Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Rotation Dynamics and Angular Momentum PDF
Hochgeladen von
Tarun GuptaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rotation Dynamics and Angular Momentum PDF
Hochgeladen von
Tarun GuptaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
www.IITwikipedia.
com
ROTATION DYNAMICS AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM 1. When a steady torque is acting on a body, the body a) continues in its state of rest or uniform motion along a straight line b) gets linear acceleration c) gets angular acceleration d) rotates at a constant speed 2. A dancer on ice spins faster when she folds her arms. This is due to a) increase in energy and increase in angular momentum b) decrease in friction at the skates c) constant angular momentum and decrease in Moment of Inertia d) increase in energy and decrease in angular momentum 3. A man is standing on a table rotating with an angular speed . He is holding two equal masses at arm's length. Without moving his arms, he just drops the two masses on the table. How will his angular speed change ? a) it will be less than c) it will remain equal to d) may be less than, greater than or equal to depending on the quantity of masses. 4. A hollow cylinder and a solid cylinder having the same mass and same diameter are released from rest simultaneously from the top of an inclined plane. Which will reach the bottom first a) the solid cylinder b) the hollow cylinder c) both will reach the bottom together d) the one having greater density 5. A body of mass m slides down an incline and reaches the bottom with a velocity v. If the same mass were in the form of a ring which rolls down this incline, the velocity of the ring at bottom would have been a) v b) b) it will be more than
2v
c)
6. A particle of mass m is moving in a plane along a circular path of radius r. Its angular momentum about the axis of rotation is L. The centripetal force acting on the particle is a) L2 / mr b) L2 mr c) L2 / mr3 d) L2 / mr2
1 v 2
d)
7. A disc of radius R rotating about its axis, has a moment of inertia I about that axis. When it is rotating about that axis at a constant angular velocity ' ' a heavy particle of mass m is placed gently at the rim of the disc. The resulting angular velocity of the system is a) b) I ( I + mR ) c) ( I + mR )/ d) I /( I + mR2 )
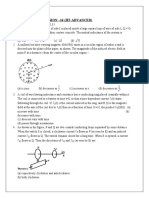
8. A thin circular ring of mass M and radius r is rotating about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with a constant angular velocity . Two objects, each of mass m are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring now rotates with angular velocity a)
( M 2m) M + 2m
b)
M ( M m)
c)
( M + 2m) M
d)
M M + 2m
9. A solid iron sphere A rolls down an inclined plane, while an identical sphere B slides down the plane in a frictionless manner. At the bottom of the inclined plane, the total kinetic energy of sphere A is a) less than that of B b) equal to that of B c) more than that of B d) sometimes more and sometimes less 10. A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R rolls down an inclined plane without slipping from height h. The speed of its centre of mass when it reaches the bottom is a)
(2 gh)
b)
gh
c)
gh
d)
( 4 g / h)
www.IITwikipedia.com
11. The angular velocity of a body changes from 1 to 2 without applying torque but by changing radius of gyration. The ratio of initial radius of gyration of the final radius of gyration is a) 2 : 1
2 b) 2 2 :1
c)
2 : 1
d) 1 / 2 :1 / 1
12. A circular disc rotates in a vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis which passes through a point X on the circumference of the disc. When the centre of the disc moves with speed V, the speed of the opposite end of the diameter through X is a) 2 V b)
2V
c) V
d) V/2
13. Two circular discs A and B of equal masses and thickness are made of metals with densities dA and dB ( dA > dB ). If their moments of inertia about an axis passing through the centre and normal to the circular faces be IA and IB, then a) I A = I B b) I A > I B c) I A < I B d) I A I B
