Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
P Hmetry
Hochgeladen von
dhungelsubhash8154Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
P Hmetry
Hochgeladen von
dhungelsubhash8154Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Title:To calibrate pH meter and measure the pH of a provided sample.
Theory:
The pH scale is a series of numbers. These numbers express the degree of acidity or alkalinity of a solution. According to Sorensen pH is defined as negative logarithm(to the base 10) of molar hydrogen ion concentration. pH= log10 1/[H+] = -log10[H+], or [H+] = 10-pH Actually, it is the activity of hydrogen ion that is compatible with the thermodynamics. Hence activity definition of pH is: pH = -log10 aH+ = -log10 [H+].f H+ But being pragmatic, the ionic activity coefficient is assumed unity and therefore activities become equivalent to concentrations is an accepted simplification for our purpose. However pure the water is, it possesses a small but definite conductivity due to ionization: H2O H++ OHBy applying the law of mass action in the above equation: [H+][OH-] = Constant [ H2O] In pure water or dilute aqueous solution, [H2O] is a constant; hence [H+][OH-] = Kw Where, Kw is the ionic product of water( 1.008 X 10-14). In pure water or in neutral solution when the concentration of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions are equal: [H+] = [OH-] = Kw= 10-7(at 25C) or [H+][OH-] = Kw = 10-14 or log[H+] + log[OH-] = logKw= -14 Hence, pH + pOH = pKw = 14 For a neutral solution pH= pKw/2. Acid and alkaline solutions have pH values less and more than pKw/2. For pure water pH=7.0, for a solution with 1M hydrogen ion concentration pH=0 and for a solution with 1M hydroxide ion concentration pH= 14. H+= 10-010-110-210-310-410-510-610-710-810-910-1010-1110-1210-1310-14
pH= 0
7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Alkaline solution Neutral Only with the definition and mathematical explanations as above pH of a solution can not be measured. There are many methods are employed for the measurement of pH. The most accurate method is potentiometric determination of pH in which an indicatior electrode reversible to H+ is coupled with a reference electrode to form a cell. The emf of the cell varies with the hydrogen ion concentration of the solution in the cell.The emf of the cell is measure by potentiometer. If the other variables in the cell are controlled, the emf of the cell can be correlated with the pH and this correlation is the basis potentiometric measurement of pH. Hydrogen, quinhydrone, antimony-antimony oxide and glass electrodes are the indicator electrodes for the measurement of pH. However due to the existence of high resistance in glass electrode(which is nowadays in use) simple potentiometer is not applicable. Hence, the modern pH meter is an electronic digital voltmeter, scaled to read pH directly. Saturated calomel electrode is the most popularly used reference electrode. pH of an aqueous solution can be measured by coupling a glass electrode with a saturated calomel electrode. Outer connection is completed via a pH meter or potentiometer. The resulting cell can be represented as follows: HgHg2Cl2,KCl(satd.) H+(a=x) glass HCl(0.1M), AgClAg ______SCE________ _Test Soln_ _______Glass electrode_______
1 2 3 4 Acidic solution
5 6
In the above schematic cell diagram, a reference electrode is placed in each of the solutions separated by the glass membrane. So that, any change in the cell voltage when changed is made in the test solution must reflect a change in the potential developed across the glass membrane. Additionally, any change in the liquid junction potential between the SCE and the test solution be reflected. It is found experimentally that the voltage of this cell follows the relation at 25C over a pH range in the test solution from about 0 or 1 up to 10 or 13, depending upon the composition of the electrode. E = k+ 0.0592pH i.e. E/pH = 0.0592
A linear relation exists between the pH of a solution , at a given temperature and emf of cell(E). Thus, a calibration in mV may be converted into pH units by dividing by 0.0592. K is a constant which is lumped with asymmetry potential, liquid junction potential, standard potential of glass electrode, potential of reference electrode. To maintain uniformity in pH measuring technique and measured value of pH throughout the world, it is necessary to redefined pH in operational terms. According to the definition, first of all the meter is directly calibrated against standard buffers followed by potentiometric determination of the pH of unknown solution. Eu= k+ 0.0592 pHu or pHu = Eu- k ---------------(1) 0.0592 Es= k+ 0.0592 pHs or pHu = Es- k ---------------(2) 0.0592 Subtracting equation (2) from (1), pHu= pHs+ Eu Es 0.0592 According to this relation, pH of test solution is related to the difference between the emf due to standard buffer and test solution. With this operational definition liquid junction potential and asymmetry potential(which changes with time) are almost alleviated.
