Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Case Study Near Drowning
Hochgeladen von
Nashwa FathiraCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Case Study Near Drowning
Hochgeladen von
Nashwa FathiraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Conclusion: Near Drowning Outline: Case Study
Outline: Case Study
Case Study: Case Study: Near Drowning
Near Drowning
RN, BScN
Annabelle Smith RN, BScN Annabelle Smith
Effects on surfactant key to treatment requirements and survival Initial hypothermia may be protective to CVS & neurological systems Water source importance debatable on Definition Near Drowning outcome results Presentation of our Amount of water & length in elements Pathophysiology more important
Review of case study Conclusion
Near Drowning
Aka submersion injury injury survival, at least temporarily after suffocation by submersion in a liquid medium medium wet wet near drowning - aspiration of fluid into lungs dry dry near drowning period of asphyxia secondary to laryngospasm
Near Drowning Syndrome
Depends on:
Duration of submersion Amount of fluid aspirated Severity of hypoxia
One tough little lady lady
Aboriginal, 73 year old female PMHX: DM2; HTN; Hypothyroidism PSHX: Cholecystectomy; Cholecystectomy; R knee replacement
Meds
ASA Amitriptyline Norvasc Lipitor Enalapril Glyburide Metformin Avandia L-thyroxine
One tough little lady lady
October 1 @ 1800 Hunting moose in the Island Lake water system, Northern Manitoba Fell out of canoe while trying to assist her group Submerged for unknown amount of time Son performed rescue breathing Walked over an hour to STP nursing station
@ STP nursing station
Initial vitals:
Pulse 74 Resp. rate 3030-40 Temperature 30 degrees C O2 satssats- unable due to temp Neuro: Neuro: intact EKGEKG- no acute changes; sinus rhythm C/S: crackles to bases; pink frothy sputum Projectile emesis RBS: 22.6
During Medivac Transfer
Frequent desaturations during flight c/o:
Generalized pain SOB Cough
Arrives @ HSC
T 34 P 84 BP 96/59 RR 32 O2 sats with 15L 92% GCS 15/15 Transferred to MICU
RR 53 BIPAP Resp crackles at bases
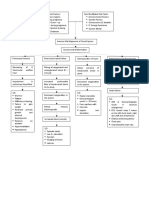
Pathophysiology
Drowning begins with:
Period of panic Loss of normal breathing pattern Breath holding Air hunger Struggle by victim to stay above water
Patient outcomes affected by:
Aspiration > 11 ml/kg of body weight weightbefore blood volume changes occur Aspiration > 22 ml/kg of body weight before electrolyte changes occur Initial treatment & time to treatment centre Temperature of water Length of submersion time Presence of contaminants Freshwater / saltwater different microorganisms
Patient outcomes affected by:
Gram negative bacteria in drowning victims more virulent Can cause immediate lethal sepsis or infections months after incident Strep or staph can also be present Fungus: incubation time 11-4 weeks to 6 months; often resistant
Near Drowning: Pulmonary Effects
Pulmonary insufficiency can develop insiduously or rapidly Leads to varying degrees of hypoxemia s/s: s/s:
SOB Rales Wheezing
CXR / CT: vary from normal to localized, perhilar, perhilar, or diffuse pulmonary edema
Causes of Hypoxemia
Reflex inspiratory effort Damage to surfactant Decreased lung compliance Ventilation perfusion mismatching Intrapulmonary shunting causes diffuse organ dysfunction
Near Drowning: Pulmonary Effects
Surface tension properties of surfactant affected Surfactant washed out out Water in alveoli
Damages type 2 pneumocytes Prevents production of new surfactant
Loss of surfactant function
Near Drowning: Pulmonary Effects Alveoli become unstable Complete/partial alveolar collapse collapse Loss of ventilation resulting in intrapulmonary shunting & hypoxemia