14. Two bodies with moment of inertias I1 and I 2 ( I 1 > I 2 ) have equal angular momenta. If K.E. of rotation are E1 and E2 , then a) E1 = E 2 b) E1 > E 2 c) E1 < E 2 d) E1 E 2
15. A disc rolls over a horizontal floor without slipping with a linear speed of 5 cm/sec. Then the linear speed of a particle on its rim, with respect to the floor, when it is in its highest position is a) 10 cm/sec b) 5 cm/sec c) 2.5 cm/sec d) 0 16. Without weighing, how can you distinguish between the two identical balls of same material, but one being solid and the other one being hollow a) by rolling them down on inclined plane, b) by determing their moment of inertia about the centre, c) by spinning them by equal torque, d) all the above 17. A mass M is moving with a constant velocity parallel to x-axis. Its angular momentum with respect to origin is a) zero b) constant c) goes on increasing d) goes on decreasing 18. A wheel of moment of inertia 5 10-3 kg-metre2 is making 20 revolutions per second. It is stopped in 20 seconds, then angular retardation is a) radian/sec2 b) 2 radian/sec2 c) 4 radian/sec2 d) 8 radian/sec2
19. A solid spherical ball rolls on a table without slipping. Then the fraction of its total energy associated with rotation is a) 2/5 b) 2/7 c) 3/5 d) 3/7
20. An inclined plane makes an angle of 30 with the horizontal. A solid sphere rolling down this inclined plane from rest without slipping has a linear acceleration equal to a) g/3 b) 2g/3 c) 5g/7 d) 5g/14
21. A constant torque acting on a uniform circular wheel changes its angular momentum from A0 to 4A0 in 4 seconds. The magnitude of this torque is a) 3A0 / 4 b) A0 c) 4A0 d) 12A0 Y = X + 4. The magnitude of the
22. A particle of mass m = 5 is moving with a uniform speed angular momentum about origin is a) zero b) 60 units
v = 3 2 in the XOY plane along the line
c) 7.5 units d)
40 2
www.IITwikipedia.com
23. A particle of mass M and radius of gyration K is rotating with angular acceleration . The torque acting on the particle is
1 Mk 2 b) MK2 c) MK2 / d) ( MK2 2 / 4 ) 2 24. K.E. (E) and the angular momentum L of a rigid body are related to each other by the relation( I = moment of inertia )
a)
a) L =
E2 2I
b)
E = 2 IL
c)
E 2 = 2I / L
d)
E = L2 / 2 I
25. Mass is whirled in a circular path with a constant angular velocity and its angular momentum is L. If the string is now halved keeping the angular velocity same, the angular momentum is a) L/4 b) L c) 2L d) L/2
26. A small hole is made in a disc ( Mass M, radius R ) at a distance R/4 from centre. The disc is supported on horizontal peg through this hole. The moment of inertia of disc about horizontal peg is
Mr 2 a) 2
5 MR 2 b) 16
9 MR 2 c) 16
d)
5 MR 2 4
27. Moment of inertia of uniform circular disc about a diameter is I . Its moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to its plane and passing through a point on its rim will be a) 5 I b) 3 I c) 6 I d) 4 I 28. A particle performs uniform circular motion with an angular momentum L. If the frequency of particle's motion is doubled and its kinetic energy halved, the angular momentum becomes a) 2 L b) 4 L c) L / 2 d) L / 4 29. A particle of mass m is projected with a velocity v making an angle of 45 with the horizontal. The magnitude of angular momentum of the projectile about an axis of projection when the particle is at maximum height h is a) 0 b) mv 3 / 4 2 g c) mv 2 / 2 g d) mv 3 / 2 2 g
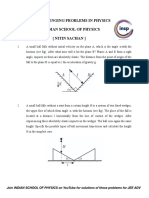
30. The moment of inertia of a thin square plate ABCD ( shown below in the figure ) of uniform thickness about an axis passing through the centre O and perpendicular to the plane of plate is (where I1 , I 2 , I 3 and I 4 are moments of inertia about axes 1, 2, 3 and 4 respectively which are in the plane of paper). a) I 1 + I 2 b) ( I 3 + I 4 )/2 c) I 1 + I 3 d) I1 + I 2 + I 3 + I 4
