Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lenses Notes: Convex or Converging Lens
Hochgeladen von
Athena HuynhOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lenses Notes: Convex or Converging Lens
Hochgeladen von
Athena HuynhCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lenses Notes
Convex or Converging Lens
Concave or Diverging Lens
Determining the Focal Length of a Lens
Ray Diagrams
Definitions:
We will deal only with thin lenses when solving lens problems. I. Locating a Real Image
1 2
Rules: 1. Rays parallel to the principal axis will refract so that they pass through the focal point F. 2. Rays passing through the middle of the lens will continue through without refracting. 3. Rays passing through the focal point F will refract so that they are parallel to the principal axis.
II.
Locating an Imaginary (Virtual) Image
Ray Diagram for a Thin Concave (Diverging) Lens
The Lens Equation
f is the focal length (distance from lens to focal point) do is the distance from lens to the object di is the distance from lens to the image We can locate the image with the lens equation The Magnification Equation
hi: negative when inverted (h - height) di: negative when on the same side of the lens as do (virtual image) f: positive for convex/converging lens and negative for concave/diverging lens
Example: A glowing object 4 cm tall is placed 9 cm from a concave lens. If the lens has a focal length of 5 cm, what is a) the distance of the image from the lens? OR
( ( )
)( (
) )
Virtual Imagesame side of the lens as the object (because di is negative) b) the size of the image? ( )( )
Uprighthi is positive c) the characteristics of the image? virtual, diminished (smaller), upright image d) Draw the ray diagram to confirm. Refer to Ray Diagram for a Thin Concave (Diverging) Lens
| | | |
| | | | ( )
Curved Mirrors Converging (Concave) Mirrors
When the object is farther away than the focal length, the image is inverted.
When the object is at the focal length, there is no image.
When the object is closer than the focal length, there is a larger, virtual image. The Mirror Equation and Magnification Equation We can determine the location and size of the image from a mirror with the following equation:
( ) ( ) ( )( ( ) ( )
( (
) ) )
Converging of real light rays
Uses reflecting telescopes car headlamps
Diverging (Convex) Mirrors
Uses Parking lot mirror. Security mirror in stores (you can see more in a convex mirror than in a concave mirror).
Example Find the location and the characteristics of the image if an object 2 cm in height is 5 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
Enlarged, Upright, Virtual Image
( (
)( ) (
) )
( ( Out of Focus? Spherical Aberration
)( )
Chromatic Aberration
Solved with the addition of an achromatic lens
Correcting Myopia (nearsightedness)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Image Formation and Ray Diagrams Involving MirrorsDokument75 SeitenImage Formation and Ray Diagrams Involving Mirrorsjohn charles garalde100% (1)
- Lab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesDokument16 SeitenLab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesOtto ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report For Science 10 PETA (3rd Quarter)Dokument33 SeitenReport For Science 10 PETA (3rd Quarter)luistabaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- REFLECTION OF LIGHT: MIRRORSDokument42 SeitenREFLECTION OF LIGHT: MIRRORSLester MarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Notes Light - Reflection & RefractionDokument10 SeitenChapter Notes Light - Reflection & Refractionroseanneblossom.kimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curved MirrorsDokument28 SeitenCurved Mirrorskaziba stephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory: Lab 10/11 Phys 214 & 316 LensesDokument14 SeitenTheory: Lab 10/11 Phys 214 & 316 Lensesmalik awaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S EoDokument6 Seiten2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S Eony9197171Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science10 Q2 Mod5 v4Dokument6 SeitenScience10 Q2 Mod5 v4Kim TaehyungNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0490f1d4-6cb3-4dfa-b85d-9087d2d549c5Dokument10 Seiten0490f1d4-6cb3-4dfa-b85d-9087d2d549c5Rafiya95z MynirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Lenses and Vision DefectsDokument27 SeitenUnderstanding Lenses and Vision DefectsJohn Lester GenizeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Reflection On Curved MirrorsDokument56 Seiten5 Reflection On Curved MirrorsBianca ManimtimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convex Mirrors: Mirror Sphere Parabolic Reflectors Reflecting Telescopes Spherical AberrationDokument8 SeitenConvex Mirrors: Mirror Sphere Parabolic Reflectors Reflecting Telescopes Spherical AberrationBastab DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF 10TH CLASS PHYSICS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS SSC ABYASA DEEPIKADokument9 SeitenPDF 10TH CLASS PHYSICS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS SSC ABYASA DEEPIKAprakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optics Lab: Forming Images with Lenses and MirrorsDokument10 SeitenOptics Lab: Forming Images with Lenses and MirrorsGabriel Eyapan100% (1)
- Reflection of LightDokument21 SeitenReflection of LightenricoluismendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Light 3Dokument31 SeitenReflection Light 3api-296824694Noch keine Bewertungen
- G-10 Physics Important Questions FinalDokument29 SeitenG-10 Physics Important Questions FinalRohan SenapathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Reflection and Image Formation Using Spherical MirrorsDokument18 SeitenUnderstanding Reflection and Image Formation Using Spherical MirrorsPrinceNeilCedrickCastro100% (1)