Near Drowning: Pulmonary Effects
Increased airway resistance secondary to:
Plugging of airway with debris Release of inflammatory mediators that result on vasoconstriction May impair gas exchange
Combination damage to alveolar capillaries & interstitium interstitium leads to ARDS
Near Drowning: Pulmonary Effects
ARDS: develops within 48 hours in approximately 40% of neardrowning victims
Hallmarks of ARDS: Decreased lung compliance Severe hypoxemia Bilateral infiltrates on CXR
Neurologic Effects
Hypoxemia & ischemia cause neuronal damage Can produce cerebral edema & elevation in ICP 20% sustain neurologic damage limits functional recovery
Recovery occurs in 80% of cases Only effective treatment is reversal of hypoxemia with mechanical ventilator support
Cardiovascular effects
Arrhythmias secondary to hypothermia & hypoxemia Sinus bradycardia & atrial fibrillation more common than ventricular fibrillation or asystole
Acid Base & Electrolytes
Metabolic & respiratory acidosis Significant electrolyte balances do not generally occur except those submerged in unusual media Dead Sea: extremely concentrated seawater leads to:
Hypernatremia Hypermagnesemia hypercalcemia
Renal Effects
Failure rarely occurs If it does does
Usually due to acute tubular necrosis
Back to our case study study
Respiratory complication:
Bipap Oct 2 4th ABG Oct 2:
7.41 / 33 / 92 / 21
Results from:
Hypoxemia Shock Hemoglobinuria Myoglobinuria
Pre intubation further decompensation: decompensation:
7.42 / 35 / 60 / 22 Sats: Sats: 88% with decrease to 20% during intubation attempts
CXR : bilateral edema
Case study cont contd
Required AC ventilation with paralysis
Fentanyl; Fentanyl; midazolam; midazolam; propofol; propofol; & rocuronium
CXR results
Oct 2: bibasilar pulmonary opacities with probable bilateral pleural effusions Oct 3: opacities predominate in mid/lower lungs; significant progression; pulmonary edema Oct 4: @ 08300830- no new changes; later in dayday- R sided effusion; intubated
AC : ARDS net protocol ventilation with trials of PSV for 8 days Hospital day 11: able to tolerate PSV ventilation Hospital day 14: transfer to Seven Oaks Hospital ICU
PSV 20; peep 14 ABG: pO2 76; sats 94
CXR results cont contd
Oct 5: worsening L base R/T pulm. pulm. Edema or ARDS Oct 6: extensive alveolar consolidation Oct 10: extensive bilateral opacities and consolidation; ARDS Oct 11: increasing degree of consolidation
Culture Reports
Oct 3: MSUMSU- >10*8 E. Coli Oct 4:
SPT - 3+ PMN; 4+ GPC; 3+ GPB; 1+ GNB ETT 4+ PMN; 1+ GPB; 2+ GPC; 1+ GNB
Positive ETT secretions: strep pneumonia & staph aureus Temp did not elevate; WBC elevated ABx: ABx: cefuroxime; cefuroxime; cefotaxime; cefotaxime; azithromycin; azithromycin; & vancomycin
Renal Function
Scanty urinary output throughout hospital stay Lasix used On transfer: fluid balance +ve : 17 L +ve: Creatinine rise to 85 (admission 67) No dialysis required Possible GI bleed (no source found)
Hgb drop to 68
CT abd: abd: normal CT brain: normal
Patient Patients final outcome outcome
Transferred out of Seven Oaks ICU to general ward
Conclusion: Near Drowning
Effects on surfactant key to treatment requirements and survival Initial hypothermia may be protective to CVS & neurological systems Importance of water source debatable in regards to treatment & patient outcome Amount of water & length in elements more important
Died November 15, 2007 due to persistent pulmonary issues
Be vigilant Be prepared Be vigilant . vigilant Be prepared just a matter of prepared Its It of time Its a mattertime time Appropriate, aggressive respiratory & Appropriate, multisystem support is the key aggressive respiratory & multisystem support is key
QUESTIONS ???
Questions???