31. A solid, homogeneous sphere of mass M and radius R is moving on a rough horizontal surface, partly rolling and partly sliding. During this kind of motion of the sphere a) total kinetic energy is conserved b) the angular momentum of the sphere about the point of contact with the plane is conserved c) only the rotational kinetic energy about the centre of mass is conserved d) angular momentum about the centre of mass is conserved. 32. A solid sphere of mass 2 kg and radius 5 cm rolls without slipping along a horizontal plane. The velocity of its centre of mass is 10 cm s-1. The kinetic energy of the sphere is a) 0.07 J b) 0.014 J c) 0.025 J d) 1.25 J 33. If I1 is the moment of inertia of a thin rod about an axis perpendicular to its length and passing through its centre of mass, and I 2 is the moment of inertia of the ring formed by bending the rod, then a) I1: I 2 = 1:1 b) I1: I 2 = 2 : 3 c) I 1: I 2 = : 4 d) I1: I 2 = 3: 5
www.IITwikipedia.com
34. A thin uniform heavy rod of length l hangs from a horizontal axis passing through one end. The initial angular velocity that must be imparted to it to rotate it through 90 is a)
g/l
b)
3g / l
c)
2g / l
d)
6g / l
35. An initial momentum is imparted to a homogeneous cylinder, as a result of which it begins to roll without slipping up an inclined plan e at a speed of vo = 4 ms 1 . The plane makes an angle = 30 with the horizontal. What height h will the cylinder rise to ? (g = 10 m/s 2 ) a) 0.8 m b) 1.2 m c) 1.0 m d) 1.6 m
Answers 1. 7. 13. 19. 25. 31. c d c b a b 2. 8. 14. 20. 26. 32. c d c d c b 3. 9. 15. 21. 27. 33. c b a a b b 4. 10. 16. 22. 28. 34. a b d b d b 5. 11. 17. 23. 29. 35. c c b b b b 6. 12. 18. 24. 30. c a b d a
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Rotational MechanicsDokument6 SeitenRotational MechanicsHemant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion EtoosDokument24 SeitenProjectile Motion EtoosT sidharthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Harmonic MotionDokument29 SeitenSimple Harmonic MotionthinkiitNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Gravity and Circular MotionDokument27 SeitenIB Gravity and Circular Motionnoman21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Target: Jee (Advanced) 2019: P H Y S I C SDokument12 SeitenTarget: Jee (Advanced) 2019: P H Y S I C SraghavbhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TARGET: JEE (Main + Advanced) 2017 Course: VIKAAS (JA)Dokument15 SeitenTARGET: JEE (Main + Advanced) 2017 Course: VIKAAS (JA)mail2sgarg_841221144Noch keine Bewertungen
- TPT-1 - PhysicsDokument6 SeitenTPT-1 - PhysicsSantosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational Motion Iit JeeDokument23 SeitenRotational Motion Iit JeeSahil0% (1)
- Conservation of Linear MomentumDokument15 SeitenConservation of Linear MomentumSiddharth Acharya100% (1)
- CPP 11 Circular MotionDokument2 SeitenCPP 11 Circular MotionullasagwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Last Revision BookletDokument106 SeitenPhysics Last Revision BookletMohit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NLM 13Dokument4 SeitenNLM 13Ramesh BadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA Worksheet Geometry IDokument10 SeitenQA Worksheet Geometry ISiddharth YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper JeeDokument20 SeitenQuestion Paper JeeSourabhThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centre of Mass QUESTIONDokument12 SeitenCentre of Mass QUESTIONrgcsm88100% (1)
- Math 1151 Sample Questions For MID Exam Summer 2023Dokument8 SeitenMath 1151 Sample Questions For MID Exam Summer 2023Shurav DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective Booklet - 2/physics: Motion in Two Dimension Chapter - 3Dokument8 SeitenObjective Booklet - 2/physics: Motion in Two Dimension Chapter - 3abhishekagarwala21Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Multiple Choice Questions) : Iit - Jee TW TEST (3 Yrs.) MARKS:360 Time: 3 Hrs. Topic: Full Mechanics DATE:30/9/18Dokument21 Seiten(Multiple Choice Questions) : Iit - Jee TW TEST (3 Yrs.) MARKS:360 Time: 3 Hrs. Topic: Full Mechanics DATE:30/9/18Hemendra PrasannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPP 8 Projectile MotionDokument2 SeitenCPP 8 Projectile Motionullasagw100% (2)