Chemicals required:
1)Standard buffer solution of 9.0,7.0 and 4.0, 2)Sodium chloride injection ,3)Ammonium chloride,4)ORS Sachets,5)Freshly boiled and cooled water.
Apparatus required:
1) Digital pH meter, 2)Beakers,3)Volumetric flasks .
Procedure:
Preparation of standard buffer solutions. Tranfer buffer tablets of pH 4.00 , 7.00 and 9.20 into different 100ml V.F. and shake to dissolve and dilute to the mark with boiled and cooled water. Maintain their temperature at 25C. Preparation of sample solution: a.Prepare 5.0%w/v solution of ammonium chloride in boiled and cooled water. pH limits: 4.5 6.0 b.Transfer a sachet full of ORS into a beaker(1L) containing about 900ml boiled and cooled water, stir to dissolve and dilute to the mark. pH limits:7.0-8.8 c.Sodium chloride injection. pH limits:4.5-7.0 Calibration of pH meter and measurement of pH of test solution:
1)Switch on and allow the instrument to warm up. Align the function switch to Stand by. 2)Wash the combination glass electrode with a small amount of buffer solution of pH 4.00 and dip it into the buffer in a small beaker. Measure the temperature of the solution and set the temperature control to this value. 3)Turn the function switch to pH. Adjust the Calibrate control until the meter reading agrees with the known pH of the buffer solution(25C) or temperature compensated buffer value. 4)Remove the electrode assembly and rinse in distilled water followed by second buffer and place into a small beaker containing a little of the second buffer(pH 7.00 or 9.20) solution. If the meter reading does not agree exactly with the known pH, adjust the Slope control until the required reading is obtained. 5.Remove the electrode assembly, rinse in distilled water, place in the first buffer solution and confirm that the correct pH reading is shown on the meter, if not, repeat the calibration procedure. 6.Following the completion of calibration, rinse the electrode with water followed by test solution and introduce into the test solution contained in a smaller beaker. Read off the pH of the solution. 7.Remove the electrode ,rinse in distilled water, and leave standing in distilled water.
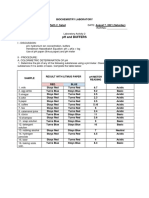
Observations:
a. Ammonium chloride/ b.ORS/c.Sodium chloride injection, measured pH:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Potentiometric TitrationDokument9 SeitenPotentiometric Titrationiah_guevarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisVon EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- PH Measurement BasicsDokument8 SeitenPH Measurement Basicsviralshukla85Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4500 - PH Value (H+) PDFDokument5 Seiten4500 - PH Value (H+) PDFClaudia BarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Test B: Chapter: Acids and BasesDokument7 SeitenChapter Test B: Chapter: Acids and BasesWeng50% (2)
- Determination of PHDokument2 SeitenDetermination of PHnp27031990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Potentiometric Determination of The Purity and Ka of KHPDokument5 SeitenPotentiometric Determination of The Purity and Ka of KHPAuvrae Jherxel SeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt.1 BiochemDokument4 SeitenExpt.1 BiochemMc de RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH Analyzers PH MetersDokument16 SeitenPH Analyzers PH Meterskamala 123Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Ka & Molar Mass of A Monoprotic Weak AcidDokument7 SeitenThe Ka & Molar Mass of A Monoprotic Weak AcidLeslie Sarah100% (1)
- Experiment 3 CHM421Dokument8 SeitenExperiment 3 CHM421pufff witches100% (1)
- Determination of Aluminium Back TitrationDokument2 SeitenDetermination of Aluminium Back Titrationdhungelsubhash8154100% (4)
- Determination of Aluminium Back TitrationDokument2 SeitenDetermination of Aluminium Back Titrationdhungelsubhash8154100% (4)
- Determination of Aluminium Back TitrationDokument2 SeitenDetermination of Aluminium Back Titrationdhungelsubhash8154100% (4)
- Determination of Aluminium Back TitrationDokument2 SeitenDetermination of Aluminium Back Titrationdhungelsubhash8154100% (4)
