Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Afro-Asian Flags
Hochgeladen von
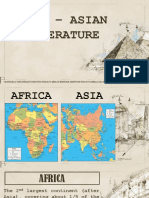
FretzieOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Afro-Asian Flags
Hochgeladen von
FretzieCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1. What is Literature? 2.
As man started to walk theearth, he developed a system of recording down things around him and interpreting themaccording to his own perception. 3. This act of documenting may have been the start of the medium.Not all written material may be considered literature. Only those that closely emulate the humanexperience, emotion and thought are regarded as literature. 4. South Korea North Korea Japan Saudi Arabia Vietnam China Indonesia India Egypt Malaysia Israel Africa Thailand Philippines 5. Afro-Asian Literature is a termfor writing;written by people from mixedAfrican-Arab ethnicity, orAfrican-Asian ethnicity. 6. Why do we always need to consider the culture of the people when we study literature? 7. Afro-Asian Literature mirrors not only the customs and traditions of African and Asian countries but also their philosophy of life which on the whole are deeply and predominantly contemplative and hauntingly sweet. 8. Afro-Asian Literature is the reflection of the storm and the stress of developing nations seeking a place under the sun which every student must understand so he may know how this literature affects the history and culture of a nation. 9. Many of the literary works are handed down byoral tradition. In Africa, the lack of literacy didnot make it possible to write literature down. 10. Histories, myths, legends, including stories,dramas, riddles, songs, proverbs and other literaryworks were handed by mouth from generation togeneration to entertain, educate and remind thepeople about their past, heroic deeds of theirpeople, ancestry and culture.
11. The importance comes from the fact that Afro-Asian literature is a sign of new and modern times. 12. the other importance is that this writing is able to teach people and allow them to learn about different experiences and cultures from all over the world. 13. History Of Afro-Asian Literature 14. - Told of the unique struggles and successes of Afro-Asian people. 15. In most cultures, oral histories marked the beginning of teaching history. Later, when more people were able to read and write, history became recorded in prose, plays, and textbooks. 16. Poetry/Songs - about the history and culture of the Afro-Asian people were written and performed, and then passed down.Genres Today, Afro-Asians still express their creativity, and honour their culture, by crafting beautiful poems, such as haikus, ballads, or sonnets. Freeform poems with specific structures or meters are also prevalent - these have a free-spirited, stream of consciousness feeling...
17. Genres Plays - Playwrights use dialogue and monologue to Plays, when performed, will feature backdrops, reinforce ideas, emotions costumes, and jargon that and themes. reflects the culture and unique spirit of AfroAsianMany playwrights celebrate people.their own culture andancestry by setting plays inthe past, andreferencing historicalevents in their storylines.
18. references www.afroasianliterature.wordpress.com www.katsandogz.com www.broadcaster.org.uk
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Afro AsianDokument35 SeitenAfro AsianJohn Harold Casyao Barba50% (2)
- Afro Asian Literature Intro 1Dokument24 SeitenAfro Asian Literature Intro 1ATHEENA KAE CAYABYABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro AsianDokument13 SeitenAfro AsianOwien SubrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 3,4 & 5Dokument2 SeitenActivity 3,4 & 5nulllllNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q4 - Module 1 (21ST Century Literature)Dokument15 SeitenQ4 - Module 1 (21ST Century Literature)bea ackermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro Asian Literature HardDokument9 SeitenAfro Asian Literature HardRichelle Storment100% (9)
- Introduction and BackgroundDokument35 SeitenIntroduction and BackgroundRomina DaquelNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON 1: What Is Afro-Asian Literature?Dokument2 SeitenLESSON 1: What Is Afro-Asian Literature?Joey GalongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro Asian Lit Module Final2222Dokument48 SeitenAfro Asian Lit Module Final2222Yurameku HonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro Asian LiteratureDokument62 SeitenAfro Asian LiteraturePearl ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro Asian LiteratureDokument62 SeitenAfro Asian LiteratureNicsyumulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arabic Literary Salons in the Islamic Middle Ages: Poetry, Public Performance, and the Presentation of the PastVon EverandArabic Literary Salons in the Islamic Middle Ages: Poetry, Public Performance, and the Presentation of the PastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro Asian LiteratureDokument2 SeitenAfro Asian LiteratureRosevie Golias Mernado100% (4)
