.-slope, slope-intercept, and std). Carry out procedures to solve linear equations for one variable algebraically. Carry out procedures to solve linear inequalities for one variable algebraically and then to graph the solution. Carry out a procedure to solve systems of two linear equations graphically. Carry out a procedure to solve systems of two linear equations algebraically.
Standard EA-2:The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the real number system and operations involving exponents, matrices, and algebraic expressions. Indicators EA-2.1 EA-2.2 EA-2.3 EA-2.4 EA-2.5 EA-2.6 EA-2.7 EA-2.8 EA-2.9 EA-2.10 Exemplify elements of the real number system (including integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers). Apply the laws of exponents and roots to solve problems. Carry out a procedure to perform operations (including multiplication and division) with numbers written in scientific notation. Use dimensional analysis to convert units of measure within a system. Carry out a procedure using the properties of real numbers (including commutative, associative, and distributive) to simplify expressions. Carry out a procedure to evaluate an expression by substituting a value for the variable. Carry out a procedure (including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division by a monomial) to simplify polynomial expressions. Carry out a procedure to factor binomials, trinomials, and polynomials by using various techniques (including the greatest common factor, the difference between two squares, and quadratic trinomials). Carry out a procedure to perform operations with matrices (including addition, subtraction, and scalar multiplication). Represent applied problems by using matrices.
Standard EA-5: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the graphs and characteristics of linear equations and inequalities. Indicators EA-5.1 EA-5.2 EA-5.3 EA-5.4 EA-5.5 EA-5.6 EA-5.7 EA-5.8 EA-5.9 EA-5.10 EA-5.11 EA-5.12 Carry out a procedure to graph a line when given the equation of the line. Analyze the effects of changes in the slope, m, and the y-intercept, b, on the graph of y = mx + b. Carry out a procedure to graph the line with a given slope and a y-intercept. Carry out a procedure to graph the line with a given slope passing through a given point. Carry out a procedure to determine the x-intercept and y-intercept of lines from data given tabularly, graphically, symbolically, and verbally. Carry out a procedure to determine the slope of a line from data given tabularly, graphically, symbolically, and verbally. Apply the concept of slope as a rate of change to solve problems. Analyze the equations of two lines to determine whether the lines are perpendicular or parallel. Analyze given information to write a linear function that models a given problem situation. Analyze given information to determine the domain and range of a linear function in a problem situation. Analyze given information to write a system of linear equations that models a given problem situation. Analyze given information to write a linear inequality in one variable that models a given problem situation.
Standard EA-3: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of relationships and functions. Indicators EA-3.1 EA-3.2 EA-3.3 EA-3.4 EA-3.5 Classify a relationship as being either a function or not a function when given data as a table, set of ordered pairs, or graph. Use function notation to represent functional relationships. Carry out a procedure to evaluate a function for a given element in the domain. Analyze the graph of a continuous function to determine the domain and range of the function. Carry out a procedure to graph parent functions (including
Standard EA-6: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of quadratic relationships and functions. Indicators EA-6.1 EA-6.2 EA-6.3 EA-6.4 EA-6.5 EA-6.6 Analyze the effects of changing the leading coefficient a on the graph of
2
y = ax 2 .
y = x, y = x 2 , y =
EA-3.6 EA-3.7
x , y = x , and y =
1 x
).
Classify a variation as either direct or inverse. Carry out a procedure to solve literal equations for a specified variable.
Analyze the effects of changing the constant c on the graph of y . = x+ c Analyze the graph of a quadratic function to determine its equation. Carry out a procedure to solve quadratic equations by factoring. Carry out a graphic procedure to approximate the solutions of quadratic equations. Analyze given information to determine the domain of a quadratic function in a problem situation.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- LG LFX31945 Refrigerator Service Manual MFL62188076 - Signature2 Brand DID PDFDokument95 SeitenLG LFX31945 Refrigerator Service Manual MFL62188076 - Signature2 Brand DID PDFplasmapete71% (7)
- Algebra 2 Curriculum AlignmentDokument43 SeitenAlgebra 2 Curriculum Alignmentapi-254765842Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Equations Unit PlanDokument10 SeitenSolving Equations Unit Planapi-253299522Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2013-2014 Algebra 1 Concept ListDokument2 Seiten2013-2014 Algebra 1 Concept ListLisa HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eccentric FootingDokument3 SeitenEccentric FootingVarunn VelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alg 2 Math Correlations 2010Dokument6 SeitenAlg 2 Math Correlations 2010Harish MulevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mccrs-Compacted Math 8Dokument7 SeitenMccrs-Compacted Math 8api-318685719Noch keine Bewertungen