- 1.13 Determination of PH: The International Pharmacopoeia - Eleventh Edition, 2022Dokument2 Seiten1.13 Determination of PH: The International Pharmacopoeia - Eleventh Edition, 2022tuecaiccNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 221 Text 1Dokument19 SeitenCHE 221 Text 1Candy PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH Measurement-15.7.2014Dokument45 SeitenPH Measurement-15.7.2014urvish_soniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sarthak Dadkar PIIAL Prac 4 PDFDokument5 SeitenSarthak Dadkar PIIAL Prac 4 PDFAjuba AbujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4Dokument7 SeitenExperiment 4Lakshmankumar TjpsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4 PDFDokument7 SeitenExperiment 4 PDFsaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No: 5 Experiment Name: Study of PH Metric TitrationDokument11 SeitenExperiment No: 5 Experiment Name: Study of PH Metric TitrationRafid JawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of PH by PH MeterDokument8 SeitenDetermination of PH by PH MeterAbdullah NayyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viva Questions and Answers: Determination of The Unknown Concentration of HCL Using P MeterDokument3 SeitenViva Questions and Answers: Determination of The Unknown Concentration of HCL Using P MeterNikhil SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potentiometric Titration Ex17Dokument10 SeitenPotentiometric Titration Ex17Tien HaminhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 〈791〉 pHDokument4 Seiten〈791〉 pHThu PhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- KaDokument5 SeitenKaSonu DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH MeterDokument4 SeitenPH MeterThomas AgungNoch keine Bewertungen
- USP791 PHDokument4 SeitenUSP791 PHJoaquín Andrés Aravena PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH and TemperatureDokument4 SeitenPH and TemperatureWONG TSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment PHDokument8 SeitenExperiment PHMohamed MubarakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ph. Principles and MeasurementDokument6 SeitenPh. Principles and MeasurementAndré FerrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH of Various Water SamplesDokument3 SeitenPH of Various Water SamplesdarshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Biochemistry JournalDokument6 SeitenIntroductory Biochemistry JournalUsman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Bases: Acid TypesDokument11 SeitenAcids and Bases: Acid Typesసతీష్ పసులNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labexercise 2Dokument7 SeitenLabexercise 2Ma Catherine MalanogNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH BuffersDokument5 SeitenPH BuffersReem NasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- GA7 Potentio Titr Rev7 99Dokument9 SeitenGA7 Potentio Titr Rev7 99Jerome SadudaquilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 222 Chapter 5Dokument32 Seiten222 Chapter 5priyankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 4Dokument2 SeitenPractical 4vimukthi gunasinghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH ScalDokument6 SeitenPH ScalTanzil ZaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEP Toolbox 08 FrequentlyAskedQuestionsDokument14 SeitenGEP Toolbox 08 FrequentlyAskedQuestionsabdelali.bajNoch keine Bewertungen
- History: Puissance (Also Meaning Power But Then The Carlsberg Laboratory Was French Speaking) or That PH Stands For TheDokument10 SeitenHistory: Puissance (Also Meaning Power But Then The Carlsberg Laboratory Was French Speaking) or That PH Stands For TheoktrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1Dokument17 SeitenExp 1Nor SyuhailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Completing Lab Data: Acids Bases and BuffersDokument7 SeitenCompleting Lab Data: Acids Bases and Buffers蔺雄人Noch keine Bewertungen
- PI Exp9 CompiledDokument12 SeitenPI Exp9 CompiledZaid SalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TT - PH MeterDokument1 SeiteTT - PH MeternuroniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Navigation Search PH (Disambiguation) : From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To:, For Other Uses, SeeDokument10 SeitenNavigation Search PH (Disambiguation) : From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To:, For Other Uses, SeeHitesh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Oxidation Reduction Potential Measurement PDFDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To Oxidation Reduction Potential Measurement PDFanastasya357Noch keine Bewertungen