- Revision - 16 (Iit-Advanced)Dokument7 SeitenRevision - 16 (Iit-Advanced)Devansh SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ap Gov Practice TestDokument47 SeitenAp Gov Practice Testapi-255064087Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aiits 1820 HCT III Jeea Paper 1Dokument14 SeitenAiits 1820 HCT III Jeea Paper 1Rajdeep Nandy100% (1)
- Sat - 3 Section - IDokument6 SeitenSat - 3 Section - IullasagwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy & Chem - MT - 04 - XII - WBJEE - (Ques) - ENG + BENG - (W)Dokument20 SeitenPhy & Chem - MT - 04 - XII - WBJEE - (Ques) - ENG + BENG - (W)Rishabh RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiitjee 38Dokument5 SeitenFiitjee 38BHAAJI0001100% (1)
- SRG Aod AnswersDokument14 SeitenSRG Aod AnswersHarshul DuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 3 2S AY 20182019Dokument3 SeitenProblem Set 3 2S AY 20182019Allein Loisse EspinozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Equation AssignmentDokument2 SeitenTrigonometric Equation AssignmentShehbaz ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Paper 1 ElectrostaticsDokument5 SeitenTest Paper 1 ElectrostaticsPratik SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Adiabatic InvariantsDokument6 Seiten5 Adiabatic InvariantsStephen NatanaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT JEE - Mains Model Test Paper - 1 (Physics, Chemistry, Maths)Dokument12 SeitenIIT JEE - Mains Model Test Paper - 1 (Physics, Chemistry, Maths)studysteps.in83% (6)
- INSP Champs 2022 NLM 1 FinalDokument25 SeitenINSP Champs 2022 NLM 1 FinalYash VardhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascent Classes: NLM Advanced AssignmentDokument15 SeitenAscent Classes: NLM Advanced AssignmentShweta AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Center of MassDokument5 SeitenCenter of MassMahesh VashisthNoch keine Bewertungen
- KinematicsDokument33 SeitenKinematicstai58Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure PracticeDokument10 SeitenAtomic Structure Practicerajesh.justiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document PDF 331Dokument13 SeitenDocument PDF 331Aman0% (1)
- Fiitjee 37Dokument6 SeitenFiitjee 37BHAAJI0001100% (1)
- Rotation Dynamics AssigntyrftyugrroooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooomentDokument9 SeitenRotation Dynamics AssigntyrftyugrroooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooomentAnju Sahai100% (1)
- Ian's: Aits Test - 7Dokument25 SeitenIan's: Aits Test - 7Maruti ShelkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test 6 Rotation Angular MomentumDokument18 SeitenPractice Test 6 Rotation Angular MomentumLynn Hollenbeck BreindelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion (Theory)Dokument5 SeitenProjectile Motion (Theory)Mohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- Insp Challenging ProblemsDokument4 SeitenInsp Challenging Problemsshivam bhartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank (S.C)Dokument54 SeitenQuestion Bank (S.C)Mohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- Class: CC (Advanced) Electrostatics M.M. 78 Test No. 1 (Single Correct Choice Type)Dokument4 SeitenClass: CC (Advanced) Electrostatics M.M. 78 Test No. 1 (Single Correct Choice Type)QgqhahsjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XI Physics DPP Set (06) - Mathematical Tools & KinematicsDokument15 SeitenClass XI Physics DPP Set (06) - Mathematical Tools & KinematicsAshish RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit Model Paper 7Dokument19 SeitenIit Model Paper 7studysteps.in100% (1)
- AP Physics C Magnetism FRQ PDFDokument28 SeitenAP Physics C Magnetism FRQ PDFShameem AkhterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Newton Laws of Motion DCET IIT JEEDokument11 SeitenPhysics Newton Laws of Motion DCET IIT JEEprem19999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Additional 3 Chapter 3 PDFDokument16 SeitenAdditional 3 Chapter 3 PDFnazreensofeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asif Insight Physics OpticsDokument14 SeitenAsif Insight Physics OpticsMOHAMMED ASIF67% (3)