Conclusion: Near Drowning
Effects on surfactant key to treatment requirements and survival Initial hypothermia may be protective to CVS & neurological systems Water source importance debatable on outcome results Amount of water & length in elements more important
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Near DrowningDokument53 SeitenNear DrowningDr. Anish GolchhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Near DrowningDokument15 SeitenNear DrowningshenysusantisinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Dokument4 SeitenNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drowning Statistics and Physiology: Understanding the Drowning ProcessDokument2 SeitenDrowning Statistics and Physiology: Understanding the Drowning ProcessAnonymous 0SYzMqje2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lumbar Compression FractureDokument47 SeitenLumbar Compression FractureAngelie Sanchez50% (2)
- Status AsthmaticusDokument6 SeitenStatus AsthmaticusMae Azores100% (1)
- Nontoxic Nodular GoiterDokument9 SeitenNontoxic Nodular GoiterKayshey Christine ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN The Child Undergoing Surgery For ScoliosisDokument3 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN The Child Undergoing Surgery For ScoliosisscrewdriverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care for Chest TraumaDokument100 SeitenNursing Care for Chest TraumaGabriel Liberon P. JazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spirometry findings in a 65-year old male with respiratory distressDokument5 SeitenSpirometry findings in a 65-year old male with respiratory distressAaron ConstantinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On Mild Compression Deformity L1Dokument25 SeitenA Case Study On Mild Compression Deformity L1JM UncianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Diseases Case Study 18 ADokument4 SeitenHuman Diseases Case Study 18 Aairickann100% (1)
- NCP For Rapid Shallow BreathingDokument1 SeiteNCP For Rapid Shallow Breathingbamboo2dNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPPDokument3 SeitenPPPJack BangcoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MI Case Study FinalDokument25 SeitenMI Case Study FinalAlmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Exacerbation of CopdDokument28 SeitenAcute Exacerbation of CopdMohd RafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmphysemaDokument3 SeitenEmphysemaKhalid Mahmud ArifinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 100 Case AnaDokument3 SeitenNCM 100 Case AnaCharissa Magistrado De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vii. NCPDokument4 SeitenVii. NCPmariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seizure PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenSeizure PathophysiologyqwertyuiopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leptospirosis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDokument6 SeitenLeptospirosis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsJackii DoronilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical-Surgical Nursing 3Dokument2 SeitenMedical-Surgical Nursing 3Charissa Magistrado De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Care in NursingDokument32 SeitenEmergency Care in NursingPauline Añes100% (1)
- Amoebiasis Case StudyDokument13 SeitenAmoebiasis Case StudymelvinpasionaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BFCDokument8 SeitenBFCIrene GunongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Charting PDFDokument2 SeitenSample Charting PDFjeffersonswallNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Focus Charting FDARDokument15 Seiten2019 Focus Charting FDARGrape JuiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- ER equipments & drugsDokument3 SeitenER equipments & drugsApple LlanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Contusion - WikipediaDokument15 SeitenPulmonary Contusion - WikipediaRony OktarizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study ObcsDokument41 SeitenCase Study ObcsKrischelle Abella Sabordo100% (1)
- Nursing MalpracticeDokument5 SeitenNursing MalpracticeKath SicatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular HealthDokument20 SeitenCardiovascular HealthChrrieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDokument8 SeitenImpaired Skin IntegrityMacmac ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology PneumoniaDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology PneumoniaJohnson MallibagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PasmaDokument1 SeitePasmaPersonnel PeacemakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Happ Lab 1Dokument5 SeitenHapp Lab 1Jerwin TullaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care for Measles and DiphtheriaDokument5 SeitenNursing Care for Measles and DiphtheriaChristian Eduard de DiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETDokument6 SeitenComplications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETRadiyan MeidhiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Balanced Skeletal TractionDokument6 SeitenApplication Balanced Skeletal TractionLorenz ChristopherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type and Indication of IV Therapy 2Dokument33 SeitenType and Indication of IV Therapy 2Ruth Jazelle MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance Skeletal TractionDokument3 SeitenBalance Skeletal TractionLourdes PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular DiseaseDokument37 SeitenHemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular Diseasejbvaldez100% (1)