- Mirror Reflection and Image FormationDokument44 SeitenMirror Reflection and Image FormationJennifer Bernas BerdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Cl10 Assign2Dokument2 SeitenPhysics Cl10 Assign2Tapas BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mirrors and Lenses ExplainedDokument46 SeitenMirrors and Lenses Explainednvze999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetDokument4 SeitenClass 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetFrederic Francois ChopinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Light RevDokument24 SeitenGrade 10 Light RevDanny BlessyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Worksheet Padhleakshay PDFDokument18 SeitenLight Worksheet Padhleakshay PDFanandatulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture and Worksheet - LensesDokument13 SeitenLecture and Worksheet - LensesJaymar Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mirror and Lenses 10Dokument59 SeitenMirror and Lenses 10Mesheil TaladroNoch keine Bewertungen
- G10 Geometric Optics: Reflection and MirrorsDokument11 SeitenG10 Geometric Optics: Reflection and Mirrorsbort kortNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light - Padhle TenthiesDokument92 SeitenLight - Padhle Tenthiesa9758127118Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mirrors: Lesson 4 (3 Hours)Dokument24 SeitenMirrors: Lesson 4 (3 Hours)Donna100% (1)
- Adobe Scan 15-Feb-2022Dokument8 SeitenAdobe Scan 15-Feb-2022Aditya GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierDokument13 SeitenPlease Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierXhenel Vincent LirioNoch keine Bewertungen
- L9. 13.4 Lens EquationsDokument16 SeitenL9. 13.4 Lens Equationszhuhu2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFDokument45 Seiten5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFPiyushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 30 Lesson 9 Optics - Thin Lenses: Refraction 2 Refraction 1Dokument11 SeitenPhysics 30 Lesson 9 Optics - Thin Lenses: Refraction 2 Refraction 1John JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightDokument3 SeitenPhysics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightKhushi AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse Test Paper-02 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDokument6 SeitenCbse Test Paper-02 10 Light Reflection and RefractionAchyut SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Dokument5 SeitenExtra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Zoha AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- COT PresentationDokument42 SeitenCOT PresentationCedric BaldozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionDokument15 SeitenChapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionVineet SierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Unit 7 Part 2 NotesDokument38 SeitenPhysics Unit 7 Part 2 NotesTaylor Waddell-SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy 102 (2) Curved Mirrors - 075230Dokument23 SeitenPhy 102 (2) Curved Mirrors - 075230Pamela MagboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Notes Grade 10Dokument9 SeitenReflection Notes Grade 10Parv GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray DiagramDokument47 SeitenRay Diagramjimmy cocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- G10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Dokument10 SeitenG10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Urmila GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray DiagramsDokument18 SeitenRay DiagramsJan IrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Based On Reflection of LightDokument3 SeitenAssignment Based On Reflection of Lightnamansaraswat2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Class XIIDokument177 SeitenPhysics Class XIIManavendra PratapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23 - Mirrors and LensesDokument29 SeitenChapter 23 - Mirrors and LensesrichardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cermin Lengkung-2Dokument23 SeitenCermin Lengkung-2Ofik Mahesa ChannelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optics Section Two FinalDokument49 SeitenOptics Section Two FinalNahoo BekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class X Science (Physics) Ch10 Question-AnswersDokument9 SeitenClass X Science (Physics) Ch10 Question-AnswersAnkur MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XDokument4 SeitenPhysics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XSyed Ahmed AdeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spherical Mirrors: Symmetric About This Axis. Hence, We Can Represent A Three-Dimensional Mirror in ADokument13 SeitenSpherical Mirrors: Symmetric About This Axis. Hence, We Can Represent A Three-Dimensional Mirror in AAlankrit BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- By: Aries Triwidajati Soenoko SMP Negeri 2 CileunyiDokument21 SeitenBy: Aries Triwidajati Soenoko SMP Negeri 2 Cileunyiaries triwidajatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Dokument28 SeitenChapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Heindrich Lloyd Mendoza BasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34b Reflection and Mirrors II AnalyticalDokument27 Seiten34b Reflection and Mirrors II AnalyticalseijikellsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADokument9 SeitenChapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADaiwik GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium of Forces and TorquesDokument12 SeitenEquilibrium of Forces and TorquesAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CapacitorsDokument3 SeitenCapacitorsAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum PhysicsDokument3 SeitenQuantum PhysicsAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy and EnzymesDokument10 SeitenEnergy and EnzymesAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics: Some DefinitionsDokument6 SeitenThermodynamics: Some DefinitionsAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrostaticsDokument5 SeitenElectrostaticsAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System and NutritionDokument6 SeitenDigestive System and NutritionAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Momentum, Energy, and WorkDokument11 SeitenMomentum, Energy, and WorkAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA in DetailDokument15 SeitenDNA in DetailAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDokument12 SeitenThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- The Power of One Notes On Landscape For P. 132-136Dokument1 SeiteThe Power of One Notes On Landscape For P. 132-136Athena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument14 SeitenCardiovascular SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Rotational MotionDokument4 SeitenRotational MotionAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic TheoryDokument4 SeitenKinetic TheoryAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom AnimaliaDokument14 SeitenKingdom AnimaliaAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- VectorsDokument11 SeitenVectorsAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
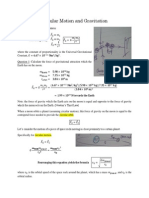
- Circular Motion: Q: in Which Direction Is TheDokument6 SeitenCircular Motion: Q: in Which Direction Is TheAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- GravitationDokument8 SeitenGravitationAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- DynamicsDokument7 SeitenDynamicsAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowDokument13 SeitenKingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Biology Diagrams NotesDokument1 SeiteBiology Diagrams NotesAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom FungiDokument5 SeitenKingdom FungiAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom ProtistaDokument3 SeitenKingdom ProtistaAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingdom MoneraDokument3 SeitenKingdom MoneraAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Lab NotesDokument2 SeitenBiology Lab NotesAthena HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology NotesDokument3 SeitenMicrobiology NotesAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Diffraction ProblemsDokument4 SeitenDiffraction ProblemsRachit_Goyal25_10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science Study Committee-2018Dokument682 SeitenPhysical Science Study Committee-2018kerooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Janelle Test 2023Dokument3 SeitenJanelle Test 2023Mary Grace RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- WBPSC Civil Service Exam 2011: Scheme, Syllabus and PapersDokument14 SeitenWBPSC Civil Service Exam 2011: Scheme, Syllabus and PapersPawandeep Singh MatharuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 6b Transmission Through A Layer Normal Incidence PDFDokument14 SeitenChapter - 6b Transmission Through A Layer Normal Incidence PDFAlinaBogoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugasan 2: SFU3023 General Physics IiDokument4 SeitenTugasan 2: SFU3023 General Physics IiShahidan SidekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Comparison of WDM PON With TDM PON at 10 GbpsDokument4 SeitenPerformance Comparison of WDM PON With TDM PON at 10 GbpsMuhammad UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanderson, Jeremy B - Biological Microtechnique-Bios Scientific Publishing (1994)Dokument241 SeitenSanderson, Jeremy B - Biological Microtechnique-Bios Scientific Publishing (1994)Frederico Henrique da Silva CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam. SolutionDokument9 SeitenFinal Exam. SolutionSelvaraju ChellappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Bio (Ain)Dokument8 SeitenLab Report Bio (Ain)23005852Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMZ645 660Dokument5 SeitenSMZ645 660satryo wibowoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ppcatalogue 2 PDFDokument527 SeitenPpcatalogue 2 PDFrutwickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strengthened Glass Detector: MODEL# SG2700Dokument8 SeitenStrengthened Glass Detector: MODEL# SG2700Ramón MataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endoscopy Systems CatalogueDokument58 SeitenEndoscopy Systems CatalogueJuliano BelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM580Dokument7 SeitenCHM580Azreen AnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photodiode and LIGHT Emitting DiodeDokument38 SeitenPhotodiode and LIGHT Emitting DiodekaneeshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EatonDokument1 SeiteEatonzubair1951Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluating Non-Contacting Optical Strain Measurement SystemsDokument7 SeitenEvaluating Non-Contacting Optical Strain Measurement SystemshoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee231 PDFDokument15 SeitenEee231 PDFJagadish YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Holographic Projection Technology: Submitted ByDokument22 Seiten3D Holographic Projection Technology: Submitted BySoham GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet-22 Reflection & Refraction of LightDokument2 SeitenWorksheet-22 Reflection & Refraction of Lightanjalitashu01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Youngs Double SlitDokument4 SeitenYoungs Double Slitpmc9q544vwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway Sign Visibility: Philip M. GarveyDokument17 SeitenHighway Sign Visibility: Philip M. GarveyRJ Baluyot MontallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DWDM Theory: ZTE University Transmission Course TeamDokument51 SeitenDWDM Theory: ZTE University Transmission Course TeamWubie NegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D800 Setup GuideDokument2 SeitenD800 Setup GuideAnonymous 4Altbm6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Night Time Lapse Photography Saint John Astronomy Club: Tom RaithbyDokument18 SeitenNight Time Lapse Photography Saint John Astronomy Club: Tom Raithbyebi18750Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radiographic Terminology BSEN 1330-3 PDFDokument45 SeitenRadiographic Terminology BSEN 1330-3 PDFThe Normal HeartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anger Scitillation CameraDokument8 SeitenAnger Scitillation CameraTuấn Hồ TrọngNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Seminar Report On PlasmonicsDokument24 SeitenA Seminar Report On Plasmonicsgoyal_monika12388% (8)
- Full Download Religion Matters What Sociology Teaches Us About Religion in Our World 1st Edition Mirola Test BankDokument36 SeitenFull Download Religion Matters What Sociology Teaches Us About Religion in Our World 1st Edition Mirola Test Banksteevesalannah100% (37)