- Energy ExercisesDokument29 SeitenEnergy Exercisesyuxing lieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet-1 ELECTROSTATICS STUDENT COPY With Ans PDFDokument77 SeitenSheet-1 ELECTROSTATICS STUDENT COPY With Ans PDFKhilav Bhadja0% (1)
- Chapter 4 Force and Newtons Laws of MotionDokument23 SeitenChapter 4 Force and Newtons Laws of MotionQassem MohaidatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - Rigid Body DynamicsDokument9 SeitenPhysics - Rigid Body DynamicsPranavMachingal100% (3)
- Insp NLMDokument9 SeitenInsp NLMAmar SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP Nlm-IiDokument8 SeitenDPP Nlm-IiMohammed Aftab Ahmed0% (1)
- NEET: (11th) Rotational Motion: QuestionsDokument32 SeitenNEET: (11th) Rotational Motion: QuestionsSuriyanarayana KNoch keine Bewertungen
- RotnDokument23 SeitenRotnDeepanshu LullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS - SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION WorksheetDokument10 SeitenPHYSICS - SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION Worksheetanubhab256224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is.1573.1986 ED Coating StandardDokument24 SeitenIs.1573.1986 ED Coating StandardUlhas Kavathekar100% (1)
- D7130A11Dokument1 SeiteD7130A11Tarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- N 1-Metric Equivalent: 1 In. 25.4 MMDokument1 SeiteN 1-Metric Equivalent: 1 In. 25.4 MMTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SWR Bill FormatDokument3 SeitenSWR Bill FormatTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Circuits Prepared by Dr. SrivastavaDokument17 SeitenNotes On Circuits Prepared by Dr. SrivastavaTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity NotesDokument24 SeitenElectricity NotesTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menges CrowningDokument8 SeitenMenges CrowningTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex UreaDokument1 SeiteAnnex UreaTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2P79000XDokument1 Seite2P79000XTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMS0058EDokument1 SeiteEMS0058ETarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digitally Signed by Jyoti 903807 Date: 2011.06.07 14:09:59 ISTDokument1 SeiteDigitally Signed by Jyoti 903807 Date: 2011.06.07 14:09:59 ISTTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bimco Engineering Enterprise Bimco Engineering Enterprise Bimco Engineering EnterpriseDokument1 SeiteBimco Engineering Enterprise Bimco Engineering Enterprise Bimco Engineering EnterpriseTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digitally Signed by Jyoti 903807 Date: 2011.10.04 11:21:08 PDTDokument1 SeiteDigitally Signed by Jyoti 903807 Date: 2011.10.04 11:21:08 PDTTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1P62870 NilDokument1 Seite1P62870 NilTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digitally Signed by Jyoti 903807 Date: 2011.09.14 10:54:12 PDTDokument1 SeiteDigitally Signed by Jyoti 903807 Date: 2011.09.14 10:54:12 PDTTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digitally Signed by Bharat Bhushan 904633 Diesel Loco Modernisation Works Date: 2012.01.07 12:11:59 ISTDokument5 SeitenDigitally Signed by Bharat Bhushan 904633 Diesel Loco Modernisation Works Date: 2012.01.07 12:11:59 ISTTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SK0130NILDokument1 SeiteSK0130NILTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NABL103Dokument93 SeitenNABL103ajaylamba1980Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4320Dokument1 Seite4320Tarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Electron NegDokument2 SeitenTable of Electron NegTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kit06 10272860Dokument1 SeiteKit06 10272860Tarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bansal Coordinationcompounds PDFDokument10 SeitenTest Bansal Coordinationcompounds PDFTarun Gupta100% (2)