- Issues Related To The Measurement of The pH-Value in Pure and Ultrapure WaterDokument4 SeitenIssues Related To The Measurement of The pH-Value in Pure and Ultrapure Waterekrem turanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-314 Lab Experiment 5Dokument4 SeitenCH-314 Lab Experiment 5Fatima tahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Store PH Electrode.Dokument29 SeitenHow To Store PH Electrode.E.C.MADHUDUDHANA REDDYNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH MeasurementDokument6 SeitenPH MeasurementZamran mengalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH MeterDokument17 SeitenPH MeterNitesh Bhura100% (2)
- S Y PH MeterDokument2 SeitenS Y PH MeterNeelam KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH TheoryDokument2 SeitenPH TheoryLuis FonsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2 PDFDokument4 SeitenExperiment 2 PDFabdullah nadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- No 3Dokument12 SeitenNo 3Punit Ratna ShakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF PH TITRATIONDokument16 SeitenPDF PH TITRATIONعبدالله هنيةNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.13 Determination of PH: The International Pharmacopoeia - Ninth Edition, 2019Dokument2 Seiten1.13 Determination of PH: The International Pharmacopoeia - Ninth Edition, 2019حسام عقلانNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To Log P and Pka Measurements and Their UseDokument24 SeitenA Guide To Log P and Pka Measurements and Their UseBer GuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH and BufferDokument3 SeitenPH and BufferMuhammad YaseenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry /pi Eɪtʃ/ Hydrogen Power Acidity Basicity Aqueous Solution H AlkalineDokument22 SeitenChemistry /pi Eɪtʃ/ Hydrogen Power Acidity Basicity Aqueous Solution H AlkalineCHUKWU VICTORNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermometric Titrimetry: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryVon EverandThermometric Titrimetry: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base Disorders: Clinical Evaluation and ManagementVon EverandAcid-Base Disorders: Clinical Evaluation and ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProverbDokument3 SeitenProverbdhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dissolution For PharmacyDokument4 SeitenDissolution For Pharmacydhungelsubhash8154100% (1)
- Titration of Iodine With Standard Thisulphate SolutionDokument3 SeitenTitration of Iodine With Standard Thisulphate Solutiondhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment: Determination of Acetic Acid Content of Vinegar. Apparatus: Burette, Pipette, Conical Flask, Beakers, Volumetric FlaskDokument2 SeitenExperiment: Determination of Acetic Acid Content of Vinegar. Apparatus: Burette, Pipette, Conical Flask, Beakers, Volumetric Flaskdhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- TLCDokument3 SeitenTLCdhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Titration of Iodine With Standard Thisulphate SolutionDokument3 SeitenTitration of Iodine With Standard Thisulphate Solutiondhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Properties of LiquidsDokument7 SeitenPhysical Properties of LiquidsSubhamshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Na CLDokument1 SeiteNa CLdhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fajans MethodDokument3 SeitenFajans MethodSubhash Dhungel50% (2)
- Title:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)Dokument2 SeitenTitle:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)dhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fajans MethodDokument3 SeitenFajans MethodSubhash Dhungel50% (2)
- Title:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)Dokument2 SeitenTitle:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)dhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- CopperDokument3 SeitenCopperdhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- CompositionDokument3 SeitenCompositiondhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- ProverbDokument3 SeitenProverbdhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- ChlorpromazineDokument3 SeitenChlorpromazinedhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fajans MethodDokument3 SeitenFajans MethodSubhash Dhungel50% (2)