- Case Presentation Meyke Liechandra C11109130 Fracture ClavicleDokument24 SeitenCase Presentation Meyke Liechandra C11109130 Fracture ClavicleWahyunita IlhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Burn Injury - 11Dokument15 SeitenCase Study Burn Injury - 11Evelyn MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetralogy of Fallot Pathophysiology & Risk FactorsDokument1 SeiteTetralogy of Fallot Pathophysiology & Risk FactorsEiztirfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation TetanusDokument15 SeitenCase Presentation TetanusukhtianitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uremic EncephalophatyDokument48 SeitenUremic EncephalophatySindi LadayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDokument39 SeitenAcute TonsillopharyngitisCin AtianzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Paper ERDokument1 SeiteReaction Paper ERVann Anthony FuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tension Pneumothorax: Modifiable FactorsDokument3 SeitenTension Pneumothorax: Modifiable FactorsJustin MaverickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greenstick Fracture Guide for StudentsDokument27 SeitenGreenstick Fracture Guide for Students3amabelle arevaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Left-Sided Heart FailureDokument3 SeitenLeft-Sided Heart FailureKhalid Mahmud ArifinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submersion Injuries: Diagnosis and ManagementDokument29 SeitenSubmersion Injuries: Diagnosis and ManagementRuDy RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 InfographicDokument2 SeitenWeek 1 InfographicHannah BangkilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDokument36 SeitenAcute Respiratory Distress Syndromedr9348345000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Urosepsis 1Dokument7 SeitenUrosepsis 1Anonymous Xajh4w100% (1)
- SOAPIE - Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Altered Heart RateDokument1 SeiteSOAPIE - Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Altered Heart RateKian Herrera100% (1)
- Management of ARDSDokument57 SeitenManagement of ARDSRajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypotension and Respiratory DistressDokument15 SeitenHypotension and Respiratory DistressEmily EresumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards) : Muamar Aldalaeen, RN, Mba, HCRM, Cic, Ipm, MSN, Phd. Haneen Alnuaimi, MSNDokument59 SeitenAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards) : Muamar Aldalaeen, RN, Mba, HCRM, Cic, Ipm, MSN, Phd. Haneen Alnuaimi, MSNAboodsha ShNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Adddress Game Online IndonesiaDokument8 SeitenIP Adddress Game Online IndonesiaIbenk MyraldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Readme12 Icd 9Dokument2 SeitenReadme12 Icd 9Nashwa FathiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines TBC TerbaruDokument160 SeitenGuidelines TBC TerbaruSutoto MoeljadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebral EdemaDokument6 SeitenCerebral EdemaantonopoulosalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arnold CCS FinalDokument23 SeitenArnold CCS FinalNashwa FathiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZincDokument7 SeitenZincNashwa FathiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument1 SeiteDaftar PustakaNashwa FathiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulir 1b UKDIDokument1 SeiteFormulir 1b UKDIcyelzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menveo Full Promotional PIDokument15 SeitenMenveo Full Promotional PINashwa FathiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EYE Emergency Manual An Illustrated Guide: Second EditionDokument56 SeitenEYE Emergency Manual An Illustrated Guide: Second Editionmanleyj5305Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Discharge Begins Admission PpsDokument9 SeitenEffective Discharge Begins Admission PpsNashwa FathiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- FebrileDokument7 SeitenFebrileCaterina PrepelitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DATA GURU PAIS APLIKASI WEB BASE TAHUN AJARAN 2011 - 2012Dokument310 SeitenDATA GURU PAIS APLIKASI WEB BASE TAHUN AJARAN 2011 - 2012Nashwa FathiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar in 15 Minutes A DayDokument240 SeitenGrammar in 15 Minutes A Daylalith.shankar7971100% (9)