- Towards an African Literature: The Emergence of Literary Form in XhosaVon EverandTowards an African Literature: The Emergence of Literary Form in XhosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Afro-Asian LiteratureDokument27 SeitenIntroduction To Afro-Asian LiteratureNina Romina NavaltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro - Asian LiteratureDokument49 SeitenAfro - Asian LiteratureJehanessa PalacayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer keyFOR SURVEY TO AFRO ASIAN LITERATURE 1Dokument3 SeitenAnswer keyFOR SURVEY TO AFRO ASIAN LITERATURE 1Cornelia, GeraldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro m1Dokument15 SeitenAfro m1Janica Alido LuzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- African Literature HandoutsDokument4 SeitenAfrican Literature HandoutsDemirose GercanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro Asian LiteratureDokument19 SeitenAfro Asian LiteratureAireen Joy Carandang MadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- African Literat-WPS OfficeDokument21 SeitenAfrican Literat-WPS OfficeJhonalen OrtezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black Orpheus, Transition, and Modern Cultural Awakening in AfricaVon EverandBlack Orpheus, Transition, and Modern Cultural Awakening in AfricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Literature ? What Is Afro - Asian Literature?: Group 3Dokument3 SeitenWhat Is Literature ? What Is Afro - Asian Literature?: Group 3Francis Destroyer88888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 English Module 1ST QuarterDokument70 SeitenGrade 8 English Module 1ST QuarterFelix Torrimocha Jr.100% (3)
- Introduction To African LiteratureDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To African Literaturemandzd90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Survey of African Literature An IntroductionDokument16 SeitenSurvey of African Literature An IntroductionoserobritonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afroasian LitDokument83 SeitenAfroasian LitBaldonado, Howard Kent C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Note On African LiteratureDokument6 SeitenA Note On African LiteratureMichelle Labajo MaunesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reporting in WLDokument11 SeitenReporting in WLKyle AmaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Literature: African Literature Refers ToDokument5 SeitenOral Literature: African Literature Refers ToRodel Bryan Coronejo ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- EL113 Afro-Asian LiteCHAPTER1Dokument12 SeitenEL113 Afro-Asian LiteCHAPTER1Impang, Sammuel R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 African LiteratureDokument15 SeitenLesson 1 African LiteratureXyrene Escandor0% (1)
- Handout Overview Africanlit PDFDokument4 SeitenHandout Overview Africanlit PDFRonah Vera B. TobiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng 302lesson1-2023Dokument24 SeitenEng 302lesson1-2023Fedil TinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21cl-African LiteratureDokument50 Seiten21cl-African LiteratureMRC VILLAFLOR-BRAZASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro AsianDokument18 SeitenAfro AsiangraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cry The Beloved Country (Intro To Lit and Author)Dokument20 SeitenCry The Beloved Country (Intro To Lit and Author)NOORULFALEELANoch keine Bewertungen
- Memories of Africa: Home and Abroad in the United StatesVon EverandMemories of Africa: Home and Abroad in the United StatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- African Literature 1Dokument64 SeitenAfrican Literature 1Regina100% (1)
- Module 1Dokument6 SeitenModule 1Hanz Patricia SilvallanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- African LitDokument3 SeitenAfrican LitRicardo SantillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro Asian LiteratureDokument30 SeitenAfro Asian LiteratureRodelyn Barroga100% (1)
- African Literature Students'Dokument3 SeitenAfrican Literature Students'tfbcschoolinc2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- African LiteratureDokument64 SeitenAfrican LiteratureTrisha Lei Taguinod BatangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 STDokument9 Seiten21 STrenzjireyllNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Literature IntroductionDokument12 SeitenPhilippine Literature Introductionmarc gorospeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey of Afro-Asian LiteratureDokument264 SeitenSurvey of Afro-Asian LiteratureRona dela RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- African LiteratureDokument7 SeitenAfrican LiteratureRaouf CarloNoch keine Bewertungen
- African Literature Written ReportDokument4 SeitenAfrican Literature Written Reportriann leigh TrangiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Study Resource Was: African LiteratureDokument3 SeitenThis Study Resource Was: African LiteratureYamato De Jesus NakazawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: Module 1 (Lesson 1) : Introduction To Afro-Asian Literature Learning TargetsDokument145 SeitenTopic: Module 1 (Lesson 1) : Introduction To Afro-Asian Literature Learning TargetsJohn Carl Aparicio100% (1)
- EoDokument180 SeitenEoFranklinCovey SouthasiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- African LiteratureDokument17 SeitenAfrican LiteratureGAMEPORIUMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Las 21STCL Q4 W1 PDFDokument17 SeitenLas 21STCL Q4 W1 PDFacebealsabasNoch keine Bewertungen
- African-Literature-Group-1 2Dokument42 SeitenAfrican-Literature-Group-1 2Mariah Sophia DUMAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON 1 Afro Asian LiteratureDokument20 SeitenLESSON 1 Afro Asian LiteraturecabauatanmariaangelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culture, Language and Evolution of African LiteratureDokument1 SeiteCulture, Language and Evolution of African LiteraturePatrick San AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word With BeginningsDokument1 SeiteWord With BeginningsFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipil National High School: /I/ B. /i/ C. /S/ D. /ƩDokument6 SeitenIpil National High School: /I/ B. /i/ C. /S/ D. /ƩFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) : To Be Filled in During Planning To Be Filled During EvaluationDokument9 SeitenIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) : To Be Filled in During Planning To Be Filled During EvaluationFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accomplishment