- Total Hardness of WaterDokument3 SeitenTotal Hardness of Waterdhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- CompositionDokument3 SeitenCompositiondhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Na CLDokument1 SeiteNa CLdhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Title:P: Reparation of Sodium CitrateDokument3 SeitenTitle:P: Reparation of Sodium Citratedhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Title:P: Reparation of Sodium CitrateDokument3 SeitenTitle:P: Reparation of Sodium Citratedhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Title:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)Dokument2 SeitenTitle:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)dhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- CiproDokument2 SeitenCiprodhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fumar AteDokument3 SeitenFumar Atedhungelsubhash8154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Notes: DilutionDokument5 SeitenScience Notes: DilutionKylie smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potentiometric PH Measurement Lab ReportDokument6 SeitenPotentiometric PH Measurement Lab Reportrhima shineyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SALUD - LAB ACTIVITY 2 - PH and Buffers - BIOCHEM - BSN 1-COC A.Dokument3 SeitenSALUD - LAB ACTIVITY 2 - PH and Buffers - BIOCHEM - BSN 1-COC A.Faye SaludNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conductomeric TitrationDokument12 SeitenConductomeric TitrationKoio KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2Dokument5 SeitenExp 221413温邦宏Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 11th Project On PH ScaleDokument17 SeitenChemistry 11th Project On PH ScaleAlex100% (1)
- CHEMISTRY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT of Class XIIDokument15 SeitenCHEMISTRY INVESTIGATORY PROJECT of Class XIIsoumya.sj09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indicator PreparationDokument2 SeitenIndicator PreparationLendl PayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 160.1 Ex2 BufferDokument8 SeitenChem 160.1 Ex2 BufferAsi JenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ElectrolytesDokument24 SeitenTypes of ElectrolytesPranoy Baishya100% (1)
- Ionic Equilibrium 520Dokument19 SeitenIonic Equilibrium 520sarbajit mazumdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson in Acid and BasesDokument5 SeitenLesson in Acid and BasesmarcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory - of - Indicators OswalDokument3 SeitenTheory - of - Indicators OswalHitansh KotadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCES1124 Fundamentals of Chemistry IIDokument4 SeitenSCES1124 Fundamentals of Chemistry IISN2-0622 NURUL ADLYNA BINTI LOKMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- GHS Honors Chem Acid Base Titration LabDokument5 SeitenGHS Honors Chem Acid Base Titration LabWilliam SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acid TitrationDokument9 SeitenAmino Acid TitrationuğurNoch keine Bewertungen
- September 09, 2019 DealsDokument7 SeitenSeptember 09, 2019 DealsKevin Fernandez MendioroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibria SlidesDokument33 SeitenEquilibria SlidesHamna MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan - Acids and AlkalisDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan - Acids and AlkalisKim GabaynoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acidic Reactions of Ethanoic AcidDokument5 SeitenAcidic Reactions of Ethanoic AcidKevin DevastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boardgamedisplay14671 140524165124 Phpapp01Dokument1 SeiteBoardgamedisplay14671 140524165124 Phpapp01KitkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceac 103 - Exp 5Dokument7 SeitenCeac 103 - Exp 5mohsmmad AbdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Test Paper For Class & (Science)Dokument4 SeitenSample Test Paper For Class & (Science)Surya SalariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Chem Answers 18Dokument3 SeitenIb Chem Answers 18Nick BinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 5Dokument4 SeitenNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 5Ayesha KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry PBLDokument27 SeitenChemistry PBLZLLL0930Noch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 6Dokument9 SeitenHomework 6Jaskirat MannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Equilibrium (Elementary) : Table-1Dokument19 SeitenIonic Equilibrium (Elementary) : Table-1Yogesh GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen