Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
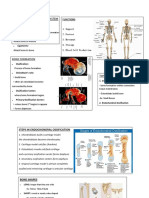
Knee Joint Anatomy
Hochgeladen von
kep1313Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Knee Joint Anatomy
Hochgeladen von
kep1313Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Osteology: 3 bones - femur, tibia, patella Position of femur atop of tibia = unstable Mechanisms to compensate: - Bearing surfaces of femur
and tibia are large - Articulate with each other as lateral and medial tibiofemoral joint o Separate d by intercondylar fossa on femur o Intercondylar eminence on the tibia o Patella articulates with the femur - 3 points of articulate are separate but share synovial joint space by virtue of openings between cavities o * Permit infection to spread from one are of articular to another Movements of knee joint 1. Hinge (flex-ext) with rolling, gliding on articular surfaces 2. Some rotation around vertical axis of the femur on the tibia Femoral condyles - large and convex - covered in hyaline cartilage Medial condyle is narrower and longer are on distal femur for the articulation of thee patella Tibial condyles - covered in hyaline cartilage separated by intercondylar eminence ad slightly concave. The medial condyle is slightly larger and slight more concave than lateral Menisci - on tibial condyles Menisci - non-congruent joint- menisci positioned on top of tibial condyles to create more concave tibial surfaces Medial and lateral menisci thicker at lateral borders Each menisci cover 2/3 of articular surface Medial - C shaped, lateral is O shaped Attached by variety of ligaments to the tibia bot h at me margins and to intercondylar region Periphery of each meniscus attached to fibrous joint capsule Medial meniscus attached to MCL Lateral meniscus less firmly attached to lateral capsule and collateral ligament Popliteus tendon lies between lateral capsule and LCL When muscle contracts lateral meniscus is pulled posteriorly Injuries to menisci - detachment of horn form bone, tear or longitudinal split. McMurrays test - Patient is supine with hip flexed - Knee maximally flexed to 140 - Leg is rotated medially or laterally - While maintaining rotated position, leg is then extended to about 90 degrees of flexion. - If pain or audible click positive Ligaments I. Ligaments A. Collateral - limit side to side (abduction and adduction) 1. Medial collateral ligament - vertical thickened band between medial epicondyle of femur and medial condyle of tibia. Thickening of joint capsule and attached to medial meniscus
2. Lateral collateral ligament - between lateral epicondyle and head of fibula separate from knee joint capsule 3. Testing: a. Valgus stress test - integrity of MCL i. Knee flexed to 30 ii. Push the lateral side of the knee while forcing the leg laterally iii. Very little movement should occur in MCL is intact b. Varus stress test - lateral collateral ligament i. Applying pressure on the medial side of the knee while trying to force the leg medially ii. Knee is tested at 30 degrees of flexion because collateral are tauter than the cruciate ligaments B. Cruciate ligaments - strong rounded cords that cross each other as they span between intercondylar eminence and intercondylar surface of femur. Provide stability to the knee joint by holding femur and tibia together 1. ACL - arises from anterior aspect of tibia plateau a. Slightly longer and attached to lateral femoral condyle b. Positioned to prevent anterior displacement of the tibia relative to a fixed femur 2. PCL - arise from posterior aspect of tibia a. Attached to medial femoral condyle b. Prevents posterior displacement of the tibia c. Injuries occur when knee is semi flexed 3. Clinical testing a. Anterior drawer test - ACL i. Grasp leg btwn knee positioned at 90 of flexion and pulling firmly in anterior position ii. If leg moves forward relative to femur more than 1 cm, test is positive b. Posterior drawer test PCL Knee has fibrous capsule being reinforced by multiple tendons and ligaments Synovial membrane lines the fibrous capsule, attached to the margins of articular surface and to peripheral edges of menisci Passes anterior to the ACL and PCL (excludes from joint cavity) Patellofemoral joint: sesamoid bone - formed in tendon of quadriceps muscles and glides on femur during flexion and extension of leg at knee joint
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Case Studies 4Dokument4 SeitenCase Studies 4kep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem MedicineDokument27 SeitenBiochem Medicinekep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Studies 5Dokument4 SeitenCase Studies 5kep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatry - BSDokument15 SeitenPsychiatry - BSkep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1: Cystic FibrosisDokument5 SeitenCase 1: Cystic Fibrosiskep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology - BSDokument14 SeitenPhysiology - BSkep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem MedicineDokument27 SeitenBiochem Medicinekep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia DifferentialDokument1 SeiteAnemia Differentialkep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune DisordersDokument2 Seiten2-5-10 HCT For Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune Disorderskep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-8-10 Introduction