- Pelayanan Kerohanian FormDokument1 SeitePelayanan Kerohanian FormNashwa FathiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Pathophysiology of AmenorrheaDokument6 SeitenThe Pathophysiology of AmenorrheaTri Suci UtamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RECALLS - Key points from Preboard 2015 Clinical ChemistryDokument2 SeitenRECALLS - Key points from Preboard 2015 Clinical ChemistrySheanalene CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skripsi Tanpa Pembahasan PDFDokument64 SeitenSkripsi Tanpa Pembahasan PDFBillyDwiSaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Technologies History of Medtech in United StatesDokument1 SeiteMedical Technologies History of Medtech in United StatesAthaliah Del MonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hoa Silver Edition Manual V1 5-0-120308 enDokument23 SeitenHoa Silver Edition Manual V1 5-0-120308 enAlex KrobbachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Resection of Cancer of The Buccal MucosaDokument21 SeitenSurgical Resection of Cancer of The Buccal MucosapradeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of The Method Quality Control: Alkaline PicrateDokument1 SeitePrinciple of The Method Quality Control: Alkaline PicrateRisqon Anjahiranda Adiputra100% (1)
- Inductions To LearnDokument7 SeitenInductions To LearnMichael HobbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPTEL Stress Management MCQ AssignmentDokument5 SeitenNPTEL Stress Management MCQ AssignmentSnehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Host defense mechanisms overviewDokument7 SeitenHost defense mechanisms overviewmyfilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guillain Barre SyndromeDokument2 SeitenGuillain Barre SyndromeTheresia Avila KurniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Urinary System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDokument91 SeitenThe Urinary System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeNicole NipasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Tongue of Leopard Gecko (Eublepharis Macularius) LMDokument9 SeitenThe Tongue of Leopard Gecko (Eublepharis Macularius) LMSandra Clavero ClopèsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ayurveda Physical BodyDokument11 SeitenAyurveda Physical BodyanantNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Body in Health and Illness e Book 6th Edition Ebook PDFDokument61 SeitenThe Human Body in Health and Illness e Book 6th Edition Ebook PDFcraig.suarez45797% (33)
- Neurology Crossword Puzzle Answer KeyDokument1 SeiteNeurology Crossword Puzzle Answer KeyRavinaAhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omsb Part I - 2010Dokument10 SeitenOmsb Part I - 2010Firyal Balushi100% (1)
- Rubins-Q A ENDOCRINEDokument14 SeitenRubins-Q A ENDOCRINECRUZ Jill EraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANS & CVS Response To Exercise v2Dokument18 SeitenANS & CVS Response To Exercise v2chow wing yin amandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- From: Rapid Interpretation of EKG'sDokument14 SeitenFrom: Rapid Interpretation of EKG'sLucija Kljaić100% (1)
- FCA (SA) - Part - II - Past - Papers 10Dokument30 SeitenFCA (SA) - Part - II - Past - Papers 10matentenNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Ketone Bodies Fuel Brain and HeartDokument3 SeitenHow Ketone Bodies Fuel Brain and Heartdaef32Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive ExamDokument13 SeitenDigestive Examapi-294622133Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Physiology Lecture 2Dokument9 SeitenEndocrine Physiology Lecture 2Tofunmi Kunle-KunbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Non-Ruminants: Principles of Animal Nutrition Dr. Cristine W. MaramagDokument30 SeitenSimple Non-Ruminants: Principles of Animal Nutrition Dr. Cristine W. MaramagMc Kjell Dagman RaveloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain Herniation SyndromeDokument28 SeitenBrain Herniation SyndromeSarahScandy100% (4)
- Module 1. General and Special Questions of Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics Text Test QuestionDokument229 SeitenModule 1. General and Special Questions of Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics Text Test QuestionA.h.MuradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hernia Inguinal - ShouldiceDokument25 SeitenHernia Inguinal - ShouldiceBrunoRochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing DictionaryDokument353 SeitenNursing DictionaryEmmanuel BoadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Administration and Transfusion Reactions QuizDokument5 SeitenBlood Administration and Transfusion Reactions Quizremooheshmat100% (1)