- Overland TrailDokument8 SeitenOverland Trailapi-245623862Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Grade CcssDokument1 Seite8th Grade Ccssapi-237059911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation On Transformations of GraphsDokument7 SeitenInvestigation On Transformations of Graphsted exNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 Math AlgebraiDokument7 Seiten2006 Math AlgebraitashcroxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Map Math 3-8 Blueprint Interpretive GuideDokument6 SeitenMap Math 3-8 Blueprint Interpretive Guideapi-431340065Noch keine Bewertungen
- Growing Growing Growing Unit PlanDokument22 SeitenGrowing Growing Growing Unit Planapi-250461623100% (1)
- NC Math 1 2016-17Dokument7 SeitenNC Math 1 2016-17api-236042577Noch keine Bewertungen
- K-12 Math Crosswalks Algebra IDokument17 SeitenK-12 Math Crosswalks Algebra Iestabloid1169Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 MathxDokument5 SeitenGrade 8 Mathxapi-2542992270% (1)
- SCCCR AlgebraiDokument2 SeitenSCCCR Algebraiapi-269559470Noch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Khan Academy Correlation To Spring BoardDokument18 SeitenAlgebra Khan Academy Correlation To Spring Boardapi-293229664Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Map - Math8Dokument5 SeitenCurriculum Map - Math8api-242927075Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLD Algebra IDokument13 SeitenPLD Algebra Iapi-310256368Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Assignment Guide: Date Sectio N Objectives HomeworkDokument2 SeitenChapter 1 - Assignment Guide: Date Sectio N Objectives HomeworkNicole Booth HollandNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionDokument10 SeitenA Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionxcrunitccNoch keine Bewertungen
- CcssDokument5 SeitenCcssapi-237229475Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDokument6 Seiten8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardNoch keine Bewertungen
- FunctionsDokument44 SeitenFunctionsSudhakar Chollangi100% (1)
- End of Instruction - Algebra 1 Content Standards and ObjectivesDokument3 SeitenEnd of Instruction - Algebra 1 Content Standards and ObjectivesAhmet OzturkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 2 TEKS From TEADokument9 SeitenAlgebra 2 TEKS From TEAganesh8sundaresanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plank Algebra 1 Curriculum MapDokument5 SeitenPlank Algebra 1 Curriculum MapE. Ryan PlankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam Review GuideDokument4 SeitenMidterm Exam Review GuidexneoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLD Algebra IIDokument18 SeitenPLD Algebra IIapi-310256368Noch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra I Pacing Guides 2015-2016 1Dokument9 SeitenAlgebra I Pacing Guides 2015-2016 1api-252392763Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tnready Blueprint g6 MathDokument9 SeitenTnready Blueprint g6 Mathapi-282869532Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 3. EquationsDokument3.741 Seiten1 3. EquationsRoss HamiltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21-22 8th Grade Pacing (EnVision)Dokument4 Seiten21-22 8th Grade Pacing (EnVision)Greg WalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify Desired Results (Stage 1) Content StandardsDokument9 SeitenIdentify Desired Results (Stage 1) Content Standardsapi-283548263Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Describing FunctionsDokument12 SeitenModule 1 Describing FunctionsChris Jann Dale ManabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 1 StandardsDokument6 SeitenAlgebra 1 Standardsapi-306943671Noch keine Bewertungen
- Least Learned Most Essential Learning CompetenciesDokument2 SeitenLeast Learned Most Essential Learning CompetenciesNathaniel Artajo GalopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Least Learned Most Essential Learning CompetenciesDokument2 SeitenLeast Learned Most Essential Learning CompetenciesNathaniel Artajo GalopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 MathDokument12 Seiten8 Mathdestiny_eastepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standards-K-12 8th GradeDokument3 SeitenStandards-K-12 8th Gradeapi-296039056Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ccss 8Dokument3 SeitenCcss 8api-237676777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 2 Mid-Term - 2 - ReviewDokument5 SeitenAlgebra 2 Mid-Term - 2 - ReviewMohammed SaeedainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Math Curriculum MapDokument7 Seiten8th Math Curriculum Mapapi-261608473Noch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 2Dokument7 SeitenAlgebra 2api-262893996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ut3 ConceptsDokument2 SeitenUt3 Conceptsapi-261139685Noch keine Bewertungen
- Schaffert Unit Plan Linear EquationsDokument7 SeitenSchaffert Unit Plan Linear Equationsapi-284366080Noch keine Bewertungen
- Graphing Linear EquationsDokument12 SeitenGraphing Linear EquationsJen GoldschmidtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinate Algebra Unit 3Dokument8 SeitenCoordinate Algebra Unit 3crazymrstNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 11 Advanced Mathematics Assessment 2022Dokument12 SeitenYear 11 Advanced Mathematics Assessment 2022sumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional MathematicsDokument10 SeitenAdditional MathematicsAnonymous jqevOeP7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vergauwen Chapter 4 Unit PlanDokument6 SeitenVergauwen Chapter 4 Unit Planapi-284884626Noch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithmic Skills FinalDokument8 SeitenAlgorithmic Skills Finalapi-245023409Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 Physics SectionDokument44 SeitenForm 2 Physics Sectiongora.aleckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Equations From PatternsDokument7 SeitenWriting Equations From Patternsecho_meNoch keine Bewertungen
- PreCalculus Unit 1 PDFDokument48 SeitenPreCalculus Unit 1 PDFSundaram NatarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yr 9 Add Math Normal Track 2010Dokument9 SeitenYr 9 Add Math Normal Track 2010Lim Chee ChangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pure Mathematics AM 27: SyllabusDokument15 SeitenPure Mathematics AM 27: SyllabusAshley MorganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 8 (Module 2 Second Quarter)Dokument11 SeitenMathematics 8 (Module 2 Second Quarter)Selene AckermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integer Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementVon EverandInteger Optimization and its Computation in Emergency ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsVon EverandAlgebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puma PypDokument20 SeitenPuma PypPrashanshaBahetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyramid Type Plate Bending MachineDokument10 SeitenPyramid Type Plate Bending MachineAswin JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consecration of TalismansDokument5 SeitenConsecration of Talismansdancinggoat23100% (1)
- TIA Guidelines SingaporeDokument24 SeitenTIA Guidelines SingaporeTahmidSaanidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Pumping.: Squeeze PumpsDokument2 SeitenConcrete Pumping.: Squeeze PumpsALINDA BRIANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Documentation Report On School's Direction SettingDokument24 SeitenDocumentation Report On School's Direction SettingSheila May FielNoch keine Bewertungen
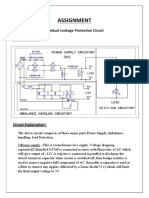
- Assignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramDokument2 SeitenAssignment: Residual Leakage Protection Circuit Circuit DiagramShivam ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Essence of Technology Is by No Means Anything TechnologicalDokument22 SeitenThe Essence of Technology Is by No Means Anything TechnologicalJerstine Airah SumadsadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscar Industrial Capacity LTD Company ProfileDokument36 SeitenViscar Industrial Capacity LTD Company ProfileTechnician MwangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- .CLP Delta - DVP-ES2 - EX2 - SS2 - SA2 - SX2 - SE&TP-Program - O - EN - 20130222 EDITADODokument782 Seiten.CLP Delta - DVP-ES2 - EX2 - SS2 - SA2 - SX2 - SE&TP-Program - O - EN - 20130222 EDITADOMarcelo JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustic Glass - ENDokument2 SeitenAcoustic Glass - ENpeterandreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wine TourismDokument9 SeitenWine Tourismyarashovanilufar1999Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Step Worksheet With QuestionsDokument26 Seiten12 Step Worksheet With QuestionsKristinDaigleNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTW Site Instruction NewDokument17 SeitenPTW Site Instruction NewAnonymous JtYvKt5XENoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnt NBR 16868 1 Alvenaria Estrutural ProjetoDokument77 SeitenAbnt NBR 16868 1 Alvenaria Estrutural ProjetoGIOVANNI BRUNO COELHO DE PAULANoch keine Bewertungen
- ABS Service Data SheetDokument32 SeitenABS Service Data SheetMansur TruckingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spanish Greeting Card Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenSpanish Greeting Card Lesson Planrobert_gentil4528Noch keine Bewertungen
- Core CompetenciesDokument3 SeitenCore Competenciesapi-521620733Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clustering Menggunakan Metode K-Means Untuk Menentukan Status Gizi BalitaDokument18 SeitenClustering Menggunakan Metode K-Means Untuk Menentukan Status Gizi BalitaAji LaksonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5620 SAM Rel 14 License Point Configuration ToolDokument416 Seiten5620 SAM Rel 14 License Point Configuration Toolluis100% (1)
- Strategic Management SlidesDokument150 SeitenStrategic Management SlidesIqra BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- solidworks ขั้นพื้นฐานDokument74 Seitensolidworks ขั้นพื้นฐานChonTicha'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Michael Clapis Cylinder BlocksDokument5 SeitenMichael Clapis Cylinder Blocksapi-734979884Noch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, KalavaiDokument31 SeitenDepartment of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, KalavaiGiri PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- WWW Ranker Com List Best-Isekai-Manga-Recommendations Ranker-AnimeDokument8 SeitenWWW Ranker Com List Best-Isekai-Manga-Recommendations Ranker-AnimeDestiny EasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis Kebutuhan Bahan Ajar Berbasis EDokument9 SeitenAnalisis Kebutuhan Bahan Ajar Berbasis ENur Hanisah AiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Ethics in Practice ShorterDokument79 SeitenEngineering Ethics in Practice ShorterPrashanta NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source:: APJMR-Socio-Economic-Impact-of-Business-Establishments - PDF (Lpubatangas - Edu.ph)Dokument2 SeitenSource:: APJMR-Socio-Economic-Impact-of-Business-Establishments - PDF (Lpubatangas - Edu.ph)Ian EncarnacionNoch keine Bewertungen