- CE-101 Lec 5 Impulse and MomentumDokument10 SeitenCE-101 Lec 5 Impulse and MomentumRaquib AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP 4 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDokument18 SeitenLP 4 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesKent JazminesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic PropulsionDokument9 SeitenElectromagnetic Propulsionpras_scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAMCET 2015 - EngineeringDokument26 SeitenEAMCET 2015 - EngineeringNeepur Garg100% (1)
- C1.Vector AnalysisDokument27 SeitenC1.Vector AnalysisRudy ObrienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compound Pendulum 2Dokument5 SeitenCompound Pendulum 2GNag R'VarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classical MechanicsDokument57 SeitenClassical MechanicsAbdul QuaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational Motion - DPPsDokument17 SeitenRotational Motion - DPPs:-Noch keine Bewertungen
- Homework Assignment 13 - SolutionsDokument4 SeitenHomework Assignment 13 - SolutionsSaswataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 04-Dynamic Response of Buildings PDFDokument64 SeitenChapter 04-Dynamic Response of Buildings PDFAngelique EsquillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Most Important Topics of PhysicsDokument4 SeitenMost Important Topics of PhysicsAshraf AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP 222: Classical Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 3Dokument12 SeitenEP 222: Classical Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 3haroldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mdcat LoversDokument784 SeitenMdcat Loverssobaanakhtar123Noch keine Bewertungen
- DC Muttur PDFDokument615 SeitenDC Muttur PDFNiveCeciliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction LQ GDokument277 SeitenIntroduction LQ Gbez_180210559Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ in Engineering Mechanics - 1Dokument16 SeitenMCQ in Engineering Mechanics - 1Rovina Lacuna100% (1)
- How To Enhance Effectiveness of Direct Attack Judo Throws: Attilio SacripantiDokument37 SeitenHow To Enhance Effectiveness of Direct Attack Judo Throws: Attilio SacripantilubajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spin and Dirac Notation: 1.1 Stern-Gerlach ExperimentDokument22 SeitenSpin and Dirac Notation: 1.1 Stern-Gerlach Experimentsaleem saleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Updated Neet 2024 SyllubusDokument6 SeitenPhysics Updated Neet 2024 SyllubusAbhinave SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Test Paper (STP) : ContentDokument80 SeitenSample Test Paper (STP) : ContentAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH9 MomentumpptDokument42 SeitenCH9 Momentumpptarvin junior domingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSMSC MPhil PH DSyllabusDokument108 SeitenBSMSC MPhil PH DSyllabusmoix khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Integral Forms of The Fundamental Laws - 2Dokument24 SeitenThe Integral Forms of The Fundamental Laws - 2Jenille C. VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of InertiaDokument13 SeitenMoment of InertiaRahmatullah RahmatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nassim Haramein - The Origin of SpinDokument16 SeitenNassim Haramein - The Origin of SpinBogdan Popa100% (1)
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDokument22 SeitenHapter: Conceptual ProblemsAbdullah ArabiyatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Iqra Saleem Roll No: BSF 1904879 Program: BS Mathematics (2 Semester) Subject: Mechanics - II TopicDokument5 SeitenName: Iqra Saleem Roll No: BSF 1904879 Program: BS Mathematics (2 Semester) Subject: Mechanics - II Topiciqra saleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- LinearangularconceptsDokument2 SeitenLinearangularconceptsCarlos MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photonic Aspects of Dowsing and Feng ShuiDokument10 SeitenPhotonic Aspects of Dowsing and Feng Shuimkrinker1296Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 06Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 06Supriyo Dutta100% (1)