Report November 2013Dokument15 SeitenAccomplishment Report November 2013FretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking Skills: Corich, Stephen PaulDokument2 SeitenCritical Thinking Skills: Corich, Stephen PaulFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking Skills ReviewerDokument29 SeitenCritical Thinking Skills ReviewerFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accomplishment Report November 2013Dokument3 SeitenAccomplishment Report November 2013FretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd MT 2012 2013Dokument10 Seiten3rd MT 2012 2013FretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Excel FretzieDokument30 SeitenMS Excel FretzieFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Script Science FestivalDokument2 SeitenScript Science FestivalFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certifications PAST 2012 2013Dokument11 SeitenCertifications PAST 2012 2013FretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st MT English IVDokument2 Seiten1st MT English IVFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - Score: - Rating: - Year/Section: - DateDokument1 SeiteName: - Score: - Rating: - Year/Section: - DateFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Career Assessment Examination Data UtilizationDokument2 SeitenNational Career Assessment Examination Data UtilizationFretzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revisiting Approaches and Strategies in Araling PanlipunanDokument32 SeitenRevisiting Approaches and Strategies in Araling PanlipunanFretzie97% (73)
- Module in 21 Century Literature From The Philippines To The WorldDokument24 SeitenModule in 21 Century Literature From The Philippines To The WorldJenine Oliver ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 - Aboriginal CultureDokument5 SeitenLesson 2 - Aboriginal Cultureapi-236965103Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme of Work English Form 5 2018Dokument10 SeitenScheme of Work English Form 5 2018Shereen LinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roteiro hp7-2Dokument14 SeitenRoteiro hp7-2Guilherme CavalcantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- La CelestinaDokument4 SeitenLa CelestinaAnonymous J5vpGuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal and External Conflict inDokument3 SeitenInternal and External Conflict inbibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staging The Ethical in The State of Emer PDFDokument12 SeitenStaging The Ethical in The State of Emer PDFGile BrankovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Poison TreeDokument9 SeitenA Poison TreeazirazizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hours in A Library, Volume I. (Of III.) by Stephen, Leslie, 1832-1904Dokument148 SeitenHours in A Library, Volume I. (Of III.) by Stephen, Leslie, 1832-1904Gutenberg.org100% (1)
- HabibDokument92 SeitenHabibalsanendiaye257Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emerging Literature Is A Threat To Classic Literature.Dokument3 SeitenEmerging Literature Is A Threat To Classic Literature.Geneva TabiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises For Lessons 3 Thru End Unit 1 of Henle FYLDokument49 SeitenExercises For Lessons 3 Thru End Unit 1 of Henle FYLJennifer Jones100% (10)
- The Background: Dr. Shobana Kumar Assistant Professor Dept of EnglishDokument11 SeitenThe Background: Dr. Shobana Kumar Assistant Professor Dept of EnglishFranklin RyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phrasal VerbsDokument4 SeitenPhrasal VerbsAnonymous Ix2FQhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloze Test The Fruitcake Special and Other StoriesDokument2 SeitenCloze Test The Fruitcake Special and Other StoriesPatricia LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blackwashing History-WatchmenDokument3 SeitenBlackwashing History-WatchmenmejilsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English - Grade 7 - Second Term Test 2022 - Kegalle ZoneDokument5 SeitenEnglish - Grade 7 - Second Term Test 2022 - Kegalle Zone50premahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Tim Burton Quotes On LifeDokument8 Seiten21 Tim Burton Quotes On LifeAbel ClaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcendental MagicDokument317 SeitenTranscendental MagicHarmony Pax100% (5)
- Korean Language Guide - PDF Learn Korean: LP's Korean Language Learning by Luke Park 2013Dokument7 SeitenKorean Language Guide - PDF Learn Korean: LP's Korean Language Learning by Luke Park 2013Aayush Anand SahayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Nadine Gordimer's NovelsDokument29 SeitenAnalysis of Nadine Gordimer's NovelsHaritha k sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dorian GrayDokument3 SeitenDorian GrayElena DrăguţNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indirect SpeechDokument1 SeiteIndirect SpeechtrangthukNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmaterasuDokument3 SeitenAmaterasuLance SayurinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wired For Story by Lisa Cron - ExcerptDokument15 SeitenWired For Story by Lisa Cron - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group50% (12)
- Chapter III Elements of Prose FictionDokument9 SeitenChapter III Elements of Prose FictionFaizal RisdiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chief Ki DaawatDokument1 SeiteChief Ki DaawatSnigdho Bhattacharya67% (3)
- Monthly Library Program Report TurnerDokument3 SeitenMonthly Library Program Report Turnerht00630Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reading LegendsDokument3 SeitenReading LegendsAilla NajwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2101 Study QuestionsDokument13 Seiten2101 Study QuestionsMarcusKlahnTokoeJr.Noch keine Bewertungen