To Clinical Aspects of Lymphoproliferative DisordersDokument7 Seiten2-8-10 Introduction To Clinical Aspects of Lymphoproliferative Disorderskep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-3-10 Principles of Therapy For HIV DiseaseDokument2 Seiten2-3-10 Principles of Therapy For HIV Diseasekep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-2-10 The Role of Chemokine Networks in DiseaseDokument2 Seiten2-2-10 The Role of Chemokine Networks in Diseasekep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Theraband Wrist ExercisesDokument1 SeiteTheraband Wrist ExercisesLorena AraújoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AOSpine Manual Thoracic Spine AnatomyDokument18 SeitenAOSpine Manual Thoracic Spine AnatomySebastián MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise and Ankle Sprain Injuries: A Comprehensive ReviewDokument6 SeitenExercise and Ankle Sprain Injuries: A Comprehensive Reviewabraham landaetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IM Injections Clinical TechsadaniqueDokument2 SeitenIM Injections Clinical TechsadaniqueGeminiQueenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 21 Best Stretching Exercises For Better Flexibility - SELFDokument10 SeitenThe 21 Best Stretching Exercises For Better Flexibility - SELFjohnsonkk125Noch keine Bewertungen
- RMT KLSF DR Blondina 2009Dokument21 SeitenRMT KLSF DR Blondina 2009Fadhly SharimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ponseti Management of Clubfoot in Chittagong DisvisionDokument34 SeitenPonseti Management of Clubfoot in Chittagong Disvisionmuthia saniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redcon1 Calformation ProgramDokument20 SeitenRedcon1 Calformation ProgramWacharin Cheepsaritdiphong100% (1)
- Components of Skeletal SystemDokument4 SeitenComponents of Skeletal SystemShanie Lee CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual/Assisted Stretching Techniques: WWW - Fisiokinesiterapia.bizDokument26 SeitenManual/Assisted Stretching Techniques: WWW - Fisiokinesiterapia.bizLuca AnamariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rig O MaticDokument9 SeitenRig O MaticrendermanuserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal SystemDokument5 SeitenSkeletal SystemSobia KanwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reconstruction of Posttraumatic Disorders of The ForearmDokument12 SeitenReconstruction of Posttraumatic Disorders of The Forearmsinung bawonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temporo Mandibular Joint Disorder Oral SurgeryDokument59 SeitenTemporo Mandibular Joint Disorder Oral SurgeryFourthMolar.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Hip DysplasiaDokument32 SeitenCongenital Hip DysplasiaChristine AllonarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenosynovitis Tendons Thumb Swiss Surgeon Fritz de Quervain de Quervain's ThyroiditisDokument4 SeitenTenosynovitis Tendons Thumb Swiss Surgeon Fritz de Quervain de Quervain's ThyroiditisFelisitas NasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonsurgical Treatment of Acetabular Labrum Tears: A Case SeriesDokument8 SeitenNonsurgical Treatment of Acetabular Labrum Tears: A Case SeriesJonathan BaldeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Practical Guide For Performing Arthrography Under Fluoroscopic or Ultrasound GuidanceDokument10 SeitenA Practical Guide For Performing Arthrography Under Fluoroscopic or Ultrasound GuidanceSnehanshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knee Joint Anatomy ManualDokument6 SeitenKnee Joint Anatomy ManualDungani AllanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalkaneal OsteotomiDokument11 SeitenKalkaneal Osteotomitravma777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of Skeletal Remains, Techniques of Recovery of Skeletal Remains and Sex Determination of Skeletal RemainsDokument22 SeitenIdentification of Skeletal Remains, Techniques of Recovery of Skeletal Remains and Sex Determination of Skeletal RemainsShimona Mae Dias100% (1)
- Module Three Wellness PlanDokument14 SeitenModule Three Wellness Planmark scalabrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIFA Soccer 11 Plus ManualDokument76 SeitenFIFA Soccer 11 Plus ManualtheroguetrainerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common ErrorsDokument5 SeitenCommon Errorsvikas guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-8 Body Movements - Day1Dokument12 SeitenCh-8 Body Movements - Day1dr satnam kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Bony PelvisDokument16 SeitenAnatomy of The Bony Pelvismichael0202Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vertebra Anatomy 125Dokument110 SeitenVertebra Anatomy 125Jennifer FirestoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- PWR 1.0Dokument25 SeitenPWR 1.0Elizabeth SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study BoneDokument2 SeitenCase Study BoneRodolf Gerone G. MacahilosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agur, A. M. R. - Dalley, Arthur F. - Moore, Keith L. - Clinically Oriented Anatomy-Wolters Kluwer Health - Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2014) (Dragged) PDFDokument3 SeitenAgur, A. M. R. - Dalley, Arthur F. - Moore, Keith L. - Clinically Oriented Anatomy-Wolters Kluwer Health - Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2014) (Dragged) PDFdivinaNoch keine Bewertungen